Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Marking Scheme - DME 214 - SEP18 Q6
Marking Scheme - DME 214 - SEP18 Q6
Uploaded by
Sheda RumCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Bahasa Inggeris Kertas 1Document13 pagesBahasa Inggeris Kertas 1Sheda Rum100% (5)
- Hernandez - Activity 8Document3 pagesHernandez - Activity 8Ma Lourdes Diona HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cast Metal RestorationDocument9 pagesCast Metal RestorationELAINE DE OCAMPONo ratings yet
- RefractoryDocument17 pagesRefractoryabdullah2110154No ratings yet
- R e F R A C T o R y M e T A L S A N D R e F R A C T o R y M e T A L A L L o y SDocument24 pagesR e F R A C T o R y M e T A L S A N D R e F R A C T o R y M e T A L A L L o y Saustenita14No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Learning Activity SheetDocument55 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Learning Activity Sheetmary joy nemenzoNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Technology Grade 10 Term 1 Week 6Document8 pagesAgricultural Technology Grade 10 Term 1 Week 6louis.clensieNo ratings yet
- MT2006D Metallurgy: AssignmentDocument4 pagesMT2006D Metallurgy: AssignmentMunawar MNo ratings yet
- Nickel Base Alloys: Topics To Discuss .Document15 pagesNickel Base Alloys: Topics To Discuss .Muhammad Zam-zamNo ratings yet
- 1 RefreactoriesDocument18 pages1 Refreactoriesengr kazamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Welding Matl Properties & Classification VR 0905Document31 pagesChapter 6 Welding Matl Properties & Classification VR 0905khairy2013No ratings yet
- Manufactured Substances in Industry: Name: Irdina BT Azhar CLASS: 401 Teacher'S Name: Pn. NorlizaDocument10 pagesManufactured Substances in Industry: Name: Irdina BT Azhar CLASS: 401 Teacher'S Name: Pn. NorlizaKHAYRA AZHARNo ratings yet
- Alloys in FPDDocument6 pagesAlloys in FPDharshita parasharNo ratings yet
- Nonprecious Alloys For Use in Fixed Prosthodontics: A Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesNonprecious Alloys For Use in Fixed Prosthodontics: A Literature ReviewNadya RaudillahNo ratings yet
- Maraging SteelsDocument14 pagesMaraging SteelsJoseph JoelNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Various Heat-Treatment Processes.: PROBLEM: 11.5Document8 pagesDiscuss The Various Heat-Treatment Processes.: PROBLEM: 11.5Rizki Amalia Tri CahyaniNo ratings yet
- AlloysDocument8 pagesAlloysyousif alrafaeiNo ratings yet
- 4th SeminarDocument70 pages4th SeminarVeena Goud100% (1)
- Ni and Its AlloysDocument17 pagesNi and Its Alloys18Y212 - KIRAN BABU MNo ratings yet
- Full MetalDocument36 pagesFull MetalNoha WaleedNo ratings yet
- Project 2018 RefDocument36 pagesProject 2018 Reffaisalmir27No ratings yet
- 22-09-13 2022 Fall Grad Fun. Ads. & Cats. W2 V1 YADocument64 pages22-09-13 2022 Fall Grad Fun. Ads. & Cats. W2 V1 YANatoli AbebeNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Alloys Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument3 pagesAluminium Alloys Advantages and DisadvantagesSaad AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2 - Structure of MetalsDocument19 pages2 - Structure of Metalsahmedmarwan82030No ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument13 pagesSolid StateIntan NurhaslindaNo ratings yet
- Refractories: Khinyaram Kakar MNIT JaipurDocument22 pagesRefractories: Khinyaram Kakar MNIT JaipurTaha KhanNo ratings yet
- TALAT Lecture 5205: Plating On AluminiumDocument19 pagesTALAT Lecture 5205: Plating On AluminiumCORE Materials100% (1)
- Refractories 01Document22 pagesRefractories 01dika wahyu0% (1)
- PDF 15jan24 1209 SplittedDocument1 pagePDF 15jan24 1209 Splittedrokesh123ee3No ratings yet
- ReffraaDocument7 pagesReffraaSruthi ShineyNo ratings yet
- Refractory Theory PDFDocument54 pagesRefractory Theory PDFArss Sakti SetyaNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Type Characteristics: AluminaDocument8 pagesCeramic Type Characteristics: AluminaAnne OliverosNo ratings yet
- Lecture40-40 - 16938 - Lecture 40Document16 pagesLecture40-40 - 16938 - Lecture 40Hozaan Najmi nFniwITMQmNo ratings yet
- Cu ZN 05Document2 pagesCu ZN 05wjjt6chgtmNo ratings yet
- CH 03 - Physical PropertiesDocument12 pagesCH 03 - Physical PropertiesBelgium WafflesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 MaterialsDocument7 pagesAssignment 2 MaterialsNursafika BahiraNo ratings yet
- Chemistryproject2019 2020Document14 pagesChemistryproject2019 2020avik JoshiNo ratings yet
- Motivation:-: WWW - Parhladsharma.inDocument8 pagesMotivation:-: WWW - Parhladsharma.insurajit biswasNo ratings yet
- Full Refractory DetailsDocument54 pagesFull Refractory DetailsSaravana Kumar100% (1)
- 8-6-2020 G4 PHOENIX For Diffusible Hydrogen in Welds and Metals PresentationDocument42 pages8-6-2020 G4 PHOENIX For Diffusible Hydrogen in Welds and Metals PresentationAliFriendNo ratings yet
- Product Description SheetDocument2 pagesProduct Description SheetFabio ParceroNo ratings yet
- Unidad 61Document36 pagesUnidad 61Eloisa OvandoNo ratings yet
- Dow Thermal MaterialsDocument16 pagesDow Thermal MaterialsRudyXPNo ratings yet
- Lect 2 - Introduction and Overview of Engineering Materials - Part 1Document47 pagesLect 2 - Introduction and Overview of Engineering Materials - Part 1l3No ratings yet
- API 571 Damage MechanismsDocument42 pagesAPI 571 Damage MechanismsIsmail Jamaluddin100% (1)
- Advantages and Disadvantages Each MaterialDocument25 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages Each MaterialPewe WulandariNo ratings yet
- 06 Chapter1Document36 pages06 Chapter1MonishaNo ratings yet
- RefractoriesDocument6 pagesRefractoriesBHAVINNo ratings yet
- Motivation:-: WWW - Parhladsharma.inDocument6 pagesMotivation:-: WWW - Parhladsharma.inDeekshith DileepNo ratings yet
- 9 - Ceramics Manufacturing, Properties and ApplicationsDocument39 pages9 - Ceramics Manufacturing, Properties and ApplicationsPradeep krNo ratings yet
- High-Temperature Corrosion and Materials Applications George Y. Lai, Editor, p1 DOI: 10.1361/hcma2007p001 All Rights ReservedDocument445 pagesHigh-Temperature Corrosion and Materials Applications George Y. Lai, Editor, p1 DOI: 10.1361/hcma2007p001 All Rights ReservedFaraj HaiderNo ratings yet
- 3 - Ni AlloysDocument21 pages3 - Ni AlloysAbhishek GuddadNo ratings yet
- 01 - Overview of Advanced CeramicsDocument19 pages01 - Overview of Advanced CeramicsMd. Rafiqul IslamNo ratings yet
- 09C Processing and Applications of CeramicsDocument26 pages09C Processing and Applications of CeramicsAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Lec 8Document67 pagesLec 8Pejman HNo ratings yet
- MD Mat 2Document43 pagesMD Mat 2Rounak AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Specialty Metals FactsDocument1 pageSpecialty Metals FactsLisbeth Roos RoosNo ratings yet
- Base Metals and Base-Metal Family Groups: Metallurgical ReactionsDocument114 pagesBase Metals and Base-Metal Family Groups: Metallurgical ReactionsYasa CossioNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials 2: An Introduction to Microstructures, Processing and DesignFrom EverandEngineering Materials 2: An Introduction to Microstructures, Processing and DesignNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- Lance Taylor Jessi Hartman Adam Flournoy: ENGR 45, SRJC, Fall 2013Document35 pagesLance Taylor Jessi Hartman Adam Flournoy: ENGR 45, SRJC, Fall 2013Sheda RumNo ratings yet
- Program: Cme Course Title: Applied Mechanics Course Code: CGE 220 Groups: 2K14CME1, 2K14CME4 Lecturer(s) : Siti Syahidah Mohd RumDocument5 pagesProgram: Cme Course Title: Applied Mechanics Course Code: CGE 220 Groups: 2K14CME1, 2K14CME4 Lecturer(s) : Siti Syahidah Mohd RumSheda RumNo ratings yet
- LIMIT An IntroductionDocument20 pagesLIMIT An IntroductionSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Types Simple Cubic (SC) Body Centered Cubic (BCC) Face Centered Cubic (FCC)Document1 pageTypes Simple Cubic (SC) Body Centered Cubic (BCC) Face Centered Cubic (FCC)Sheda RumNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks Q3 I) Calculate, Assuming Slow Cooling, The Volume Fraction and Composition of The Solid at 600ºC 6 MarksDocument2 pagesAnswers Marks Q3 I) Calculate, Assuming Slow Cooling, The Volume Fraction and Composition of The Solid at 600ºC 6 MarksSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Atoms Are Basic Building Blocks of Matter That Make Up Everyday Objects. A Desk The Air, Even Human Is Made Up of AtomsDocument1 pageAtoms Are Basic Building Blocks of Matter That Make Up Everyday Objects. A Desk The Air, Even Human Is Made Up of AtomsSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks Q4 (A) Corrosion 8 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringDocument2 pagesAnswers Marks Q4 (A) Corrosion 8 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Material ScienceDocument1 pageMaterial ScienceSheda RumNo ratings yet
- What Does An Atom Look Like (Draw The Atomic Structure and Label) ?Document3 pagesWhat Does An Atom Look Like (Draw The Atomic Structure and Label) ?Sheda RumNo ratings yet
- Learn The Names of Simple MachinesDocument2 pagesLearn The Names of Simple MachinesSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks Q4 (A) 7 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringDocument1 pageAnswers Marks Q4 (A) 7 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks Q3 (A) Boyle's Law 8 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringDocument1 pageAnswers Marks Q3 (A) Boyle's Law 8 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks Q2 (A) 4 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringDocument1 pageAnswers Marks Q2 (A) 4 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Lampiran B (I) Table 2 (A) : List of Course/module Offered in The Programme (Full Time)Document3 pagesLampiran B (I) Table 2 (A) : List of Course/module Offered in The Programme (Full Time)Sheda RumNo ratings yet
- Syarahan English NurinDocument2 pagesSyarahan English NurinSheda RumNo ratings yet
Marking Scheme - DME 214 - SEP18 Q6
Marking Scheme - DME 214 - SEP18 Q6
Uploaded by
Sheda RumOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Marking Scheme - DME 214 - SEP18 Q6
Marking Scheme - DME 214 - SEP18 Q6
Uploaded by
Sheda RumCopyright:
Available Formats
KOLEJ WIT
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
QUESTION ANSWERS MARKS
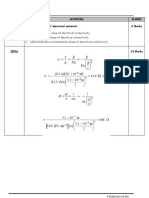
Q6(a) The main difference between heat-treatable and non-heat treatable alloys are 2 Marks
that heat-treatable alloys may be strengthened by a heat treatment wherein a
precipitate phase is formed (precipitation hardening) or a martensitic
transformation occurs. Non-heat treatable alloys are not amenable to
strengthening by such treatments.
Q6(b) TITANIUM ALLOYS 4 Marks
Distinctive features: Relatively low density, high melting temperature, and high
strengths are possible.
Limitation: Because of chemical reactivity with other materials at elevated
temperatures, these alloys
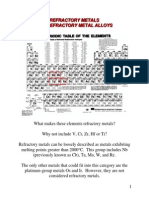
REFRACTORY METALS 4 Marks
Distinctive features: Extremely high melting temperature; large elastic moduli,
hardness and strengths.
Limitation: Some experience rapid oxidation at elevated temperatures
Applications: Extrusion dies, structural parts in space vehicles, incandescent light
filaments, x-ray tubes, and welding electrodes
SUPERALLOYS 4 Marks
Distinctive features: Able to withstand high temperatures and oxidizing
atmosphere for long time period.
Applications: Aircraft turbines, nuclear reactors, and petrochemical equipment
NOBLE METALS 4 Marks
Distinctive features: Highly resistant to oxidation, especially at elevated
temperature; soft and ductile
Limitation: expensive
Application: Jewelry, dental restoration materials, coins, catalyst, and
thermocouples
F-SOEN-004-05-R01
You might also like
- Bahasa Inggeris Kertas 1Document13 pagesBahasa Inggeris Kertas 1Sheda Rum100% (5)
- Hernandez - Activity 8Document3 pagesHernandez - Activity 8Ma Lourdes Diona HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cast Metal RestorationDocument9 pagesCast Metal RestorationELAINE DE OCAMPONo ratings yet
- RefractoryDocument17 pagesRefractoryabdullah2110154No ratings yet
- R e F R A C T o R y M e T A L S A N D R e F R A C T o R y M e T A L A L L o y SDocument24 pagesR e F R A C T o R y M e T A L S A N D R e F R A C T o R y M e T A L A L L o y Saustenita14No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Learning Activity SheetDocument55 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Learning Activity Sheetmary joy nemenzoNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Technology Grade 10 Term 1 Week 6Document8 pagesAgricultural Technology Grade 10 Term 1 Week 6louis.clensieNo ratings yet
- MT2006D Metallurgy: AssignmentDocument4 pagesMT2006D Metallurgy: AssignmentMunawar MNo ratings yet
- Nickel Base Alloys: Topics To Discuss .Document15 pagesNickel Base Alloys: Topics To Discuss .Muhammad Zam-zamNo ratings yet
- 1 RefreactoriesDocument18 pages1 Refreactoriesengr kazamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Welding Matl Properties & Classification VR 0905Document31 pagesChapter 6 Welding Matl Properties & Classification VR 0905khairy2013No ratings yet
- Manufactured Substances in Industry: Name: Irdina BT Azhar CLASS: 401 Teacher'S Name: Pn. NorlizaDocument10 pagesManufactured Substances in Industry: Name: Irdina BT Azhar CLASS: 401 Teacher'S Name: Pn. NorlizaKHAYRA AZHARNo ratings yet
- Alloys in FPDDocument6 pagesAlloys in FPDharshita parasharNo ratings yet
- Nonprecious Alloys For Use in Fixed Prosthodontics: A Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesNonprecious Alloys For Use in Fixed Prosthodontics: A Literature ReviewNadya RaudillahNo ratings yet
- Maraging SteelsDocument14 pagesMaraging SteelsJoseph JoelNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Various Heat-Treatment Processes.: PROBLEM: 11.5Document8 pagesDiscuss The Various Heat-Treatment Processes.: PROBLEM: 11.5Rizki Amalia Tri CahyaniNo ratings yet
- AlloysDocument8 pagesAlloysyousif alrafaeiNo ratings yet
- 4th SeminarDocument70 pages4th SeminarVeena Goud100% (1)
- Ni and Its AlloysDocument17 pagesNi and Its Alloys18Y212 - KIRAN BABU MNo ratings yet
- Full MetalDocument36 pagesFull MetalNoha WaleedNo ratings yet
- Project 2018 RefDocument36 pagesProject 2018 Reffaisalmir27No ratings yet
- 22-09-13 2022 Fall Grad Fun. Ads. & Cats. W2 V1 YADocument64 pages22-09-13 2022 Fall Grad Fun. Ads. & Cats. W2 V1 YANatoli AbebeNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Alloys Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument3 pagesAluminium Alloys Advantages and DisadvantagesSaad AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2 - Structure of MetalsDocument19 pages2 - Structure of Metalsahmedmarwan82030No ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument13 pagesSolid StateIntan NurhaslindaNo ratings yet
- Refractories: Khinyaram Kakar MNIT JaipurDocument22 pagesRefractories: Khinyaram Kakar MNIT JaipurTaha KhanNo ratings yet
- TALAT Lecture 5205: Plating On AluminiumDocument19 pagesTALAT Lecture 5205: Plating On AluminiumCORE Materials100% (1)
- Refractories 01Document22 pagesRefractories 01dika wahyu0% (1)
- PDF 15jan24 1209 SplittedDocument1 pagePDF 15jan24 1209 Splittedrokesh123ee3No ratings yet
- ReffraaDocument7 pagesReffraaSruthi ShineyNo ratings yet
- Refractory Theory PDFDocument54 pagesRefractory Theory PDFArss Sakti SetyaNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Type Characteristics: AluminaDocument8 pagesCeramic Type Characteristics: AluminaAnne OliverosNo ratings yet
- Lecture40-40 - 16938 - Lecture 40Document16 pagesLecture40-40 - 16938 - Lecture 40Hozaan Najmi nFniwITMQmNo ratings yet
- Cu ZN 05Document2 pagesCu ZN 05wjjt6chgtmNo ratings yet
- CH 03 - Physical PropertiesDocument12 pagesCH 03 - Physical PropertiesBelgium WafflesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 MaterialsDocument7 pagesAssignment 2 MaterialsNursafika BahiraNo ratings yet
- Chemistryproject2019 2020Document14 pagesChemistryproject2019 2020avik JoshiNo ratings yet
- Motivation:-: WWW - Parhladsharma.inDocument8 pagesMotivation:-: WWW - Parhladsharma.insurajit biswasNo ratings yet
- Full Refractory DetailsDocument54 pagesFull Refractory DetailsSaravana Kumar100% (1)
- 8-6-2020 G4 PHOENIX For Diffusible Hydrogen in Welds and Metals PresentationDocument42 pages8-6-2020 G4 PHOENIX For Diffusible Hydrogen in Welds and Metals PresentationAliFriendNo ratings yet
- Product Description SheetDocument2 pagesProduct Description SheetFabio ParceroNo ratings yet
- Unidad 61Document36 pagesUnidad 61Eloisa OvandoNo ratings yet
- Dow Thermal MaterialsDocument16 pagesDow Thermal MaterialsRudyXPNo ratings yet
- Lect 2 - Introduction and Overview of Engineering Materials - Part 1Document47 pagesLect 2 - Introduction and Overview of Engineering Materials - Part 1l3No ratings yet
- API 571 Damage MechanismsDocument42 pagesAPI 571 Damage MechanismsIsmail Jamaluddin100% (1)
- Advantages and Disadvantages Each MaterialDocument25 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages Each MaterialPewe WulandariNo ratings yet
- 06 Chapter1Document36 pages06 Chapter1MonishaNo ratings yet
- RefractoriesDocument6 pagesRefractoriesBHAVINNo ratings yet
- Motivation:-: WWW - Parhladsharma.inDocument6 pagesMotivation:-: WWW - Parhladsharma.inDeekshith DileepNo ratings yet
- 9 - Ceramics Manufacturing, Properties and ApplicationsDocument39 pages9 - Ceramics Manufacturing, Properties and ApplicationsPradeep krNo ratings yet
- High-Temperature Corrosion and Materials Applications George Y. Lai, Editor, p1 DOI: 10.1361/hcma2007p001 All Rights ReservedDocument445 pagesHigh-Temperature Corrosion and Materials Applications George Y. Lai, Editor, p1 DOI: 10.1361/hcma2007p001 All Rights ReservedFaraj HaiderNo ratings yet
- 3 - Ni AlloysDocument21 pages3 - Ni AlloysAbhishek GuddadNo ratings yet
- 01 - Overview of Advanced CeramicsDocument19 pages01 - Overview of Advanced CeramicsMd. Rafiqul IslamNo ratings yet
- 09C Processing and Applications of CeramicsDocument26 pages09C Processing and Applications of CeramicsAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Lec 8Document67 pagesLec 8Pejman HNo ratings yet
- MD Mat 2Document43 pagesMD Mat 2Rounak AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Specialty Metals FactsDocument1 pageSpecialty Metals FactsLisbeth Roos RoosNo ratings yet
- Base Metals and Base-Metal Family Groups: Metallurgical ReactionsDocument114 pagesBase Metals and Base-Metal Family Groups: Metallurgical ReactionsYasa CossioNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials 2: An Introduction to Microstructures, Processing and DesignFrom EverandEngineering Materials 2: An Introduction to Microstructures, Processing and DesignNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- Lance Taylor Jessi Hartman Adam Flournoy: ENGR 45, SRJC, Fall 2013Document35 pagesLance Taylor Jessi Hartman Adam Flournoy: ENGR 45, SRJC, Fall 2013Sheda RumNo ratings yet
- Program: Cme Course Title: Applied Mechanics Course Code: CGE 220 Groups: 2K14CME1, 2K14CME4 Lecturer(s) : Siti Syahidah Mohd RumDocument5 pagesProgram: Cme Course Title: Applied Mechanics Course Code: CGE 220 Groups: 2K14CME1, 2K14CME4 Lecturer(s) : Siti Syahidah Mohd RumSheda RumNo ratings yet
- LIMIT An IntroductionDocument20 pagesLIMIT An IntroductionSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Types Simple Cubic (SC) Body Centered Cubic (BCC) Face Centered Cubic (FCC)Document1 pageTypes Simple Cubic (SC) Body Centered Cubic (BCC) Face Centered Cubic (FCC)Sheda RumNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks Q3 I) Calculate, Assuming Slow Cooling, The Volume Fraction and Composition of The Solid at 600ºC 6 MarksDocument2 pagesAnswers Marks Q3 I) Calculate, Assuming Slow Cooling, The Volume Fraction and Composition of The Solid at 600ºC 6 MarksSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Atoms Are Basic Building Blocks of Matter That Make Up Everyday Objects. A Desk The Air, Even Human Is Made Up of AtomsDocument1 pageAtoms Are Basic Building Blocks of Matter That Make Up Everyday Objects. A Desk The Air, Even Human Is Made Up of AtomsSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks Q4 (A) Corrosion 8 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringDocument2 pagesAnswers Marks Q4 (A) Corrosion 8 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Material ScienceDocument1 pageMaterial ScienceSheda RumNo ratings yet
- What Does An Atom Look Like (Draw The Atomic Structure and Label) ?Document3 pagesWhat Does An Atom Look Like (Draw The Atomic Structure and Label) ?Sheda RumNo ratings yet
- Learn The Names of Simple MachinesDocument2 pagesLearn The Names of Simple MachinesSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks Q4 (A) 7 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringDocument1 pageAnswers Marks Q4 (A) 7 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks Q3 (A) Boyle's Law 8 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringDocument1 pageAnswers Marks Q3 (A) Boyle's Law 8 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks Q2 (A) 4 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringDocument1 pageAnswers Marks Q2 (A) 4 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Lampiran B (I) Table 2 (A) : List of Course/module Offered in The Programme (Full Time)Document3 pagesLampiran B (I) Table 2 (A) : List of Course/module Offered in The Programme (Full Time)Sheda RumNo ratings yet
- Syarahan English NurinDocument2 pagesSyarahan English NurinSheda RumNo ratings yet