Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STEEL
STEEL
Uploaded by
Shara Palos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesRigid frame structures connect beams and columns monolithically to resist moments from applied loads. They provide more stability than other frames and resist shear, moment, and torsion more effectively. Braced frames use diagonal bracing to resist lateral forces. Shear walls use rigid connections between members to resist lateral forces parallel to the plane of the wall. Frame structures transmit loads from slabs to beams to columns to foundations.
Original Description:
Original Title
STEEL.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRigid frame structures connect beams and columns monolithically to resist moments from applied loads. They provide more stability than other frames and resist shear, moment, and torsion more effectively. Braced frames use diagonal bracing to resist lateral forces. Shear walls use rigid connections between members to resist lateral forces parallel to the plane of the wall. Frame structures transmit loads from slabs to beams to columns to foundations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesSTEEL
STEEL
Uploaded by
Shara PalosRigid frame structures connect beams and columns monolithically to resist moments from applied loads. They provide more stability than other frames and resist shear, moment, and torsion more effectively. Braced frames use diagonal bracing to resist lateral forces. Shear walls use rigid connections between members to resist lateral forces parallel to the plane of the wall. Frame structures transmit loads from slabs to beams to columns to foundations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
STRUCTURAL FRAMES
Frames structures can be differentiated into: 2. Braced frame structure
Which is further subdivided into:
1. Rigid frame structure Gabled frames
The word rigid means ability to resist the Gabeled Structural Frame:
deformation. Rigid frame structures can be
Gabled frame structures usually have the peak
defined as the structures in which beams &
at their top. These frames systems are in use
columns are made monolithically and act
where there are possibilities of heavy rain and
collectively to resist the moments which are
snow.
generating due to applied load.
Rigid Frame: When a rigid frame structure is
subjected to a vertical load, it is also picked up
by the beams and eventually transferred
through the columns to the ground. However,
the joints are strongly connected, preventing
any free rotation from occurring at the beams
ends. This slight difference changes everything
about the behavior of the beams, which is now
the same as a fix-ended beam.
Rigid frame structures provide more stability.
Portal structural frames usually look like a door.
This type of frame structures resists the shear,
This frame system is very much in use for
moment and torsion more effectively than any
construction of industrial and commercial
other type of frame structures. That's why this
buildings
frame system is used in world's most
astonishing building Burj Al-Arab. Load path in Frame Structure:
It is a path through which the load of a frame
structure is transmitted to the foundations. In
Which are further subdivided into:
frame structures, usually the load path is:
A pinned ended rigid frame system usually has
Load first transfers from slab to beams then to
pins as their support conditions. This frame
from beam to columns, then from columns it
system is considered to be non rigid if its
transfers to the foundation.
support conditions are removed.
fix Ended Rigid Frame Structure:
In this type of rigid frame systems end
conditions are usually fixed.
MOMENT FRAMES
A moment frame is a special type of frame that
SHEAR WALL
uses rigid connections between each of its
Shear wall is a structural member used to resist constituent members. This configuration is able
lateral forces i.e parallel to the plane of the to resist lateral and overturning forces because
wall. For slender walls where the bending of the bending moment and shear strength that
deformation is more Shear wall resists the loads is inherent in its members and the connecting
due to Cantilever Action and for short walls joints. Therefore, the stiffness and strength of
where the shear deformation is more it resists the moment frame in seismic design depends
the loads due to Truss Action. on the stiffness and strength of its members.
Strength of Shear Walls A fundamental structure in engineering – the
frame – is a two-dimensional series of
The strength of a wall system depends on many
interconnected members joined together. The
factors including the strength of the sheathing;
members are not necessarily straight and may
the type, size, and spacing of the fasteners; the
be free jointed anywhere along their length. In
panel aspect ratio (ratio of long to short
real structures, moment frames in two
dimension of shear panel); and the strength of
orthogonal directions are often connected
the studs. Because of these variables, the
together to form a three-dimensional frame of
design strength of shear walls is usually based
columns and beams. Moment frames are
on tests of full height specimens.
designed to carry vertical and horizontal loads
in the same plane but may also be drawn on to
provide resistance to horizontal loads out of the
Shear walls that are perforated with openings plane of the frame. They can be found in many
are called coupled walls. These walls act as different materials and building applications.
isolated cantilevered walls connected by
coupling beams (also called spandrel beams or
lintels) designed for bending and shear effects.
load, the risk of structural and non-structural
damage can be minimized. For high-rise
buildings, particularly in seismic active zone or
wind load dominant, this system can be chosen
as an appropriate structure.
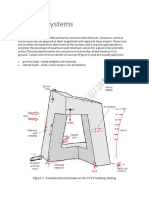
TRUSS/BELT/OUTRIGGER
The outrigger and belt truss system is
commonly used as one of the structural system
to effectively control the excessive drift due to
lateral load, so that, during small or medium
lateral load due to either wind or earthquake
You might also like
- Structural Framing SystemDocument6 pagesStructural Framing SystemMelchor Jaramilla Oronos100% (3)
- 10.1201 9781003098508 PreviewpdfDocument134 pages10.1201 9781003098508 PreviewpdfJalal KeNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hollow Core DiaphragmDocument10 pagesHollow Core DiaphragmJaher WasimNo ratings yet
- CCIP Concrete Building SchemeDocument140 pagesCCIP Concrete Building Schemedimitrios2588% (16)
- Structural Frame of A BuildingDocument3 pagesStructural Frame of A BuildingNeil Philip BlanzaNo ratings yet
- S4 - Steel - 2 - Introduction To Seismic Design Concept of Steel StructuresDocument93 pagesS4 - Steel - 2 - Introduction To Seismic Design Concept of Steel StructuresReaidNo ratings yet
- Frame StructuresDocument6 pagesFrame StructuresTayaabaranNo ratings yet
- Vertical Structure SystemsDocument51 pagesVertical Structure SystemsANJALI GAUTAMNo ratings yet
- Adamson UniversityDocument20 pagesAdamson UniversityKim Yun Shik PegoriaNo ratings yet
- 333 Frame StructuresDocument7 pages333 Frame StructuresBrian LuisNo ratings yet
- Seismic Comparison of The Structural SystemsDocument2 pagesSeismic Comparison of The Structural SystemsHasantNo ratings yet
- Framed Structures: Submitted By:-Submitted ToDocument15 pagesFramed Structures: Submitted By:-Submitted ToNidhi MehtaNo ratings yet
- Final PresebtationDocument21 pagesFinal PresebtationHisham AbdehNo ratings yet
- Advanced Structures: Amatul Wasey 14131AA001Document27 pagesAdvanced Structures: Amatul Wasey 14131AA001amatul waseyNo ratings yet
- Lateral Load Resisting Systems in BuildingsDocument13 pagesLateral Load Resisting Systems in Buildingsgirma kebedeNo ratings yet
- Rodrigo PCS002 Tla2pDocument4 pagesRodrigo PCS002 Tla2pChristian John SaludarNo ratings yet
- LFRSDocument43 pagesLFRShsnaterNo ratings yet
- Framed Structures 1Document4 pagesFramed Structures 1Festus NgumbiNo ratings yet
- Building Construction: Assignment 1 Report On Long Span StructuresDocument18 pagesBuilding Construction: Assignment 1 Report On Long Span StructuresPrerana CholakheNo ratings yet
- Ces 822 Assignment 2 PDFDocument3 pagesCes 822 Assignment 2 PDFSaniiNo ratings yet
- BIP - Makkah Royal Clock Tower (2) - Group2Document10 pagesBIP - Makkah Royal Clock Tower (2) - Group2Moch. FatkurrohmanNo ratings yet
- Lect - 2 - Earthquake - Resistant - Systems - Part 3Document5 pagesLect - 2 - Earthquake - Resistant - Systems - Part 3jana ShmaysemNo ratings yet
- Designing For EQDocument68 pagesDesigning For EQUmit OzkanNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Behaviour of Tall BuildingDocument22 pages1.0 Behaviour of Tall BuildingOne The100% (1)
- Lateral Stability of Building Structures (Rev. Ed.), Wolfgang SchuellerDocument148 pagesLateral Stability of Building Structures (Rev. Ed.), Wolfgang Schuellerwolfschueller90% (10)
- Structural Design: 2008 New York City Building Code 303Document52 pagesStructural Design: 2008 New York City Building Code 303Vinaykumar RatnaniNo ratings yet
- RCC Moment Framed RCC Flate Plate and Slab: Presented by Ashish, Bhavana, Hasita, Manoj and NaveedDocument22 pagesRCC Moment Framed RCC Flate Plate and Slab: Presented by Ashish, Bhavana, Hasita, Manoj and NaveedNidhi MehtaNo ratings yet
- What You Should You Know About LFRS and Diaphragm DesignDocument65 pagesWhat You Should You Know About LFRS and Diaphragm DesignMarwa HamzaNo ratings yet
- Seismic Issues in Architectural Design: by Christopher ArnoldDocument54 pagesSeismic Issues in Architectural Design: by Christopher ArnoldM Refaat FathNo ratings yet
- Stuctural Elements - EscalatorDocument47 pagesStuctural Elements - EscalatorPrakhar VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Types of Structures and Loads: IntroductionDocument14 pagesTypes of Structures and Loads: IntroductionMohammed ShalaanNo ratings yet
- Notes CE60StabilityDeterminacyDocument4 pagesNotes CE60StabilityDeterminacyMusicMeowNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Steel RC Shear Walls in Building Structures - ETN-D-8-21Document4 pagesBenefits of Steel RC Shear Walls in Building Structures - ETN-D-8-21Babrak Khan NoorzoiNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures: BEAMS. Beams Are Usually StraightDocument6 pagesTheory of Structures: BEAMS. Beams Are Usually StraightCaila PanerioNo ratings yet
- Ibc 16Document114 pagesIbc 16Luis Fernando BaqueNo ratings yet
- Exploring Structure Systems of High-RisebuildingsDocument20 pagesExploring Structure Systems of High-Risebuildingszuhaferoz2No ratings yet
- SHEAR WALLS FOR HIGH RISE BUILDINGS (WWW - Ebmfiles.com)Document63 pagesSHEAR WALLS FOR HIGH RISE BUILDINGS (WWW - Ebmfiles.com)Ashutosh Nag75% (4)
- Highrise BuildingsDocument13 pagesHighrise BuildingsPratik ShindeNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Continuous Load Path: 4.3 Overall FormDocument10 pages4.2 Continuous Load Path: 4.3 Overall FormSirajMalikNo ratings yet
- Steel Design PresentationDocument90 pagesSteel Design Presentationraghav abudhabiNo ratings yet
- Beam and Wall InteractionDocument15 pagesBeam and Wall Interactionmikailadam656No ratings yet
- Lateral Force ResistanceDocument11 pagesLateral Force ResistanceAWNo ratings yet
- Floor DiaphragmsDocument4 pagesFloor DiaphragmsKiran BasuNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Earthquake Resistant Design and PrinciplesDocument31 pagesUnit 6 Earthquake Resistant Design and PrinciplesShivam SinghNo ratings yet
- Construction Technology Unit 1Document43 pagesConstruction Technology Unit 1Kabilesh SNo ratings yet
- Structural Forms Systems For Tall Building Structures: AbstractDocument4 pagesStructural Forms Systems For Tall Building Structures: AbstractHETVI PATELNo ratings yet
- Structural Systems: Reference: NSCP 2015 Section 208.4.10.2Document26 pagesStructural Systems: Reference: NSCP 2015 Section 208.4.10.2Katherine Shayne YeeNo ratings yet
- Chap3 FramesDocument76 pagesChap3 FramesPalaniappan ArasappanNo ratings yet
- 03-Ashik Gowda-Bs PortfolioDocument12 pages03-Ashik Gowda-Bs PortfolioAshik gowdaNo ratings yet
- Stability Systems PDFDocument4 pagesStability Systems PDFmohamedyahaiNo ratings yet
- Design To Resist High WindDocument5 pagesDesign To Resist High WindAhmed SadekNo ratings yet
- Construction Technology Unit 1Document43 pagesConstruction Technology Unit 1Naviz Joyl S100% (1)
- Bs PortfolioDocument12 pagesBs PortfolioAshik gowdaNo ratings yet
- Definitions and Terminologies in Theory of Structures 1Document6 pagesDefinitions and Terminologies in Theory of Structures 1Lemuel John CristobalNo ratings yet
- Multi Storey Building FramesDocument24 pagesMulti Storey Building Framespriyanka0% (2)
- ARCH 162: Statics and Strength of MaterialsDocument35 pagesARCH 162: Statics and Strength of MaterialsFurkan AktaşNo ratings yet
- Basic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandBasic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Structural Concrete: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionFrom EverandStructural Concrete: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Earthquake isolation method with variable natural frequencyFrom EverandEarthquake isolation method with variable natural frequencyNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Design of Building StructuresFrom EverandIntroduction to Design of Building StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (22)
- Earthquake Resistant Steel StructureDocument31 pagesEarthquake Resistant Steel StructureraihanaNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design and Detailing of Reinforced Concrete Structures Based On CSA A23.3 - 2004 - Presentation - Murat SaatciogluDocument146 pagesSeismic Design and Detailing of Reinforced Concrete Structures Based On CSA A23.3 - 2004 - Presentation - Murat Saatciogluoscargon19100% (1)
- 152.prefabricated Multistory Structure Exposure To Engineering Seismicity by UsingDocument6 pages152.prefabricated Multistory Structure Exposure To Engineering Seismicity by UsingVishvajit KohakadeNo ratings yet
- Moses Mabhida Stadium PDFDocument4 pagesMoses Mabhida Stadium PDFHCStepNo ratings yet
- 2016 Zeynalian X-BracedDocument13 pages2016 Zeynalian X-BracedmabuhamdNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument85 pagesFinalRavi Dutta100% (1)
- CE8022 NOTES PFS by WWW - Easyengineering.net 3Document126 pagesCE8022 NOTES PFS by WWW - Easyengineering.net 3Wpdark HelpNo ratings yet
- Techniques For The Seismic Rehabilitation of Existing BuildingsDocument573 pagesTechniques For The Seismic Rehabilitation of Existing BuildingsGiuseppe GentileNo ratings yet
- Seismic Conceptual DesignDocument11 pagesSeismic Conceptual DesignDkicksNo ratings yet
- Recommendations For Modeling The Nonlinear Response of Slender Reinforced Concrete Walls Using PERFORM-3DDocument18 pagesRecommendations For Modeling The Nonlinear Response of Slender Reinforced Concrete Walls Using PERFORM-3Dpaulami das choudhuryNo ratings yet
- Structural Framing SystemDocument20 pagesStructural Framing SystemOdee EbitaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of The USA China and Japan Seismic Design Procedures 20160302Document17 pagesComparison of The USA China and Japan Seismic Design Procedures 20160302Usman AfzalNo ratings yet
- Journal of Constructional Steel Research: Bin Wang, Huanjun Jiang, Xilin LuDocument12 pagesJournal of Constructional Steel Research: Bin Wang, Huanjun Jiang, Xilin LuPrapa KaranNo ratings yet
- How's That?: How To Achieve A SCORS A RatingDocument52 pagesHow's That?: How To Achieve A SCORS A RatingESNo ratings yet
- Falcon RCD ColumnsDocument4 pagesFalcon RCD ColumnsJerome Adduru100% (1)
- Steel Plate Shear WallDocument5 pagesSteel Plate Shear WallKapil Nandwana100% (1)
- Recent Advances in Earthquake Resistant Construction PracticesDocument13 pagesRecent Advances in Earthquake Resistant Construction PracticesBenmark JabayNo ratings yet
- Moment FrameDocument16 pagesMoment FrameSanchithaNo ratings yet
- Section C8-Unreinforced Masonry BuildingsDocument195 pagesSection C8-Unreinforced Masonry BuildingsAshNo ratings yet
- A Resource Book For Structural SteelDocument90 pagesA Resource Book For Structural SteelAbdurrahman ÇınarNo ratings yet
- Ejemplo de Aplicacion Asce Sei 41 13Document17 pagesEjemplo de Aplicacion Asce Sei 41 13Marvin DouglasNo ratings yet
- Seismic Behavior of Steel Plate Shear WallDocument34 pagesSeismic Behavior of Steel Plate Shear WallSachin Pawar100% (1)
- Research On Design of High Rise Building Based On Seismic Design TheoryDocument6 pagesResearch On Design of High Rise Building Based On Seismic Design TheoryLim TiNo ratings yet
- Analysis Design and Estimation of G7 Storey Building Structure by Using ISCode Methods and by SoftwaresDocument7 pagesAnalysis Design and Estimation of G7 Storey Building Structure by Using ISCode Methods and by SoftwaresPritam DebbarmaNo ratings yet
- 26 PPT Presentation NewDocument25 pages26 PPT Presentation Newpriyanka jadhavNo ratings yet
- CED Progress Report UTPDocument23 pagesCED Progress Report UTPMohd Fadhil MusbahNo ratings yet
- Diaphragms and Shear Walls PDFDocument32 pagesDiaphragms and Shear Walls PDFMikeNo ratings yet