Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mobile - Scaffolds JSA
Mobile - Scaffolds JSA
Uploaded by
Bojie AbogadieOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mobile - Scaffolds JSA
Mobile - Scaffolds JSA
Uploaded by
Bojie AbogadieCopyright:
Available Formats
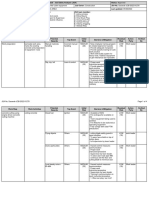
Hazard identification tool – Aluminium mobile scaffolding
Job activity What can harm What can happen Causes which need to be
(Tasks) you (Hazards) (Risks) managed (Controlled)
General planning Inadequate Injury due to • Insufficient skills
training, inexperience or (competency) to complete the
consultation, failure to provide required task correctly.
planning and or use appropriate • Inadequate consultation with
improvisation. equipment relevant employees.
• Competent person not used
for scaffold erection up to 4
metres in height.
• Certificated scaffolder not
used to erect scaffold in
excess of 4 metres in height
or where complex
configurations are involved.
Unstable scaffold Injury due to • Competent person not used
due to lack of scaffold collapse for scaffold erection up to 4
competency in or partial collapse. metres in height.
erection. • Certificated scaffolder not
used to erect scaffold where
the working platform exceeds
4 metres in height or if the
scaffold has cantilevers or
outriggers.
• Foundation or ground not
suitable for mobile scaffold.
• Different scaffold systems
mixed together. (mix and
match problems)
Overload of Collapse causing • Wrong type of scaffold used
scaffold fall from height. for the job.
components. • Scaffold components
overloaded beyond design
limits.
• Different scaffold systems
mixed together. (mix and
match problems).
Hazard identification tool for aluminium mobile scaffolding Page 1 of 10
Hazard identification tool – Aluminium mobile scaffolding
Job activity What can harm What can happen Causes which need to be
(Tasks) you (Hazards) (Risks) managed (Controlled)
Unstable or Injury due to • Instructions are not provided,
incorrect erection scaffold collapse or are not clear – print is too
of scaffold. or partial collapse. small and/or photocopy
cannot be accurately
followed.
• Scaffold poorly maintained by
supplier – colour coding
referred to in instructions is
not visible on components.
• Damaged scaffold.
Planning by Scaffold erected Electric shock or • Earth Leakage Switch not
Principal too close to power electrocution. installed on mains supply or
Contractor or lines or completed portable generator.
Subcontractor scaffold is moved • Working on or moving mobile
depending on too close to power scaffold too close to live
contract lines during use. power lines.
conditions • Scaffold components or
material handled are greater
than 4 metres in length.
• Scaffold component or
material contacts power lines.
Insulation (tiger tails) not in
place on power lines or wet
conditions makes them
ineffective.
• Strong wind causes power
lines to swing closer to work
area.
Erection of base Unsupported Frames fall over • Bracing or team member not
frames and frames being striking person used to support first frames.
bracing erected at ground erecting scaffold • Foundation not level or
level. or other person unsuitable for mobile scaffold.
close to the work • Castor wheels not adjusted
area. correctly or not locked.
Hazard identification tool for aluminium mobile scaffolding Page 2 of 10
Hazard identification tool – Aluminium mobile scaffolding
Job activity What can harm What can happen Causes which need to be
(Tasks) you (Hazards) (Risks) managed (Controlled)
Incorrectly Fall from • Insufficient skills
assembled first completed (competency) to complete the
frames causing scaffold or fall required task.
unstable scaffold from scaffold • Instructions are not provided
base. during erection. or are not clear – print is too
small and/or photocopy
cannot be read.
• Scaffold poorly maintained –
colour coding referred to in
instructions is not visible on
components.
• Base frame assembled
upside down – castor wheels
will not fit correctly.
Erection of Climbing Scaffold tips over • Climbing up the outside of the
second level lightweight causing fall. frame causing scaffold to tip
frames and scaffold base sideways.
bracing frames during • Only one person used in
erection. frame erection.
• Foundation not level or
unsuitable for mobile scaffold.
Base frames not Instability/ • Scaffold distorts out of square
adequately braced collapse of base due to plan bracing being left
or supported. frames causing out.
fall. • Insufficient diagonal bracing
or bracing fixed incorrectly.
• Castor wheels not locked to
prevent movement or lock/s
broken.
• Foundation not level or
unsuitable for mobile scaffold.
• Castor wheels not adjusted
correctly when levelling the
base frames.
Hazard identification tool for aluminium mobile scaffolding Page 3 of 10
Hazard identification tool – Aluminium mobile scaffolding
Job activity What can harm What can happen Causes which need to be
(Tasks) you (Hazards) (Risks) managed (Controlled)
Live power lines Electric shock • Earth Leakage Switch not
too close to work burns or installed on mains supply or
area. electrocution. portable generator.
• Working too close to live
power lines.
• Scaffold components or
materials handled are greater
than 4 metres in length.
• Tiger Tails (insulation) not in
place on power lines or wet
conditions make them
ineffective.
• High wind causes power lines
to swing closer to work area.
• Scaffold component strikes
and shatters unprotected light
bulb.
Scaffold used Scaffold topples • General height of the light
without following over causing a fall duty prefabricated aluminium
manufacturers from height. mobile scaffold exceeds three
instructions (e.g. times the minimum base
indoor or outdoor dimension (ref AS/NZS4576).
specifications). • e.g. a scaffold with base
dimensions of 2.4m x 1.8m
the height to the working
platform should be no more
than 5.4m.
• For a scaffold with a narrow
base width of less than 1.2m
the height of the light duty
prefabricated aluminium
mobile scaffold exceeds twice
the base width (ref AS4576).
• e.g. a scaffold with a base of
2.4m x 1.2m the height to the
working platform should be
no more than 2.4m.
Erection of Manual Handling. Sprains, strains • Only one person used to lift
working platform and fractures. platforms onto second level
frames.
Hazard identification tool for aluminium mobile scaffolding Page 4 of 10
Hazard identification tool – Aluminium mobile scaffolding
Job activity What can harm What can happen Causes which need to be
(Tasks) you (Hazards) (Risks) managed (Controlled)
Split (uneven) Step backward off • Working platform installed
decks installed higher deck with split decks, i.e. both deck
onto second causing fall from platforms are not set at the
frames. height. same height.
Erection of edge Climbing on Scaffold moves • Only one person used in
protection, lightweight unexpectedly or frame erection.
ladder and scaffold base tips over causing • Foundation uneven or soft.
toeboards frames. fall. • Planks and ply or steel plates
not used where soft ground is
a problem.
Movement of Fall from • Castor wheels not locked to
scaffold tower. unprotected prevent movement whilst
working platform. edge protection is erected.
Edge protection Fall from the edge • Handrail not positioned 900 –
incomplete. of the working 1100mm above the working
platform. platform on all sides.
• No midrail or fenderboard
installed to all sides.
Ladder access Fall through • Hatch not closed or trapdoor
hatch (trap door) ladder access missing.
in working deck. hatch.
Hazard identification tool for aluminium mobile scaffolding Page 5 of 10
Hazard identification tool – Aluminium mobile scaffolding
Job activity What can harm What can happen Causes which need to be
(Tasks) you (Hazards) (Risks) managed (Controlled)
Inappropriate Fall whilst gaining • Climbing up or down the
access to working access to working outside of the scaffold – no
deck. platform. ladder access.
• Ladder not positioned
internally and at the
appropriate angle 1:4 i.e. for
every 4 metres in height 1
metre out from the base.
• Ladder not secured at the top
and the bottom.
• Ladder does not project at
least 900 mm above the
working platform.
• Ladder does not access the
working platform through a
trapdoor.
• Ladder hung vertically off the
handrail or ledger on the
external or internal face of the
scaffold.
Unsecured tools Struck by falling • No fenderboards fitted to the
and/or equipment object. working platform.
lying on working • No exclusion zone around
platform. scaffold positioned in a public
or work area.
• Area around base of scaffold
not barricaded or bunted off.
Use of scaffold Vehicle or mobile Injury due to • Scaffold positioned too close
plant strikes scaffold collapse. to plant operating area.
scaffold. • Plant not operated in a
defined exclusion zone.
• Base of scaffold not
adequately protected from
impact e.g. concrete kerbs.
• “Spotter” not used to
supervise plant.
Hazard identification tool for aluminium mobile scaffolding Page 6 of 10
Hazard identification tool – Aluminium mobile scaffolding
Job activity What can harm What can happen Causes which need to be
(Tasks) you (Hazards) (Risks) managed (Controlled)
Carrying out “hot Burns. • Fire extinguisher not
work” from the maintained or adjacent to
scaffold. work area on scaffold working
platform.
• Worker/s not trained in the
use of fire fighting equipment.
• Incorrect type of fire
extinguisher provided for the
required task.
• No PPE or incorrect PPE for
the required task.
Incomplete Fall from scaffold • Un-authorised removal of or
scaffold. frames or working interference with scaffold
platform. components.
• Scaffold not inspected by
competent person prior to
use.
• No isolation system for
incomplete scaffolds, e.g.
Danger tag warning signs not
in place.
• Incomplete edge protection to
working platform – no
Handrail, midrail, or
fenderboards.
Split (uneven) Step backward off • Working platform installed
decks installed higher deck with split decks, i.e. both deck
onto second causing fall from platforms are not set at the
frames. height. same height.
Scaffold left Scaffold accessed • Scaffold not barricaded to
unattended and by inexperienced prevent un-authorised use.
unsecured. person or scaffold Scaffold not secured to
falls onto person prevent movement e.g.
or object. during windy weather.
• Castor wheels not locked.
Hazard identification tool for aluminium mobile scaffolding Page 7 of 10
Hazard identification tool – Aluminium mobile scaffolding
Job activity What can harm What can happen Causes which need to be
(Tasks) you (Hazards) (Risks) managed (Controlled)
Moving scaffold Moving scaffold to Scaffold topples • Failure to descend from
to new location a new location. over resulting in a scaffold and re-position from
fall. the base of scaffold.
• Moving scaffold whilst a
person is still positioned aloft
on the working platform, e.g.
grasping overhead roof
trusses to pull scaffold along.
• Scaffold moved onto bitumen
or other soft surface causing
castor wheels to subside.
• Planks and ply or steel plates
not used where soft ground is
a problem.
• Scaffold too close to an
exposed edge or penetration,
i.e. within 1 metre.
Electrical supply Electric shock • Earth Leakage Switch not
too close to work burns or installed on mains supply or
area. electrocution. portable generator.
• New work area not inspected
for electrical hazards.
• Working too close to live
power line, check for danger
zones.
• Scaffold components are
greater than 4 metres in
length.
• Insulation - Tiger Tails not in
place over power lines.
• Strong wind causes power
lines to swing closer to the
work area.
• Scaffold component strikes
and shatters unprotected light
bulb.
Hazard identification tool for aluminium mobile scaffolding Page 8 of 10
Hazard identification tool – Aluminium mobile scaffolding
Job activity What can harm What can happen Causes which need to be
(Tasks) you (Hazards) (Risks) managed (Controlled)
Dismantling Scaffold Fall from scaffold. • Un-authorised removal of or
and/or alteration incomplete or interference with scaffold
partly dismantled. components.
• Scaffold not inspected by
competent person prior to
use.
• Isolation system for
incomplete scaffold, e.g.
danger tag or warning signs,
not in place.
Unstable or Injury due to • Insufficient skills
incorrect scaffold collapse. (competency) to complete the
dismantling of required task.
scaffold. • Instructions are not provided
or are not clear – print is too
small and/or photocopy
cannot be accurately
followed.
• Scaffold poorly maintained by
supplier – colour coding
referred to in instructions is
not visible on components.
Inappropriate Scaffold collapse • Competent person not used
alterations to or fall from for scaffold alteration.
scaffold. scaffold. • Certificated scaffolder not
used for complex alteration,
e.g. cantilever or outrigger.
• Scaffold not inspected by
competent person prior to
use.
• Isolation system for
incomplete scaffold, e.g.
danger tag or warning signs,
not in place.
Hazard identification tool for aluminium mobile scaffolding Page 9 of 10
Check-list for Lightweight Aluminium Mobile Scaffolds
Clear of electrical hazards
during erection and use
Only light duty work carried out
Handrail at correct height
Ladder projects minimum
900mm above deck
Midrail at correct height
Ladder across trapdoor
operational
Toeboard fitted
Deck at suitable working height All end clip mechanisms in place
Full platform for working deck
Diagonal bracing secured
All standard joints firmly fitted
Ladder placed at correct angle
All standards (uprights) plumb
Ladder correctly fixed at base
Plan brace as low as possible
Castor locking device Base frame in square and level
operational
Castor adjustment device
Ladder clear of the ground operational
Foundation suitable – level and
firm
Source: Adapted from
diagram by Instant Access
At all times refer to manufacturers
recommendations
W:\POLICYS\WPARTY\CISAC\Hazard Profiles\from Construction Team\HazProfAlumScafWA.doc
Hazard identification tool for aluminium mobile scaffolding Page 10 of 10
You might also like
- Concrete & Form Work: Job Safety Analysis Pouring ConcreteDocument1 pageConcrete & Form Work: Job Safety Analysis Pouring ConcreteHortencio Samuel100% (4)
- JSA Wall and Ceiling PanelsDocument5 pagesJSA Wall and Ceiling PanelsPAVANKUMAR67% (6)
- Risk Assessment For Demolition WorksDocument5 pagesRisk Assessment For Demolition Worksappu pocom3100% (4)
- Risk Assessment - Use of Mobile Crane & Boom TruckDocument3 pagesRisk Assessment - Use of Mobile Crane & Boom TruckSarfraz Randhawa100% (5)
- JSA Epoxy Coating Machine ShopDocument10 pagesJSA Epoxy Coating Machine ShopMarhendra100% (1)
- JSA Appendix Cutting, Grinding ConcreteDocument8 pagesJSA Appendix Cutting, Grinding ConcreteĐặng Quang Huy100% (1)
- TEIPL-JSA-058 Carpentry Wood WorkDocument3 pagesTEIPL-JSA-058 Carpentry Wood Workba ratnaparkheNo ratings yet
- Concrete Cutting JsaDocument4 pagesConcrete Cutting JsaMohammad Irfan Kiki IsmailNo ratings yet
- Jsa Cable TerminationDocument4 pagesJsa Cable TerminationSyed Yousuf Ali100% (1)
- C&C-EHS-F-002 HIRARC Eraction and Use of Scaffolding PDFDocument4 pagesC&C-EHS-F-002 HIRARC Eraction and Use of Scaffolding PDFNajman Hamdi100% (3)
- JSA For Plaster WorkDocument8 pagesJSA For Plaster WorkZakeer Shaikh100% (1)
- JSA For Concrete PouringDocument8 pagesJSA For Concrete Pouringfayaz fayazhotmail.com100% (1)
- Jsa For Gypsum Fixing & DismentlingDocument5 pagesJsa For Gypsum Fixing & DismentlingSushil Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- JSA-003 Excavation & BackfillingDocument3 pagesJSA-003 Excavation & Backfillingba ratnaparkhe100% (1)
- Jsa For Installation of Pipe Railing On SkidDocument6 pagesJsa For Installation of Pipe Railing On SkidLokesh Aravindan100% (1)
- JSA Ladders Working at Heights 001Document2 pagesJSA Ladders Working at Heights 001Raman SawNo ratings yet
- Jsa For Steel ErectionDocument7 pagesJsa For Steel ErectionRajuNo ratings yet
- Draft JSA Levelling & GradingDocument9 pagesDraft JSA Levelling & GradingAzeem Khan33% (3)
- JSA - Installation of U G PipingDocument11 pagesJSA - Installation of U G PipingOws Anish100% (1)
- Jsa Working at Height (Maintenance & Cleaning)Document2 pagesJsa Working at Height (Maintenance & Cleaning)Nur Syafiqah Mat Rapie100% (2)
- 9.JSA For Night Work Activity - Rev 01Document7 pages9.JSA For Night Work Activity - Rev 01ibrahim80% (10)
- Job Safety Analysis: Organization: JSA Number: Work Type: Work Activity: Specific SiteDocument5 pagesJob Safety Analysis: Organization: JSA Number: Work Type: Work Activity: Specific SiteM M PRADHANNo ratings yet
- New Pta Complex: Jsa For Reinforcing Steel BarsDocument12 pagesNew Pta Complex: Jsa For Reinforcing Steel BarsUMUTNo ratings yet
- Excavation Job Safety AnalysisDocument1 pageExcavation Job Safety AnalysisVishal Upadhyay100% (3)
- JSA For Concrete, Brecking, ExavationDocument6 pagesJSA For Concrete, Brecking, ExavationBinay0% (1)
- RA-Suspended Gypsum, Metallic Tiles Celling WorksDocument4 pagesRA-Suspended Gypsum, Metallic Tiles Celling Worksfaizan khanNo ratings yet
- ULSADO-JSA-Demolation Existing Concrete FoundationDocument2 pagesULSADO-JSA-Demolation Existing Concrete FoundationKelvin Tan75% (4)
- Design of CorbelDocument9 pagesDesign of Corbelalurabhilash1No ratings yet
- Area Hard Barrication JsaDocument7 pagesArea Hard Barrication JsaJanakiramanNo ratings yet
- HIRA - Night Work Hazard ControlDocument3 pagesHIRA - Night Work Hazard ControlHiralal Pattanayak100% (2)
- Jsa For Brick WorkDocument4 pagesJsa For Brick WorkSushil Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis (Jsa) : Title of Activity / Work: Reinforcement WorkDocument2 pagesJob Safety Analysis (Jsa) : Title of Activity / Work: Reinforcement Workba ratnaparkhe67% (3)
- Jsa For Operating A BobcatDocument2 pagesJsa For Operating A Bobcatsoubhagya100% (2)
- Jsa forOperatingAForkliftDocument2 pagesJsa forOperatingAForkliftsupahing supahingNo ratings yet
- Thyssenkrupp Industrial Solutions (India) Job Safety AnalysisDocument5 pagesThyssenkrupp Industrial Solutions (India) Job Safety AnalysisNitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Jsa PCC & RCCDocument2 pagesJsa PCC & RCCNilesh koliNo ratings yet
- JSA Column Errection, Shuttering, Casting, Deshuttering Raw Material Ware HouseDocument9 pagesJSA Column Errection, Shuttering, Casting, Deshuttering Raw Material Ware Houseradeep100% (1)
- Chain Pulley Block JsaDocument2 pagesChain Pulley Block JsaAKBAR ALINo ratings yet
- PTA-JSA-005-Material Handling by Farhana F-15 CraneDocument6 pagesPTA-JSA-005-Material Handling by Farhana F-15 CraneSaiyad RiyazaliNo ratings yet
- 02concreting & Block Bricks Work JSADocument3 pages02concreting & Block Bricks Work JSAJayendra Patel100% (1)
- Hira Plastering Finishing WorkDocument2 pagesHira Plastering Finishing WorkDwitikrushna Rout0% (2)
- HIRA, TCS-ACP Sheet FixingDocument2 pagesHIRA, TCS-ACP Sheet FixingGowtham Kishore75% (4)
- JSA For Concrete PouringDocument1 pageJSA For Concrete PouringHSE fahadNo ratings yet
- JSA Earthpit Construction GeneralDocument4 pagesJSA Earthpit Construction Generalmukka88No ratings yet
- JSA For Lifting of RebarsDocument5 pagesJSA For Lifting of RebarsNiraNo ratings yet
- JSA For Brick WorkDocument3 pagesJSA For Brick Workwahyu nugroho71% (7)
- JSA For HILTIDocument3 pagesJSA For HILTIMohammed Minhaj100% (1)
- Glass Installation - JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS (JSA) WORKSHEETDocument3 pagesGlass Installation - JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS (JSA) WORKSHEETusman rasheed100% (1)
- Up Dated Job Safety Analysis-Gypsum Plastering WorksDocument12 pagesUp Dated Job Safety Analysis-Gypsum Plastering WorksAkhtar Ali100% (1)
- JSA For Installation of Out Door UnitsDocument4 pagesJSA For Installation of Out Door UnitsMohammed MinhajNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis - Cone ErectionDocument7 pagesJob Safety Analysis - Cone ErectionMohammed MinhajNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment What Work Excavation Work With Help of JCB Location PM Warehouse Area Contractor Company-Aalanna Project PVT LTDDocument2 pagesRisk Assessment What Work Excavation Work With Help of JCB Location PM Warehouse Area Contractor Company-Aalanna Project PVT LTDhemant yadav0% (2)
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA) - Carpentry Works DateDocument1 pageJob Safety Analysis (JSA) - Carpentry Works DatenabeelNo ratings yet
- Jsa Pipe Cutting at Fire PumpDocument5 pagesJsa Pipe Cutting at Fire PumpHow Chin Engineering Sdn Bhd100% (1)
- Jsa Civil Work (00000002)Document6 pagesJsa Civil Work (00000002)Ali AlahmaNo ratings yet
- PTA-JSA-003-Material Handling by Farhana F-15 CraneDocument6 pagesPTA-JSA-003-Material Handling by Farhana F-15 CraneSaiyad RiyazaliNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis:: RTR DRAIN LINE REPLACEMENT (Excavation and Backfilling)Document5 pagesJob Safety Analysis:: RTR DRAIN LINE REPLACEMENT (Excavation and Backfilling)Madhan KannanNo ratings yet
- Jsa For Manual Backfiling Usin Hand Roller CompactorDocument5 pagesJsa For Manual Backfiling Usin Hand Roller CompactorAbdus SamadNo ratings yet
- Jsa For Cutting, Grinding and Welding For GulfconDocument3 pagesJsa For Cutting, Grinding and Welding For GulfconOgunwa Emmanuel100% (1)
- Jsa For Applying Bituminous Roof Treatment On BuildingsDocument3 pagesJsa For Applying Bituminous Roof Treatment On BuildingsMohammed Minhaj100% (1)
- Scaffold HiracDocument15 pagesScaffold HiracSafety JosephNo ratings yet
- Defensive DrivingDocument23 pagesDefensive DrivingBojie AbogadieNo ratings yet
- RKform300pkg InstruxOnly PDFDocument1 pageRKform300pkg InstruxOnly PDFBojie AbogadieNo ratings yet
- Sample HSE Plan XXDocument37 pagesSample HSE Plan XXBojie Abogadie100% (1)
- HSE Business PlanDocument32 pagesHSE Business PlanBojie AbogadieNo ratings yet
- Training & CompetenceDocument20 pagesTraining & CompetenceBojie AbogadieNo ratings yet
- Cal/Osha Pocket Guide For The Construction IndustryDocument91 pagesCal/Osha Pocket Guide For The Construction IndustryBojie AbogadieNo ratings yet
- Slip Test - Board Retaining Coupler PDFDocument1 pageSlip Test - Board Retaining Coupler PDFBojie AbogadieNo ratings yet
- Alarkan-Perf Helmet Certificate PDFDocument3 pagesAlarkan-Perf Helmet Certificate PDFBojie AbogadieNo ratings yet
- Load Test - Base Jack PDFDocument1 pageLoad Test - Base Jack PDFBojie AbogadieNo ratings yet
- Steel Wire Rope PDFDocument1 pageSteel Wire Rope PDFBojie AbogadieNo ratings yet
- Helmet-Alarkan - Data Sheet of Helmet 20160830Document1 pageHelmet-Alarkan - Data Sheet of Helmet 20160830Bojie AbogadieNo ratings yet
- Delta Plus - Harness PDFDocument3 pagesDelta Plus - Harness PDFBojie AbogadieNo ratings yet
- Gin Wheel OperationDocument13 pagesGin Wheel OperationBojie AbogadieNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Roofing TermsDocument47 pagesGlossary of Roofing Termslilia_jNo ratings yet
- Colt Presentation - Smoke and Environmental Ventilation of Multi-Storey Buildings Using ShaftsDocument54 pagesColt Presentation - Smoke and Environmental Ventilation of Multi-Storey Buildings Using ShaftsNenad MutavdzicNo ratings yet
- ESO Port Facilities and Baywalk ExtensionDocument3 pagesESO Port Facilities and Baywalk ExtensionSharmaine MercadoNo ratings yet
- PIP IndexDocument46 pagesPIP Indexcui jackyNo ratings yet
- LimconDocument12 pagesLimconharishram123456No ratings yet
- Reference: AASHTO Guide For The Design of Pavement Structures, 1993Document25 pagesReference: AASHTO Guide For The Design of Pavement Structures, 1993Kevin SotoNo ratings yet
- Vision Mission Objectives: Ordinary Portland Cement 43 Grade Cement (OPC 43 Grade)Document2 pagesVision Mission Objectives: Ordinary Portland Cement 43 Grade Cement (OPC 43 Grade)M. HaripriyaNo ratings yet
- Residential Masonry Fireplaces and ChimneysDocument5 pagesResidential Masonry Fireplaces and Chimneysmami chanNo ratings yet
- Cable T SpecsDocument8 pagesCable T Specsdr reNo ratings yet
- Abel Zenebe Negash: +251-9-24-30-41-14 +251-9-11-10-78-00 +251-9-11-96-13-29 E-MailDocument3 pagesAbel Zenebe Negash: +251-9-24-30-41-14 +251-9-11-10-78-00 +251-9-11-96-13-29 E-MailfayoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Sour Service Performace of Coiled TubingDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Sour Service Performace of Coiled TubingMubeenNo ratings yet
- Canada Stormwater Management Guidelines - HalifaxDocument282 pagesCanada Stormwater Management Guidelines - HalifaxFree Rain Garden Manuals100% (1)
- Frontier Works Organisattion (Fwo)Document2 pagesFrontier Works Organisattion (Fwo)Shahrukh Shaikh50% (2)
- Basics of Concrete Repair and Structural StrengtheningDocument65 pagesBasics of Concrete Repair and Structural StrengtheningEdmond ChowNo ratings yet
- Manual Servicio Refrigerador Daewoo Erf-384aDocument56 pagesManual Servicio Refrigerador Daewoo Erf-384aevalencia4808100% (1)
- Caltrans Standard Plans, 2015Document27 pagesCaltrans Standard Plans, 2015Afolabi OladunniNo ratings yet
- Gate Valve: Typical Use Valve ConstructionDocument4 pagesGate Valve: Typical Use Valve ConstructionCegrow Ber BersabalNo ratings yet
- Deluge PosterDocument1 pageDeluge PosterAhamed KyanaNo ratings yet
- Design Standard: ASME VIII / API 520: Design of Safety ValvesDocument27 pagesDesign Standard: ASME VIII / API 520: Design of Safety ValvesMoe MozhganNo ratings yet
- Different Types of FoundationDocument30 pagesDifferent Types of Foundationsmodi_92No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 STR 3 Beams Shear BondDocument8 pagesChapter 3 STR 3 Beams Shear BonddaniNo ratings yet
- FE Geotech Eng PDFDocument5 pagesFE Geotech Eng PDFgrNo ratings yet
- Steel Profile CatalogDocument32 pagesSteel Profile CatalogBilgehanNo ratings yet
- Kaiyuan CatalogDocument6 pagesKaiyuan CatalogGogyNo ratings yet
- Stone Masonry (Training Element and Technical Guide For SPWP Workers Booklet 3)Document86 pagesStone Masonry (Training Element and Technical Guide For SPWP Workers Booklet 3)Wubetie MengistNo ratings yet
- TF 10-8-22Document1 pageTF 10-8-22SanjayNo ratings yet
- Unitor CO2 Hoses DiagramDocument9 pagesUnitor CO2 Hoses DiagramPrasad BangaruNo ratings yet
- Bs 534Document26 pagesBs 534Lucian Chitu75% (4)
- Triple B Stadium Statement of Claim F March 4 2015Document27 pagesTriple B Stadium Statement of Claim F March 4 2015ChrisDcaNo ratings yet