Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Survey Paper On Cloud Computing-38295886
Survey Paper On Cloud Computing-38295886
Uploaded by
FisehaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Survey Paper On Cloud Computing-38295886
Survey Paper On Cloud Computing-38295886
Uploaded by
FisehaCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Technology (IJIET)
Survey Paper on Cloud Computing
Palvinder Singh
M-Tech Student
Department of Computer Science & Engg.
Geeta Institute of Management & Technology, Kurukshetra
Er. Anurag Jain
Assistant Professor
Department of Computer Science & Engg.
Geeta Institute of Management & Technology, Kurukshetra
anuragjain@gimtkkr.com
Abstract - Cloud computing is a new computational model which is primarily based on grid computing. Cloud computing
are often outlined as a computing surroundings wherever computing wants by one party are often outsourced to a
different party and once would like be arise to use the computing power or resources like information or emails, they will
access them via web. This paper is for anyone who will have recently detected regarding cloud computing and desires to
grasp a lot of regarding cloud computing. During this paper, we described Cloud Computing, Architecture of Cloud
Computing, Characteristics of Cloud Computing, and different Services and Deployment model of Cloud Computing.
Keywords - Cloud computing, On Demand computing, Distributed computing, Data center
I. INTRODUCTION
Cloud Computing provides a surroundings for resource sharing in terms of ascendance frameworks, middleware’s
and application development platforms, and business applications. The operation models of cloud computing grasp
free infrastructure services with value another platform services, subscription-based infrastructure services with
supplemental application services, and free services for sellers but sharing of revenues generated from shoppers [1].
The term Cloud Computing has been out lined in some ways by analyst corporations, academics, business
practitioners and IT corporations. Clouds is an over sized pool of simply usable and accessible virtualized resources.
These resources may be dynamically reconfigured to regulate to a variable load (scale), permitting additionally for
an optimum resource utilization [2].
Figure 1. Cloud Computing [2]
There is no doubt that cloud computing is that the most famous topic in IT business. Google, Amazon, Yahoo and
alternative web service suppliers, IBM, Microsoft and alternative IT vendors have imply their own cloud computing
Vol. 3 Issue 4 April 2014 84 ISSN: 2319 – 1058
International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Technology (IJIET)
strategy, numerous medium operators are have place an excellent deal of attention on cloud computing, the terribly
low price of cloud computing platform becomes the main focus of the business.
II. ARCHITECTURE OF CLOUD COMPUTING
Cloud computing system can be divided into two sections: the front end and the back end. They each area unit
connected with one another through a network, sometimes the net. Front is what the consumer (user) sees whereas
the rear end is that the cloud of the system. Face has the client's laptop and therefore the application needed to access
the cloud and therefore the back has the cloud computing services like numerous computers, servers and information
storage [3].
A. Architectural layers of cloud computing
The architecture of a cloud computing can be categories into four layers:
The Physical layer, the infrastructure layer, the platform layer and the application layer, as indicated in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Architecture layers of cloud computing [4]
i. The Hardware layer:
The hardware layer is responsible for dealing with the physical assets of the cloud, including routers, servers,
switches, cooling systems and power.
ii. The Infrastructure layer:
The infrastructure layer is also called as virtualization layer. The infrastructure layer makes a pool of storage
capacity and computing resources by partitioning the physical resources using virtualization technologies such as
KVM and VMware.
iii. The Platform layer:
The platform layer based on top of the infrastructure layer, and this layer comprises of operating systems and
requisition structures.
iv. The Application layer:
The application layer comprises of the actual cloud provisions, for e.g. Business Applications, Multimedia & Web
Services [4].
Vol. 3 Issue 4 April 2014 85 ISSN: 2319 – 1058
International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Technology (IJIET)
B. Service Models of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing has various different service models such as Infrastructure as a Service (IAAS), Platform as a
Service (PAAS), and Software as a Service (SAAS).
i. Infrastructure as a Service (IAAS)
Cloud consumers can directly use IT infrastructures (processing, storage, networks, and other fundamental
computing resources) provided in the IaaS cloud. Iaas cloud provides “Virtualization” in order to
integrate/decompose physical resources in an ad-hoc manner to meet growing or shrinking resource demand from
cloud consumers. An example of IaaS is Amazon's EC2.
ii. Platform as a Service (PAAS)
PaaS provides a development platform that supports the full "Software Lifecycle" which allows cloud consumers to
develop their cloud services and applications (e.g. SaaS) directly on the PaaS cloud. The main difference between
SaaS and PaaS is that SaaS only hosts completed cloud applications whereas PaaS offers a development platform
that hosts both completed and in-progress cloud applications. Example of PaaS is Google AppEngine.
iii. Software as a Service (SAAS)
Cloud consumers can release their applications on a hosting environment, which can be accessed through internet
from various clients (e.g. web browser, PDA, etc.) by application clients. Examples of SaaS are SalesForce.com,
Google Docs, and Google Mail.
III. CHARACTERSTICS OF CLOUD COMPUTING
x In cloud computing, users access the information, applications or the other services with the assistance of a
browser notwithstanding the device used and also the user's location. The infrastructure that is mostly
provided by a third-party is accessed with the assistance of web. Price is reduced to a major level because
the infrastructure is provided by a third-party.
x Less IT skills are needed for implementation.
x Reliable services are often obtained by the employment of multiple sites that is appropriate for business
continuity and disaster recovery.
x Sharing of resources and prices amongst an outsized assortment of users permits economical utilization of
the infrastructure.
x Maintenance is simpler just in case of cloud computing applications as they have not been put in on every
user's pc.
x Pay per use facility permits activity the usage of application per shopper on regular bases.
x Performance is often monitored and so it's ascendible.
x Security is often pretty much as good as or higher than ancient systems as a result of suppliers are able to
devote resources to resolution security problems that several customers cannot afford. However, security
still remains a crucial concern once the information is sort of confidential [6].
x Cloud could be a massive resource pool that you just should buy in keeping with your need; cloud is simply
like running water, electric, and gas which will be charged by the quantity that you just used.
x Cloud computing makes user get service anyplace, through any reasonably terminal. The resources it
needed return from cloud rather than visible entity. Users will attain or share it safely through a simple
method, anytime, anywhere. Users will complete a task that can’t be completed in an exceedingly single
personal computer [7].
IV. DEPLOYMENT OF CLOUD COMPUTING
Clouds can generally be deployed according to the owner of the Cloud data centers. A Cloud atmosphere will
comprise either one Cloud or multiple Clouds. Thus, it can often be distinguished between single-Cloud
environments and multiple-Cloud environments. The subsequent subsections give a classification of single
cloud environments consistent with the Cloud information centre possession and a classification of multiple-
Cloud environments consistent with which sort of Clouds area unit combined (see figure 3) [8].
Vol. 3 Issue 4 April 2014 86 ISSN: 2319 – 1058
International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Technology (IJIET)
Figure 3. Cloud Computing Deployment model [8]
a. Public cloud
In public cloud, users access to the services victimization external interfaces which may be offered by internet
browsers via web. The users share a standard cloud infrastructure and that they don't seem to be intimate it. though
public clouds square measure rather less secure, they're terribly advantageous in costs. For those organizations that
cannot afford huge IT investments and do not have a lot of confidential information, public cloud appears to be an
honest selection [9].
b. Private Cloud
A private clouds operation is inside associate organization's internal enterprise information center. The most
advantage here is that it's easier to manage security, maintenance and upgrades and conjointly provides additional
management over the preparation and use. Non-public cloud is often compared to computer network. Compared to
public cloud wherever all the resources and applications were managed by the service supplier, in camera cloud
these services square measure pooled along and created out there for the users at the structure level. The resources
and applications square measure managed by the organization itself [10].
c. Community Cloud
A community cloud is a collaborative effort made for sharing infrastructure between multiple organizations. It forms
into a degree of economic scalability and democratic equilibrium. The community cloud is managed and secured by
all the participating organization or by a third party service provider.
d. Hybrid Computing
Hybrid cloud is a combination of two or more clouds (private, community, or public) that remain unique entities but
are bound together by standardized or proprietary technology that enables data and application portability (e.g.,
cloud bursting for load-balancing between clouds) [11].
V. CHALLENGES OF CLOUD COMPUTING
Based on a survey conducted by IDC in 2008, the main challenges that forestall Cloud Computing from being
adopted square measure recognized by organizations square measure as follows:
A. Security:
It is clear that the safety issue has competed the foremost necessary role in preventive cloud computing acceptance.
No doubt, golf shot your information, running your software system on somebody else's magnetic disc victimization
somebody else's hardware seems frightening several. Well-known security problems like information loss, phishing
cause serious threats to organization's information and software system. Moreover, the multi-tenancy model and
therefore the pooled computing resources in cloud computing has introduced new security challenges that need
novel techniques to tackle with. For instance, hackers will use Cloud to arrange as Cloud typically provides a lot of
reliable infrastructure services at a comparatively cheaper worth for them to begin an attack.
B. Cost Accounting Model:
Vol. 3 Issue 4 April 2014 87 ISSN: 2319 – 1058
International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Technology (IJIET)
Cloud customers should think about the tradeoffs amongst computation, communication, and integration. Whereas
migrating to the Cloud will considerably scale back the infrastructure value, it will raise the price of information
communication, i.e. the value of transferring an organization's information to and from the general public and
community Cloud and therefore the cost per unit of computing resource used is probably going to be higher. This
downside is especially distinguished if the patron uses the hybrid cloud preparation model wherever the
organization's information is distributed amongst variety of public/private (in-house IT infrastructure) clouds.
Intuitively, on demand computing is sensible just for hardware intensive jobs [9].
C. Charging Model:
The elastic resource pool has created the value analysis lots additional difficult than regular information centers,
which regularly calculates their price supported consumptions of static computing. Moreover, associate degree
instantiated virtual machine has become the unit of analysis instead of the underlying physical server. For SaaS
cloud suppliers, the value of developing multi residency among their giving is terribly substantial. These include: re-
design and improvement of the package that was originally used for single-tenancy, price of providing new options
that afford intensive customization, performance and security improvement for coinciding user access, and
managing complexities induced by the higher than changes.
D. Service Level Agreement (SLA):
Although cloud customers don't have management over the underlying computing resources, they are doing got to
make sure the quality, convenience, responsible, and performance of those resources once customers have migrate
their core business functions onto their entrusted cloud. In alternative words, it's important for customers to get
guarantees from suppliers on service delivery.
E. Cloud Interoperability Issue:
Currently, every cloud giving has its own approach on however cloud clients move with the cloud, resulting in the
"Hazy Cloud" development. This severely hinders the event of cloud ecosystems by forcing marketer protection that
prohibits the flexibility of users to decide on from various vendors at the same time so as to optimize resources at
completely different levels inside a company. a lot of significantly, proprietary cloud arthropod genus makes it
terribly tough to integrate cloud services with Associate in Nursing organization's own existing bequest systems
(e.g. Associate in Nursing on-premise knowledge centre for extremely interactive modeling applications in an
exceedingly pharmaceutical company).The primary goal of ability is to comprehend the seamless fluid knowledge
across clouds and between cloud and native applications [12].
VI. CONCLUSION
Cloud computing is a new technology wide studied in recent years. Currently there are several cloud platforms that
are employed in each in trade and in educational. The way to use these platforms could be a huge issue. During this
paper, we have a tendency to delineate the definition, styles, and characteristics of cloud computing, cloud
computing services, readying model and challenges of cloud computing. There are several issues in cloud
computing. As an example of cloud computing issues is ability, Performance, Service Level Agreement (SLA),
knowledge Confidentiality and measurability, knowledge Integrity, Load equalization, Synchronization in numerous
clusters in cloud platform, and standardization, the protection of cloud platform.
REFERENCES
[1] Liang-Jie Zhang; Qun Zhou, "CCOA: Cloud Computing Open Architecture," in proceeding of IEEE International Conference on Web
Services (ICWS), 2009, pp. 607-616, 6-10 July 2009.
[2] Shyam Patidar; Dheeraj Rane; Pritesh Jain “A Survey Paper on Cloud Computing” in proceeding of Second International Conference on
Advanced Computing & Communication Technologies, 2012.
[3] Yashpalsinh Jadeja; Kirit Modi, “Cloud Computing - Concepts, Architecture and Challenges” in Proceeding of International Conference on
Computing, Electronics and Electrical Technologies [ICCEET], 2012.
[4] Qi Zhang, Lu Cheng and Raouf Boutaba, “Cloud computing: state-of-the-art and research challenges”.
[5] Tharam Dillon, Chen Wu and Elizabeth Chang, “Cloud Computing: Issues and Challenges,” in Proceeding of 2010 24th IEEE International
Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications, pp. 27-33, 20-23 April 2010.
[6] Yashpalsinh Jadeja; Kirit Modi, “Cloud Computing - Concepts, Architecture and Challenges” in Proceeding of International Conference on
Computing, Electronics and Electrical Technologies [ICCEET], 2012.
Vol. 3 Issue 4 April 2014 88 ISSN: 2319 – 1058
International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Technology (IJIET)
[7] Xu Wang; Beizhan Wang; Jing Huang, “Cloud computing and its key techniques” in Proceeding of IEEE Conference, 2011.
[8] Shyam Patidar; Dheeraj Rane; Pritesh Jain “A Survey Paper on Cloud Computing” in proceeding of Second International Conference on
Advanced Computing & Communication Technologies, 2012.
[9] Adem TEPE, Güray YILMAZ, “A Survey on Cloud Computing Technology and Its Application to Satellite Ground Systems”.
[10] Yashpalsinh Jadeja; Kirit Modi, “Cloud Computing - Concepts, Architecture and Challenges” in Proceeding of International Conference on
Computing, Electronics and Electrical Technologies [ICCEET], 2012.
[11] Tharam Dillon, Chen Wu and Elizabeth Chang, “Cloud Computing: Issues and Challenges,” in Proceeding of 2010 24th IEEE International
Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications, pp. 27-33, 20-23 April 2010.
[12] Kuyoro S. O.; Ibikunle F; & Awodele O., “Cloud Computing Security Issues and challenges” in Proceeding of International Journal of
Computer Networks (IJCN), Volume (3), Issue (5), 2011.
Vol. 3 Issue 4 April 2014 89 ISSN: 2319 – 1058
You might also like
- Exam - Cloud Computing ACADocument11 pagesExam - Cloud Computing ACArangel24100% (2)
- Data Abstraction and Problem Solving With Java Walls and Mirrors 3rd Edition Prichard Test BankDocument9 pagesData Abstraction and Problem Solving With Java Walls and Mirrors 3rd Edition Prichard Test Bankamandahillmpsxfbkrny100% (15)
- File Upload Template For Onehub Pag-Ibig TransactionsDocument35 pagesFile Upload Template For Onehub Pag-Ibig TransactionsAngelo Labios100% (1)
- Article Review Group Assignment#1Document7 pagesArticle Review Group Assignment#1Fiseha100% (5)
- Pixinsight 1.8 - E3Ddy UtorrentlDocument3 pagesPixinsight 1.8 - E3Ddy UtorrentlAmandaNo ratings yet
- B0193uc HDocument68 pagesB0193uc HMiguel Angel GiménezNo ratings yet
- Survey Paper On Cloud Computing: International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Technology April 2014Document7 pagesSurvey Paper On Cloud Computing: International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Technology April 2014Princess JeanNo ratings yet
- Ijet V4i3p33 PDFDocument10 pagesIjet V4i3p33 PDFInternational Journal of Engineering and TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing - Concepts, Architecture and Challenges: Yashpalsinh Jadeja Kirit ModiDocument4 pagesCloud Computing - Concepts, Architecture and Challenges: Yashpalsinh Jadeja Kirit ModiShivam AngadiNo ratings yet
- M.M. Polytechnic, Thergaon, Pune-33: Cloud ComputingDocument14 pagesM.M. Polytechnic, Thergaon, Pune-33: Cloud ComputingaishwaryawaghmaleNo ratings yet
- Survey of Cloud ComputingDocument13 pagesSurvey of Cloud ComputingijwscNo ratings yet
- Abstract-: Keywords: Applications, Architecture, Business Component of CloudDocument15 pagesAbstract-: Keywords: Applications, Architecture, Business Component of CloudKrishna BoreddyNo ratings yet
- Ijett V21P256Document8 pagesIjett V21P256Bharath KumarNo ratings yet
- FOG COMPUTING AN ABLE EXTENSION TO CLOUD COMPUTING Research Paper - NewDocument16 pagesFOG COMPUTING AN ABLE EXTENSION TO CLOUD COMPUTING Research Paper - NewMinahil Ahmad100% (1)
- A Comparative Study For Cloud Computing PDFDocument8 pagesA Comparative Study For Cloud Computing PDFRafsanjany SamirNo ratings yet
- Advanced Survey On Ultra-Modern Cloud Computing TechnologyDocument5 pagesAdvanced Survey On Ultra-Modern Cloud Computing TechnologyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cloud Computing Security: (Chapter One)Document17 pagesIntroduction To Cloud Computing Security: (Chapter One)hmsa7863No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing in Resource ManagementDocument6 pagesCloud Computing in Resource ManagementIJEMR JournalNo ratings yet
- Axioms of Cloud Computing: International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)Document4 pagesAxioms of Cloud Computing: International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Job Scheduling in Cloud Computing: A Review of Selected TechniquesDocument5 pagesJob Scheduling in Cloud Computing: A Review of Selected TechniquesInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Architecture, Services, Deployment Models, Storage, Benefits and ChallengesDocument6 pagesCloud Computing Architecture, Services, Deployment Models, Storage, Benefits and ChallengesEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: History, Architecture, Security Issues: March 2015Document8 pagesCloud Computing: History, Architecture, Security Issues: March 2015Prabhakar VermaNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Security For Protecting Data in Cloud Using Layered ApproachDocument7 pagesEnhanced Security For Protecting Data in Cloud Using Layered ApproachInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Cloud ComputingDocument16 pagesA Survey On Cloud Computingmehajol272No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Overview & Current Research Challenges: Mohsin NazirDocument9 pagesCloud Computing: Overview & Current Research Challenges: Mohsin NazirAbdullah AlwaqdyNo ratings yet
- Abdoo - On Graphtree PDFDocument9 pagesAbdoo - On Graphtree PDFAbdullah AlwaqdyNo ratings yet
- UNIT I - CS8791 - Cloud ComputingDocument21 pagesUNIT I - CS8791 - Cloud ComputingabiNo ratings yet
- Synposis VirtualizationDocument6 pagesSynposis Virtualizationharshit96023No ratings yet
- Investigations On Different Security Techniques For Data Protection in Cloud Computing Using Cryptography SchemesDocument16 pagesInvestigations On Different Security Techniques For Data Protection in Cloud Computing Using Cryptography SchemesIIJSR JournalNo ratings yet
- Compusoft, 2 (12), 404-409 PDFDocument6 pagesCompusoft, 2 (12), 404-409 PDFIjact EditorNo ratings yet
- A Review Paper On Cloud Computing: Nikhil RanjanDocument6 pagesA Review Paper On Cloud Computing: Nikhil RanjanNikhil Ranjan 211No ratings yet
- DOM205 - Individual Project - Cloud Computing ABHARIKA MOHANTYDocument18 pagesDOM205 - Individual Project - Cloud Computing ABHARIKA MOHANTYAbharika MohantyNo ratings yet
- Acta 2014 4 25 PDFDocument19 pagesActa 2014 4 25 PDFNikunj PatelNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing A Survey On Cloud ComputingDocument5 pagesCloud Computing A Survey On Cloud ComputingThang Nguyen QuangNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Cloud Computing UtilitiesDocument6 pagesComparative Analysis of Cloud Computing UtilitiesshahhinNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Data Security and Privacy in Cloud ComputingDocument9 pagesReview Article: Data Security and Privacy in Cloud Computingsagar sagNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Security Issues and Challenges: Pranita P. Khairnar, Prof. V.S. UbaleDocument13 pagesCloud Computing Security Issues and Challenges: Pranita P. Khairnar, Prof. V.S. Ubalewww.irjes.comNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument17 pagesReportsaurabh128No ratings yet
- 19BCON403 Cloud Computing ReportDocument20 pages19BCON403 Cloud Computing ReportDank BoiiNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar Reportshinchan noharaNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar Reportshinchan noharaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing PDFDocument103 pagesCloud Computing PDFRafiq MagdyNo ratings yet
- Secure Cloud Using RGB Value and Homomorphic Encryption For Shared Data in CloudDocument4 pagesSecure Cloud Using RGB Value and Homomorphic Encryption For Shared Data in CloudEditor IJRITCCNo ratings yet
- Chapter8 PDFDocument42 pagesChapter8 PDFBhavneet SinghNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is A Model For Enabling Ubiquitous, Convenient, On-Demand Network Access To ADocument10 pagesCloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is A Model For Enabling Ubiquitous, Convenient, On-Demand Network Access To ABharath MadalaNo ratings yet
- Security Issues in Cloud ComputingDocument19 pagesSecurity Issues in Cloud ComputingSalau DamilolaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing & Its Application in LibrariesDocument6 pagesCloud Computing & Its Application in LibrariesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing 2Document12 pagesCloud Computing 2madhu08nangelNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Research PaperDocument16 pagesCloud Computing Research PaperRonak ChawlaNo ratings yet
- II NotesDocument18 pagesII Notes19Q91A1231 NALDEEGA SAKETHA CHARYNo ratings yet
- A Study of Infrastructure Clouds: International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology-volume3Issue1 - 2012Document5 pagesA Study of Infrastructure Clouds: International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology-volume3Issue1 - 2012surendiran123No ratings yet
- Cloud Computoing Module IDocument24 pagesCloud Computoing Module IJEEVA P GNo ratings yet
- Cloud-Computing-Current-Research-Summary: March 2016Document11 pagesCloud-Computing-Current-Research-Summary: March 2016Ankit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: The Simplified Format of Pay - To - Use: Dr. M E Purushoththaman Ms. Bhavani ButhukuriDocument5 pagesCloud Computing: The Simplified Format of Pay - To - Use: Dr. M E Purushoththaman Ms. Bhavani ButhukuriAnonymous lPvvgiQjRNo ratings yet
- A Review of Cloud Security Issues and Data Protection TechniquesDocument11 pagesA Review of Cloud Security Issues and Data Protection TechniquesInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- A Study On Cloud Computing Services IJERTCONV4IS34014Document6 pagesA Study On Cloud Computing Services IJERTCONV4IS34014vikasNo ratings yet
- Study of Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesStudy of Cloud ComputingInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Reliability of Cloud Computing Services: Anju Mishra & Dr. Viresh Sharma & Dr. Ashish PandeyDocument10 pagesReliability of Cloud Computing Services: Anju Mishra & Dr. Viresh Sharma & Dr. Ashish PandeyIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNo ratings yet
- 3 IoT-Cloud Convergence - The Convergence of Internet of Things and Cloud For Smart ComputingDocument49 pages3 IoT-Cloud Convergence - The Convergence of Internet of Things and Cloud For Smart ComputingHemanthreddy MandhaNo ratings yet
- Multifactor Biometric Authentication For Cloud Computing: Abstract-Cloud Computing Is A Fast-Growing TechnologyDocument7 pagesMultifactor Biometric Authentication For Cloud Computing: Abstract-Cloud Computing Is A Fast-Growing TechnologyMartin Cardenas MorenoNo ratings yet
- Arun GangwarDocument7 pagesArun GangwarArun GangwarNo ratings yet
- 303 HasanDocument7 pages303 HasanSuriya ShopnaNo ratings yet
- Information Security in Cloud Computing: August 2014Document6 pagesInformation Security in Cloud Computing: August 2014Aseer Istiaq Azad 1813654630No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionFrom EverandCloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing For Beginners: Your First Step into the Future of TechFrom EverandCloud Computing For Beginners: Your First Step into the Future of TechNo ratings yet
- List of Tanneries in Addis AbabaDocument4 pagesList of Tanneries in Addis AbabaFisehaNo ratings yet
- Types of Cooperatives Benefits and ConstraintsDocument6 pagesTypes of Cooperatives Benefits and ConstraintsFisehaNo ratings yet
- The Best: PPT TemplatesDocument25 pagesThe Best: PPT TemplatesFisehaNo ratings yet
- Asm S 35 87Document26 pagesAsm S 35 87FisehaNo ratings yet
- Cooperatives: Characteristics, Activities, Status, ChallengesDocument12 pagesCooperatives: Characteristics, Activities, Status, ChallengesFisehaNo ratings yet
- Business Model ComparisonDocument2 pagesBusiness Model ComparisonFisehaNo ratings yet
- Be Dru Overview of Ethiopian CooperativesDocument26 pagesBe Dru Overview of Ethiopian CooperativesFisehaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Cooperative Development ModelDocument83 pagesIntroduction To The Cooperative Development ModelFisehaNo ratings yet
- Amhara Model RegulationDocument18 pagesAmhara Model RegulationFisehaNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Prospects of Cooperatives in Ethiopia With Reference Sough Gondar Zone-EthiopiaDocument13 pagesChallenges and Prospects of Cooperatives in Ethiopia With Reference Sough Gondar Zone-EthiopiaFisehaNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian Cooperative MovementDocument114 pagesEthiopian Cooperative MovementFisehaNo ratings yet
- Nebiyu Krishina PDFDocument64 pagesNebiyu Krishina PDFFisehaNo ratings yet
- Colorful Pitch Deck: Presentation TemplateDocument8 pagesColorful Pitch Deck: Presentation TemplateFisehaNo ratings yet
- 14 VOL 10S2016 LiaYuldinawatiSmallFamily... Pages197 210Document15 pages14 VOL 10S2016 LiaYuldinawatiSmallFamily... Pages197 210FisehaNo ratings yet
- Template: Insert The Subtitle of Your PresentationDocument30 pagesTemplate: Insert The Subtitle of Your PresentationFisehaNo ratings yet
- State of Competition EthiopiaDocument232 pagesState of Competition EthiopiaFisehaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Information System SecurityDocument34 pagesChapter Five Information System SecurityFisehaNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document27 pagesChap 4FisehaNo ratings yet
- Review Paper On Mobile Cloud Computing S-44590720 PDFDocument4 pagesReview Paper On Mobile Cloud Computing S-44590720 PDFFisehaNo ratings yet
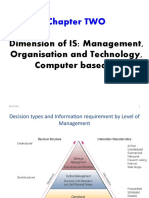
- Chapter TWO: Dimension of IS: Management, Organisation and Technology, Computer Based ISDocument44 pagesChapter TWO: Dimension of IS: Management, Organisation and Technology, Computer Based ISFisehaNo ratings yet
- MIS-chapter 1Document24 pagesMIS-chapter 1FisehaNo ratings yet
- Survey Paper On CP-ABE Cloud Computing-51129037 PDFDocument3 pagesSurvey Paper On CP-ABE Cloud Computing-51129037 PDFFisehaNo ratings yet
- 2 Project Diversity Managment in Workplace PDFDocument22 pages2 Project Diversity Managment in Workplace PDFFisehaNo ratings yet
- Clearing The Clouds On Cloud Computing S-51490823 PDFDocument6 pagesClearing The Clouds On Cloud Computing S-51490823 PDFFisehaNo ratings yet
- Organizational Structure: An OverviewDocument10 pagesOrganizational Structure: An OverviewFisehaNo ratings yet
- Article Review Group AssignmentDocument7 pagesArticle Review Group AssignmentFiseha100% (1)
- 1 CompFundamentals-BSME IntroductionDocument18 pages1 CompFundamentals-BSME IntroductionMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Wamsim For Mike UsersDocument1 pageWamsim For Mike UsersJonathan AmaralNo ratings yet
- ZTE Blade S6 Upgrade Guide PDFDocument5 pagesZTE Blade S6 Upgrade Guide PDFImam PramonoNo ratings yet
- Nilesh Kumar Yadav'sDocument1 pageNilesh Kumar Yadav'svinayNo ratings yet
- Klisipcam 2 MirudvengDocument2 pagesKlisipcam 2 MirudvengShareef KoyaNo ratings yet
- Simove: Maximize Your Production FlexibilityDocument2 pagesSimove: Maximize Your Production FlexibilityJose L. CamarilloNo ratings yet
- NAPIX LGD API Consumer Guidelines v1.1Document14 pagesNAPIX LGD API Consumer Guidelines v1.1mihirmddNo ratings yet
- Rec Vas6150 Ukd V200Document16 pagesRec Vas6150 Ukd V200Giovanny ValenciaNo ratings yet
- A Little Java, A Few Patterns PDFDocument182 pagesA Little Java, A Few Patterns PDFAnutosh Ghosh100% (1)
- Civil 3D Handling of Survey Points Practice ManualDocument7 pagesCivil 3D Handling of Survey Points Practice ManualjeewmNo ratings yet
- SAP BI Business Intelligence Outline 2014Document6 pagesSAP BI Business Intelligence Outline 2014cooliliaNo ratings yet
- My ResumeDocument1 pageMy Resumeapi-313429712No ratings yet
- Cisco Meraki MX Cloud Managed Security AppliancesDocument22 pagesCisco Meraki MX Cloud Managed Security AppliancesDmitri DicusarNo ratings yet
- Mis - Monthly For HRDocument59 pagesMis - Monthly For HRAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- L490 and L590 Hardware Maintenance ManualDocument131 pagesL490 and L590 Hardware Maintenance ManualAndreaNo ratings yet
- General Brochure 2021Document14 pagesGeneral Brochure 2021Ivan Rudolf De FretesNo ratings yet
- 1 IP Network FundamentalDocument25 pages1 IP Network FundamentalYeinner Jose Perez AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 3IT05Document2 pages3IT05Saakshi PatelNo ratings yet
- Uspex ManualDocument113 pagesUspex ManualarnoldNo ratings yet
- Stack Vs Heap Memory Allocation: Memory Layout of C ProgramDocument9 pagesStack Vs Heap Memory Allocation: Memory Layout of C ProgramChandan JhaNo ratings yet
- MC Notes Unit-1Document27 pagesMC Notes Unit-1DURGA PRAKASH SENAPATHINo ratings yet
- Exam Readiness Checklist - Salesforce Admin ExamDocument3 pagesExam Readiness Checklist - Salesforce Admin ExamJaie AmNo ratings yet
- PLSQL 7 3 PracticeDocument5 pagesPLSQL 7 3 Practiceliliana100% (1)
- Key To Content - Upload Files To Alfresco Via Email - Inbound EmailsDocument4 pagesKey To Content - Upload Files To Alfresco Via Email - Inbound EmailsBeatrice DanielaNo ratings yet
- Output With Images 3 DifferntDocument6 pagesOutput With Images 3 Differntuckotsst karahahubusNo ratings yet