Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio F5 C6 Variation
Bio F5 C6 Variation
Uploaded by
LIEW XIU JING MoeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Anti-Diet Reclaim Your Time, Money, Well-Being and Happiness Through Intuitive Eating by Christy HarrisonDocument281 pagesAnti-Diet Reclaim Your Time, Money, Well-Being and Happiness Through Intuitive Eating by Christy HarrisonDann' Mendoza Ü100% (1)
- KPMG Boxwood TL Omni-Platform Paper November 2017 FinalDocument24 pagesKPMG Boxwood TL Omni-Platform Paper November 2017 FinalSeptiana Ayu Estri MahaniNo ratings yet
- Variation: Variation: The Differences Between Individuals of The Same SpeciesDocument39 pagesVariation: Variation: The Differences Between Individuals of The Same SpeciesmarziahNo ratings yet
- VariationDocument39 pagesVariationmarziahNo ratings yet
- Variation F 5Document8 pagesVariation F 5Angie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Evolution NotesDocument5 pagesHeredity and Evolution NotesCapt Pradeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Variation NotesDocument24 pagesVariation NotesMakanaka HoveNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18. VARIATION AND SELECTIONDocument82 pagesChapter 18. VARIATION AND SELECTIONMrs CoolNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Evolution (Notes)Document4 pagesHeredity and Evolution (Notes)anju dixitNo ratings yet
- Class-10 Notes CH-9 Heredity and EvolutionDocument13 pagesClass-10 Notes CH-9 Heredity and EvolutionN.R. ShirishaNo ratings yet
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument14 pagesHeredity and EvolutionprathushaNo ratings yet
- 18.1 VariationDocument14 pages18.1 Variationmi9gx5No ratings yet
- GENETICSDocument6 pagesGENETICSSamyak JainNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument6 pagesGeneticsSamyak JainNo ratings yet
- CH 18 Process of EvolutionDocument41 pagesCH 18 Process of EvolutionBenedicto IluminNo ratings yet
- Hereditary and EvolutionDocument11 pagesHereditary and EvolutionvaibhavNo ratings yet
- 2a Inheritance CDocument9 pages2a Inheritance Capi-238529408No ratings yet
- Biology Form 5: Chapter 6 (Variation)Document5 pagesBiology Form 5: Chapter 6 (Variation)Gerard Selvaraj100% (5)
- Heredity and Variation IDocument21 pagesHeredity and Variation Ismbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument30 pagesUntitledAdugna Mekuria BoteNo ratings yet
- Variations in OrganismsDocument10 pagesVariations in Organismsburned2ashesNo ratings yet
- Heredity and VariationDocument25 pagesHeredity and VariationDre ParkerNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms That Produces Change in PopulationsDocument6 pagesMechanisms That Produces Change in PopulationsblablaNo ratings yet
- VariationsDocument3 pagesVariationsshazeen shoaibNo ratings yet
- Genetic Basis For VariationDocument4 pagesGenetic Basis For VariationNicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - BiologyDocument34 pagesChapter 9 - BiologyNikhil ChettyarNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes F4Document59 pagesBiology Notes F4Nathan SsekamatteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 HeredityDocument23 pagesChapter 8 Heredityfortwitt18No ratings yet
- Honors Bio 9 Study GuideDocument5 pagesHonors Bio 9 Study GuideMalek KamalNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 EvolutionDocument9 pagesTopic 7 EvolutionAddan AddanNo ratings yet
- HEREDITYDocument14 pagesHEREDITYGt FansNo ratings yet
- Evolution Mechanisms 17 18Document44 pagesEvolution Mechanisms 17 18GABRIEL AUDREY SOLONNo ratings yet
- Heredity Class 10Document40 pagesHeredity Class 10ChaithraNo ratings yet
- Genetic Variation Is Caused byDocument5 pagesGenetic Variation Is Caused bySara Angélica Pimentel BonillaNo ratings yet
- Continuity and VariationDocument7 pagesContinuity and Variationamara williamsNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document8 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!sushantNo ratings yet
- Genetics (Autosaved) NDocument64 pagesGenetics (Autosaved) NSuraj kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A2 Biology Revision NotesDocument79 pagesEdexcel A2 Biology Revision NotesAbdalla AhmedNo ratings yet
- What Are Species?Document10 pagesWhat Are Species?homamunfatNo ratings yet
- MSG - 11 - 500169 - Heredity and EvolutionDocument5 pagesMSG - 11 - 500169 - Heredity and EvolutionUllhas Y KumarNo ratings yet
- Bio Final RevisionDocument8 pagesBio Final Revisionbisma nadeemNo ratings yet
- Genetics and PopulationsDocument7 pagesGenetics and PopulationsAlchemist CyanideNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument5 pagesNotesMady ffNo ratings yet
- Notes HeredityDocument8 pagesNotes Heredityvaibhav4gameNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of EvolutionDocument29 pagesMechanisms of EvolutionBukhari DiangkaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 VariationDocument13 pagesChapter 14 VariationLisa AllisyaNo ratings yet
- G12 Bio2 LM 4 Micro vs. MacroevolutionDocument29 pagesG12 Bio2 LM 4 Micro vs. MacroevolutionHannah AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument14 pagesHeredity and EvolutionLakshit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 07 Quantitative InheritanceDocument2 pages07 Quantitative InheritanceBen AbellaNo ratings yet
- Biology Cell Presentation in Green White Illustrative StyleDocument60 pagesBiology Cell Presentation in Green White Illustrative StyleDaisy Rizza AgnesNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution Revision NotesDocument20 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution Revision NotesYaseen BepariNo ratings yet
- 10.3 Gene Pools and SpeciationDocument8 pages10.3 Gene Pools and SpeciationAbdelrahman HarrathNo ratings yet
- Class X - HeredityDocument38 pagesClass X - HeredityRohit NairNo ratings yet
- Genetics ActivityDocument3 pagesGenetics ActivityBio SciencesNo ratings yet
- Biology Grade 8 - Variation & InheritanceDocument27 pagesBiology Grade 8 - Variation & InheritanceMokshitha Reddy YanamalNo ratings yet
- Heredity (Genetics) CLASS 10Document7 pagesHeredity (Genetics) CLASS 10shallowNo ratings yet
- AGN001Document3 pagesAGN001Jet Ronnie DacayaNo ratings yet
- Evolution: How Life Adapts to a Changing Environment with 25 ProjectsFrom EverandEvolution: How Life Adapts to a Changing Environment with 25 ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Contemparary Issues in ManagementDocument4 pagesSeminar On Contemparary Issues in ManagementNaimish BodarNo ratings yet
- Organoboranes in Organic Syntheses Including Suzuki Coupling ReactionDocument29 pagesOrganoboranes in Organic Syntheses Including Suzuki Coupling Reactionratul mahataNo ratings yet
- Pupillary Pathways &reactions: Assistant Professor, Department of Ophthalmology Nepalgunj Medical CollegeDocument16 pagesPupillary Pathways &reactions: Assistant Professor, Department of Ophthalmology Nepalgunj Medical CollegeDrBikram ThapaNo ratings yet
- CAVENDISHDocument2 pagesCAVENDISHMarvin LagascaNo ratings yet
- Daniel James - English A SbaDocument13 pagesDaniel James - English A Sbadanieltjames5092No ratings yet
- Effects of Pole Dance On Mental Wellbeing and The Sexual Self-Concept-A Pilot Randomized-Controlled TrialDocument7 pagesEffects of Pole Dance On Mental Wellbeing and The Sexual Self-Concept-A Pilot Randomized-Controlled Trialnoemi.hegedus11No ratings yet
- 19-CPS Student Induction Presentation-RAZAK FinalDocument18 pages19-CPS Student Induction Presentation-RAZAK FinalbaderNo ratings yet
- A Brief Biography of Hazrat Khaja Hussian Shah Wali HyderabadDocument17 pagesA Brief Biography of Hazrat Khaja Hussian Shah Wali HyderabadMohammed Abdul Hafeez, B.Com., Hyderabad, IndiaNo ratings yet
- Manila Pavilion v. DeladaDocument2 pagesManila Pavilion v. Deladasitsee watchNo ratings yet
- Johansson Kurt Aleksej Gastev Proletarian Bard of The Machine Age PDFDocument174 pagesJohansson Kurt Aleksej Gastev Proletarian Bard of The Machine Age PDFtalespintoNo ratings yet
- Base Connection DesignDocument7 pagesBase Connection Designmsiddiq1No ratings yet
- Ee5121 Tutorial 1Document2 pagesEe5121 Tutorial 1ananNo ratings yet
- Prophetic ProtocolDocument36 pagesProphetic ProtocolNeil SoansNo ratings yet
- Attachment 1Document468 pagesAttachment 1Ali JarkhiNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Global WarmingDocument11 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Global WarmingA Aldika Farlis50% (2)
- ADAMS v. SCHULTZ - Document No. 5Document6 pagesADAMS v. SCHULTZ - Document No. 5Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Early Adolescence (Ages 10 To 13) : Females MalesDocument5 pagesEarly Adolescence (Ages 10 To 13) : Females MalesBea Valerie GrislerNo ratings yet
- Peterson, Anand - The Production of Culture PerspectiveDocument25 pagesPeterson, Anand - The Production of Culture Perspectiveqthestone45No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Boolean Algebra Logic GatesDocument29 pagesChapter 2 Boolean Algebra Logic GatesZahra JafarNo ratings yet
- Movie Review: - Efforts By-Riya Maan - Rishabh Saxena - 12 CDocument11 pagesMovie Review: - Efforts By-Riya Maan - Rishabh Saxena - 12 CRishabh SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Literary Criticism - 21st CDocument2 pagesLiterary Criticism - 21st CGabrielle mari BulawanNo ratings yet
- Discourse Analysis: Ove K. PedersenDocument9 pagesDiscourse Analysis: Ove K. Pedersenmervat_aastNo ratings yet
- History of English LiteratureDocument59 pagesHistory of English LiteratureMarghescu AngelNo ratings yet
- CC15 Laminar FlowDocument22 pagesCC15 Laminar Flow999impactNo ratings yet
- BootcampDocument34 pagesBootcampPurvi JainNo ratings yet
- Ict Resources For Information, Collaboration and LearningDocument10 pagesIct Resources For Information, Collaboration and LearningBea HdbfbfjNo ratings yet
- Course Outline MATH 361 Probability and StatisticsDocument3 pagesCourse Outline MATH 361 Probability and StatisticsSkiwordy MediaNo ratings yet
- m1010 Final sp12Document8 pagesm1010 Final sp12DEANGELO AVILESNo ratings yet
Bio F5 C6 Variation
Bio F5 C6 Variation
Uploaded by
LIEW XIU JING MoeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio F5 C6 Variation
Bio F5 C6 Variation
Uploaded by
LIEW XIU JING MoeCopyright:
Available Formats
0BIO F5C6
6.1 Variation
S+D (Variations) 10m
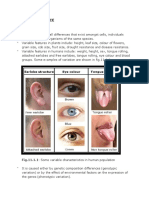
Similarities :
- Both continuous and discontinuous variation phenotypic differences among individuals of the same
species.
- Both help the species to survive and adapt to changes in the environment (ensure survival from
predators.
Differences :
Continuous Discontinuous
Differences in a character are not distinctive. Differences in a character are distinctive.
Produce normal distribution. Produce discrete distribution.
(bell-shaped curve)
Characters are quantitative, can be measured or Characters are qualitative, cannot be measured or
graded from one extreme to another. graded from one extreme to another.
Caused by environmental factors. Caused by genetic factors.
Characters cannot be inherited. Characters can be inherited.
Controlled by many genes. Controlled by a single gene.
Phenotype controlled by several pairs of allele. Phenotype controlled by a pair of allele.
Examples such as height,weight,skin colour and Examples such as ability to roll tongue,attached or
intelligence. free ear lobes,blood group and type of
fingerprints.
In. characteristic undergoes gradual changes. No gradual changes between two extremes.
6.2 Genetic factors 10m
1. when (during….) 3. Explain the process
2. what happen 4. The effect of the process
A] Crossing over during Meiosis
1. During prophase I , when two homologous chromosomes are paired up in a bivalent,crossing over
occurs. What is crossing over ?
2. - Chromatids of chromosomes cross over and break at chiasma. How??
- Segments of DNA exchange places between non-sister chromatids.
3. - New genetic recombination are produced.
4. - Chromatids then separate during anaphase II . so?? different combination of genes in gametes are
produced. Then??
- Fusion of gametes during fertilisation will produce a variety of child.
B] Independent assortment of chromosomes
1. During metaphase I of meiosis, the homologous chromosomes arrange themselves randomly on the
metaphase plate.
2. The random arrangement and separation of each homologous pair is independent to each other.
3. Hence, there is an independent assortment of maternal and paternal chromosomes. Why?? as the
homologous pair may lined up in different way.
4. This produces various genetic combinations in the gametes.
C] Random fertilisation
1. During fertilisation ,each gamete has a unique genetic combination. Ya?? they fuse together
randomly.
2. - A male gamete can fertilise any of the female gametes.
- The fertilisation between a male gamete and a female gamete occurs randomly.
3. As a result , a zygote which is unique is formed. (greater variety of genetic combination )
4. This cause genetic variation occurs in offsprings.
You might also like
- Anti-Diet Reclaim Your Time, Money, Well-Being and Happiness Through Intuitive Eating by Christy HarrisonDocument281 pagesAnti-Diet Reclaim Your Time, Money, Well-Being and Happiness Through Intuitive Eating by Christy HarrisonDann' Mendoza Ü100% (1)
- KPMG Boxwood TL Omni-Platform Paper November 2017 FinalDocument24 pagesKPMG Boxwood TL Omni-Platform Paper November 2017 FinalSeptiana Ayu Estri MahaniNo ratings yet
- Variation: Variation: The Differences Between Individuals of The Same SpeciesDocument39 pagesVariation: Variation: The Differences Between Individuals of The Same SpeciesmarziahNo ratings yet
- VariationDocument39 pagesVariationmarziahNo ratings yet
- Variation F 5Document8 pagesVariation F 5Angie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Evolution NotesDocument5 pagesHeredity and Evolution NotesCapt Pradeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Variation NotesDocument24 pagesVariation NotesMakanaka HoveNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18. VARIATION AND SELECTIONDocument82 pagesChapter 18. VARIATION AND SELECTIONMrs CoolNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Evolution (Notes)Document4 pagesHeredity and Evolution (Notes)anju dixitNo ratings yet
- Class-10 Notes CH-9 Heredity and EvolutionDocument13 pagesClass-10 Notes CH-9 Heredity and EvolutionN.R. ShirishaNo ratings yet
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument14 pagesHeredity and EvolutionprathushaNo ratings yet
- 18.1 VariationDocument14 pages18.1 Variationmi9gx5No ratings yet
- GENETICSDocument6 pagesGENETICSSamyak JainNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument6 pagesGeneticsSamyak JainNo ratings yet
- CH 18 Process of EvolutionDocument41 pagesCH 18 Process of EvolutionBenedicto IluminNo ratings yet
- Hereditary and EvolutionDocument11 pagesHereditary and EvolutionvaibhavNo ratings yet
- 2a Inheritance CDocument9 pages2a Inheritance Capi-238529408No ratings yet
- Biology Form 5: Chapter 6 (Variation)Document5 pagesBiology Form 5: Chapter 6 (Variation)Gerard Selvaraj100% (5)
- Heredity and Variation IDocument21 pagesHeredity and Variation Ismbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument30 pagesUntitledAdugna Mekuria BoteNo ratings yet
- Variations in OrganismsDocument10 pagesVariations in Organismsburned2ashesNo ratings yet
- Heredity and VariationDocument25 pagesHeredity and VariationDre ParkerNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms That Produces Change in PopulationsDocument6 pagesMechanisms That Produces Change in PopulationsblablaNo ratings yet
- VariationsDocument3 pagesVariationsshazeen shoaibNo ratings yet
- Genetic Basis For VariationDocument4 pagesGenetic Basis For VariationNicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - BiologyDocument34 pagesChapter 9 - BiologyNikhil ChettyarNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes F4Document59 pagesBiology Notes F4Nathan SsekamatteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 HeredityDocument23 pagesChapter 8 Heredityfortwitt18No ratings yet
- Honors Bio 9 Study GuideDocument5 pagesHonors Bio 9 Study GuideMalek KamalNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 EvolutionDocument9 pagesTopic 7 EvolutionAddan AddanNo ratings yet
- HEREDITYDocument14 pagesHEREDITYGt FansNo ratings yet
- Evolution Mechanisms 17 18Document44 pagesEvolution Mechanisms 17 18GABRIEL AUDREY SOLONNo ratings yet
- Heredity Class 10Document40 pagesHeredity Class 10ChaithraNo ratings yet
- Genetic Variation Is Caused byDocument5 pagesGenetic Variation Is Caused bySara Angélica Pimentel BonillaNo ratings yet
- Continuity and VariationDocument7 pagesContinuity and Variationamara williamsNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document8 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!sushantNo ratings yet
- Genetics (Autosaved) NDocument64 pagesGenetics (Autosaved) NSuraj kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A2 Biology Revision NotesDocument79 pagesEdexcel A2 Biology Revision NotesAbdalla AhmedNo ratings yet
- What Are Species?Document10 pagesWhat Are Species?homamunfatNo ratings yet
- MSG - 11 - 500169 - Heredity and EvolutionDocument5 pagesMSG - 11 - 500169 - Heredity and EvolutionUllhas Y KumarNo ratings yet
- Bio Final RevisionDocument8 pagesBio Final Revisionbisma nadeemNo ratings yet
- Genetics and PopulationsDocument7 pagesGenetics and PopulationsAlchemist CyanideNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument5 pagesNotesMady ffNo ratings yet
- Notes HeredityDocument8 pagesNotes Heredityvaibhav4gameNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of EvolutionDocument29 pagesMechanisms of EvolutionBukhari DiangkaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 VariationDocument13 pagesChapter 14 VariationLisa AllisyaNo ratings yet
- G12 Bio2 LM 4 Micro vs. MacroevolutionDocument29 pagesG12 Bio2 LM 4 Micro vs. MacroevolutionHannah AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument14 pagesHeredity and EvolutionLakshit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 07 Quantitative InheritanceDocument2 pages07 Quantitative InheritanceBen AbellaNo ratings yet
- Biology Cell Presentation in Green White Illustrative StyleDocument60 pagesBiology Cell Presentation in Green White Illustrative StyleDaisy Rizza AgnesNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution Revision NotesDocument20 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution Revision NotesYaseen BepariNo ratings yet
- 10.3 Gene Pools and SpeciationDocument8 pages10.3 Gene Pools and SpeciationAbdelrahman HarrathNo ratings yet
- Class X - HeredityDocument38 pagesClass X - HeredityRohit NairNo ratings yet
- Genetics ActivityDocument3 pagesGenetics ActivityBio SciencesNo ratings yet
- Biology Grade 8 - Variation & InheritanceDocument27 pagesBiology Grade 8 - Variation & InheritanceMokshitha Reddy YanamalNo ratings yet
- Heredity (Genetics) CLASS 10Document7 pagesHeredity (Genetics) CLASS 10shallowNo ratings yet
- AGN001Document3 pagesAGN001Jet Ronnie DacayaNo ratings yet
- Evolution: How Life Adapts to a Changing Environment with 25 ProjectsFrom EverandEvolution: How Life Adapts to a Changing Environment with 25 ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Contemparary Issues in ManagementDocument4 pagesSeminar On Contemparary Issues in ManagementNaimish BodarNo ratings yet
- Organoboranes in Organic Syntheses Including Suzuki Coupling ReactionDocument29 pagesOrganoboranes in Organic Syntheses Including Suzuki Coupling Reactionratul mahataNo ratings yet
- Pupillary Pathways &reactions: Assistant Professor, Department of Ophthalmology Nepalgunj Medical CollegeDocument16 pagesPupillary Pathways &reactions: Assistant Professor, Department of Ophthalmology Nepalgunj Medical CollegeDrBikram ThapaNo ratings yet
- CAVENDISHDocument2 pagesCAVENDISHMarvin LagascaNo ratings yet
- Daniel James - English A SbaDocument13 pagesDaniel James - English A Sbadanieltjames5092No ratings yet
- Effects of Pole Dance On Mental Wellbeing and The Sexual Self-Concept-A Pilot Randomized-Controlled TrialDocument7 pagesEffects of Pole Dance On Mental Wellbeing and The Sexual Self-Concept-A Pilot Randomized-Controlled Trialnoemi.hegedus11No ratings yet
- 19-CPS Student Induction Presentation-RAZAK FinalDocument18 pages19-CPS Student Induction Presentation-RAZAK FinalbaderNo ratings yet
- A Brief Biography of Hazrat Khaja Hussian Shah Wali HyderabadDocument17 pagesA Brief Biography of Hazrat Khaja Hussian Shah Wali HyderabadMohammed Abdul Hafeez, B.Com., Hyderabad, IndiaNo ratings yet
- Manila Pavilion v. DeladaDocument2 pagesManila Pavilion v. Deladasitsee watchNo ratings yet
- Johansson Kurt Aleksej Gastev Proletarian Bard of The Machine Age PDFDocument174 pagesJohansson Kurt Aleksej Gastev Proletarian Bard of The Machine Age PDFtalespintoNo ratings yet
- Base Connection DesignDocument7 pagesBase Connection Designmsiddiq1No ratings yet
- Ee5121 Tutorial 1Document2 pagesEe5121 Tutorial 1ananNo ratings yet
- Prophetic ProtocolDocument36 pagesProphetic ProtocolNeil SoansNo ratings yet
- Attachment 1Document468 pagesAttachment 1Ali JarkhiNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Global WarmingDocument11 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Global WarmingA Aldika Farlis50% (2)
- ADAMS v. SCHULTZ - Document No. 5Document6 pagesADAMS v. SCHULTZ - Document No. 5Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Early Adolescence (Ages 10 To 13) : Females MalesDocument5 pagesEarly Adolescence (Ages 10 To 13) : Females MalesBea Valerie GrislerNo ratings yet
- Peterson, Anand - The Production of Culture PerspectiveDocument25 pagesPeterson, Anand - The Production of Culture Perspectiveqthestone45No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Boolean Algebra Logic GatesDocument29 pagesChapter 2 Boolean Algebra Logic GatesZahra JafarNo ratings yet
- Movie Review: - Efforts By-Riya Maan - Rishabh Saxena - 12 CDocument11 pagesMovie Review: - Efforts By-Riya Maan - Rishabh Saxena - 12 CRishabh SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Literary Criticism - 21st CDocument2 pagesLiterary Criticism - 21st CGabrielle mari BulawanNo ratings yet
- Discourse Analysis: Ove K. PedersenDocument9 pagesDiscourse Analysis: Ove K. Pedersenmervat_aastNo ratings yet
- History of English LiteratureDocument59 pagesHistory of English LiteratureMarghescu AngelNo ratings yet
- CC15 Laminar FlowDocument22 pagesCC15 Laminar Flow999impactNo ratings yet
- BootcampDocument34 pagesBootcampPurvi JainNo ratings yet
- Ict Resources For Information, Collaboration and LearningDocument10 pagesIct Resources For Information, Collaboration and LearningBea HdbfbfjNo ratings yet
- Course Outline MATH 361 Probability and StatisticsDocument3 pagesCourse Outline MATH 361 Probability and StatisticsSkiwordy MediaNo ratings yet
- m1010 Final sp12Document8 pagesm1010 Final sp12DEANGELO AVILESNo ratings yet