Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Daspros Resume
Daspros Resume
Uploaded by
Adelia SalsabilaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Approaches in Teaching Social StudiesDocument86 pagesApproaches in Teaching Social StudiesWasakna Buhay100% (6)
- Unit 4 Lesson Planning Module 1 Classroom Management: All The Students All The TimeDocument2 pagesUnit 4 Lesson Planning Module 1 Classroom Management: All The Students All The TimeMary Ann D. Gaboy50% (2)
- Hg-Module 5-Answer SheetsDocument4 pagesHg-Module 5-Answer SheetsMathPad with Teacher Anabel80% (5)
- Developmental Plan KoDocument1 pageDevelopmental Plan KoEly Rose Apple MarianoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Mathematics With Innovative MethodsDocument5 pagesTeaching Mathematics With Innovative MethodsAdelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Teaching MethodsDocument22 pagesTeaching MethodsAilyaNo ratings yet
- Theories Narrative NotesDocument8 pagesTheories Narrative Notesapi-642706138No ratings yet
- Problem Solving MethodDocument11 pagesProblem Solving MethodcsrtratriNo ratings yet
- Manjusha SeminarDocument18 pagesManjusha SeminarMANJUSHA S SNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument8 pagesProblem SolvingJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Theories Narrative NotesDocument8 pagesTheories Narrative Notesapi-608094438No ratings yet
- Week 6 - Unit 5.1: Learning Processes: Curriculum and Course Design - PER 3260Document22 pagesWeek 6 - Unit 5.1: Learning Processes: Curriculum and Course Design - PER 3260Alexandra Bachero BeltránNo ratings yet
- Health EducDocument10 pagesHealth EducFlorence TimosaNo ratings yet
- 2 TERM (S.Y. 2021-2022) BPHE-II: Philippine Normal University MindanaoDocument4 pages2 TERM (S.Y. 2021-2022) BPHE-II: Philippine Normal University MindanaoLovely PadernaNo ratings yet
- Teaching ApproachesDocument16 pagesTeaching Approachesgabgabb1123zNo ratings yet
- Hannah Wilson Theories Narrative TemplateDocument8 pagesHannah Wilson Theories Narrative Templateapi-728296607No ratings yet
- Habits of MindDocument1 pageHabits of Mindapi-548756435No ratings yet
- CPE 104 Lesson 1 - ModuleDocument8 pagesCPE 104 Lesson 1 - ModuleHuda MadiNo ratings yet
- Teaching Mathematics With Innovative MethodsDocument4 pagesTeaching Mathematics With Innovative MethodsijcnesNo ratings yet
- Lyva ActDocument6 pagesLyva Actletlyvalenzuela03No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan FormatDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Formatapi-559796953No ratings yet
- Instructional Project 2Document18 pagesInstructional Project 2api-584550604No ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument10 pagesReviewerNicole AgustinNo ratings yet
- Effective Pedagogies in PersonDocument24 pagesEffective Pedagogies in PersonKiwinKoreaNo ratings yet
- The Investigative Learning Process: Former Director. Scsst/Dti Natiolull Project: Practical Problem Solving 5-13Document9 pagesThe Investigative Learning Process: Former Director. Scsst/Dti Natiolull Project: Practical Problem Solving 5-13Rocine GallegoNo ratings yet
- Portfolio IN Field Study: Episode11Document6 pagesPortfolio IN Field Study: Episode11Junnel CasanovaNo ratings yet
- Admin - Lesson Plan GuidelinesDocument4 pagesAdmin - Lesson Plan GuidelinesDamion BrusselNo ratings yet
- Learning ContinuumDocument2 pagesLearning ContinuumcorinaNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Teaching: (Chapter 4)Document64 pagesApproaches To Teaching: (Chapter 4)Abby YambaoNo ratings yet
- 8 Theories NarrativeDocument6 pages8 Theories Narrativeapi-745816440No ratings yet
- Reviewer in SSC1 FinalsDocument10 pagesReviewer in SSC1 FinalsJahnine BaisNo ratings yet
- Handouts From Week 10 To Week 12 Summation of ReportDocument5 pagesHandouts From Week 10 To Week 12 Summation of ReportAkoni si ARARNo ratings yet
- UNIT III Lesson I Direct Expository ApproachDocument12 pagesUNIT III Lesson I Direct Expository Approachmikkajaneaguinaldo15No ratings yet
- SLP Theory Notes 1Document7 pagesSLP Theory Notes 1api-676757295No ratings yet
- Module 5Document26 pagesModule 5Merry Grace TamundongNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgA EXdkC-DrNj8rekv4AFMbTRACSFgC5H15QPiegZKaP7bsNW SQUGXZCSywfs3xEgY9urLjOQxT-itM AHdsDfueYFK05-1EudxxhI6hCmP11hwNHAxYswWrgd9gvk R8ux 0kmY9gxVk6Document26 pagesACFrOgA EXdkC-DrNj8rekv4AFMbTRACSFgC5H15QPiegZKaP7bsNW SQUGXZCSywfs3xEgY9urLjOQxT-itM AHdsDfueYFK05-1EudxxhI6hCmP11hwNHAxYswWrgd9gvk R8ux 0kmY9gxVk6Erlena MiradorNo ratings yet
- Tubigan - Modern Approaches Applicable To College TeachingDocument25 pagesTubigan - Modern Approaches Applicable To College TeachingihlaNo ratings yet
- GEE PMT Module 7 Week 13-14Document12 pagesGEE PMT Module 7 Week 13-14TimothyLimNo ratings yet
- Tsos Final Exam NotesDocument6 pagesTsos Final Exam NotesAleslie ReforealNo ratings yet
- Tsos Final Exam NotesDocument10 pagesTsos Final Exam NotesAleslie ReforealNo ratings yet
- General Methods of Teaching 4Document12 pagesGeneral Methods of Teaching 4M.Muneeb -ur-RehmanNo ratings yet
- Learning Theories Group 2 Chapter 5Document41 pagesLearning Theories Group 2 Chapter 5Alondra L. FormenteraNo ratings yet
- Wa0002.Document14 pagesWa0002.pritidinda3070No ratings yet
- FLCT Beed - 2a (Daran)Document10 pagesFLCT Beed - 2a (Daran)Jeanette Fernandez DNo ratings yet
- Scientific Approach & Quantum Learning-2Document36 pagesScientific Approach & Quantum Learning-2Noob GamersNo ratings yet
- (Chapter VI) Teaching StrategyDocument55 pages(Chapter VI) Teaching Strategychrisvincent_19ups35No ratings yet
- Instructional StrategiesSarahDocument47 pagesInstructional StrategiesSarahPaulo B. turaNo ratings yet
- A Pathway To Equitable Math Instruction Stride 2Document15 pagesA Pathway To Equitable Math Instruction Stride 2ThePoliticalHatNo ratings yet
- Seven JumpDocument22 pagesSeven JumpMoch. Ivan KurniawanNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument6 pagesReviewernicole.goco7No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lecture PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Lecture PDFCt AynNo ratings yet
- Resecrhbaseffectivtchgprinc 11 27 18wbaDocument2 pagesResecrhbaseffectivtchgprinc 11 27 18wbaMorente Hazel F.No ratings yet
- UNIT III Lesson I Direct Expository ApproachDocument12 pagesUNIT III Lesson I Direct Expository Approachmikkajaneaguinaldo15No ratings yet
- Teaching Multi-Grade Classes: Topic 16. Direct and Indirect Strategy Direct InstructionDocument2 pagesTeaching Multi-Grade Classes: Topic 16. Direct and Indirect Strategy Direct InstructionMaricel ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document4 pagesGroup 2ewolramnasomitelimusNo ratings yet
- Assignment Project and Active MethodDocument7 pagesAssignment Project and Active Methodmaster,gujratiNo ratings yet
- Approaches, Techniques, Methods, & Strategies, ActivityDocument10 pagesApproaches, Techniques, Methods, & Strategies, ActivityManolo Servise HiloNo ratings yet
- Cognitivism Talking Paper 04032018Document6 pagesCognitivism Talking Paper 04032018api-371890611No ratings yet
- 1 2 3 4 MergedDocument9 pages1 2 3 4 MergedAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Approach, Methods & Techniques: Jon Vennie IbaleDocument22 pagesApproach, Methods & Techniques: Jon Vennie IbaleJON VENNIE IBALENo ratings yet
- Educational ContinuumDocument2 pagesEducational ContinuumcorinaNo ratings yet
- O Estudo Acompanhado: Como Ensinar e Auxiliar um Estudante a Aprender com AutonomiaFrom EverandO Estudo Acompanhado: Como Ensinar e Auxiliar um Estudante a Aprender com AutonomiaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource WasAdelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Adelia Salsabila-Assign-5 2Document10 pagesAdelia Salsabila-Assign-5 2Adelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- GROUP A - Project SPL (Matrix Inverse, Gauss Jordan, LU Factorization, Jacobi, Gauss-Seidel)Document22 pagesGROUP A - Project SPL (Matrix Inverse, Gauss Jordan, LU Factorization, Jacobi, Gauss-Seidel)Adelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Group A-Project Report ExcelDocument12 pagesGroup A-Project Report ExcelAdelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Sources of The Problem in ResearchDocument5 pagesSources of The Problem in ResearchAdelia Salsabila100% (2)
- Uas FilsmatDocument9 pagesUas FilsmatAdelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Adelia Salsabila - Task 1 Resume MEM1Document1 pageAdelia Salsabila - Task 1 Resume MEM1Adelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- RPS Daspros PDFDocument12 pagesRPS Daspros PDFAdelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Mathematics With Innovative MethodsDocument5 pagesTeaching Mathematics With Innovative MethodsAdelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - Summary PSMDocument33 pagesGroup 4 - Summary PSMAdelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Relevance of Educational Psychology For Secondary TeachersDocument3 pagesRelevance of Educational Psychology For Secondary TeachersAgrippa MungaziNo ratings yet
- My Teaching Philosophy Statement TpsDocument5 pagesMy Teaching Philosophy Statement Tpsapi-224515604100% (1)
- Sample Lesson Plan My Hopes and DreamsDocument6 pagesSample Lesson Plan My Hopes and DreamsJeannette CortésNo ratings yet
- Ipi Rubric Original 1450362516Document1 pageIpi Rubric Original 1450362516api-260107993100% (1)
- BPT1501 Assigment04 and Declar.Document6 pagesBPT1501 Assigment04 and Declar.DuduNo ratings yet
- Stetson University Music Education Daily Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesStetson University Music Education Daily Lesson Planapi-509544932No ratings yet
- Bridge To Success Curriculum 2016 / 2017 English Literacy-Grade 4Document17 pagesBridge To Success Curriculum 2016 / 2017 English Literacy-Grade 4HamadNo ratings yet
- Strength and Weakness of KTSP and KBKDocument2 pagesStrength and Weakness of KTSP and KBKRenni Vorkia SinagaNo ratings yet
- Black & Orange Simple Shape Highschool Teacher ResumeDocument1 pageBlack & Orange Simple Shape Highschool Teacher ResumeJoannah Rose PenarobiaNo ratings yet
- Mcea Esl Lesson Plan TemplateDocument4 pagesMcea Esl Lesson Plan Templateapi-335986821No ratings yet
- Reflective Pedagogy Test QuestionDocument2 pagesReflective Pedagogy Test QuestionRex Evangelista100% (1)
- D1-Template-Curriculum-Map Tle CaregivingDocument3 pagesD1-Template-Curriculum-Map Tle CaregivingAngelyn LingatongNo ratings yet
- Learning Styles and PreferencesDocument5 pagesLearning Styles and Preferencesapi-3716467No ratings yet
- Why Is The English Language Curriculum Changing?Document7 pagesWhy Is The English Language Curriculum Changing?Milla MahaliNo ratings yet
- Principal OPCRFDocument24 pagesPrincipal OPCRFErnilyn Ligan100% (1)
- Developing An Instructional StrategyDocument22 pagesDeveloping An Instructional StrategyDonatBulatNo ratings yet
- Issues and Trends in Teaching 21st Century LiteraciesDocument19 pagesIssues and Trends in Teaching 21st Century LiteraciesGracielle ValdezNo ratings yet
- Classroom Climate and Learning EnvironmentDocument16 pagesClassroom Climate and Learning EnvironmentHermie Cardenas100% (4)
- Worksheet 2-Module 1 - PROF ED 104Document3 pagesWorksheet 2-Module 1 - PROF ED 104ANTHONY LUMBAONo ratings yet
- The Teaching of ScienceDocument80 pagesThe Teaching of ScienceAngeles, Mark Allen C100% (1)
- WLP IN eNGLISH 5 WEEK3 5 LandscapeDocument2 pagesWLP IN eNGLISH 5 WEEK3 5 LandscapeLilyAnnIlaganDollienteNo ratings yet
- Global Reciprocal Colleges: Lesson Plan in MAPEH VIIDocument2 pagesGlobal Reciprocal Colleges: Lesson Plan in MAPEH VIIMaria Evelyn WonNo ratings yet
- Don Eulogio de Guzman Memorial National High School: Calumbaya, Bauang, La UnionDocument2 pagesDon Eulogio de Guzman Memorial National High School: Calumbaya, Bauang, La UnionChristine Manjares - OañaNo ratings yet
- Week 6 DLLDocument2 pagesWeek 6 DLLAnonymous yElhvOhPn100% (1)
- Schallert Newsletter FebruaryDocument10 pagesSchallert Newsletter FebruaryGrace PerezNo ratings yet
- Guided Discovery MatrixDocument1 pageGuided Discovery Matrixapi-238292382No ratings yet
- Cooperative LearningDocument31 pagesCooperative LearningakashNo ratings yet
Daspros Resume
Daspros Resume
Uploaded by
Adelia SalsabilaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Daspros Resume
Daspros Resume
Uploaded by
Adelia SalsabilaCopyright:
Available Formats
Individual Task Name : Adelia Salsabila
Meeting 4 NIM : 4101418127
Basic of Mathematics Learning Process
Problems and problem solving in mathematics activities are extremely
important. Students are active participation in the activities of problem
and resolution of access to knowledge, the development of Mathematics.
There are many ways of thinking, and the kind of thinking one learns in
mathematics is an ability to handle abstractions, and an approach to
problem solving.
Classify the members working in the
1. Sense of insecurity and fear
organization
of failure.
2. Low self esteem.
× Innovators People who
3. Closed mindedness.
innovate the new
4. Inadequate exposes to mass
ideas or modify
media.
the existing idea
5. Lack of training.
in the unique.
6. Lack of clarity of innovations.
× Early React positively
7. Unwillingness to work.
adopters
8. Unrealistic time target
× Adopters Adopt the idea by
looking towards
the effect that is
wait for the
result.
1. Lecturing method × Late Reluctant
2. Unit method Adopters respondents.
3. Project method × Laggards Rejecters of
4. Laboratory method innovation.
5. Problem method
~ ~
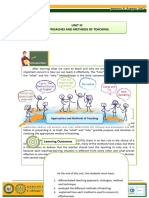
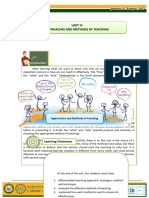
In mathematics , it is better to use this method in minimum way
“Lecture method” can be largely overcome by the teachers by
adopting techniques like questioning, black-board working and
dictating in the middle in order to overcome the monologue of the
teachers. Importance activities towards learner centered teaching
approaches, which is termed as group procedures.
To make the lecture method
effective , the teacher has to
follow certain guidelines.
a. Objective should be kept It is an easy ,concise and
in mind attractive method.
b. It involves narration or The lecturer feels safe aand
description secure.
c. They should be
coordinated with life
experiences of students
Students are likely to be
d. Students participation
passive listerners.
should be encouraged
Not suitable for developing
(asking questions,
skills.
clarifying the doubts and
reviewing the key points)
~ ~
A unit may be defined as a means of organizing material for
instructional purposes which utilizes significant subject matter
content involves pupil in learning activities through active
participation intellectually and physically and modifies the pupil’s
behaviour to the extent that he is able to cope with new problems
and situations more competently.
Exploration Exploring the entering behaviour of the students.
Presentation Providing new experiences to the learner. With a view to
encourage students’ participation in teaching, question-
answer strategy is employed.
Motivation Creation of motivational situations to facilitates learning.
Drill Opportunity to the students for drill or practice which
enables them to retain longer what is learnt.
Organisation Giving assignments to the students to organize their
learning experiences of their own.
Evaluation Ascertaining how far the teacher has been successful in
achieving the objectives of the lesson.
× Learning does not just × It is time consuming.
memorization and develops × More suitable for
understanding. intelligent students.
× Encourages the habit of
independent and self study.
× Learning process becomes
organized, systematic and
sequenced.
~ ~
Projects defined as form of coordinated activity that directed
towards the learning of a significant skill or process, involves four
steps (purposing, planning, executing and judging).
Planning the points to be taken
into consideration are
× The nature and scope of
the project
× The degree of complexity
of the projects
× Time allotted to finish the
project
× The availability of material
resources × Member of the group
should active
× The teacher should
carefully supervise and
× It develops self confidence guide the students
and self discipline of students. × The project should be
purposeful, useful and
practically applicable to
the daily life of the
× Syllabus cannot be completed students
on time. × The level of complexity
× It's not provide any training in of the project should
mathematical thinking and match the ability level
reasoning. of the students
~ ~
In Maths lab, we encourage student to practice more problems
which are used in practical life. This method proceeds from
concrete to abstract. It is competent to relate the theoretical
knowledge with practical base.
The success of this method depends on
× an able and skilled of mathematics teacher
× availability of a well equipped mathematic laboratory.
× Provides an opportunity × It is suitable only for the
for the student to verify lower classes.
the validity of the × It has limited
mathematical rules applicability since only
through this application. very few topics in
mathematics can be
taught through this
method.
~ ~
In the process of solving the problem the students required to
gather data, analyse and interpret the information. Its to stimulate
the reflective and creative thinking of the students and helps to
learn how to act in a new situation.
× Not all students are
problem solvers.
× References and resource
materials may be difficult
to compile.
× Problem solving provides a
real life experiences to
the children.
× It helps the students to
approach the future
problem with confidence
× Discussion × Debate × Case study
× Seminar × Pick and speak × Assignments
× Symposium × Questioning × Team teaching
× Workshop × Quiz × Panel discussion
× Tutorial
1. Authoritarian approach
Teachers prepare lectures and × accurate knowledge of the
present. student,
There is no interaction. × self confidence,
Students will have to accept × knowledge of evaluation,
the monotonous of the × ability techniques in questioning
teachers. × respect for students opinion.
2. Spontaneous approach
The two way interaction bet
teachers and students
stimulate the whole class to Purpose: improve the teaching work
participate activity in the and to achieve maximum learning
teaching–learning activities. outcomes in the students.
3. Nucleus Approach × Entrance test
Mixing of authoritarian and × Formative test
spontaneous approaches. × Summative test
× Teacher response
× Pupil response
× Pupil initiated talk The total classroom interaction is into
three major sections : Teachers talk,
Students talk, Silence or confusion.
× Teacher talk & student talk
× Enrichment Programmes (To
enrich our student’s knowledge,
we can focus outside the syllabus
The effectiveness of the institution also)
largely depends upon the strength
of the classs-room activities. A wide
range of activities are: × Special lectures
× OHP
× Library/ self study
× Audio-Video facilities
× Computer
You might also like
- Approaches in Teaching Social StudiesDocument86 pagesApproaches in Teaching Social StudiesWasakna Buhay100% (6)
- Unit 4 Lesson Planning Module 1 Classroom Management: All The Students All The TimeDocument2 pagesUnit 4 Lesson Planning Module 1 Classroom Management: All The Students All The TimeMary Ann D. Gaboy50% (2)
- Hg-Module 5-Answer SheetsDocument4 pagesHg-Module 5-Answer SheetsMathPad with Teacher Anabel80% (5)
- Developmental Plan KoDocument1 pageDevelopmental Plan KoEly Rose Apple MarianoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Mathematics With Innovative MethodsDocument5 pagesTeaching Mathematics With Innovative MethodsAdelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Teaching MethodsDocument22 pagesTeaching MethodsAilyaNo ratings yet
- Theories Narrative NotesDocument8 pagesTheories Narrative Notesapi-642706138No ratings yet
- Problem Solving MethodDocument11 pagesProblem Solving MethodcsrtratriNo ratings yet
- Manjusha SeminarDocument18 pagesManjusha SeminarMANJUSHA S SNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument8 pagesProblem SolvingJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Theories Narrative NotesDocument8 pagesTheories Narrative Notesapi-608094438No ratings yet
- Week 6 - Unit 5.1: Learning Processes: Curriculum and Course Design - PER 3260Document22 pagesWeek 6 - Unit 5.1: Learning Processes: Curriculum and Course Design - PER 3260Alexandra Bachero BeltránNo ratings yet
- Health EducDocument10 pagesHealth EducFlorence TimosaNo ratings yet
- 2 TERM (S.Y. 2021-2022) BPHE-II: Philippine Normal University MindanaoDocument4 pages2 TERM (S.Y. 2021-2022) BPHE-II: Philippine Normal University MindanaoLovely PadernaNo ratings yet
- Teaching ApproachesDocument16 pagesTeaching Approachesgabgabb1123zNo ratings yet
- Hannah Wilson Theories Narrative TemplateDocument8 pagesHannah Wilson Theories Narrative Templateapi-728296607No ratings yet
- Habits of MindDocument1 pageHabits of Mindapi-548756435No ratings yet
- CPE 104 Lesson 1 - ModuleDocument8 pagesCPE 104 Lesson 1 - ModuleHuda MadiNo ratings yet
- Teaching Mathematics With Innovative MethodsDocument4 pagesTeaching Mathematics With Innovative MethodsijcnesNo ratings yet
- Lyva ActDocument6 pagesLyva Actletlyvalenzuela03No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan FormatDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Formatapi-559796953No ratings yet
- Instructional Project 2Document18 pagesInstructional Project 2api-584550604No ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument10 pagesReviewerNicole AgustinNo ratings yet
- Effective Pedagogies in PersonDocument24 pagesEffective Pedagogies in PersonKiwinKoreaNo ratings yet
- The Investigative Learning Process: Former Director. Scsst/Dti Natiolull Project: Practical Problem Solving 5-13Document9 pagesThe Investigative Learning Process: Former Director. Scsst/Dti Natiolull Project: Practical Problem Solving 5-13Rocine GallegoNo ratings yet
- Portfolio IN Field Study: Episode11Document6 pagesPortfolio IN Field Study: Episode11Junnel CasanovaNo ratings yet
- Admin - Lesson Plan GuidelinesDocument4 pagesAdmin - Lesson Plan GuidelinesDamion BrusselNo ratings yet
- Learning ContinuumDocument2 pagesLearning ContinuumcorinaNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Teaching: (Chapter 4)Document64 pagesApproaches To Teaching: (Chapter 4)Abby YambaoNo ratings yet
- 8 Theories NarrativeDocument6 pages8 Theories Narrativeapi-745816440No ratings yet
- Reviewer in SSC1 FinalsDocument10 pagesReviewer in SSC1 FinalsJahnine BaisNo ratings yet
- Handouts From Week 10 To Week 12 Summation of ReportDocument5 pagesHandouts From Week 10 To Week 12 Summation of ReportAkoni si ARARNo ratings yet
- UNIT III Lesson I Direct Expository ApproachDocument12 pagesUNIT III Lesson I Direct Expository Approachmikkajaneaguinaldo15No ratings yet
- SLP Theory Notes 1Document7 pagesSLP Theory Notes 1api-676757295No ratings yet
- Module 5Document26 pagesModule 5Merry Grace TamundongNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgA EXdkC-DrNj8rekv4AFMbTRACSFgC5H15QPiegZKaP7bsNW SQUGXZCSywfs3xEgY9urLjOQxT-itM AHdsDfueYFK05-1EudxxhI6hCmP11hwNHAxYswWrgd9gvk R8ux 0kmY9gxVk6Document26 pagesACFrOgA EXdkC-DrNj8rekv4AFMbTRACSFgC5H15QPiegZKaP7bsNW SQUGXZCSywfs3xEgY9urLjOQxT-itM AHdsDfueYFK05-1EudxxhI6hCmP11hwNHAxYswWrgd9gvk R8ux 0kmY9gxVk6Erlena MiradorNo ratings yet
- Tubigan - Modern Approaches Applicable To College TeachingDocument25 pagesTubigan - Modern Approaches Applicable To College TeachingihlaNo ratings yet
- GEE PMT Module 7 Week 13-14Document12 pagesGEE PMT Module 7 Week 13-14TimothyLimNo ratings yet
- Tsos Final Exam NotesDocument6 pagesTsos Final Exam NotesAleslie ReforealNo ratings yet
- Tsos Final Exam NotesDocument10 pagesTsos Final Exam NotesAleslie ReforealNo ratings yet
- General Methods of Teaching 4Document12 pagesGeneral Methods of Teaching 4M.Muneeb -ur-RehmanNo ratings yet
- Learning Theories Group 2 Chapter 5Document41 pagesLearning Theories Group 2 Chapter 5Alondra L. FormenteraNo ratings yet
- Wa0002.Document14 pagesWa0002.pritidinda3070No ratings yet
- FLCT Beed - 2a (Daran)Document10 pagesFLCT Beed - 2a (Daran)Jeanette Fernandez DNo ratings yet
- Scientific Approach & Quantum Learning-2Document36 pagesScientific Approach & Quantum Learning-2Noob GamersNo ratings yet
- (Chapter VI) Teaching StrategyDocument55 pages(Chapter VI) Teaching Strategychrisvincent_19ups35No ratings yet
- Instructional StrategiesSarahDocument47 pagesInstructional StrategiesSarahPaulo B. turaNo ratings yet
- A Pathway To Equitable Math Instruction Stride 2Document15 pagesA Pathway To Equitable Math Instruction Stride 2ThePoliticalHatNo ratings yet
- Seven JumpDocument22 pagesSeven JumpMoch. Ivan KurniawanNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument6 pagesReviewernicole.goco7No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lecture PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Lecture PDFCt AynNo ratings yet
- Resecrhbaseffectivtchgprinc 11 27 18wbaDocument2 pagesResecrhbaseffectivtchgprinc 11 27 18wbaMorente Hazel F.No ratings yet
- UNIT III Lesson I Direct Expository ApproachDocument12 pagesUNIT III Lesson I Direct Expository Approachmikkajaneaguinaldo15No ratings yet
- Teaching Multi-Grade Classes: Topic 16. Direct and Indirect Strategy Direct InstructionDocument2 pagesTeaching Multi-Grade Classes: Topic 16. Direct and Indirect Strategy Direct InstructionMaricel ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document4 pagesGroup 2ewolramnasomitelimusNo ratings yet
- Assignment Project and Active MethodDocument7 pagesAssignment Project and Active Methodmaster,gujratiNo ratings yet
- Approaches, Techniques, Methods, & Strategies, ActivityDocument10 pagesApproaches, Techniques, Methods, & Strategies, ActivityManolo Servise HiloNo ratings yet
- Cognitivism Talking Paper 04032018Document6 pagesCognitivism Talking Paper 04032018api-371890611No ratings yet
- 1 2 3 4 MergedDocument9 pages1 2 3 4 MergedAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Approach, Methods & Techniques: Jon Vennie IbaleDocument22 pagesApproach, Methods & Techniques: Jon Vennie IbaleJON VENNIE IBALENo ratings yet
- Educational ContinuumDocument2 pagesEducational ContinuumcorinaNo ratings yet
- O Estudo Acompanhado: Como Ensinar e Auxiliar um Estudante a Aprender com AutonomiaFrom EverandO Estudo Acompanhado: Como Ensinar e Auxiliar um Estudante a Aprender com AutonomiaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource WasAdelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Adelia Salsabila-Assign-5 2Document10 pagesAdelia Salsabila-Assign-5 2Adelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- GROUP A - Project SPL (Matrix Inverse, Gauss Jordan, LU Factorization, Jacobi, Gauss-Seidel)Document22 pagesGROUP A - Project SPL (Matrix Inverse, Gauss Jordan, LU Factorization, Jacobi, Gauss-Seidel)Adelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Group A-Project Report ExcelDocument12 pagesGroup A-Project Report ExcelAdelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Sources of The Problem in ResearchDocument5 pagesSources of The Problem in ResearchAdelia Salsabila100% (2)
- Uas FilsmatDocument9 pagesUas FilsmatAdelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Adelia Salsabila - Task 1 Resume MEM1Document1 pageAdelia Salsabila - Task 1 Resume MEM1Adelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- RPS Daspros PDFDocument12 pagesRPS Daspros PDFAdelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Mathematics With Innovative MethodsDocument5 pagesTeaching Mathematics With Innovative MethodsAdelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - Summary PSMDocument33 pagesGroup 4 - Summary PSMAdelia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Relevance of Educational Psychology For Secondary TeachersDocument3 pagesRelevance of Educational Psychology For Secondary TeachersAgrippa MungaziNo ratings yet
- My Teaching Philosophy Statement TpsDocument5 pagesMy Teaching Philosophy Statement Tpsapi-224515604100% (1)
- Sample Lesson Plan My Hopes and DreamsDocument6 pagesSample Lesson Plan My Hopes and DreamsJeannette CortésNo ratings yet
- Ipi Rubric Original 1450362516Document1 pageIpi Rubric Original 1450362516api-260107993100% (1)
- BPT1501 Assigment04 and Declar.Document6 pagesBPT1501 Assigment04 and Declar.DuduNo ratings yet
- Stetson University Music Education Daily Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesStetson University Music Education Daily Lesson Planapi-509544932No ratings yet
- Bridge To Success Curriculum 2016 / 2017 English Literacy-Grade 4Document17 pagesBridge To Success Curriculum 2016 / 2017 English Literacy-Grade 4HamadNo ratings yet
- Strength and Weakness of KTSP and KBKDocument2 pagesStrength and Weakness of KTSP and KBKRenni Vorkia SinagaNo ratings yet
- Black & Orange Simple Shape Highschool Teacher ResumeDocument1 pageBlack & Orange Simple Shape Highschool Teacher ResumeJoannah Rose PenarobiaNo ratings yet
- Mcea Esl Lesson Plan TemplateDocument4 pagesMcea Esl Lesson Plan Templateapi-335986821No ratings yet
- Reflective Pedagogy Test QuestionDocument2 pagesReflective Pedagogy Test QuestionRex Evangelista100% (1)
- D1-Template-Curriculum-Map Tle CaregivingDocument3 pagesD1-Template-Curriculum-Map Tle CaregivingAngelyn LingatongNo ratings yet
- Learning Styles and PreferencesDocument5 pagesLearning Styles and Preferencesapi-3716467No ratings yet
- Why Is The English Language Curriculum Changing?Document7 pagesWhy Is The English Language Curriculum Changing?Milla MahaliNo ratings yet
- Principal OPCRFDocument24 pagesPrincipal OPCRFErnilyn Ligan100% (1)
- Developing An Instructional StrategyDocument22 pagesDeveloping An Instructional StrategyDonatBulatNo ratings yet
- Issues and Trends in Teaching 21st Century LiteraciesDocument19 pagesIssues and Trends in Teaching 21st Century LiteraciesGracielle ValdezNo ratings yet
- Classroom Climate and Learning EnvironmentDocument16 pagesClassroom Climate and Learning EnvironmentHermie Cardenas100% (4)
- Worksheet 2-Module 1 - PROF ED 104Document3 pagesWorksheet 2-Module 1 - PROF ED 104ANTHONY LUMBAONo ratings yet
- The Teaching of ScienceDocument80 pagesThe Teaching of ScienceAngeles, Mark Allen C100% (1)
- WLP IN eNGLISH 5 WEEK3 5 LandscapeDocument2 pagesWLP IN eNGLISH 5 WEEK3 5 LandscapeLilyAnnIlaganDollienteNo ratings yet
- Global Reciprocal Colleges: Lesson Plan in MAPEH VIIDocument2 pagesGlobal Reciprocal Colleges: Lesson Plan in MAPEH VIIMaria Evelyn WonNo ratings yet
- Don Eulogio de Guzman Memorial National High School: Calumbaya, Bauang, La UnionDocument2 pagesDon Eulogio de Guzman Memorial National High School: Calumbaya, Bauang, La UnionChristine Manjares - OañaNo ratings yet
- Week 6 DLLDocument2 pagesWeek 6 DLLAnonymous yElhvOhPn100% (1)
- Schallert Newsletter FebruaryDocument10 pagesSchallert Newsletter FebruaryGrace PerezNo ratings yet
- Guided Discovery MatrixDocument1 pageGuided Discovery Matrixapi-238292382No ratings yet
- Cooperative LearningDocument31 pagesCooperative LearningakashNo ratings yet