Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Jobelyn TunayOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Jobelyn TunayCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan
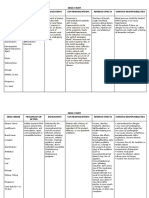
Name of the Patient: RR
Medical Diagnosis: Breast CA Stage 4
Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for infection related to frequent vomiting
ASSESSMENT NURSING DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: Deficient Fluid Volume Short-Term Goal: After 1. Monitor vital signs. -To provide baseline data. Short-Term Goal: After 8
“Nanunuyo na ang related to Dysphagia as 8 hours of nursing hours of nursing
llalamunanan ko…” as evidenced by dry mucous intervention, the client 2. Measure and monitor intake and -To provide baseline data. intervention, the client will
verbalized by the membranes, decrease pulse will be able to maintain output including urine, stool, and be able to maintain fluid
patient. volume, and pressure. fluid volume at vomitus. volume at functional level
functional level with with good mucous
Objective: good mucous membrane, good skin turgor,
→ T= 36.5°C membrane, good skin 3. Assess client’s behaviour and -A person with dehydration may and normal elimination
→weight loss turgor, and normal activity level every shift. develop anorexia, decreased pattern.
→dry lips elimination pattern. activity level and general malaise.
→abnormal color of
urine 4. Compare current weight gain -Daily body weight is best monitor
→hair is dry with admission or previous stated of fluid status. A weight gain of
weight gain. more than 0.5kg/day suggest fluid
retention.
5. Review laboratory results. BUN, -To evaluate degree of fluid excess,
Creatinine and Serum electrolytes. and obtain baseline data.
6. Monitor IV infusion after every -Infusing too rapidly or too slow can
hour. lead to fluid imbalance.
7. Observe skin mucous -To prevent ulcerations.
membranes.
8. Evaluate mental status for -May reflect fluid shifts,
confusion and personality changes. accumulation of toxins, acidosis,
electrolyte imbalance, or
developing hypoxia.
Nursing Care Plan
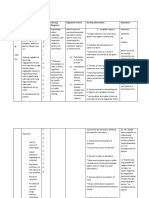
ASSESSMENT NURSING DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
1. Ascertain understanding of 1. To determine informational
Subjective: “Nahihirapan Risk for imbalance nutrition: Short-Term Goal: After 6 individual nutritional needs. needs of client Short-Term Goal: After 6
ako lumunok less than body requirements hours of nursing hours of nursing
pakiramdam ko ang sikip related to esophageal interventions client will 2. Assess weight, measure or 2. To establish baseline interventions, the client
ng lalamunan ko…” as narrowing secondary to verbalize understanding calculate body fat and muscle parameters. verbalized understanding of
verbalized by the patient. extraluminal compression: of causative factors and mass and other causative factors and
esophageal gastroduodenitis necessary interventions anthropometric necessary interventions to
Objective: to promote optimum measurements. promote optimum nutrition.
→dysphagia nutrition.
→Esophageal Narrowing 3. Observe for absence of 3. Indicates protein-energy Long-Term Goal: After 1-2
(endoscopy) Long-Term Goal: After 1-2 subcutaneous fat and muscle malnutrition. days of nursing
→Esophageal stricture days of nursing wasting, hair loss, fissuring of interventions, the client
(esophagram) interventions client will nail, delayed healing of demonstrated behaviors,
→weight loss from 57kg. be able to demonstrate wounds, gum bleeding or lifestyle changes and was
down to 55kg in 3 days behaviors, lifestyle swollen abdomen. able to regain and maintain
changes to regain and appropriate nutrition intake.
maintain appropriate 4. Auscultate bowel sounds. 4. Auscultation of the abdomen is
nutrition intake. Note for characteristic of stool performed for detection of altered
(color, amount, frequency) bowel sounds, rubs or vascular
bruits.
5. Provide diet modification as 5. Therapeutic diets are also used
indicated. (formula tube by dietitians to either maintain a
feedings, parenteral nutrition healthy lifestyle or improve health.
infusion)
6. Instruct client to avoid 6. Foods that are hard to digest
foods that causes intolerance leads to symptoms such as
or increase gastric motility intestinal gas, abdominal pain or
according to individual needs. diarrhea.
7. Assist with or provide oral 7. To ensure the patients mouth
care before and after meals are cared for.
and at bedtime.
8. Promote adequate and 8. To ensure that there is an
timely fluid intake. adequate body hydration.
Nursing Care Plan
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: “Nanunuyo na Deficient fluid volume Short-Term Goal: At the end 1. Assess for signs of 1. To determine the cause of Short-Term Goal: At the end
ung lalamunan ko…” as related to fluid loss of the shift, the client will be dehydration including skin pharyngeal pain. This will of the shift, the client was
verbalized by the patient. secondary to vomiting able to reduce vomiting by turgor, oral mucosa etc. provide a data that could be able to reduce vomiting by
promoting an environment used to evaluate the proper promoting an environment
Objective: conducive for doing ADL’s intervention that the client conducive for doing ADL’s
• V/S and improve skin turgor. needs. and improved skin turgor.
T= 36.5
PR= Long-Term Goal: After 1 day 2. Monitor I & O and IV fluids 2. To determine if IV fluid Long-Term Goal: After 1 day
RR= of thorough nursing and electrolyte replacement of thorough nursing
BP= intervention, the client will are needed. intervention, the client was
•pale conjunctiva be able to maintain body 3. Keep a quiet environment able to maintain body fluid
•decreased skin turgor fluid levels and completely and calm activities 3. To reduce stress and levels and completely
• frequent vomiting eliminate occurrence of anxiety. eliminate occurrence of
vomiting. 4. Provide health teachings vomiting.
on avoidance of dehydration. 4. To promote awareness on
related factors.
5. provide frequent oral and
skin care. 5. To prevent injury from
dryness.
6. Promote well ventilated
environment conducive for 6. To avoid the occurrence of
eating. vomiting.
7. Change position
frequently. 7. To promote proper
circulation of blood, thus,
preventing from fluid deficit.
8. Administer medication for
vomiting (as ordered) 8. To decrease occurrence of
vomiting.
9. Administer fluids and
electrolytes ( as ordered) 9. To gradually correct the
deficiency in fluids.
You might also like
- Power Booty 2.0 Education by Lauren SimpsonDocument42 pagesPower Booty 2.0 Education by Lauren SimpsonBernadett Kálucz100% (11)
- Main Prakriti Ebook FDocument21 pagesMain Prakriti Ebook FddswamyNo ratings yet
- Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis by DR - DoaaDocument24 pagesDecompensated Liver Cirrhosis by DR - DoaaAyu DewiNo ratings yet
- Essene Science of FastingDocument43 pagesEssene Science of FastingJose Suipaccha100% (3)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument15 pagesNursing Care PlanZhel Geron MercadoNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Patients in CCUDocument75 pagesAssessment of Patients in CCUShubham Singh BishtNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Terapi Dan PrinsipelDocument16 pagesOxygen Terapi Dan PrinsipelAmrita KaurNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPJerome Vergel RubianesNo ratings yet
- PeritonitisDocument6 pagesPeritonitisDiane ArgoteNo ratings yet
- Pot Term pregnancy-MOMANYIDocument2 pagesPot Term pregnancy-MOMANYISally Gesembe100% (1)
- Student NurseDocument2 pagesStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.No ratings yet
- Osteomalacia Care Plan/OthersDocument11 pagesOsteomalacia Care Plan/OthersJill Jackson, RNNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions EvaluationsDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions EvaluationsAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- NCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thDocument2 pagesNCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Is Derived From Greek Word, Meaning 'Flowing Through'. It Is The Second Leading Cause of Death in Children Under 5 Years of AgeDocument12 pagesDiarrhea Is Derived From Greek Word, Meaning 'Flowing Through'. It Is The Second Leading Cause of Death in Children Under 5 Years of AgefitahsinghNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plankreny1050% (2)
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Document6 pagesRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument15 pagesNCPCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Health Management Related To Mrs. Gama: Provide The Client Enough Knowledge About The ProblemDocument5 pagesIneffective Health Management Related To Mrs. Gama: Provide The Client Enough Knowledge About The ProblemAndrea Albester GarinoNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study NCPDocument5 pagesDrug-Study NCPMURILLO, FRANK JOMARI C.No ratings yet
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocument6 pagesWord Ncp.......... TetanusaianrNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument15 pagesAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRanusha AnushaNo ratings yet
- NCP PPHDocument2 pagesNCP PPHMark Joseph Christian100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Peptic UlcerDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Peptic UlcerJefferson Baluyot PalmaNo ratings yet
- Fluorosis: Fluoride Toxicity: Patient Management & MonitoringDocument24 pagesFluorosis: Fluoride Toxicity: Patient Management & MonitoringdrjriNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermYumeko JabamiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Care Plan HyponitremiaDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Care Plan HyponitremiaAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument3 pagesNCP FinalCheska Mae PalicNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On HyperlipidemiaDocument4 pagesLesson Plan On HyperlipidemiaBinita Shakya100% (1)
- BibliographyDocument3 pagesBibliographyJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPNaidin Catherine De Guzman-AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKatrene Lequigan100% (1)
- NCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia and Risk For AspirationDocument3 pagesHyperthermia and Risk For AspirationAlmyr RimandoNo ratings yet
- Cholera N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesCholera N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Surgical Management For Cryptorchidism With Nursing ManagementsDocument4 pagesSurgical Management For Cryptorchidism With Nursing ManagementsAprille Claire MoralesNo ratings yet
- Otitis Media AcuteDocument30 pagesOtitis Media AcuteDede Gustina AyuNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlandeliejoyceNo ratings yet
- Artillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument5 pagesArtillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaAl TheóNo ratings yet
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanCj LowryNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan - Fatigue (Antepartum)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan - Fatigue (Antepartum)kaimimiyaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ColestipolDocument3 pagesDrug Study ColestipolAbby AngNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElla EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument8 pages1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceEsel Mae DinamlingNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan FinalDocument16 pagesNursing Care Plan FinalErickson OcialNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument14 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJennifer ArdeNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument6 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJamaica SaranquinNo ratings yet
- Medication ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- Risk Diagnosis For Hirschsprung DiseaseDocument4 pagesRisk Diagnosis For Hirschsprung DiseaseAngelica Floreza DullasNo ratings yet
- Case Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomsDocument2 pagesCase Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomskslhfwoiebvNo ratings yet
- NCP For ConcussionDocument3 pagesNCP For Concussiontamtam_antonio100% (1)
- Date and Time Objectives Learning Contents Strategies Target Population Resources Evaluation OutcomeDocument8 pagesDate and Time Objectives Learning Contents Strategies Target Population Resources Evaluation OutcometrizzlecNo ratings yet
- Tonsilitis NCPDocument2 pagesTonsilitis NCPFATIMA MARYAMA USMANNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Document2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Jesse James Advincula Edjec100% (15)
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Nausea and VomitDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Nausea and VomitJakeNo ratings yet
- HydroceleDocument10 pagesHydroceleRyan ReNo ratings yet
- NCP Nausea and VomitingDocument4 pagesNCP Nausea and VomitingKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPLevyanne GsanchezNo ratings yet
- Diabetes GenogramDocument2 pagesDiabetes GenogramJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- St. Paul University Philippines: Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500Document2 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines: Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500Jobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics Handout # 3 Computer Based Clinical Decision Support SystemDocument11 pagesNursing Informatics Handout # 3 Computer Based Clinical Decision Support SystemJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- .archivetempMODULE 2 GUIDE QQ 9th Ed, 2018Document2 pages.archivetempMODULE 2 GUIDE QQ 9th Ed, 2018Jobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- FNP PartialDocument5 pagesFNP PartialJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- Stress Test: BY: Jobelyn Delena Tunay, RNDocument92 pagesStress Test: BY: Jobelyn Delena Tunay, RNJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- International HealthDocument11 pagesInternational HealthJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- MI SlidesDocument65 pagesMI SlidesJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- Mi PresentationDocument65 pagesMi PresentationJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Catheterization and PCIDocument75 pagesCardiac Catheterization and PCIJobelyn Tunay100% (1)
- Homework 3 ProblemsDocument3 pagesHomework 3 ProblemsSittie Ainna A. UnteNo ratings yet
- Laxatives and PugatiivesDocument4 pagesLaxatives and PugatiivesSultan Abdul Hamid IINo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Physical SelfDocument36 pagesChapter 6 - Physical SelfMary Grace BantaNo ratings yet
- 09 ASA SK Vit MineralsDocument25 pages09 ASA SK Vit MineralsmarofNo ratings yet
- Extreme Health Resolution Secrets by Edwin PatrickDocument22 pagesExtreme Health Resolution Secrets by Edwin PatrickMark ChangNo ratings yet
- Physical Education (048) HMJ 4 Class Xii Marking Scheme 2020Document13 pagesPhysical Education (048) HMJ 4 Class Xii Marking Scheme 2020kunju molNo ratings yet
- January Free Chapter - French Women Don't Get Facelifts by Mireille GuilianoDocument28 pagesJanuary Free Chapter - French Women Don't Get Facelifts by Mireille GuilianoRandomHouseAU80% (5)
- Stomach CancerDocument11 pagesStomach CancerJumar Vallo ValdezNo ratings yet
- Beginners Basic Bodyweight Program NEWDocument26 pagesBeginners Basic Bodyweight Program NEWStevanovic VladimirNo ratings yet
- Systemic Candidiasis: Pandemic of The 21st Century!: by Dr. George John GeorgiouDocument14 pagesSystemic Candidiasis: Pandemic of The 21st Century!: by Dr. George John GeorgiouDr George GeorgiouNo ratings yet
- Concept of Pregnancy Final NCM 107 07172019Document6 pagesConcept of Pregnancy Final NCM 107 07172019Jarod Hembrador100% (1)
- Hoof Anatomy, Care and Management in LivestockDocument9 pagesHoof Anatomy, Care and Management in LivestockmtrankerNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityAl-Qadry NurNo ratings yet
- Dupont Et Al 2018 Can Dynamic in Vitro Digestion...Document18 pagesDupont Et Al 2018 Can Dynamic in Vitro Digestion...Camila Mella CaroNo ratings yet
- PJPHM 15 005 Takrama CocoaDocument6 pagesPJPHM 15 005 Takrama CocoaandruzanchezNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition: Ch10: Energy MetabolismDocument21 pagesAnimal Nutrition: Ch10: Energy Metabolism溫.No ratings yet
- Nutrition Diet TherapyDocument70 pagesNutrition Diet TherapyMay Rodeo100% (1)
- Nutrients: Current Food Consumption Amongst The Spanish ANIBES Study PopulationDocument15 pagesNutrients: Current Food Consumption Amongst The Spanish ANIBES Study PopulationAntony LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Page 1 Case StudyDocument3 pagesPage 1 Case Studymba 20190% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S0924224421005124 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0924224421005124 MainLau CondeNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarterly ExaminationDocument4 pages3rd Quarterly ExaminationMa Donna Geroleo0% (1)
- The Effect of Supplementary Feeding PDFDocument12 pagesThe Effect of Supplementary Feeding PDFholyangelparepareNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document41 pagesGroup 1SELEMAYE ZENEBENo ratings yet
- Cae Speaking Test Part 3Document6 pagesCae Speaking Test Part 3ali_nusNo ratings yet
- Fat Loss MatrixDocument4 pagesFat Loss MatrixDeepak Singh100% (3)
- Exercising For 180 DaysDocument19 pagesExercising For 180 DaysRaj KarkiNo ratings yet