Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Marik Covid Protocol Summary PDF
Marik Covid Protocol Summary PDF
Uploaded by
Jody VivasCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Basic Biometrics StudentDocument71 pagesBasic Biometrics StudentKatie100% (1)
- ACLS Pocket GuideDocument5 pagesACLS Pocket Guidedragnu100% (1)
- Makalah SleDocument48 pagesMakalah Slesalini_sadhna17No ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol SummaryInternos YopalNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol Summaryshubham rathodNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol SummaryelasticemperorNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol SummaryCamille05No ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol SummaryCaterina PrepelitaNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol Summary PDFDocument1 pageMarik Covid Protocol Summary PDFCiuvat Dumitru ValentinNo ratings yet
- CCF IpDocument1 pageCCF IpBryan FjbNo ratings yet
- FLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDocument2 pagesFLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHBhanu Kumar100% (1)
- FLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDocument3 pagesFLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHJhonn BlackNo ratings yet
- FLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDocument3 pagesFLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHfernandohNo ratings yet
- CVD Protocol ENGLISHDocument2 pagesCVD Protocol ENGLISHCornel ComanNo ratings yet
- FLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDocument3 pagesFLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDavid GrayNo ratings yet
- Hospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Document4 pagesHospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Adrian BoboceaNo ratings yet
- AmiodaroneDocument10 pagesAmiodaronesarahhhNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord CompressionDocument4 pagesSpinal Cord Compressionian3yeung-2No ratings yet
- COVID MX BsmmuDocument2 pagesCOVID MX BsmmuNuhiat NahreenNo ratings yet
- Hospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Document2 pagesHospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Nandor KissNo ratings yet
- Ambulatory Care MedicineDocument26 pagesAmbulatory Care MedicineJustineValJadeLacabaNo ratings yet
- CMSCN R IgevDocument2 pagesCMSCN R Igevdiana8827534No ratings yet
- CNS: Ent:: Review Antibiotic Therapy Daily - Can You: Stop? Switch? Simplify? or State Duration?Document1 pageCNS: Ent:: Review Antibiotic Therapy Daily - Can You: Stop? Switch? Simplify? or State Duration?Fitri RachmadaniNo ratings yet
- Medical TherapyDocument6 pagesMedical Therapyvinay reddyNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Hospital ManDocument1 pageAntibiotic Hospital Manarshiya.manasekiNo ratings yet
- VTE-Prophylaxis-Protocol - MOHDocument13 pagesVTE-Prophylaxis-Protocol - MOHreham ONo ratings yet
- WB Covid Protocol Book 25.09 .20 (1)Document49 pagesWB Covid Protocol Book 25.09 .20 (1)El MirageNo ratings yet
- BNF - 76 - British - National - Formulary - Septem-357-358 PhenobarbtalDocument2 pagesBNF - 76 - British - National - Formulary - Septem-357-358 Phenobarbtalnur aisahNo ratings yet
- MX Protocol Book FinalDocument42 pagesMX Protocol Book FinalPawan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 4.2016. Update On PlendilDocument2 pages4.2016. Update On PlendilKhor Chin PooNo ratings yet
- Farma StrokeDocument37 pagesFarma StrokeDAHLIANo ratings yet
- Medad TeamDocument18 pagesMedad TeamAxmed MaxamedNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation TDDocument6 pagesAtrial Fibrillation TDapi-594366475No ratings yet
- AtropinDocument9 pagesAtropinarfitaaaaNo ratings yet
- Suspected COVID-19 Cases Management in Triage HospitalsDocument6 pagesSuspected COVID-19 Cases Management in Triage HospitalsMuhamed RamadanNo ratings yet
- PRN Medications: Indications & UseDocument23 pagesPRN Medications: Indications & Usedis_is_me100% (1)
- Antibiotics & Analgesics Used in DentistryDocument4 pagesAntibiotics & Analgesics Used in DentistryDominique AbelaNo ratings yet
- Palliative Care FormularyDocument12 pagesPalliative Care FormularyRicardo FernandesNo ratings yet
- Phenytoin Administration GuideDocument2 pagesPhenytoin Administration GuideNoorHaziqZ1926No ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms Adult 2010Document12 pagesACLS Algorithms Adult 2010anon_336736395No ratings yet
- Mandatory Emergency MedicationDocument2 pagesMandatory Emergency MedicationVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- NICU Drugs GuideDocument49 pagesNICU Drugs GuideArhanNo ratings yet
- Syringe PumpDocument22 pagesSyringe PumpDanuNo ratings yet
- Charts and Hearts PDFDocument51 pagesCharts and Hearts PDFBen ScottNo ratings yet
- Acls Algorithms 2012Document12 pagesAcls Algorithms 2012kivuNo ratings yet
- Opioids MedicalDocument11 pagesOpioids MedicalduckyouisaacNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Dosage CalculationsDocument5 pagesPediatric Dosage CalculationsLovely Anjenell MacalingaNo ratings yet
- NSAIDSDocument18 pagesNSAIDSduckyouisaacNo ratings yet
- Drugs That Require Loading Doses Table FinalDocument1 pageDrugs That Require Loading Doses Table Finalandirio7486No ratings yet
- BairdDocument6 pagesBairdMuhammad salahuddinNo ratings yet
- Revised COVID 19 SARS-COV2 Treatment Protocol - FinalDocument6 pagesRevised COVID 19 SARS-COV2 Treatment Protocol - FinalupsahuNo ratings yet
- Seven Ps For RSI BOARDDocument2 pagesSeven Ps For RSI BOARDJames BrownNo ratings yet
- Master Drug ChartDocument22 pagesMaster Drug ChartMahadhir AkmalNo ratings yet
- Anti-Anginal DrugsDocument39 pagesAnti-Anginal Drugspoonam rana100% (1)
- Clinical Asthma Pathway: ED Phase 1a: Initial Assessment - 1st HourDocument2 pagesClinical Asthma Pathway: ED Phase 1a: Initial Assessment - 1st Hourd'Agung NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Cases Pharmacology PDFDocument7 pagesClinical Cases Pharmacology PDFAnkur HazraNo ratings yet
- ConnectorDocument4 pagesConnectoryetaung8No ratings yet
- Pediatric Emergency Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesPediatric Emergency Pocket GuideHongMingNo ratings yet
- Drugs in PregnancyDocument40 pagesDrugs in PregnancyhkkanhaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Health Guidelines Children Down SyndromeDocument17 pagesHealth Guidelines Children Down Syndromerick5963No ratings yet
- East-Mab IVD Products List20230608Document19 pagesEast-Mab IVD Products List20230608ashutosh pandeyNo ratings yet
- Hypoalbuminemia in Acute Illness: Is There A Rationale For Intervention?Document16 pagesHypoalbuminemia in Acute Illness: Is There A Rationale For Intervention?Fernando SugiartoNo ratings yet
- Extending The Host Response' Paradigm From Sepsis To Cardiogenic Shock: Evidence, Limitations and OpportunitiesDocument14 pagesExtending The Host Response' Paradigm From Sepsis To Cardiogenic Shock: Evidence, Limitations and OpportunitiesHelder LezamaNo ratings yet
- PPT Skenario A - G6 - Blok 14Document66 pagesPPT Skenario A - G6 - Blok 14Ellysa CarolinnNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Issues Related To Gastrointestinal Disease in Adults - UpToDateDocument24 pagesCOVID-19 Issues Related To Gastrointestinal Disease in Adults - UpToDateXochilt Mejia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lasting Impact of Clostridium Difficile Infection in in Ammatory Bowel Disease: A Propensity Score Matched AnalysisDocument9 pagesLasting Impact of Clostridium Difficile Infection in in Ammatory Bowel Disease: A Propensity Score Matched AnalysisOana Cristina PetreaNo ratings yet
- Parenter Enteral Nutr 2009 Mehta 260 76Document17 pagesParenter Enteral Nutr 2009 Mehta 260 76Bogdan CarabasNo ratings yet
- Systemic Response To Injury and MCQDocument3 pagesSystemic Response To Injury and MCQMalumo MisheckNo ratings yet
- Patterns of Creactive Protein Ratio Response To Antibiotics in Pediatric Sepsis A Prospective Cohort StudyDocument6 pagesPatterns of Creactive Protein Ratio Response To Antibiotics in Pediatric Sepsis A Prospective Cohort StudynicloverNo ratings yet
- Obesity Pain and Exercise SolutionsDocument15 pagesObesity Pain and Exercise SolutionsIulia ElenaNo ratings yet
- Kumar Verma: Lab NoDocument3 pagesKumar Verma: Lab NoSamar SinghNo ratings yet
- CRP WorksheetDocument2 pagesCRP WorksheetSeptheia Maeith VergaraNo ratings yet
- WLE Evaluation Inception Report - FinalDocument78 pagesWLE Evaluation Inception Report - Finalanchal kumar100% (1)
- Changing: Your Partner ForDocument16 pagesChanging: Your Partner ForsunilNo ratings yet
- FIA Meter Plus: Fluorescence Immunoassay Rapid Quantitative TestDocument4 pagesFIA Meter Plus: Fluorescence Immunoassay Rapid Quantitative TestWawan HardjomulionoNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab ReportTAMKEEN MUSTAFANo ratings yet
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and C-Reactive Protein Measurements and Their Relevance in Clinical MedicineDocument6 pagesErythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and C-Reactive Protein Measurements and Their Relevance in Clinical MedicineMonaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Diagnosis: What To Expect When You Suspect RADocument13 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis: Diagnosis: What To Expect When You Suspect RAhealthespaceNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Fever Small Group DiscussionDocument13 pagesRheumatic Fever Small Group DiscussionLyca Mae AurelioNo ratings yet
- Sidra Internship ReportDocument40 pagesSidra Internship Reporthafeez ahmed100% (1)
- BLOOD - BLD 2022 018546 mmc1Document26 pagesBLOOD - BLD 2022 018546 mmc1Susana RocheNo ratings yet
- PEDIA2 FINALS Rationale CompleteDocument110 pagesPEDIA2 FINALS Rationale CompleteDivine Grace Florita PepitoNo ratings yet
- 1-Aarogyam B + Covid Ab IgG - PO3827226873-180Document16 pages1-Aarogyam B + Covid Ab IgG - PO3827226873-180Rohit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Imse Phago & CRP LabDocument4 pagesImse Phago & CRP LabHANNA CASANDRA GARCIANo ratings yet
- IFU - R910 e CRPUHS 7Document3 pagesIFU - R910 e CRPUHS 7Agus KarwantoNo ratings yet
- Black Book SipDocument49 pagesBlack Book SipKUNAL CHAUDHARINo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Acute PancreatitisDocument31 pagesClinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Acute PancreatitisBrian WilliamNo ratings yet
Marik Covid Protocol Summary PDF
Marik Covid Protocol Summary PDF
Uploaded by
Jody VivasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Marik Covid Protocol Summary PDF
Marik Covid Protocol Summary PDF
Uploaded by
Jody VivasCopyright:
Available Formats
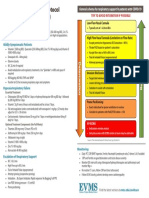
Critical Care COVID-19 Management Protocol General schema for respiratory support in patients with COVID-19
(updated 5-25-2020) TRY TO AVOID INTUBATION IF POSSIBLE
Low-Flow Nasal Cannula
Prophylaxis
■ Typically set at 1-6 Liters/Min
While there is very limited data (and none specific for COVID-19), the following “cocktail” may
have a role in the prevention/mitigation of COVID-19 disease.
■ Vitamin C 500 mg BID and Quercetin 250-500 mg BID High Flow Nasal Cannula
■ Accept permissive hypoxemia (O2 Saturation > 86%)
■ Zinc 75-100 mg/day
■ Titrate FiO2 based on patient’s saturation
■ Melatonin (slow release): Begin with 0.3mg and increase as tolerated to 2 mg ■ Accept flow rates of 60 to 80 L/min
at night
■ Trial of inhaled Flolan (epoprostenol)
■ Vitamin D3 1000-4000 u/day Attempt proning (cooperative proning)
Deterioration
■
■ Optional: Famotidine 20-40mg/day
Recovery
Mildly Symptomatic patients (at home): Invasive Mechanical Ventilation
■ Vitamin C 500mg BID and Quercetin 250-500 mg BID ■ Target tidal volumes of ~6 cc/kg
■ Zinc 75-100 mg/day ■ Lowest driving pressure and PEEP
■ Melatonin 6-12 mg at night (the optimal dose is unknown) ■ Sedation to avoid self-extubation
Trial of inhaled Flolan
Vitamin D3 2000-4000 u/day
■
■
■ Optional: Hydroxychloroquine 400mg BID day 1 followed by 200mg BID for 4 days
Prone Positioning
■ Optional: Ivermectin 150-200ug/kg (single dose) ■ Exact indication for prone ventilation is unclear
■ Optional: ASA 81/325mg/day ■ Consider in patients with PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 150
■ Optional: Famotidine 20-40mg/day
In symptomatic patients, monitoring with home pulse oximetry is recommended.
Ambulatory desaturation below 94% should prompt hospital admission VV-ECMO
■ Indications remain unclear
Mildly Symptomatic patients (on floor): ■ Early discussion with ECMO center or team may be advisable
■ Vitamin C 500 mg PO q 6 hourly and Quercetin 250-500 mg BID (if available)
■ Zinc 75-100 mg/day
■ Melatonin 6-12 mg at night (the optimal dose is unknown) ■ Optional: Remdesivir 200mg D1 then 100mg daily for 9 days.
■ Vitamin D3 2000-4000 u/day ■ Optional: Ivermectin 150-200 ug/kg (single dose)
■ Enoxaparin 60 mg daily ■ N/C 2L /min if required (max 4 L/min; consider early t/f to ICU for escalation of care).
■ Famotidine 40mg daily (20mg in renal impairment) ■ T/f EARLY to the ICU for increasing respiratory signs/symptoms and arterial
■ Methylprednisolone 40 mg q 12 hourly; increase to 80 mg q 12 if poor response desaturations.
continued on next page
Find the latest version at evms.edu/covidcare
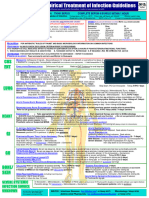
Critical Care COVID-19 Management Protocol
(updated 5-14-2020)
Respiratory symptoms (SOB; hypoxia- requiring N/C ≥ 4 L min: 13. Maintain EUVOLEMIA
admit to ICU): 14. Early norepinephrine for hypotension.
Essential Treatment (dampening the STORM)
15. Escalation of respiratory support; See General Schema for Respiratory
1. Methylprednisolone 80 mg loading dose then 40 mg q 12 hourly for at Support in Patients with COVID-19.
least 7 days and until transferred out of ICU. In patients with poor response,
increase to 80 mg q 12 hourly. Salvage Treatments
Plasma exchange. Should be considered in patients with progressive
2. Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) 3g IV q 6 hourly for at least 7 days and/or until
■
oxygenation failure despite corticosteroid therapy. Patients may require
transferred out of ICU. Note caution with POC glucose testing.
up to 5 exchanges.
3. Full anticoagulation: Unless contraindicated we suggest FULL ■ High dose corticosteroids; 120 mg methylprednisolone q 6-8 hourly
anticoagulation (on admission to the ICU) with enoxaparin, i.e 1 mg kg s/c
Siltuximab and Tocilizumab (IL-6 inhibitors)
q 12 hourly (dose adjust with Cr Cl < 30mls/min). Heparin is suggested with
■
CrCl < 15 ml/min. ■ Convalescent serum; the role and timing of convalescent serum are
uncertain.
Note: Early termination of ascorbic acid and corticosteroids will likely result in a
rebound effect. Treatment of Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS)
Additional Treatment Components (the Full Monty) ■ A sub-group of patients will develop MAS. A ferritin > 4400 ng/ml
is considered diagnostic of MAS. Other diagnostic features include
4. Melatonin 6-12 mg at night (the optimal dose is unknown).
increasing AST/ALT and increasing CRP.
5. Famotidine 40mg daily (20mg in renal impairment) ■ Methylprednisolone 120 mg q 6-8 hourly for at least 3 days, then wean
6. Vitamin D 2000-4000 u/day according to Ferritin, CRP, AST/ALT. Ferritin should decrease by at least
15% before weaning corticosteroids.
7. Thiamine 200mg IV q 12 hourly
Monitoring:
8. Simvastatin 80 mg/day
■ Daily: PCT, CRP, IL-6, BNP, Troponins, Ferritin, Neutrophil-Lymphocyte
9. Magnesium: 2 g stat IV. Keep Mg between 2.0 and 2.4 mmol/l. Prevent ratio, D-dimer and Mg. CRP, IL-6 and Ferritin track disease severity closely.
hypomagnesemia (which increases the cytokine storm and prolongs Qtc). Thromboelastogram (TEG) on admission and repeated as indicated.
10. Optional: Azithromycin 500 mg day 1 then 250 mg for 4 days Post ICU management
11. Optional: Remdesivir, 200 mg IV loading dose D1, followed by 100mg day IV a. Enoxaparin 40-60 mg s/c daily
for 9 days b. Methylprednisone 40 mg day, the wean slowly
12. Broad-spectrum antibiotics if superadded bacterial pneumonia is suspected c. Vitamin C 500 mg PO BID
based on procalcitonin levels and resp. culture (no bronchoscopy). d. Melatonin 3-6 mg at night
Developed and updated by Paul Marik, MD, Chief of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine,
Find the latest version at evms.edu/covidcare Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, VA
You might also like
- Basic Biometrics StudentDocument71 pagesBasic Biometrics StudentKatie100% (1)
- ACLS Pocket GuideDocument5 pagesACLS Pocket Guidedragnu100% (1)
- Makalah SleDocument48 pagesMakalah Slesalini_sadhna17No ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol SummaryInternos YopalNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol Summaryshubham rathodNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol SummaryelasticemperorNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol SummaryCamille05No ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol SummaryCaterina PrepelitaNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol Summary PDFDocument1 pageMarik Covid Protocol Summary PDFCiuvat Dumitru ValentinNo ratings yet
- CCF IpDocument1 pageCCF IpBryan FjbNo ratings yet
- FLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDocument2 pagesFLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHBhanu Kumar100% (1)
- FLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDocument3 pagesFLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHJhonn BlackNo ratings yet
- FLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDocument3 pagesFLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHfernandohNo ratings yet
- CVD Protocol ENGLISHDocument2 pagesCVD Protocol ENGLISHCornel ComanNo ratings yet
- FLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDocument3 pagesFLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDavid GrayNo ratings yet
- Hospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Document4 pagesHospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Adrian BoboceaNo ratings yet
- AmiodaroneDocument10 pagesAmiodaronesarahhhNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord CompressionDocument4 pagesSpinal Cord Compressionian3yeung-2No ratings yet
- COVID MX BsmmuDocument2 pagesCOVID MX BsmmuNuhiat NahreenNo ratings yet
- Hospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Document2 pagesHospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Nandor KissNo ratings yet
- Ambulatory Care MedicineDocument26 pagesAmbulatory Care MedicineJustineValJadeLacabaNo ratings yet
- CMSCN R IgevDocument2 pagesCMSCN R Igevdiana8827534No ratings yet
- CNS: Ent:: Review Antibiotic Therapy Daily - Can You: Stop? Switch? Simplify? or State Duration?Document1 pageCNS: Ent:: Review Antibiotic Therapy Daily - Can You: Stop? Switch? Simplify? or State Duration?Fitri RachmadaniNo ratings yet
- Medical TherapyDocument6 pagesMedical Therapyvinay reddyNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Hospital ManDocument1 pageAntibiotic Hospital Manarshiya.manasekiNo ratings yet
- VTE-Prophylaxis-Protocol - MOHDocument13 pagesVTE-Prophylaxis-Protocol - MOHreham ONo ratings yet
- WB Covid Protocol Book 25.09 .20 (1)Document49 pagesWB Covid Protocol Book 25.09 .20 (1)El MirageNo ratings yet
- BNF - 76 - British - National - Formulary - Septem-357-358 PhenobarbtalDocument2 pagesBNF - 76 - British - National - Formulary - Septem-357-358 Phenobarbtalnur aisahNo ratings yet
- MX Protocol Book FinalDocument42 pagesMX Protocol Book FinalPawan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 4.2016. Update On PlendilDocument2 pages4.2016. Update On PlendilKhor Chin PooNo ratings yet
- Farma StrokeDocument37 pagesFarma StrokeDAHLIANo ratings yet
- Medad TeamDocument18 pagesMedad TeamAxmed MaxamedNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation TDDocument6 pagesAtrial Fibrillation TDapi-594366475No ratings yet
- AtropinDocument9 pagesAtropinarfitaaaaNo ratings yet
- Suspected COVID-19 Cases Management in Triage HospitalsDocument6 pagesSuspected COVID-19 Cases Management in Triage HospitalsMuhamed RamadanNo ratings yet
- PRN Medications: Indications & UseDocument23 pagesPRN Medications: Indications & Usedis_is_me100% (1)
- Antibiotics & Analgesics Used in DentistryDocument4 pagesAntibiotics & Analgesics Used in DentistryDominique AbelaNo ratings yet
- Palliative Care FormularyDocument12 pagesPalliative Care FormularyRicardo FernandesNo ratings yet
- Phenytoin Administration GuideDocument2 pagesPhenytoin Administration GuideNoorHaziqZ1926No ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms Adult 2010Document12 pagesACLS Algorithms Adult 2010anon_336736395No ratings yet
- Mandatory Emergency MedicationDocument2 pagesMandatory Emergency MedicationVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- NICU Drugs GuideDocument49 pagesNICU Drugs GuideArhanNo ratings yet
- Syringe PumpDocument22 pagesSyringe PumpDanuNo ratings yet
- Charts and Hearts PDFDocument51 pagesCharts and Hearts PDFBen ScottNo ratings yet
- Acls Algorithms 2012Document12 pagesAcls Algorithms 2012kivuNo ratings yet
- Opioids MedicalDocument11 pagesOpioids MedicalduckyouisaacNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Dosage CalculationsDocument5 pagesPediatric Dosage CalculationsLovely Anjenell MacalingaNo ratings yet
- NSAIDSDocument18 pagesNSAIDSduckyouisaacNo ratings yet
- Drugs That Require Loading Doses Table FinalDocument1 pageDrugs That Require Loading Doses Table Finalandirio7486No ratings yet
- BairdDocument6 pagesBairdMuhammad salahuddinNo ratings yet
- Revised COVID 19 SARS-COV2 Treatment Protocol - FinalDocument6 pagesRevised COVID 19 SARS-COV2 Treatment Protocol - FinalupsahuNo ratings yet
- Seven Ps For RSI BOARDDocument2 pagesSeven Ps For RSI BOARDJames BrownNo ratings yet
- Master Drug ChartDocument22 pagesMaster Drug ChartMahadhir AkmalNo ratings yet
- Anti-Anginal DrugsDocument39 pagesAnti-Anginal Drugspoonam rana100% (1)
- Clinical Asthma Pathway: ED Phase 1a: Initial Assessment - 1st HourDocument2 pagesClinical Asthma Pathway: ED Phase 1a: Initial Assessment - 1st Hourd'Agung NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Cases Pharmacology PDFDocument7 pagesClinical Cases Pharmacology PDFAnkur HazraNo ratings yet
- ConnectorDocument4 pagesConnectoryetaung8No ratings yet
- Pediatric Emergency Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesPediatric Emergency Pocket GuideHongMingNo ratings yet
- Drugs in PregnancyDocument40 pagesDrugs in PregnancyhkkanhaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Health Guidelines Children Down SyndromeDocument17 pagesHealth Guidelines Children Down Syndromerick5963No ratings yet
- East-Mab IVD Products List20230608Document19 pagesEast-Mab IVD Products List20230608ashutosh pandeyNo ratings yet
- Hypoalbuminemia in Acute Illness: Is There A Rationale For Intervention?Document16 pagesHypoalbuminemia in Acute Illness: Is There A Rationale For Intervention?Fernando SugiartoNo ratings yet
- Extending The Host Response' Paradigm From Sepsis To Cardiogenic Shock: Evidence, Limitations and OpportunitiesDocument14 pagesExtending The Host Response' Paradigm From Sepsis To Cardiogenic Shock: Evidence, Limitations and OpportunitiesHelder LezamaNo ratings yet
- PPT Skenario A - G6 - Blok 14Document66 pagesPPT Skenario A - G6 - Blok 14Ellysa CarolinnNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Issues Related To Gastrointestinal Disease in Adults - UpToDateDocument24 pagesCOVID-19 Issues Related To Gastrointestinal Disease in Adults - UpToDateXochilt Mejia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lasting Impact of Clostridium Difficile Infection in in Ammatory Bowel Disease: A Propensity Score Matched AnalysisDocument9 pagesLasting Impact of Clostridium Difficile Infection in in Ammatory Bowel Disease: A Propensity Score Matched AnalysisOana Cristina PetreaNo ratings yet
- Parenter Enteral Nutr 2009 Mehta 260 76Document17 pagesParenter Enteral Nutr 2009 Mehta 260 76Bogdan CarabasNo ratings yet
- Systemic Response To Injury and MCQDocument3 pagesSystemic Response To Injury and MCQMalumo MisheckNo ratings yet
- Patterns of Creactive Protein Ratio Response To Antibiotics in Pediatric Sepsis A Prospective Cohort StudyDocument6 pagesPatterns of Creactive Protein Ratio Response To Antibiotics in Pediatric Sepsis A Prospective Cohort StudynicloverNo ratings yet
- Obesity Pain and Exercise SolutionsDocument15 pagesObesity Pain and Exercise SolutionsIulia ElenaNo ratings yet
- Kumar Verma: Lab NoDocument3 pagesKumar Verma: Lab NoSamar SinghNo ratings yet
- CRP WorksheetDocument2 pagesCRP WorksheetSeptheia Maeith VergaraNo ratings yet
- WLE Evaluation Inception Report - FinalDocument78 pagesWLE Evaluation Inception Report - Finalanchal kumar100% (1)
- Changing: Your Partner ForDocument16 pagesChanging: Your Partner ForsunilNo ratings yet
- FIA Meter Plus: Fluorescence Immunoassay Rapid Quantitative TestDocument4 pagesFIA Meter Plus: Fluorescence Immunoassay Rapid Quantitative TestWawan HardjomulionoNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab ReportTAMKEEN MUSTAFANo ratings yet
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and C-Reactive Protein Measurements and Their Relevance in Clinical MedicineDocument6 pagesErythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and C-Reactive Protein Measurements and Their Relevance in Clinical MedicineMonaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Diagnosis: What To Expect When You Suspect RADocument13 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis: Diagnosis: What To Expect When You Suspect RAhealthespaceNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Fever Small Group DiscussionDocument13 pagesRheumatic Fever Small Group DiscussionLyca Mae AurelioNo ratings yet
- Sidra Internship ReportDocument40 pagesSidra Internship Reporthafeez ahmed100% (1)
- BLOOD - BLD 2022 018546 mmc1Document26 pagesBLOOD - BLD 2022 018546 mmc1Susana RocheNo ratings yet
- PEDIA2 FINALS Rationale CompleteDocument110 pagesPEDIA2 FINALS Rationale CompleteDivine Grace Florita PepitoNo ratings yet
- 1-Aarogyam B + Covid Ab IgG - PO3827226873-180Document16 pages1-Aarogyam B + Covid Ab IgG - PO3827226873-180Rohit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Imse Phago & CRP LabDocument4 pagesImse Phago & CRP LabHANNA CASANDRA GARCIANo ratings yet
- IFU - R910 e CRPUHS 7Document3 pagesIFU - R910 e CRPUHS 7Agus KarwantoNo ratings yet
- Black Book SipDocument49 pagesBlack Book SipKUNAL CHAUDHARINo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Acute PancreatitisDocument31 pagesClinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Acute PancreatitisBrian WilliamNo ratings yet