Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inspired by A Lab From Experiment Problems by Alan Van Heuvelen
Inspired by A Lab From Experiment Problems by Alan Van Heuvelen
Uploaded by
TopHatGhostOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inspired by A Lab From Experiment Problems by Alan Van Heuvelen
Inspired by A Lab From Experiment Problems by Alan Van Heuvelen
Uploaded by
TopHatGhostCopyright:
Available Formats
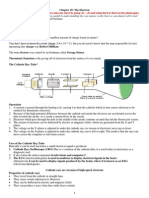
LAB: THE ELECTROPHORUS
An electrophorus is shown in the diagrams below. The foam cup is taped to the bottom of the
aluminum pie pan. The foil bit is free to swing on its string, and must be able to touch the rim
of the pie pan. Your task is to explain what is happening during the experiment described
below.
Using the foam cup as a handle, remove the aluminum pie pan from the Styrofoam insulation
pad that lies on the lab table.
Now rub the Styrofoam pad with fur or a soft cloth. Using the foam cup as a handle, slowly
lower the aluminum pie plate onto the Styrofoam pad.
Observe what happens to the tiny aluminum foil bit as the pie plate gets close to the foam.
With the pie plate now sitting on the Styrofoam pad, bring your finger near the foil bit and keep
it near the bit (you may have to move your finger closer as time progresses). Alternatively, you
can move an aluminum soft drink can near the foil bit (if the pie pan is at the edge of the
Styrofoam blue board).
1. Explain carefully and in detail all aspects of the foil bit's motion.
2. Use the diagram on the left to draw charges showing why the foil bit is initially attracted,
and the diagram on the right to draw why the foil bit is later repelled. (Note that when
removed from the Styrofoam pad, the aluminum pan is not charged.)
Inspired by a lab from E
xperiment Problems by Alan van Heuvelen
Electromagnetism, Optics, and
Nuclear Physics (PHY 302L) | 1
3. What type of charging (conduction or
induction) occurs when one object is rubbed against another and electrons are
transferred? Justify your response.
4. When a charged Electrophorus is brought near but not in contact with an uncharged
Electrophorus, it produces the charge distribution shown below. Identify the unknown
charge and explain your answer.
Inspired by a lab from E
xperiment Problems by Alan van Heuvelen
Electromagnetism, Optics, and
Nuclear Physics (PHY 302L) | 2
You might also like
- Science 6 - Q1 - Module1 - Lesson1 - Describing MixturesDocument29 pagesScience 6 - Q1 - Module1 - Lesson1 - Describing MixturesRose Merie Joy Solmia78% (27)
- Lab Report Fluid Mixing (Compile)Document28 pagesLab Report Fluid Mixing (Compile)Nor Elina Ahmad100% (1)
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Nuclear Physics (PHY 302L) - 1Document6 pagesElectromagnetism, Optics, and Nuclear Physics (PHY 302L) - 1TopHatGhostNo ratings yet
- Written Output For 3 Quarter Performance TaskDocument4 pagesWritten Output For 3 Quarter Performance TaskCarl SolivaNo ratings yet
- Electroscope Laboratory ActivityDocument3 pagesElectroscope Laboratory ActivityCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics ExperimentsDocument3 pagesElectrostatics Experimentssher123No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 ChargesDocument11 pagesLesson 1 ChargesRachel LaserNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric LabDocument5 pagesPhotoelectric LabNajma BelvanaNo ratings yet
- E Statcs Lab 1 - pt1-1Document2 pagesE Statcs Lab 1 - pt1-1Reja JoinNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment: in Physics 2Document7 pagesLaboratory Experiment: in Physics 2Charles ContridasNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics II: PurposeDocument20 pagesElectrostatics II: PurposeAmishNo ratings yet
- GenPhysics2 Q2-Module-6 RemovedDocument19 pagesGenPhysics2 Q2-Module-6 RemovedJasmin SorianoNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment 3 - Charging and ElectroscopeDocument6 pagesLab Experiment 3 - Charging and ElectroscopeMLOOK SAEEDNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic ChargeDocument14 pagesElectrostatic ChargeSwapnil MamgainNo ratings yet
- Lab 1-Electrostatic-Charging Objects by Friction, Conduction, and InductionDocument12 pagesLab 1-Electrostatic-Charging Objects by Friction, Conduction, and Inductionconstantine1106No ratings yet
- Static Electricity: Questions Accompanying Lecture 01Document4 pagesStatic Electricity: Questions Accompanying Lecture 01Aysegul GedikNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSCOPE Construction GuideDocument3 pagesELECTROSCOPE Construction GuideJose MariNo ratings yet
- The ElectronDocument16 pagesThe ElectronAyan SantraNo ratings yet
- Lab 10 Magnetic FieldsDocument22 pagesLab 10 Magnetic Fieldstaterr123412No ratings yet
- Static Electricity Balloon ExperimentDocument2 pagesStatic Electricity Balloon ExperimentRosalyn RechsteinerNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2: Activity 1: Charge It!Document20 pagesGeneral Physics 2: Activity 1: Charge It!Mariles PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect1Document42 pagesPhotoelectric Effect1Pearl Shane DomingoNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Notes ExperimentDocument13 pagesPhotoelectric Notes ExperimentVishnu KaushikNo ratings yet
- Carmille Paz SANGUILA Activity 6 Data SheetDocument5 pagesCarmille Paz SANGUILA Activity 6 Data SheetVladinir BotawanNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity No. 1 Charging by Conduction and InductionDocument5 pagesLab Activity No. 1 Charging by Conduction and InductionShane ChuchuNo ratings yet
- Ad6cf626 1651116482352Document26 pagesAd6cf626 1651116482352Chilla JagadeshNo ratings yet
- Teacher Demo/Student Activity: Charging by ContactDocument3 pagesTeacher Demo/Student Activity: Charging by ContactGerald Mark CamayNo ratings yet
- Exp16 Electrostatics Fall01Document3 pagesExp16 Electrostatics Fall01ejoy27No ratings yet
- LAB 2-Group 1Document5 pagesLAB 2-Group 1jnnpctngNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument6 pagesPhysicsMaite LarrazNo ratings yet
- Physics 121: Electricity & Magnetism - Lecture 2 Electric ChargeDocument24 pagesPhysics 121: Electricity & Magnetism - Lecture 2 Electric ChargeSunil JainNo ratings yet
- Experiment 13: ElectrostaticsDocument6 pagesExperiment 13: ElectrostaticsZhie Lou0% (1)
- General Physics 2: Quarter 3 - Week 1 Module 1 Electrostatic ChargingDocument19 pagesGeneral Physics 2: Quarter 3 - Week 1 Module 1 Electrostatic ChargingBryan OndajareNo ratings yet
- Research Status of Optical Fiber Voltage TransformDocument14 pagesResearch Status of Optical Fiber Voltage TransformRoy LuuNo ratings yet
- Dela Vega SLM General Physics 2 q4 Module1 w7 8 1Document12 pagesDela Vega SLM General Physics 2 q4 Module1 w7 8 1Jp menorNo ratings yet
- Edang Canta Dagle CreenciaDocument3 pagesEdang Canta Dagle CreenciaJego CreenciaNo ratings yet
- Physics: Third GradeDocument17 pagesPhysics: Third GradeSamadNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Exam Differentiated InstructionDocument8 pagesMid Term Exam Differentiated InstructionMARGARITA MARIANONo ratings yet
- Physics 4 169Document155 pagesPhysics 4 169Mohab Mohsen SalehNo ratings yet
- Chem 102-General Chemistry Lecture 11Document23 pagesChem 102-General Chemistry Lecture 11Takesure Mgcini MaphosaNo ratings yet
- Experiment.1 - Electroscope (Gautane, Honorio, Recondo)Document4 pagesExperiment.1 - Electroscope (Gautane, Honorio, Recondo)Janlie GautaneNo ratings yet
- Physics102 Lecture02Document25 pagesPhysics102 Lecture02Deren SelamiNo ratings yet
- Project Title Exploring The Photoelectric EffectDocument7 pagesProject Title Exploring The Photoelectric Effectakash dasNo ratings yet
- Electroscope LabDocument4 pagesElectroscope LabMatthew DiDonatoNo ratings yet
- Course Introduction Art Meyers Course Consists of The Following PartsDocument45 pagesCourse Introduction Art Meyers Course Consists of The Following Partsseia3aNo ratings yet
- S1-3-05 - A Love-Hate Relationship - Discrepant EventDocument7 pagesS1-3-05 - A Love-Hate Relationship - Discrepant EventrurryNo ratings yet
- U Electrostatics 2019 2020Document44 pagesU Electrostatics 2019 2020Budi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Periodicity)Document12 pagesChemistry (Periodicity)María JulianaNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 Photoelectric EffectDocument21 pagesExp 1 Photoelectric EffectAmul OkNo ratings yet
- Adam Proposal With 1st CommentDocument24 pagesAdam Proposal With 1st CommentJifar RayaNo ratings yet
- Physics H/W The Principle of PhotocopierDocument10 pagesPhysics H/W The Principle of PhotocopierEzequiel AnibalNo ratings yet
- Ch. 7 PDFDocument51 pagesCh. 7 PDFSophia StewartNo ratings yet
- LabutawDocument5 pagesLabutawReysel MonteroNo ratings yet
- BOE201 Principle Techniques of Basic Spectrophotometer AAS (1) LEE CHI YIEN 151877Document14 pagesBOE201 Principle Techniques of Basic Spectrophotometer AAS (1) LEE CHI YIEN 151877Chiyien LeeNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pagesElectricity and MagnetismMike MarshallNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics 1 NewDocument8 pagesNuclear Physics 1 NewFatima Habib MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- Interaction of Radiation With MatterDocument12 pagesInteraction of Radiation With MatterTheRealRivaNo ratings yet
- Training Modules in ESPDocument162 pagesTraining Modules in ESPSekar CmNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument3 pagesPhotoelectric EffectNabil NewNo ratings yet
- Ebook Topological Insulator and Related Topics 1St Edition Lu Li Editor Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesEbook Topological Insulator and Related Topics 1St Edition Lu Li Editor Online PDF All Chapterlawrence.cales406100% (7)
- EMMVEE - On-Grid PV Modules - DatasheetDocument2 pagesEMMVEE - On-Grid PV Modules - Datasheetmk gandhiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 Q.1. A Rectangular Coil, With Corners LabeledDocument2 pagesTutorial 6 Q.1. A Rectangular Coil, With Corners LabeledJohn LionelNo ratings yet
- Ma Muse M'Abuse Article - Odd Meters On The Drumset (9/16)Document10 pagesMa Muse M'Abuse Article - Odd Meters On The Drumset (9/16)Jarrod CagwinNo ratings yet
- Final 4 For Theoriees of LearningDocument2 pagesFinal 4 For Theoriees of LearningRose B Unlad67% (6)
- Modern Architectural Thought - DA2: Critic: Schauspielhaus, BerlinDocument3 pagesModern Architectural Thought - DA2: Critic: Schauspielhaus, BerlinKavvyaNo ratings yet
- Evaluating 21 Century Skills: 4.0 Intended Learning OutcomesDocument21 pagesEvaluating 21 Century Skills: 4.0 Intended Learning OutcomesAriel AbarratigueNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking A Top Down Approach 7Th Edition PDF Full ChapterDocument41 pagesComputer Networking A Top Down Approach 7Th Edition PDF Full Chapterlawrence.graves202100% (16)
- Pasteurization and Heat Sterilization - 2Document33 pagesPasteurization and Heat Sterilization - 2Taf Du Plessis Ngara50% (2)
- Lab 1Document11 pagesLab 1Saimun MahumdNo ratings yet
- Rethinking The Pattern of External Policy ReferencingDocument22 pagesRethinking The Pattern of External Policy ReferencingAlwani Bt Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Impact of Working Capital Management On PDFDocument113 pagesImpact of Working Capital Management On PDFAhmed Afridi Bin FerdousNo ratings yet
- Front End LoadingDocument2 pagesFront End LoadingRyan SykesNo ratings yet
- The Solitary Reaper - William Words WorthDocument8 pagesThe Solitary Reaper - William Words WorthLinio_92No ratings yet
- Handling Unit Management in SAP Packing During Outbound ProcessDocument48 pagesHandling Unit Management in SAP Packing During Outbound ProcessmohannaiduramNo ratings yet
- (Ebook) Goodspeed, Edgar J - A History of Early Christian Literature (Christian Library)Document125 pages(Ebook) Goodspeed, Edgar J - A History of Early Christian Literature (Christian Library)Giorgosby17No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Computers Notes and Assignments - 0 PDFDocument18 pagesCBSE Class 9 Computers Notes and Assignments - 0 PDFPonk ManNo ratings yet
- Achiever (Nov 2014)Document56 pagesAchiever (Nov 2014)gauravsukraliyaNo ratings yet
- Las Navas-Catubig-Laoang - Along The River RouteDocument2 pagesLas Navas-Catubig-Laoang - Along The River RouteChloe GalarozaNo ratings yet
- The Superlative Form of AdjectivesDocument3 pagesThe Superlative Form of AdjectivesEnglishteachervigo VigoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Large1 Template Aog and JogDocument3 pagesCambridge Large1 Template Aog and JogFresh Prince Of NigeriaNo ratings yet
- MGS & WipDocument2 pagesMGS & WipRoni HadyanNo ratings yet
- Budesonide (Drug Study)Document3 pagesBudesonide (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- Technical Manual For Design and Construction of Road Tunnels-2010 PDFDocument648 pagesTechnical Manual For Design and Construction of Road Tunnels-2010 PDFAsim Amin100% (1)
- Tap ChangerDocument6 pagesTap ChangermshahidshaukatNo ratings yet
- Eurocode 3 Stress Ratio Presentation 5 by Lee CKDocument17 pagesEurocode 3 Stress Ratio Presentation 5 by Lee CKKipodimNo ratings yet
- Manual - HSIDocument23 pagesManual - HSIrichardfloyd100% (2)
- Format of Deworming Masterlist Form 1 Modified School Level Reporting Form 7 DahliaDocument8 pagesFormat of Deworming Masterlist Form 1 Modified School Level Reporting Form 7 DahliagiareysieNo ratings yet
- Some Observations On Dispositio and Elocutio in Bach'sDocument10 pagesSome Observations On Dispositio and Elocutio in Bach'sDaniel Halaban100% (1)