Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ax BXC Ax BXC
Ax BXC Ax BXC
Uploaded by
neetiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ax BXC Ax BXC
Ax BXC Ax BXC
Uploaded by
neetiCopyright:
Available Formats
1597-14.
4-19E AID: 4446 |
22/09/2020
Consider a expression as:
4 y 2 5 y
The objective is to solve above quadratic inequality using test point.
Quadratic Inequality
An inequality written in form as ax bx c 0 or ax bx c 0 where a, b and c are
2 2
real numbers and a 0 s is called as a quadratic inequality.
Solving a quadratic inequality using test points
First of all, inequality is written in form as ax bx c 0 or ax bx c 0
2 2
Then the equation ax bx c 0 is solved.
2
The solutions of ax bx c 0 are put on a number line.
2
Then a test point is chosen in each interval for determining whether ax bx c is
2
positive or negative.
When the inequality is of the form ax bx c 0 or ax bx c 0 then the
2 2
solution set consists of the numbers in the interval where ax bx c 0 is
2
negative and when the inequality is of the form ax bx c 0 or ax bx c 0
2 2
then the solution set consists of the numbers in the interval where ax bx c 0
2
is positive.
When the inequality symbol is or then the endpoints of the interval(s) are
included in solution set and when the inequality symbol is or> then the
endpoints of the interval(s) are not included in solution set.
Now for the given inequality 4 y 5 y is solved as:
2
4 y 2 5 y
4 y2 5 y 0
y 4 y 5 0
5 5
y , y 0, y 0
Thus, the intervals that satisfy the required condition 0 are as 4 4
5
y0
Now further for interval 4 a test point is chosen as -1 and is checked in
inequality as:
4 y2 5 y 0
4 1 5 1 0
2
1 0
Thus, when y 1 , 4 y 5 y is negative. Therefore 4 y 5 y is negative for all
2 2
values of y in this interval.
5
,0
4
Thus, the solution set is as .
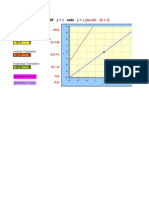
Now the graph of solution set is plotted below as:
y
You might also like
- FSMQ Additional Mathematics Revision NotesDocument84 pagesFSMQ Additional Mathematics Revision Notesapi-200177496100% (2)
- SQA Higher Mathematics Unit 2: SCHOLAR Study GuideDocument162 pagesSQA Higher Mathematics Unit 2: SCHOLAR Study GuideseamusNo ratings yet
- 70-Matrices & TransformationsDocument26 pages70-Matrices & TransformationsSameh SalahNo ratings yet
- Full download Elementary Algebra Concepts and Applications 10th Edition Bittinger Solutions Manual all chapter 2024 pdfDocument44 pagesFull download Elementary Algebra Concepts and Applications 10th Edition Bittinger Solutions Manual all chapter 2024 pdfathiampoloha100% (8)
- Instant Download PDF Elementary Algebra Concepts and Applications 10th Edition Bittinger Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument86 pagesInstant Download PDF Elementary Algebra Concepts and Applications 10th Edition Bittinger Solutions Manual Full Chapteryaqubedistel6100% (4)
- Elementary Algebra Concepts and Applications 10th Edition Bittinger Solutions Manual instant download all chapterDocument86 pagesElementary Algebra Concepts and Applications 10th Edition Bittinger Solutions Manual instant download all chapterpupkatwiky100% (2)
- Final s09 SolDocument18 pagesFinal s09 SolHadi MoshayediNo ratings yet
- Transformations Of: Vertical Stretch/compressionDocument4 pagesTransformations Of: Vertical Stretch/compressionMaher KamraNo ratings yet
- Full Elementary Algebra Concepts and Applications 10Th Edition Bittinger Solutions Manual Online PDF All ChapterDocument73 pagesFull Elementary Algebra Concepts and Applications 10Th Edition Bittinger Solutions Manual Online PDF All Chaptermegdevoted392100% (5)
- Quadratic EquationsDocument6 pagesQuadratic EquationsKaushik KaushikNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2: Transformation and Viewing: 1 Three-Dimensional Homogeneous Coordinates (15 PTS)Document6 pagesAssignment 2: Transformation and Viewing: 1 Three-Dimensional Homogeneous Coordinates (15 PTS)Gopal JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Elementary and Intermediate Algebra Concepts and Applications 7th Edition Bittinger Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument88 pagesInstant Download PDF Elementary and Intermediate Algebra Concepts and Applications 7th Edition Bittinger Solutions Manual Full Chapteryaqubedistel6100% (6)
- Full download Elementary and Intermediate Algebra Concepts and Applications 7th Edition Bittinger Solutions Manual all chapter 2024 pdfDocument35 pagesFull download Elementary and Intermediate Algebra Concepts and Applications 7th Edition Bittinger Solutions Manual all chapter 2024 pdfathiampoloha100% (8)
- Eigenvalues & EigenvectorsDocument8 pagesEigenvalues & EigenvectorsMyla VelascoNo ratings yet
- Elementary and Intermediate Algebra Concepts and Applications 7th Edition Bittinger Solutions Manual instant download all chapterDocument88 pagesElementary and Intermediate Algebra Concepts and Applications 7th Edition Bittinger Solutions Manual instant download all chapterpupkatwiky100% (2)
- Chapter 6 - Solving Quadratic EquationsDocument28 pagesChapter 6 - Solving Quadratic EquationsashNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Finding Square RootsDocument19 pages9.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Finding Square RootsRommel MorgaNo ratings yet
- Y, Z AB Is PerpendicularDocument28 pagesY, Z AB Is PerpendicularHabtamu GeremewNo ratings yet
- Maths12 06Document17 pagesMaths12 06eilyaeskandarianNo ratings yet
- MATHS Merged PDFDocument500 pagesMATHS Merged PDFVishal dandeNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Differential Equations With Boundary Value Problems Solutions PRDocument9 pagesToaz - Info Differential Equations With Boundary Value Problems Solutions PRانیس ب ٹNo ratings yet
- 10th 2A Math 17 - 01-20243Document2 pages10th 2A Math 17 - 01-20243Saeed AhmadNo ratings yet
- Math 313 (Linear Algebra) Final Exam Practice KEYDocument13 pagesMath 313 (Linear Algebra) Final Exam Practice KEYTabishNo ratings yet
- Points To Remember - Maths - Class10icseDocument8 pagesPoints To Remember - Maths - Class10icseaadithlamjonlNo ratings yet
- 03 Relations Functions and Graphs 001-006 PDFDocument6 pages03 Relations Functions and Graphs 001-006 PDFmelissa0royalNo ratings yet
- 4310 HW7Document1 page4310 HW7Gag PafNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document8 pagesLecture 6SHIVOM KUNDUNo ratings yet
- Polynomials and QuadraticsDocument26 pagesPolynomials and QuadraticsDavid ChangNo ratings yet
- Practice 4 Exam 1Document6 pagesPractice 4 Exam 1Himanshu YadavNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Conic SectionsDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Conic Sectionssir jjNo ratings yet
- Navier p8 Revised Final 2014Document34 pagesNavier p8 Revised Final 2014Annamalai VaidyanathanNo ratings yet
- BTech Mean Value TheoremDocument17 pagesBTech Mean Value TheoremMaitri ShahNo ratings yet
- Characteristics The Quadratic Equations Using The DiscriminantDocument6 pagesCharacteristics The Quadratic Equations Using The DiscriminantAhgase BirdsNo ratings yet
- Y X y X N B: Linear RegressionDocument7 pagesY X y X N B: Linear RegressionMaria ZenypherNo ratings yet
- Solusi: 4.68 2 8 .886 1 .886 2 N R 1 R TDocument4 pagesSolusi: 4.68 2 8 .886 1 .886 2 N R 1 R TwindiNo ratings yet
- EE590: Linear Algebra and Optimization Quiz 1: Time: 45 Minutes. 02-Sept 2021 Total: 40 MarksDocument29 pagesEE590: Linear Algebra and Optimization Quiz 1: Time: 45 Minutes. 02-Sept 2021 Total: 40 MarksNibha RanjanNo ratings yet
- Group III. Laplace's EquationDocument13 pagesGroup III. Laplace's EquationAnayosiNo ratings yet
- PARABOLA - TheoryDocument3 pagesPARABOLA - TheoryAYUSH UPADHYAYNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming (Theory & Exercise) Module-6-BDocument10 pagesLinear Programming (Theory & Exercise) Module-6-BRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 2exam 21 06 2021Document1 page2exam 21 06 2021LanaNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET - 8 PrmoDocument17 pagesWORKSHEET - 8 PrmoAnirudha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Handout Solving Quadratic Inequalities in Two VariablesDocument3 pagesHandout Solving Quadratic Inequalities in Two VariablesGeneva juanNo ratings yet
- Kenyon College Dana Paquin Paquind@kenyon - EduDocument3 pagesKenyon College Dana Paquin Paquind@kenyon - EduSceptic GrannyNo ratings yet
- 3.02 Exponential Functions - WorksheetDocument11 pages3.02 Exponential Functions - WorksheetKimiNo ratings yet
- Vectorspacesunit 2ppt 201129154737Document37 pagesVectorspacesunit 2ppt 201129154737tongtonghoanghaiNo ratings yet
- Tut2 SolDocument6 pagesTut2 SolEric WangNo ratings yet
- Chap 5.2Document66 pagesChap 5.2aasrithachowdarychundruNo ratings yet
- Qip Lecture36Document4 pagesQip Lecture36abirphysics101No ratings yet
- Ch4 PDFDocument76 pagesCh4 PDF王大洋No ratings yet
- Algebraic EquationDocument5 pagesAlgebraic EquationpundekNo ratings yet
- MA1200 L11 FinalreviewDocument70 pagesMA1200 L11 FinalreviewChun Hin ChanNo ratings yet
- MIT18 ProblemDocument4 pagesMIT18 ProblemJulian RestrepoNo ratings yet
- Solutions 2: Vector FieldsDocument5 pagesSolutions 2: Vector FieldsAnnas FauzyNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Quadratic FunctionsDocument2 pagesCH 5 Quadratic FunctionsNoor FarhanNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument49 pagesTrigonometric IdentitiesShriddhi MaharajNo ratings yet
- Power Series Solution of A Differential EquationDocument4 pagesPower Series Solution of A Differential EquationVijayPanchoreNo ratings yet
- SAT Maths Test Part 2Document17 pagesSAT Maths Test Part 2Nam NguyenNo ratings yet
- 2014 Quiz PaperDocument1 page2014 Quiz Paper5umit7adav.iitbNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli DEDocument2 pagesBernoulli DEMark WallowNo ratings yet
- 10 Maths N Ch. 1Document6 pages10 Maths N Ch. 1clementjamesmannasNo ratings yet
- How To Derive The Ball Joint Constraint MatricesDocument2 pagesHow To Derive The Ball Joint Constraint MatricesLalo AngelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 QuadraticsDocument64 pagesChapter 3 Quadraticsluong anh thuNo ratings yet
- Useful Web Links For Principles of Mathematics 10Document3 pagesUseful Web Links For Principles of Mathematics 10KamranNo ratings yet
- ENG Edition 1 Maths Paper 1 2023-2 - Unlocked-1 - 240317 - 081936Document106 pagesENG Edition 1 Maths Paper 1 2023-2 - Unlocked-1 - 240317 - 081936darrenstanford3100% (1)
- Complex Numbers - Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesComplex Numbers - Lesson PlanVanessa G. ManguilimotanNo ratings yet
- Algebra PDFDocument4 pagesAlgebra PDFLeon Fone100% (1)
- Intersection A Curve and A LineDocument16 pagesIntersection A Curve and A LineIr HeriawanNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1 M1Document9 pagesMark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1 M1sara jaimeNo ratings yet
- Christoff Rudolff: Born: 1499 in Jauer, Selesia (Now Jawor Poland) Died: 1543 in Vienna, AustriaDocument5 pagesChristoff Rudolff: Born: 1499 in Jauer, Selesia (Now Jawor Poland) Died: 1543 in Vienna, AustriaBettylaFeaNo ratings yet
- DLP 9 Completing The SquareDocument2 pagesDLP 9 Completing The SquareMichelle Gazzingan MalanaNo ratings yet
- MATH 9 Q1 W1b1 Solutions of QE by Extracting Square RootsDocument3 pagesMATH 9 Q1 W1b1 Solutions of QE by Extracting Square RootsVince BonosNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Characterizing Nature of Roots of A Quadratic EquationDocument21 pagesMathematics: Characterizing Nature of Roots of A Quadratic EquationZeus RomeroNo ratings yet
- Y 10 U 12 TopicsforfunctionsquadraticsDocument2 pagesY 10 U 12 Topicsforfunctionsquadraticsapi-361656924No ratings yet
- Exercise 4.1: CLASS - 10th Chapter - 4 (Quadratic Equations)Document41 pagesExercise 4.1: CLASS - 10th Chapter - 4 (Quadratic Equations)md imran ImranNo ratings yet
- Draft Notes ALG UNIT 10 SOLVING QUADRATICSDocument16 pagesDraft Notes ALG UNIT 10 SOLVING QUADRATICSAlyssa Mae Mejia CendañaNo ratings yet
- TOFAS検定システムDocument1 pageTOFAS検定システムJeffriel SisonNo ratings yet
- Junior Mathematics Competition 2020 Questions: Instructions To CandidatesDocument4 pagesJunior Mathematics Competition 2020 Questions: Instructions To Candidatesverry7No ratings yet
- Mt1review2009 10Document18 pagesMt1review2009 10Zachary LymNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Q1 Week 3Document5 pagesMath 9 Q1 Week 3John Nino DoligolNo ratings yet
- SPM Format PracticeDocument189 pagesSPM Format PracticeSyifa' IfaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PolynomialsDocument39 pagesChapter 2 PolynomialsRamesh RathoreNo ratings yet
- 2 Year KS3 3 Year GCSE 5 Year SoW Middle AttainersDocument35 pages2 Year KS3 3 Year GCSE 5 Year SoW Middle AttainersHanaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Basic AlgebraDocument86 pagesBasic Algebraapi-302731670No ratings yet
- SS2 Further Maths 1ST Term E-NoteDocument57 pagesSS2 Further Maths 1ST Term E-NoteJesse100% (1)
- NCERT Book Mathematics Class IXDocument294 pagesNCERT Book Mathematics Class IXDeepesh Gulati100% (1)
- GR 10 12 Adv Programme Maths IEB Book 1 ExtractsDocument16 pagesGR 10 12 Adv Programme Maths IEB Book 1 ExtractsAbideNo ratings yet
- A2 Chapter 5 AssignmentsDocument2 pagesA2 Chapter 5 Assignmentsklb925No ratings yet
- Mathematics 2ND Term Note1Document42 pagesMathematics 2ND Term Note1SochiNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Workbook UpdatedDocument112 pagesMath 9 Workbook UpdatedHazel KimNo ratings yet