Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 viewsFirst Page PDF
First Page PDF
Uploaded by
Harley Alejo M1) Radiopharmaceuticals have a good safety record, with adverse reactions occurring at around 1,000 times less than contrast media and drugs. A US study from 1989-1994 reported an adverse reaction rate of 0.0023% from over 780,000 administered doses.
2) A review of UK reports from 1977-1983 found a changing pattern of adverse reactions over time due to elimination of more toxic formulations and changing usage. The estimated reporting rate of reactions was between 1 in 1,000 and 1 in 10,000 administrations.
3) The most commonly used radiopharmaceutical, technetium-99m, has been associated with some adverse events including low blood
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Members' Directory 2023 ICSB FinalDocument228 pagesMembers' Directory 2023 ICSB FinalJoynul Abedin100% (1)
- Etico en RadiografiaDocument21 pagesEtico en RadiografiaHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Masterplan TemplateDocument72 pagesMasterplan TemplateMostafa FawzyNo ratings yet
- CNusat Riko The AdventurerDocument38 pagesCNusat Riko The AdventurerMuhammad Farhan Saiful AzmanNo ratings yet
- Radiopharmaceuticals (Journal) PDFDocument6 pagesRadiopharmaceuticals (Journal) PDFFrederickNo ratings yet
- Jordan 2005Document7 pagesJordan 2005SilesiaNo ratings yet
- Keller 2010Document6 pagesKeller 2010angelNo ratings yet
- Allergy: Adverse Reaction To DextromethorphanDocument3 pagesAllergy: Adverse Reaction To DextromethorphanAdina SerbanNo ratings yet
- Anesth Analg-2009-Habibi-Asl-936-42Document7 pagesAnesth Analg-2009-Habibi-Asl-936-42Mehboob AlamNo ratings yet
- Nejmra1200894 AppendixDocument14 pagesNejmra1200894 AppendixStephan CanoNo ratings yet
- ETHAMBUTOLDocument11 pagesETHAMBUTOLIrbasMantiniSyaifulNo ratings yet
- The Oncologist 2007 Jordan 1143 50Document8 pagesThe Oncologist 2007 Jordan 1143 50Rafael Eduardo Toro ManotasNo ratings yet
- Cyclophosphamide ToxicityDocument15 pagesCyclophosphamide ToxicityAnonymous 9dVZCnTXSNo ratings yet
- Cyanide PoisoningDocument5 pagesCyanide Poisoningriz04_fortitudessa5178No ratings yet
- 1 RP130001 PDFDocument8 pages1 RP130001 PDFDiga AlbrianNo ratings yet
- See Full Prescribing Information For Complete Boxed WarningDocument14 pagesSee Full Prescribing Information For Complete Boxed WarningnickeycoolNo ratings yet
- Nuclear, RadiopharmaceuticalDocument111 pagesNuclear, Radiopharmaceuticalarun231187No ratings yet
- Basic Mechanisms of Chemotherapy: Mitchison, M.BDocument10 pagesBasic Mechanisms of Chemotherapy: Mitchison, M.BDecolagueNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Antiemetic Treatment of ChemotherapDocument9 pagesGuidelines For Antiemetic Treatment of ChemotherapRky RizkyNo ratings yet
- Daunorubicin: Drug NameDocument7 pagesDaunorubicin: Drug NameEdgar Ledesma-MartínezNo ratings yet
- Topiramate 1997Document16 pagesTopiramate 1997Yo Turtle KidzNo ratings yet
- Minireview Glycopyrrolate: Et Al., Cardiovascular EffectsDocument5 pagesMinireview Glycopyrrolate: Et Al., Cardiovascular EffectsGeotamNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Anes 1Document10 pagesJurnal Anes 1Ari SamadNo ratings yet
- Isopropanol: Monographs Supplement 7 (1987)Document10 pagesIsopropanol: Monographs Supplement 7 (1987)mangala jesudossNo ratings yet
- 2014.04.17 PoltechDTPA SPCHDocument2 pages2014.04.17 PoltechDTPA SPCHLuis Fernando RicardoNo ratings yet
- Gupta 1994 Antifungal Agents - An Overview. Part IIDocument23 pagesGupta 1994 Antifungal Agents - An Overview. Part IIAdrian CNo ratings yet
- Cook Et - Al 98 Antagonist Withdrawal JpharmacolExpTherDocument24 pagesCook Et - Al 98 Antagonist Withdrawal JpharmacolExpTherМатиас Себальос ГусманNo ratings yet
- Ibrt 10 I 1 P 53Document4 pagesIbrt 10 I 1 P 53Putri YingNo ratings yet
- Carboplatin With Pemetrexed Pembrolizumab Non Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Protocol V1.1Document8 pagesCarboplatin With Pemetrexed Pembrolizumab Non Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Protocol V1.1Olaru DianaNo ratings yet
- Prolongedapnea 0410 p110-112Document3 pagesProlongedapnea 0410 p110-112Putra Endi PratamaNo ratings yet
- Erna 2009Document25 pagesErna 2009Colleen Van SchalkwykNo ratings yet
- Ijnm 33 269Document4 pagesIjnm 33 269Alex CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Significant Withdrawals of DrugsDocument8 pagesSignificant Withdrawals of DrugsBaba HamzaNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument12 pagesResearch PaperSaweeraNo ratings yet
- Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters: SciencedirectDocument5 pagesBioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters: SciencedirectHaroon Ur RashidNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Hydrochloride: Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, Adverse Side Effects, Co-Administration of Drugs and New Drug Delivery SystemsDocument5 pagesTramadol Hydrochloride: Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, Adverse Side Effects, Co-Administration of Drugs and New Drug Delivery SystemsAjeng Salsabila PawestriNo ratings yet
- 2007 HN DocetaxelDocument23 pages2007 HN DocetaxelSanuRokkuSphereNo ratings yet
- 661 Full PDFDocument3 pages661 Full PDFmisulica2010No ratings yet
- Clinical Microbiology: Open Access: The Mechanisms of Adverse Reactions To Oseltamivir: Part II. Delayed Type ReactionsDocument10 pagesClinical Microbiology: Open Access: The Mechanisms of Adverse Reactions To Oseltamivir: Part II. Delayed Type ReactionsAryanto DedyNo ratings yet
- Tektrotyd Kit For Radiopharmaceutical Preparation ENG PAR - 09001be681383ac7Document17 pagesTektrotyd Kit For Radiopharmaceutical Preparation ENG PAR - 09001be681383ac7Ruxandra LúthienNo ratings yet
- Introduction in Hospital RadiopharmacyDocument23 pagesIntroduction in Hospital RadiopharmacyEmilija JanevikNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 PharmacotoxicologyDocument19 pagesLecture 5 Pharmacotoxicologykeishini2001No ratings yet
- Retinoid AcidDocument50 pagesRetinoid AcidMirza Rahma NauliNo ratings yet
- Naphthalene: Hazard SummaryDocument5 pagesNaphthalene: Hazard Summaryrory sandikaNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic DrugsDocument20 pagesAntiarrhythmic DrugsMd FcpsNo ratings yet
- Radiopharmaceuticals and Their Therapeutic Applications in Health Care SystemDocument5 pagesRadiopharmaceuticals and Their Therapeutic Applications in Health Care SystemEsteban MalamboNo ratings yet
- New Uses For Older DrugsDocument21 pagesNew Uses For Older DrugsSand JokeNo ratings yet
- European 989 PDFDocument14 pagesEuropean 989 PDFMarlintan Sukma AmbarwatiNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Guidelines For Prescribing Azathioprine in DermatologyDocument10 pagesGuidelines Guidelines For Prescribing Azathioprine in DermatologyflashjetNo ratings yet
- Statin-Induced Rhabdomyolysis: A Complication of A Commonly Overlooked Drug InteractionDocument3 pagesStatin-Induced Rhabdomyolysis: A Complication of A Commonly Overlooked Drug InteractionHeru SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Selected Topics: Toxicology: Severe Carisoprodol Withdrawal After A 14-Year Addiction and Acute OverdoseDocument4 pagesSelected Topics: Toxicology: Severe Carisoprodol Withdrawal After A 14-Year Addiction and Acute OverdoseAhmad SyaukatNo ratings yet
- Adamgammadex Mai Bun Ca SugammadexDocument6 pagesAdamgammadex Mai Bun Ca SugammadexAdi CărbunaruNo ratings yet
- 150 Years of PharmacovigilanceDocument2 pages150 Years of PharmacovigilanceCarlos José Lacava Fernández100% (1)
- Antiarrhythmic AgentsDocument45 pagesAntiarrhythmic AgentsSoh Kae SiangNo ratings yet
- King 2012 4AP Toxicity ReviewDocument8 pagesKing 2012 4AP Toxicity ReviewzernebochNo ratings yet
- Drug-Induced QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes: Matthew Li, Pharmd and Liz G. Ramos, Pharmd, BcpsDocument5 pagesDrug-Induced QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes: Matthew Li, Pharmd and Liz G. Ramos, Pharmd, BcpsCalon DokterNo ratings yet
- Nad Karni 2014Document2 pagesNad Karni 2014pedrotuliorochaNo ratings yet
- 1 Ketamin LGDocument4 pages1 Ketamin LGUmmi QorinNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Toxicity An Overview 2165 7548.1000158Document3 pagesParacetamol Toxicity An Overview 2165 7548.1000158psNo ratings yet
- PropofolDocument9 pagesPropofolarturschander3614No ratings yet
- Effect Radiation Reproductive: of The Human SystemDocument8 pagesEffect Radiation Reproductive: of The Human SystemAndrea Kristine LumanogNo ratings yet
- Caredose SiemensDocument1 pageCaredose SiemensHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
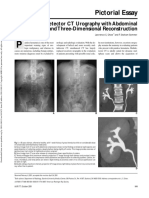
- Pictorial Essay: Multidetector CT Urography With Abdominal Compression and Three-Dimensional ReconstructionDocument13 pagesPictorial Essay: Multidetector CT Urography With Abdominal Compression and Three-Dimensional ReconstructionHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Unige 136981 Attachment01Document5 pagesUnige 136981 Attachment01Harley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Estimacion Del RiesgoDocument5 pagesEstimacion Del RiesgoHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Medical Linear Accelerators in Radiation Therapy: Haijun Song, PH.DDocument43 pagesMedical Linear Accelerators in Radiation Therapy: Haijun Song, PH.DHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- 2013 Book HandbookOfNuclearCardiologyDocument215 pages2013 Book HandbookOfNuclearCardiologyHarley Alejo M100% (1)
- Nuclear Medicine and Positron Emission Tomography: An OverviewDocument7 pagesNuclear Medicine and Positron Emission Tomography: An OverviewHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Radiation PhysicsDocument307 pagesRadiation PhysicsHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- 2017 Book QualityInNuclearMedicineDocument455 pages2017 Book QualityInNuclearMedicineHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Update Digital Mammography Protocol 01-2017Document3 pagesUpdate Digital Mammography Protocol 01-2017Harley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Practical Exercise: Effective Dose Estimate in CTDocument27 pagesPractical Exercise: Effective Dose Estimate in CTHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Corrientes de EddyDocument5 pagesCorrientes de EddyHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Covello2011 RISK COMMUNICATION, RADIATION, AND RADIOLOGICAL EMERGENCIESDocument20 pagesCovello2011 RISK COMMUNICATION, RADIATION, AND RADIOLOGICAL EMERGENCIESHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- 16303264Document36 pages16303264Harley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Vivo Placement Papers PDF Download PDFDocument28 pagesVivo Placement Papers PDF Download PDFNikhil VermaNo ratings yet
- Vedanta Solution To Our Fundamental ProblemDocument356 pagesVedanta Solution To Our Fundamental Problemspikeman42100% (1)
- Moot Court (Clinical)Document2 pagesMoot Court (Clinical)prince KumarNo ratings yet
- Bentley BrochureDocument8 pagesBentley BrochureKomolNo ratings yet
- 1359 - 1368. TingkahanDocument5 pages1359 - 1368. TingkahanRizal Daujr Tingkahan IIINo ratings yet
- Eslprintables 2009810153647888645279Document1 pageEslprintables 2009810153647888645279Mathéo DE OLIVEIRANo ratings yet
- Cambridge, 2nd Ed.-Petty Cash BookDocument3 pagesCambridge, 2nd Ed.-Petty Cash BookShannen LyeNo ratings yet
- Appendix B For CPPDocument1 pageAppendix B For CPP16 Dighe YogeshwariNo ratings yet
- Cavite Mutiny AccountsDocument4 pagesCavite Mutiny AccountsSAMANTHA ANN GUINTONo ratings yet
- Crossing The Threshold - Audrey TopazianDocument3 pagesCrossing The Threshold - Audrey Topazianapi-502833469No ratings yet
- S Bing 0605175 Chapter4Document29 pagesS Bing 0605175 Chapter4Rose GreenNo ratings yet
- Asso V EnergyDocument38 pagesAsso V Energyarriane joy insularNo ratings yet
- Aerodur Finish HF A 130: ® Akzonobel Aerospace CoatingsDocument3 pagesAerodur Finish HF A 130: ® Akzonobel Aerospace CoatingsАндрей МошкинNo ratings yet
- 2014 JC1 H2 PH BT P2 Question SolutionDocument17 pages2014 JC1 H2 PH BT P2 Question Solutionshakthee sivakumarNo ratings yet
- Pienaar Savic Accepted MsDocument32 pagesPienaar Savic Accepted MsEl LuchoNo ratings yet
- Biology Ecology Revision NotesDocument7 pagesBiology Ecology Revision NotesGeorge ArgyrouNo ratings yet
- Chemical Analysis of Caustic Soda and Caustic Potash (Sodium Hydroxide and Potassium Hydroxide)Document16 pagesChemical Analysis of Caustic Soda and Caustic Potash (Sodium Hydroxide and Potassium Hydroxide)wilfred gomezNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Topics CriminologyDocument7 pagesDissertation Topics CriminologyCustomPapersPaterson100% (1)
- Position Paper Martial LawDocument3 pagesPosition Paper Martial LawLeoncio BocoNo ratings yet
- ICEfaces Asynchronous HTTP ServerDocument33 pagesICEfaces Asynchronous HTTP ServerIniyaNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals, Eleventh CircuitDocument52 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Eleventh CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- The Victim's Autopsy ReportDocument2 pagesThe Victim's Autopsy ReportShan KNo ratings yet
- Managing Clean Core For SAP S4HANA Cloud NotesDocument59 pagesManaging Clean Core For SAP S4HANA Cloud NotesGLEN KGATLANo ratings yet
- Aztec MagicDocument2 pagesAztec MagicBob MarinoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDocument25 pagesIntroduction To 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldPj CastilloNo ratings yet
- Horn Persistence Natural HornDocument4 pagesHorn Persistence Natural Hornapi-478106051No ratings yet
- Job Characteristics and Job Satisfaction: A Test of Warr's Vitamin Model in German HorticultureDocument23 pagesJob Characteristics and Job Satisfaction: A Test of Warr's Vitamin Model in German HorticulturetaryNo ratings yet
First Page PDF
First Page PDF
Uploaded by
Harley Alejo M0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views1 page1) Radiopharmaceuticals have a good safety record, with adverse reactions occurring at around 1,000 times less than contrast media and drugs. A US study from 1989-1994 reported an adverse reaction rate of 0.0023% from over 780,000 administered doses.
2) A review of UK reports from 1977-1983 found a changing pattern of adverse reactions over time due to elimination of more toxic formulations and changing usage. The estimated reporting rate of reactions was between 1 in 1,000 and 1 in 10,000 administrations.
3) The most commonly used radiopharmaceutical, technetium-99m, has been associated with some adverse events including low blood
Original Description:
Original Title
first-page-pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Radiopharmaceuticals have a good safety record, with adverse reactions occurring at around 1,000 times less than contrast media and drugs. A US study from 1989-1994 reported an adverse reaction rate of 0.0023% from over 780,000 administered doses.
2) A review of UK reports from 1977-1983 found a changing pattern of adverse reactions over time due to elimination of more toxic formulations and changing usage. The estimated reporting rate of reactions was between 1 in 1,000 and 1 in 10,000 administrations.
3) The most commonly used radiopharmaceutical, technetium-99m, has been associated with some adverse events including low blood
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views1 pageFirst Page PDF
First Page PDF
Uploaded by
Harley Alejo M1) Radiopharmaceuticals have a good safety record, with adverse reactions occurring at around 1,000 times less than contrast media and drugs. A US study from 1989-1994 reported an adverse reaction rate of 0.0023% from over 780,000 administered doses.
2) A review of UK reports from 1977-1983 found a changing pattern of adverse reactions over time due to elimination of more toxic formulations and changing usage. The estimated reporting rate of reactions was between 1 in 1,000 and 1 in 10,000 administrations.
3) The most commonly used radiopharmaceutical, technetium-99m, has been associated with some adverse events including low blood
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Radiopharmaceuticals safety record because no adverse reactions were reported
in over 80 000 administered doses in this study [3].
In a review of UK reports of adverse reactions to radio-
See also Thorotrast
pharmaceuticals from 1977 to 1983, there was a changing
distribution pattern with time (Table 2) [4]. This was
partly due to elimination of some of the earlier, more
GENERAL INFORMATION toxic formulations and partly due to changing usage,
more particularly the increased use of phosphonate for-
Radioactive substances may be used in medicine as tracers, mulations. The authors estimated that only 10% of reac-
the quantities used in this case being merely sufficient to tions were reported and that the probable incidence rate
enable them to be detected, or as therapeutic agents, in was between one in 1000 and one in 10 000. There was one
which case the quantities employed and the amount of radi- death associated with a hypotensive reaction to colloid in
ation emitted may be considerable. Risks resulting from the a severely ill patient. One elderly patient had a cardiac
radiation itself fall outside the scope of this volume. arrest after injection of macro-aggregated albumin but
Radio-iodine is covered in a separate monograph. was resuscitated. In a European prospective survey during
1996, there was a prevalence of 11 events per 105 admin-
istrations of radio-pharmaceuticals. No serious or life-
General adverse effects and adverse threatening events were reported [5].
reactions
Radiopharmaceuticals have a good safety record. The 99m
Technetium
prevalence of adverse reactions is approximately 1000-
fold than less than that occurring with iodinated contrast The widespread use of 99mTc-diethylaminetriaminepenta-
media and drugs. The Society of Nuclear Medicine has acetate (DTPA), mostly used for renal imaging, has
maintained a register of adverse reactions to radiophar- brought with it a number of reported DTPA adverse
maceuticals occurring in USA since 1976. The frequency reactions. Typical symptoms include low pressure, loss of
of reactions appears to be falling because of improved consciousness, feeling faint and occasionally rashes and
quality control of radiopharmaceuticals. Many of the ear- bronchospasm. In Europe, a patient with a history of
lier adverse reactions were attributed to iron-containing asthma developed severe bronchospasm and died within
formulations, gelatin-stabilized formulations, materials a matter of minutes [6]. A series of very serious problem
such as albumin contaminated with pyrogens, and other developed following intrathecal injection of 99mTc-DTPA
products no longer in use. The overall incidence of reac- in what turned out to be, strictly speaking, a misformula-
tions for the year 1978 was estimated to be 1–6 per 100 000 tion incident. Almost all currently used DTPA formula-
examinations [1]. tions contain the mixed calcium/sodium salt of DTPA.
In order to determine the prevalence of adverse reac- However, one particular manufacturer used the trisodium
tions to radiopharmaceuticals, a 5-year prospective study salt. This form is capable of chelation of cerebrospinal
(1989–94) was performed in 18 institutions in the USA [2]. fluid calcium and magnesium and causing gradual onset
The reported incidence rate was 0.0023%. No adverse of severe neurological signs and severe paresthesia [7].
99m
reaction required hospitalization or had significant Tc-labeled serum albumin microspheres have in one
sequelae. The adverse reactions and types of radiophar- case caused collapse, apparently because the patient
maceuticals are shown in Table 1. in question had earlier been sensitized by blood transfu-
Another study was undertaken to determine the preva- sions [8].
lence of adverse reactions to positron-emitting radiophar- A case of anaphylaxis occurred after the injection of a
maceuticals through a prospective 4-year study in 22 leukocyte suspension labeled with 99mTc-hexamethyl pro-
institutions. PET radiopharmaceuticals have an excellent pylene amine oxime [9].
Table 1 Adverse reactions to 783 525 radiopharmaceutical doses in 1989–94 in the USA (n ¼ 18)
Radiopharmaceutical Adverse reaction Number
67
Gallium citrate Rash 1
[131I] Iobenguane (MIBG) Chest discomfort, light-headedness 1
99m
Tc-macroaggregated albumin Rash 1
99m
Tc-medronate (MDP) Rash/nausea/mild anaphylaxis 2/1/1
99m
Tc-oxidronate (HDP) Rash/sweating 4/1
99m
Tc-pentetate (DTPA) Rash 1
99m
Tc-sestamibi Rash 1
99m
Tc-sulfur colloid Nausea, vomiting, rash, headache 1
Stannous pyrophosphate (non-radioactive)* Mild anaphylaxis/light-headedness 2/1
*Given intravenously to allow in vivo radiolabeling of erythrocytes and considered part of the final radiopharmaceutical.
ã 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Members' Directory 2023 ICSB FinalDocument228 pagesMembers' Directory 2023 ICSB FinalJoynul Abedin100% (1)
- Etico en RadiografiaDocument21 pagesEtico en RadiografiaHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Masterplan TemplateDocument72 pagesMasterplan TemplateMostafa FawzyNo ratings yet
- CNusat Riko The AdventurerDocument38 pagesCNusat Riko The AdventurerMuhammad Farhan Saiful AzmanNo ratings yet
- Radiopharmaceuticals (Journal) PDFDocument6 pagesRadiopharmaceuticals (Journal) PDFFrederickNo ratings yet
- Jordan 2005Document7 pagesJordan 2005SilesiaNo ratings yet
- Keller 2010Document6 pagesKeller 2010angelNo ratings yet
- Allergy: Adverse Reaction To DextromethorphanDocument3 pagesAllergy: Adverse Reaction To DextromethorphanAdina SerbanNo ratings yet
- Anesth Analg-2009-Habibi-Asl-936-42Document7 pagesAnesth Analg-2009-Habibi-Asl-936-42Mehboob AlamNo ratings yet
- Nejmra1200894 AppendixDocument14 pagesNejmra1200894 AppendixStephan CanoNo ratings yet
- ETHAMBUTOLDocument11 pagesETHAMBUTOLIrbasMantiniSyaifulNo ratings yet
- The Oncologist 2007 Jordan 1143 50Document8 pagesThe Oncologist 2007 Jordan 1143 50Rafael Eduardo Toro ManotasNo ratings yet
- Cyclophosphamide ToxicityDocument15 pagesCyclophosphamide ToxicityAnonymous 9dVZCnTXSNo ratings yet
- Cyanide PoisoningDocument5 pagesCyanide Poisoningriz04_fortitudessa5178No ratings yet
- 1 RP130001 PDFDocument8 pages1 RP130001 PDFDiga AlbrianNo ratings yet
- See Full Prescribing Information For Complete Boxed WarningDocument14 pagesSee Full Prescribing Information For Complete Boxed WarningnickeycoolNo ratings yet
- Nuclear, RadiopharmaceuticalDocument111 pagesNuclear, Radiopharmaceuticalarun231187No ratings yet
- Basic Mechanisms of Chemotherapy: Mitchison, M.BDocument10 pagesBasic Mechanisms of Chemotherapy: Mitchison, M.BDecolagueNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Antiemetic Treatment of ChemotherapDocument9 pagesGuidelines For Antiemetic Treatment of ChemotherapRky RizkyNo ratings yet
- Daunorubicin: Drug NameDocument7 pagesDaunorubicin: Drug NameEdgar Ledesma-MartínezNo ratings yet
- Topiramate 1997Document16 pagesTopiramate 1997Yo Turtle KidzNo ratings yet
- Minireview Glycopyrrolate: Et Al., Cardiovascular EffectsDocument5 pagesMinireview Glycopyrrolate: Et Al., Cardiovascular EffectsGeotamNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Anes 1Document10 pagesJurnal Anes 1Ari SamadNo ratings yet
- Isopropanol: Monographs Supplement 7 (1987)Document10 pagesIsopropanol: Monographs Supplement 7 (1987)mangala jesudossNo ratings yet
- 2014.04.17 PoltechDTPA SPCHDocument2 pages2014.04.17 PoltechDTPA SPCHLuis Fernando RicardoNo ratings yet
- Gupta 1994 Antifungal Agents - An Overview. Part IIDocument23 pagesGupta 1994 Antifungal Agents - An Overview. Part IIAdrian CNo ratings yet
- Cook Et - Al 98 Antagonist Withdrawal JpharmacolExpTherDocument24 pagesCook Et - Al 98 Antagonist Withdrawal JpharmacolExpTherМатиас Себальос ГусманNo ratings yet
- Ibrt 10 I 1 P 53Document4 pagesIbrt 10 I 1 P 53Putri YingNo ratings yet
- Carboplatin With Pemetrexed Pembrolizumab Non Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Protocol V1.1Document8 pagesCarboplatin With Pemetrexed Pembrolizumab Non Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Protocol V1.1Olaru DianaNo ratings yet
- Prolongedapnea 0410 p110-112Document3 pagesProlongedapnea 0410 p110-112Putra Endi PratamaNo ratings yet
- Erna 2009Document25 pagesErna 2009Colleen Van SchalkwykNo ratings yet
- Ijnm 33 269Document4 pagesIjnm 33 269Alex CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Significant Withdrawals of DrugsDocument8 pagesSignificant Withdrawals of DrugsBaba HamzaNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument12 pagesResearch PaperSaweeraNo ratings yet
- Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters: SciencedirectDocument5 pagesBioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters: SciencedirectHaroon Ur RashidNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Hydrochloride: Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, Adverse Side Effects, Co-Administration of Drugs and New Drug Delivery SystemsDocument5 pagesTramadol Hydrochloride: Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, Adverse Side Effects, Co-Administration of Drugs and New Drug Delivery SystemsAjeng Salsabila PawestriNo ratings yet
- 2007 HN DocetaxelDocument23 pages2007 HN DocetaxelSanuRokkuSphereNo ratings yet
- 661 Full PDFDocument3 pages661 Full PDFmisulica2010No ratings yet
- Clinical Microbiology: Open Access: The Mechanisms of Adverse Reactions To Oseltamivir: Part II. Delayed Type ReactionsDocument10 pagesClinical Microbiology: Open Access: The Mechanisms of Adverse Reactions To Oseltamivir: Part II. Delayed Type ReactionsAryanto DedyNo ratings yet
- Tektrotyd Kit For Radiopharmaceutical Preparation ENG PAR - 09001be681383ac7Document17 pagesTektrotyd Kit For Radiopharmaceutical Preparation ENG PAR - 09001be681383ac7Ruxandra LúthienNo ratings yet
- Introduction in Hospital RadiopharmacyDocument23 pagesIntroduction in Hospital RadiopharmacyEmilija JanevikNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 PharmacotoxicologyDocument19 pagesLecture 5 Pharmacotoxicologykeishini2001No ratings yet
- Retinoid AcidDocument50 pagesRetinoid AcidMirza Rahma NauliNo ratings yet
- Naphthalene: Hazard SummaryDocument5 pagesNaphthalene: Hazard Summaryrory sandikaNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic DrugsDocument20 pagesAntiarrhythmic DrugsMd FcpsNo ratings yet
- Radiopharmaceuticals and Their Therapeutic Applications in Health Care SystemDocument5 pagesRadiopharmaceuticals and Their Therapeutic Applications in Health Care SystemEsteban MalamboNo ratings yet
- New Uses For Older DrugsDocument21 pagesNew Uses For Older DrugsSand JokeNo ratings yet
- European 989 PDFDocument14 pagesEuropean 989 PDFMarlintan Sukma AmbarwatiNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Guidelines For Prescribing Azathioprine in DermatologyDocument10 pagesGuidelines Guidelines For Prescribing Azathioprine in DermatologyflashjetNo ratings yet
- Statin-Induced Rhabdomyolysis: A Complication of A Commonly Overlooked Drug InteractionDocument3 pagesStatin-Induced Rhabdomyolysis: A Complication of A Commonly Overlooked Drug InteractionHeru SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Selected Topics: Toxicology: Severe Carisoprodol Withdrawal After A 14-Year Addiction and Acute OverdoseDocument4 pagesSelected Topics: Toxicology: Severe Carisoprodol Withdrawal After A 14-Year Addiction and Acute OverdoseAhmad SyaukatNo ratings yet
- Adamgammadex Mai Bun Ca SugammadexDocument6 pagesAdamgammadex Mai Bun Ca SugammadexAdi CărbunaruNo ratings yet
- 150 Years of PharmacovigilanceDocument2 pages150 Years of PharmacovigilanceCarlos José Lacava Fernández100% (1)
- Antiarrhythmic AgentsDocument45 pagesAntiarrhythmic AgentsSoh Kae SiangNo ratings yet
- King 2012 4AP Toxicity ReviewDocument8 pagesKing 2012 4AP Toxicity ReviewzernebochNo ratings yet
- Drug-Induced QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes: Matthew Li, Pharmd and Liz G. Ramos, Pharmd, BcpsDocument5 pagesDrug-Induced QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes: Matthew Li, Pharmd and Liz G. Ramos, Pharmd, BcpsCalon DokterNo ratings yet
- Nad Karni 2014Document2 pagesNad Karni 2014pedrotuliorochaNo ratings yet
- 1 Ketamin LGDocument4 pages1 Ketamin LGUmmi QorinNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Toxicity An Overview 2165 7548.1000158Document3 pagesParacetamol Toxicity An Overview 2165 7548.1000158psNo ratings yet
- PropofolDocument9 pagesPropofolarturschander3614No ratings yet
- Effect Radiation Reproductive: of The Human SystemDocument8 pagesEffect Radiation Reproductive: of The Human SystemAndrea Kristine LumanogNo ratings yet
- Caredose SiemensDocument1 pageCaredose SiemensHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Pictorial Essay: Multidetector CT Urography With Abdominal Compression and Three-Dimensional ReconstructionDocument13 pagesPictorial Essay: Multidetector CT Urography With Abdominal Compression and Three-Dimensional ReconstructionHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Unige 136981 Attachment01Document5 pagesUnige 136981 Attachment01Harley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Estimacion Del RiesgoDocument5 pagesEstimacion Del RiesgoHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Medical Linear Accelerators in Radiation Therapy: Haijun Song, PH.DDocument43 pagesMedical Linear Accelerators in Radiation Therapy: Haijun Song, PH.DHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- 2013 Book HandbookOfNuclearCardiologyDocument215 pages2013 Book HandbookOfNuclearCardiologyHarley Alejo M100% (1)
- Nuclear Medicine and Positron Emission Tomography: An OverviewDocument7 pagesNuclear Medicine and Positron Emission Tomography: An OverviewHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Radiation PhysicsDocument307 pagesRadiation PhysicsHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- 2017 Book QualityInNuclearMedicineDocument455 pages2017 Book QualityInNuclearMedicineHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Update Digital Mammography Protocol 01-2017Document3 pagesUpdate Digital Mammography Protocol 01-2017Harley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Practical Exercise: Effective Dose Estimate in CTDocument27 pagesPractical Exercise: Effective Dose Estimate in CTHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Corrientes de EddyDocument5 pagesCorrientes de EddyHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Covello2011 RISK COMMUNICATION, RADIATION, AND RADIOLOGICAL EMERGENCIESDocument20 pagesCovello2011 RISK COMMUNICATION, RADIATION, AND RADIOLOGICAL EMERGENCIESHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- 16303264Document36 pages16303264Harley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Vivo Placement Papers PDF Download PDFDocument28 pagesVivo Placement Papers PDF Download PDFNikhil VermaNo ratings yet
- Vedanta Solution To Our Fundamental ProblemDocument356 pagesVedanta Solution To Our Fundamental Problemspikeman42100% (1)
- Moot Court (Clinical)Document2 pagesMoot Court (Clinical)prince KumarNo ratings yet
- Bentley BrochureDocument8 pagesBentley BrochureKomolNo ratings yet
- 1359 - 1368. TingkahanDocument5 pages1359 - 1368. TingkahanRizal Daujr Tingkahan IIINo ratings yet
- Eslprintables 2009810153647888645279Document1 pageEslprintables 2009810153647888645279Mathéo DE OLIVEIRANo ratings yet
- Cambridge, 2nd Ed.-Petty Cash BookDocument3 pagesCambridge, 2nd Ed.-Petty Cash BookShannen LyeNo ratings yet
- Appendix B For CPPDocument1 pageAppendix B For CPP16 Dighe YogeshwariNo ratings yet
- Cavite Mutiny AccountsDocument4 pagesCavite Mutiny AccountsSAMANTHA ANN GUINTONo ratings yet
- Crossing The Threshold - Audrey TopazianDocument3 pagesCrossing The Threshold - Audrey Topazianapi-502833469No ratings yet
- S Bing 0605175 Chapter4Document29 pagesS Bing 0605175 Chapter4Rose GreenNo ratings yet
- Asso V EnergyDocument38 pagesAsso V Energyarriane joy insularNo ratings yet
- Aerodur Finish HF A 130: ® Akzonobel Aerospace CoatingsDocument3 pagesAerodur Finish HF A 130: ® Akzonobel Aerospace CoatingsАндрей МошкинNo ratings yet
- 2014 JC1 H2 PH BT P2 Question SolutionDocument17 pages2014 JC1 H2 PH BT P2 Question Solutionshakthee sivakumarNo ratings yet
- Pienaar Savic Accepted MsDocument32 pagesPienaar Savic Accepted MsEl LuchoNo ratings yet
- Biology Ecology Revision NotesDocument7 pagesBiology Ecology Revision NotesGeorge ArgyrouNo ratings yet
- Chemical Analysis of Caustic Soda and Caustic Potash (Sodium Hydroxide and Potassium Hydroxide)Document16 pagesChemical Analysis of Caustic Soda and Caustic Potash (Sodium Hydroxide and Potassium Hydroxide)wilfred gomezNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Topics CriminologyDocument7 pagesDissertation Topics CriminologyCustomPapersPaterson100% (1)
- Position Paper Martial LawDocument3 pagesPosition Paper Martial LawLeoncio BocoNo ratings yet
- ICEfaces Asynchronous HTTP ServerDocument33 pagesICEfaces Asynchronous HTTP ServerIniyaNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals, Eleventh CircuitDocument52 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Eleventh CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- The Victim's Autopsy ReportDocument2 pagesThe Victim's Autopsy ReportShan KNo ratings yet
- Managing Clean Core For SAP S4HANA Cloud NotesDocument59 pagesManaging Clean Core For SAP S4HANA Cloud NotesGLEN KGATLANo ratings yet
- Aztec MagicDocument2 pagesAztec MagicBob MarinoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDocument25 pagesIntroduction To 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldPj CastilloNo ratings yet
- Horn Persistence Natural HornDocument4 pagesHorn Persistence Natural Hornapi-478106051No ratings yet
- Job Characteristics and Job Satisfaction: A Test of Warr's Vitamin Model in German HorticultureDocument23 pagesJob Characteristics and Job Satisfaction: A Test of Warr's Vitamin Model in German HorticulturetaryNo ratings yet