Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ME331-QUIZ NO. 4 - Part 2 - PROBLEMS
ME331-QUIZ NO. 4 - Part 2 - PROBLEMS
Uploaded by
EdrianCliffDelPilarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationFrom EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Assessment Exam 03: Fluid Mechanics and HydraulicsDocument6 pagesAssessment Exam 03: Fluid Mechanics and HydraulicsAndrea MagtutoNo ratings yet
- Peso Interview QuestiionsDocument3 pagesPeso Interview QuestiionsrajeshNo ratings yet
- Service ManualDocument698 pagesService Manualالمهندسوليدالطويل95% (21)
- 202Document4 pages202x2ybvdw4bhNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Chapter 2 Problem SetDocument6 pagesHydraulics Chapter 2 Problem SetjosephussucoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 20232024-1Document8 pagesAssignment 2 20232024-1mhaikalirsyad03No ratings yet
- BernoulliDocument25 pagesBernoulliAlberto Preciados AlumbroNo ratings yet
- AL-Revision Chap 5,6Document10 pagesAL-Revision Chap 5,6Omar A-gNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics - Series 1 (Fundamentals of Fluid Flow) - Sample Problems PDFDocument2 pagesHydraulics - Series 1 (Fundamentals of Fluid Flow) - Sample Problems PDFNica Remollo100% (3)
- Group Assignment Presentation No. 4 Fundamentals of Fluid FlowDocument6 pagesGroup Assignment Presentation No. 4 Fundamentals of Fluid FlowJeremyNo ratings yet
- Sheet 03 - MECA - ZAGDocument6 pagesSheet 03 - MECA - ZAGMohamed AbdelrazekNo ratings yet
- Tutorial QN 6-10Document6 pagesTutorial QN 6-10clarence limNo ratings yet
- INME 4045 - Chapter 2 - Suggested ProblemsDocument2 pagesINME 4045 - Chapter 2 - Suggested ProblemsAmanda SotoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Worksheet 2Document8 pagesFluid Mechanics Worksheet 2anon_293092329No ratings yet
- CEng 6803 Course Work IDocument2 pagesCEng 6803 Course Work Iyared sitotaw100% (1)
- Tutorials-2 With SolutionsDocument3 pagesTutorials-2 With Solutionsbhanuprakash.sayapoguNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'Review Module Hydraulics 03 Part 02 May 2023' With YouDocument2 pagesI Am Sharing 'Review Module Hydraulics 03 Part 02 May 2023' With YouAlexander P. BelkaNo ratings yet
- ExamplesDocument26 pagesExamplesAli Osman AydemirNo ratings yet
- Kmu 224 - Fluid MechanicsDocument3 pagesKmu 224 - Fluid MechanicsAEdian TVNo ratings yet
- Wala LangDocument3 pagesWala LangEthyl Jean Monday GallarteNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Viscous Flow in PipesDocument5 pagesTutorial 1 Viscous Flow in PipesAcap AliasNo ratings yet
- Compile AssignmentDocument13 pagesCompile AssignmentSilva deNo ratings yet
- Tutorials-2 With SolutionsDocument3 pagesTutorials-2 With Solutionsbhanuprakash.sayapoguNo ratings yet
- PS 3Document9 pagesPS 3naverfallNo ratings yet
- HYDRODYNAMICSDocument28 pagesHYDRODYNAMICSSysy monmonNo ratings yet
- Tut 1Document2 pagesTut 1wilson0% (1)
- Total Marks: 100 Time: 3 HoursDocument3 pagesTotal Marks: 100 Time: 3 HoursTinashe MazokeraNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics PaperDocument1 pageFluid Mechanics PaperAbdul Majid KhanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Fluid Mechanics Ii - 030410041152 - 1Document11 pagesQuestion Bank For Fluid Mechanics Ii - 030410041152 - 1Bharath Waj100% (1)
- 14 MarksDocument4 pages14 MarksmohanNo ratings yet
- MCE 244 Assignment 1Document1 pageMCE 244 Assignment 1Richard AppowNo ratings yet
- HDM360S Tutorial 3 - 2024 - TurbinesDocument6 pagesHDM360S Tutorial 3 - 2024 - TurbinesSimphiweNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation Problems (1168)Document4 pagesEnergy Conservation Problems (1168)ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Sheet3 3Document3 pagesSheet3 3Jasmine KhaledNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Lecture 5 SolutionsDocument10 pagesTutorial - Lecture 5 SolutionsBastián Olfos MárquezNo ratings yet
- 9A01308 Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulic MachineryDocument4 pages9A01308 Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulic MachinerysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Energy Resources and Policy Tutorial: Tidal Power: Density of Water Is 1000 KG/M Unless Otherwise StatedDocument2 pagesEnergy Resources and Policy Tutorial: Tidal Power: Density of Water Is 1000 KG/M Unless Otherwise StatedLightninWolf32No ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document11 pagesAssignment 5Bill Wong100% (1)
- Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Department Fluid Mechanics (1), SheetDocument2 pagesFayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Department Fluid Mechanics (1), SheetMo 16No ratings yet
- Tim1 KelasADocument5 pagesTim1 KelasARiatus SNo ratings yet
- Reviewer TopicsDocument3 pagesReviewer Topicshoneylet tayactac0% (2)
- Assignment RVF HJ 1Document1 pageAssignment RVF HJ 1Abdel Samie MuhyadinNo ratings yet
- Question AnwerDocument23 pagesQuestion AnwerOnsoti NyaberaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4Document5 pagesQuiz 4Daniele Joseph HizonNo ratings yet
- CE253Document3 pagesCE253Maxwell RejilNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document5 pagesTutorial 4Amylia NatashaNo ratings yet
- Solution To HW5Document23 pagesSolution To HW5minervini markNo ratings yet
- L, Immersed in A Stream Flowing NormalDocument1 pageL, Immersed in A Stream Flowing NormalJacobo NaderNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Governing Laws and Principles: Self Evaluation Questions and AnswersDocument22 pagesLecture 4 - Governing Laws and Principles: Self Evaluation Questions and AnswersMohamedNo ratings yet
- CHE 204 Homework # 2Document3 pagesCHE 204 Homework # 2OGNo ratings yet
- Micro Gas TurbineDocument4 pagesMicro Gas TurbineArmando SuberoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Fluid FlowDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 Fluid FlowNicolHernandezNarvaezNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sheet No 2 - 2016Document8 pagesAssignment Sheet No 2 - 2016Muhammad Haseeb JavedNo ratings yet
- Sheet (2) Fluid Spring 2017Document5 pagesSheet (2) Fluid Spring 2017Mohammed SobhiNo ratings yet
- Sheet (1) Fluid Mechanics 2Document6 pagesSheet (1) Fluid Mechanics 2drawanyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Bernoulli Equation Part 2Document2 pagesTutorial Bernoulli Equation Part 2Muhamad Hazim ZaabaNo ratings yet
- HYDRAULICSDocument15 pagesHYDRAULICSHoney ApariceNo ratings yet
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronFrom EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo ratings yet
- Modern Devices: The Simple Physics of Sophisticated TechnologyFrom EverandModern Devices: The Simple Physics of Sophisticated TechnologyNo ratings yet
- ME331 - Fluid Mechanics: Assignment No.2-Fluid StaticsDocument2 pagesME331 - Fluid Mechanics: Assignment No.2-Fluid StaticsEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Vibration Engineering: By: Engr. Ray H. MalonjaoDocument15 pagesVibration Engineering: By: Engr. Ray H. MalonjaoEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Me331-Quiz No. 3 - Problems OnlyDocument1 pageMe331-Quiz No. 3 - Problems OnlyEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Week2 - Robot TechnologyDocument12 pagesWeek2 - Robot TechnologyEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Iterative Control Structure: Do (Statement ) While (Loop Repetition Condition)Document10 pagesIterative Control Structure: Do (Statement ) While (Loop Repetition Condition)EdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- ME331 - Fluid Mechanics: Assignment No.1-Fluid PropertiesDocument1 pageME331 - Fluid Mechanics: Assignment No.1-Fluid PropertiesEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- One Dimensional ArrayDocument8 pagesOne Dimensional ArrayEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- How Interface Works?Document7 pagesHow Interface Works?EdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Week5 InheritancePolymorphismAbstraction PDFDocument18 pagesWeek5 InheritancePolymorphismAbstraction PDFEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Conditional Control Structure: OperatorsDocument12 pagesConditional Control Structure: OperatorsEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Week1a VisualStudioSetUpDocument4 pagesWeek1a VisualStudioSetUpEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Week4 ClassEncapsulation PDFDocument20 pagesWeek4 ClassEncapsulation PDFEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Week1b - OverviewOf OOP PDFDocument3 pagesWeek1b - OverviewOf OOP PDFEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Week2a BasicElementsinC#Document9 pagesWeek2a BasicElementsinC#EdrianCliffDelPilar100% (1)
- Designing For DigitalDocument4 pagesDesigning For DigitalEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Liquidation Report Game CMTDocument1 pageLiquidation Report Game CMTEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- An Organizational Strategy Road Map For AnalyticsDocument12 pagesAn Organizational Strategy Road Map For AnalyticsEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Research Quiz: The Frequency, (Ƒ)Document3 pagesResearch Quiz: The Frequency, (Ƒ)EdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Things To DoDocument1 pageThings To DoEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Programming QuestionsDocument12 pagesProgramming QuestionsEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Is Hong Kong Part of China?: China's Biggest Political RetreatDocument2 pagesIs Hong Kong Part of China?: China's Biggest Political RetreatEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Excel BasicsDocument37 pagesExcel BasicsEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- RRL YouthDocument3 pagesRRL YouthEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Liquidation Report Game CMTDocument1 pageLiquidation Report Game CMTEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Essay AnswersDocument4 pagesEssay AnswersEdrianCliffDelPilar100% (1)
- CE231 Lecture NotesDocument1 pageCE231 Lecture NotesEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- RACDocument1 pageRACkulwinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument15 pagesSteam TurbinePalash Dey100% (1)
- Esquema Hidráulico 895 - OpicionalDocument9 pagesEsquema Hidráulico 895 - OpicionalFelipe Dias BarcelosNo ratings yet
- Modifikasi Putaran Fan Untuk Meningkatkan Efisiensi Pemakaian ListrikDocument8 pagesModifikasi Putaran Fan Untuk Meningkatkan Efisiensi Pemakaian Listrikrizal ardiantoNo ratings yet
- Triplex PUmp 01 ChecklistDocument7 pagesTriplex PUmp 01 ChecklistMarizon ZulkarnainiNo ratings yet
- CPT-0018 Commissioning Procedure of Fuel Oil SystemDocument5 pagesCPT-0018 Commissioning Procedure of Fuel Oil SystemJ BagienNo ratings yet
- HP LP Bypass System (Turbine)Document9 pagesHP LP Bypass System (Turbine)Debasish Dewan67% (3)
- Types of Pipe Fittings Used in PipingDocument14 pagesTypes of Pipe Fittings Used in PipingBuilding Design & Construction100% (1)
- Pipe FittingsDocument158 pagesPipe FittingsGiraldoCarpioRamosNo ratings yet
- Reverse Circulating With Coiled TubingDocument21 pagesReverse Circulating With Coiled Tubingtony100% (1)
- Taijune Fire Tube Steam BoilerDocument8 pagesTaijune Fire Tube Steam BoilerAjay GoswamiNo ratings yet
- A New Correlation For Slip Factor in Radial and Mixed Flow ImpellersDocument6 pagesA New Correlation For Slip Factor in Radial and Mixed Flow Impellersmrkshitij.sNo ratings yet
- REXROTH - Symbols PneumaticsDocument47 pagesREXROTH - Symbols PneumaticsVladan MilojevićNo ratings yet
- Injection Pump Fuel Filter And4Document3 pagesInjection Pump Fuel Filter And4Diego DfashirtsNo ratings yet
- RD9 PneumaticsDocument66 pagesRD9 PneumaticsHussein MohamedNo ratings yet
- BF Adpters Back Up Rings OnlyDocument1 pageBF Adpters Back Up Rings OnlyHomayraCarranzaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Machines LaboratoryDocument27 pagesHydraulic Machines LaboratoryAnonymous f1UCK4No ratings yet
- Detalle de Partes Planes de Mantenimiento R - 5: Zaranda Móvil Metso ST4.8Document6 pagesDetalle de Partes Planes de Mantenimiento R - 5: Zaranda Móvil Metso ST4.8Os Arroyo100% (1)
- Gas Pressure Regulator Series 240Pl: Serving The Gas Industry WorldwideDocument11 pagesGas Pressure Regulator Series 240Pl: Serving The Gas Industry WorldwideSandro RuizNo ratings yet
- Surface Safety SystemsDocument182 pagesSurface Safety Systemsbintangdyah28No ratings yet
- 30hx-8pd ChillerDocument76 pages30hx-8pd ChillermagaliNo ratings yet
- NBVMKDocument4 pagesNBVMKD SNo ratings yet
- Oral Questions For Industrial Fluid PowerDocument3 pagesOral Questions For Industrial Fluid PowerEswara RaoNo ratings yet
- Ne TRSV H012542Document2 pagesNe TRSV H012542hoss mosafaNo ratings yet
- SIDEL Peças Pasteruziador PDFDocument50 pagesSIDEL Peças Pasteruziador PDFEduarda PortellaNo ratings yet
- Standard InterfacesDocument7 pagesStandard InterfacesAngel NavarroNo ratings yet
- McENG 6221-Advanced Fluid Power System (Mechatronics)Document4 pagesMcENG 6221-Advanced Fluid Power System (Mechatronics)duraiprakash83No ratings yet
- Petroleum Development Oman LLC: Appendix-2: Pipe Stress Analysis Checklist-Input/OutputDocument5 pagesPetroleum Development Oman LLC: Appendix-2: Pipe Stress Analysis Checklist-Input/OutputAbhijeetNo ratings yet
ME331-QUIZ NO. 4 - Part 2 - PROBLEMS
ME331-QUIZ NO. 4 - Part 2 - PROBLEMS
Uploaded by
EdrianCliffDelPilarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ME331-QUIZ NO. 4 - Part 2 - PROBLEMS
ME331-QUIZ NO. 4 - Part 2 - PROBLEMS
Uploaded by
EdrianCliffDelPilarCopyright:
Available Formats
ME331 – Fluid Mechanics
QUIZ NO. 4 – Part 2 - Problem Solving
SHOW A DETAILED SOLUTION OF EACH PROBLEM
DEADLINE OF SUBMISSION IS THURSDAY @ 12:00 NOON
Any two or more students proven to have the same structure/flow of a solution of any problem
will NOT EARN any credit on that problem, regardless of who the sourceis.
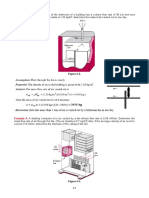
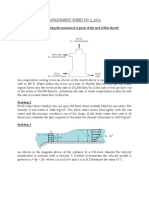
1. Water exits a pipe as a free jet 5. The water level in a tank is 20 m 8. A hydraulic turbine has 50 m of
and flows to a height h abovethe above the ground.A hose is head available at aflow rate of
exit plane as shown in the figure. connected to the bottom of the 1.30 m3/s, and its overall turbine–
The flow is steady, tank, and thenozzleat the end of generator efficiencyis 78 percent.
incompressible,and frictionless. (a) the hose is pointed straight up. Determine the electric power
Determine the height h. (b) Thetank cover is airtight, and the output ofthis turbine. 497.367 kw
Determine the velocity and air pressure above the
pressure at section (1). 11.165 watersurface is 2 atm gage. The 9. Water enters a hydraulic turbine
psi;3.9752 ft; 36 ft/s system is at sea level. through a30-cm-diameter pipe at
Determinethe maximum height to a rate of 0.6 m3/s and exits
which the water stream could rise. througha 25-cm-diameter pipe.
40.657 m The pressure drop in the turbine
ismeasured by a mercury
manometer to be 1.2 m. For a
combinedturbine– generator
efficiency of 83 %, determinethe
net electric power output.
Disregard the effect of thekinetic
energy correction factors. 54.37
kw
2. The air velocity in the duct of a
heating system is tobe measured
by a Pitot-static probe inserted
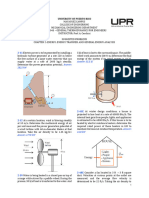
into the duct parallelto the flow. If 6. A fireboat is to fight fires at coastal
the differential height between the areas by drawing seawater with a
watercolumns connected to the density of 1030 kg/m3 through a
two outlets of the probe is 3.2 10-cm-diameter pipe at a rate of
cm,determine (a) the flow velocity 0.04 m3/s and discharging it
and (b) the pressure rise atthe tip through a hose nozzle with an 10. Water atroom temperature flows
of the probe. The air temperature exit diameter of 5 cm. The total with a volume flow rate of 0.0250
and pressure in theduct are 45°C irreversible head loss of the m3/s through a horizontal diffuser
and 98 kPa, respectively. 313.92 system is 3 m, and the position of in which the diameter increases
Pa; 1.0733 kg/m3 ;24.186 m/s the nozzle is 3 m above sea level. gradually from D1 = 6.00 to D2 =
For a pump efficiency of 70 %, 11.00 cm. The irreversible head
3. A 15-hp (shaft) pump is used to determine the required shaft loss through the diffuser is
raise water to a 45-mhigher power input to the pump and the estimated to be 0.450 m. The
elevation. If the mechanical water discharge velocity. kinetic energy correctionfactors at
efficiency of the pumpis 82 %, 20.372 m/s both the inlet and outlet of the
determine the maximum volume diffuser areassumed to be 1.05.
flow rate of water. 0.02078 m3/s (a) Calculate the pressure
difference (P2 – P1) in kPausing
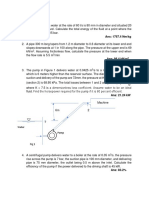
4. What is the minimum diameter at the energy equation. (b) Draw
section (1) to avoid cavitation at approximately the EGL and HGL
that point? Take D2 = 15 cm. in this diffuser. 33kpa
0.126 m
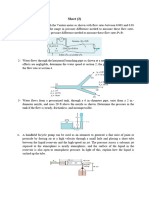
7. Water is being pumped from a
large lake to a reservoir25 m
above at a rate of 25 L/s by a
10kW pump. If theirreversible
head loss of the piping system is
5 m, determine the mechanical
efficiency of the pump. 73.58%
You might also like
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationFrom EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Assessment Exam 03: Fluid Mechanics and HydraulicsDocument6 pagesAssessment Exam 03: Fluid Mechanics and HydraulicsAndrea MagtutoNo ratings yet
- Peso Interview QuestiionsDocument3 pagesPeso Interview QuestiionsrajeshNo ratings yet
- Service ManualDocument698 pagesService Manualالمهندسوليدالطويل95% (21)
- 202Document4 pages202x2ybvdw4bhNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Chapter 2 Problem SetDocument6 pagesHydraulics Chapter 2 Problem SetjosephussucoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 20232024-1Document8 pagesAssignment 2 20232024-1mhaikalirsyad03No ratings yet
- BernoulliDocument25 pagesBernoulliAlberto Preciados AlumbroNo ratings yet
- AL-Revision Chap 5,6Document10 pagesAL-Revision Chap 5,6Omar A-gNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics - Series 1 (Fundamentals of Fluid Flow) - Sample Problems PDFDocument2 pagesHydraulics - Series 1 (Fundamentals of Fluid Flow) - Sample Problems PDFNica Remollo100% (3)
- Group Assignment Presentation No. 4 Fundamentals of Fluid FlowDocument6 pagesGroup Assignment Presentation No. 4 Fundamentals of Fluid FlowJeremyNo ratings yet
- Sheet 03 - MECA - ZAGDocument6 pagesSheet 03 - MECA - ZAGMohamed AbdelrazekNo ratings yet
- Tutorial QN 6-10Document6 pagesTutorial QN 6-10clarence limNo ratings yet
- INME 4045 - Chapter 2 - Suggested ProblemsDocument2 pagesINME 4045 - Chapter 2 - Suggested ProblemsAmanda SotoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Worksheet 2Document8 pagesFluid Mechanics Worksheet 2anon_293092329No ratings yet
- CEng 6803 Course Work IDocument2 pagesCEng 6803 Course Work Iyared sitotaw100% (1)
- Tutorials-2 With SolutionsDocument3 pagesTutorials-2 With Solutionsbhanuprakash.sayapoguNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'Review Module Hydraulics 03 Part 02 May 2023' With YouDocument2 pagesI Am Sharing 'Review Module Hydraulics 03 Part 02 May 2023' With YouAlexander P. BelkaNo ratings yet
- ExamplesDocument26 pagesExamplesAli Osman AydemirNo ratings yet
- Kmu 224 - Fluid MechanicsDocument3 pagesKmu 224 - Fluid MechanicsAEdian TVNo ratings yet
- Wala LangDocument3 pagesWala LangEthyl Jean Monday GallarteNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Viscous Flow in PipesDocument5 pagesTutorial 1 Viscous Flow in PipesAcap AliasNo ratings yet
- Compile AssignmentDocument13 pagesCompile AssignmentSilva deNo ratings yet
- Tutorials-2 With SolutionsDocument3 pagesTutorials-2 With Solutionsbhanuprakash.sayapoguNo ratings yet
- PS 3Document9 pagesPS 3naverfallNo ratings yet
- HYDRODYNAMICSDocument28 pagesHYDRODYNAMICSSysy monmonNo ratings yet
- Tut 1Document2 pagesTut 1wilson0% (1)
- Total Marks: 100 Time: 3 HoursDocument3 pagesTotal Marks: 100 Time: 3 HoursTinashe MazokeraNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics PaperDocument1 pageFluid Mechanics PaperAbdul Majid KhanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Fluid Mechanics Ii - 030410041152 - 1Document11 pagesQuestion Bank For Fluid Mechanics Ii - 030410041152 - 1Bharath Waj100% (1)
- 14 MarksDocument4 pages14 MarksmohanNo ratings yet
- MCE 244 Assignment 1Document1 pageMCE 244 Assignment 1Richard AppowNo ratings yet
- HDM360S Tutorial 3 - 2024 - TurbinesDocument6 pagesHDM360S Tutorial 3 - 2024 - TurbinesSimphiweNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation Problems (1168)Document4 pagesEnergy Conservation Problems (1168)ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Sheet3 3Document3 pagesSheet3 3Jasmine KhaledNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Lecture 5 SolutionsDocument10 pagesTutorial - Lecture 5 SolutionsBastián Olfos MárquezNo ratings yet
- 9A01308 Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulic MachineryDocument4 pages9A01308 Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulic MachinerysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Energy Resources and Policy Tutorial: Tidal Power: Density of Water Is 1000 KG/M Unless Otherwise StatedDocument2 pagesEnergy Resources and Policy Tutorial: Tidal Power: Density of Water Is 1000 KG/M Unless Otherwise StatedLightninWolf32No ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document11 pagesAssignment 5Bill Wong100% (1)
- Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Department Fluid Mechanics (1), SheetDocument2 pagesFayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Department Fluid Mechanics (1), SheetMo 16No ratings yet
- Tim1 KelasADocument5 pagesTim1 KelasARiatus SNo ratings yet
- Reviewer TopicsDocument3 pagesReviewer Topicshoneylet tayactac0% (2)
- Assignment RVF HJ 1Document1 pageAssignment RVF HJ 1Abdel Samie MuhyadinNo ratings yet
- Question AnwerDocument23 pagesQuestion AnwerOnsoti NyaberaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4Document5 pagesQuiz 4Daniele Joseph HizonNo ratings yet
- CE253Document3 pagesCE253Maxwell RejilNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document5 pagesTutorial 4Amylia NatashaNo ratings yet
- Solution To HW5Document23 pagesSolution To HW5minervini markNo ratings yet
- L, Immersed in A Stream Flowing NormalDocument1 pageL, Immersed in A Stream Flowing NormalJacobo NaderNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Governing Laws and Principles: Self Evaluation Questions and AnswersDocument22 pagesLecture 4 - Governing Laws and Principles: Self Evaluation Questions and AnswersMohamedNo ratings yet
- CHE 204 Homework # 2Document3 pagesCHE 204 Homework # 2OGNo ratings yet
- Micro Gas TurbineDocument4 pagesMicro Gas TurbineArmando SuberoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Fluid FlowDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 Fluid FlowNicolHernandezNarvaezNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sheet No 2 - 2016Document8 pagesAssignment Sheet No 2 - 2016Muhammad Haseeb JavedNo ratings yet
- Sheet (2) Fluid Spring 2017Document5 pagesSheet (2) Fluid Spring 2017Mohammed SobhiNo ratings yet
- Sheet (1) Fluid Mechanics 2Document6 pagesSheet (1) Fluid Mechanics 2drawanyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Bernoulli Equation Part 2Document2 pagesTutorial Bernoulli Equation Part 2Muhamad Hazim ZaabaNo ratings yet
- HYDRAULICSDocument15 pagesHYDRAULICSHoney ApariceNo ratings yet
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronFrom EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo ratings yet
- Modern Devices: The Simple Physics of Sophisticated TechnologyFrom EverandModern Devices: The Simple Physics of Sophisticated TechnologyNo ratings yet
- ME331 - Fluid Mechanics: Assignment No.2-Fluid StaticsDocument2 pagesME331 - Fluid Mechanics: Assignment No.2-Fluid StaticsEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Vibration Engineering: By: Engr. Ray H. MalonjaoDocument15 pagesVibration Engineering: By: Engr. Ray H. MalonjaoEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Me331-Quiz No. 3 - Problems OnlyDocument1 pageMe331-Quiz No. 3 - Problems OnlyEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Week2 - Robot TechnologyDocument12 pagesWeek2 - Robot TechnologyEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Iterative Control Structure: Do (Statement ) While (Loop Repetition Condition)Document10 pagesIterative Control Structure: Do (Statement ) While (Loop Repetition Condition)EdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- ME331 - Fluid Mechanics: Assignment No.1-Fluid PropertiesDocument1 pageME331 - Fluid Mechanics: Assignment No.1-Fluid PropertiesEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- One Dimensional ArrayDocument8 pagesOne Dimensional ArrayEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- How Interface Works?Document7 pagesHow Interface Works?EdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Week5 InheritancePolymorphismAbstraction PDFDocument18 pagesWeek5 InheritancePolymorphismAbstraction PDFEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Conditional Control Structure: OperatorsDocument12 pagesConditional Control Structure: OperatorsEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Week1a VisualStudioSetUpDocument4 pagesWeek1a VisualStudioSetUpEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Week4 ClassEncapsulation PDFDocument20 pagesWeek4 ClassEncapsulation PDFEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Week1b - OverviewOf OOP PDFDocument3 pagesWeek1b - OverviewOf OOP PDFEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Week2a BasicElementsinC#Document9 pagesWeek2a BasicElementsinC#EdrianCliffDelPilar100% (1)
- Designing For DigitalDocument4 pagesDesigning For DigitalEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Liquidation Report Game CMTDocument1 pageLiquidation Report Game CMTEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- An Organizational Strategy Road Map For AnalyticsDocument12 pagesAn Organizational Strategy Road Map For AnalyticsEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Research Quiz: The Frequency, (Ƒ)Document3 pagesResearch Quiz: The Frequency, (Ƒ)EdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Things To DoDocument1 pageThings To DoEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Programming QuestionsDocument12 pagesProgramming QuestionsEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Is Hong Kong Part of China?: China's Biggest Political RetreatDocument2 pagesIs Hong Kong Part of China?: China's Biggest Political RetreatEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Excel BasicsDocument37 pagesExcel BasicsEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- RRL YouthDocument3 pagesRRL YouthEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Liquidation Report Game CMTDocument1 pageLiquidation Report Game CMTEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Essay AnswersDocument4 pagesEssay AnswersEdrianCliffDelPilar100% (1)
- CE231 Lecture NotesDocument1 pageCE231 Lecture NotesEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- RACDocument1 pageRACkulwinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument15 pagesSteam TurbinePalash Dey100% (1)
- Esquema Hidráulico 895 - OpicionalDocument9 pagesEsquema Hidráulico 895 - OpicionalFelipe Dias BarcelosNo ratings yet
- Modifikasi Putaran Fan Untuk Meningkatkan Efisiensi Pemakaian ListrikDocument8 pagesModifikasi Putaran Fan Untuk Meningkatkan Efisiensi Pemakaian Listrikrizal ardiantoNo ratings yet
- Triplex PUmp 01 ChecklistDocument7 pagesTriplex PUmp 01 ChecklistMarizon ZulkarnainiNo ratings yet
- CPT-0018 Commissioning Procedure of Fuel Oil SystemDocument5 pagesCPT-0018 Commissioning Procedure of Fuel Oil SystemJ BagienNo ratings yet
- HP LP Bypass System (Turbine)Document9 pagesHP LP Bypass System (Turbine)Debasish Dewan67% (3)
- Types of Pipe Fittings Used in PipingDocument14 pagesTypes of Pipe Fittings Used in PipingBuilding Design & Construction100% (1)
- Pipe FittingsDocument158 pagesPipe FittingsGiraldoCarpioRamosNo ratings yet
- Reverse Circulating With Coiled TubingDocument21 pagesReverse Circulating With Coiled Tubingtony100% (1)
- Taijune Fire Tube Steam BoilerDocument8 pagesTaijune Fire Tube Steam BoilerAjay GoswamiNo ratings yet
- A New Correlation For Slip Factor in Radial and Mixed Flow ImpellersDocument6 pagesA New Correlation For Slip Factor in Radial and Mixed Flow Impellersmrkshitij.sNo ratings yet
- REXROTH - Symbols PneumaticsDocument47 pagesREXROTH - Symbols PneumaticsVladan MilojevićNo ratings yet
- Injection Pump Fuel Filter And4Document3 pagesInjection Pump Fuel Filter And4Diego DfashirtsNo ratings yet
- RD9 PneumaticsDocument66 pagesRD9 PneumaticsHussein MohamedNo ratings yet
- BF Adpters Back Up Rings OnlyDocument1 pageBF Adpters Back Up Rings OnlyHomayraCarranzaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Machines LaboratoryDocument27 pagesHydraulic Machines LaboratoryAnonymous f1UCK4No ratings yet
- Detalle de Partes Planes de Mantenimiento R - 5: Zaranda Móvil Metso ST4.8Document6 pagesDetalle de Partes Planes de Mantenimiento R - 5: Zaranda Móvil Metso ST4.8Os Arroyo100% (1)
- Gas Pressure Regulator Series 240Pl: Serving The Gas Industry WorldwideDocument11 pagesGas Pressure Regulator Series 240Pl: Serving The Gas Industry WorldwideSandro RuizNo ratings yet
- Surface Safety SystemsDocument182 pagesSurface Safety Systemsbintangdyah28No ratings yet
- 30hx-8pd ChillerDocument76 pages30hx-8pd ChillermagaliNo ratings yet
- NBVMKDocument4 pagesNBVMKD SNo ratings yet
- Oral Questions For Industrial Fluid PowerDocument3 pagesOral Questions For Industrial Fluid PowerEswara RaoNo ratings yet
- Ne TRSV H012542Document2 pagesNe TRSV H012542hoss mosafaNo ratings yet
- SIDEL Peças Pasteruziador PDFDocument50 pagesSIDEL Peças Pasteruziador PDFEduarda PortellaNo ratings yet
- Standard InterfacesDocument7 pagesStandard InterfacesAngel NavarroNo ratings yet
- McENG 6221-Advanced Fluid Power System (Mechatronics)Document4 pagesMcENG 6221-Advanced Fluid Power System (Mechatronics)duraiprakash83No ratings yet
- Petroleum Development Oman LLC: Appendix-2: Pipe Stress Analysis Checklist-Input/OutputDocument5 pagesPetroleum Development Oman LLC: Appendix-2: Pipe Stress Analysis Checklist-Input/OutputAbhijeetNo ratings yet