Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LOSARTAN (ARBs) Drug Study (GERIATRICS)
LOSARTAN (ARBs) Drug Study (GERIATRICS)
Uploaded by
CHRISTIE MONTANO0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
208 views5 pagesANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS ( ARBs)
ARBs work by blocking receptors that the hormone acts on, specifically AT1 receptors, which are found in the heart, blood vessels and kidneys. Blocking the action of angiotensin II helps to lower blood pressure and prevent damage to the heart and kidneys
ARBs:
CANDESARTAN, IRBERSARTAN, OLMESARTAN, VALSALTRAN,TELMISARTAN, EPROSARTAN
Original Title
LOSARTAN ( ARBs) Drug Study ( GERIATRICS)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS ( ARBs)
ARBs work by blocking receptors that the hormone acts on, specifically AT1 receptors, which are found in the heart, blood vessels and kidneys. Blocking the action of angiotensin II helps to lower blood pressure and prevent damage to the heart and kidneys
ARBs:
CANDESARTAN, IRBERSARTAN, OLMESARTAN, VALSALTRAN,TELMISARTAN, EPROSARTAN
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
208 views5 pagesLOSARTAN (ARBs) Drug Study (GERIATRICS)
LOSARTAN (ARBs) Drug Study (GERIATRICS)
Uploaded by
CHRISTIE MONTANOANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS ( ARBs)
ARBs work by blocking receptors that the hormone acts on, specifically AT1 receptors, which are found in the heart, blood vessels and kidneys. Blocking the action of angiotensin II helps to lower blood pressure and prevent damage to the heart and kidneys
ARBs:
CANDESARTAN, IRBERSARTAN, OLMESARTAN, VALSALTRAN,TELMISARTAN, EPROSARTAN
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
You are on page 1of 5
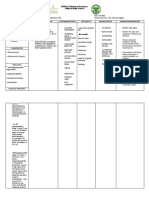
Name Dosage/ Mechanism Side Nursing
of the Drawing Classification Time/ of Effects Responsibilities
Drug Route Indication Action
ARBs For Inhibits Patient with 1. Proper hand
P.O hypertension vasoconstriction hypertension or left washing is
Generic ( angiotensin and and aldosterone ventricular always the
name: receptor Adjust – a – nephropathy. – secreting action hypertrophy number one
blockers) dose (for all To reduce the of angiotensin II protocol
Losartan indications) risk of CVA in by blocking CNS: whenever
potassium Anti – patients with angiotensin handling and
hypertensives Hypertension hypertension receptor on the Dizziness preparing
Brand and left surface of Asthenia drugs to be
name: Adults : ventricular vascular smooth Fatigue administered.
hypertrophy. muscle and other Headache RATIONALE
Cozaar Initially tissue cells. Insomnia To ensure aseptic
50mg daily technique and to
( max. of Onset - 6 hours CV: prevent cross
100mg) in 1 or contamination.
Edema
2 divided Peak – 1 – 2 hrs.
Chest pain
dosage 2. Check label
thoroughly for
EENT:
instruction
Adjust a about the
dose Nasal
administratio
For adults congestion
n including
with Sinusitis the dosage,
intravascular Pharyngitis label, and
volume Sinus disorder expiration
depletion date.
(taking GI: RATIONALE
diuretics) Abdominal To avoid error, to be
pain
Initially, Nausea certain with the drug
25 mg Diarrhea patency and to be
Dyspepsia accurate with the
drug to be
Nephropathy Musculoskeletal: administered.
in patients
with type 2 3. Monitor
diabetes
Muscle cramps
Myalgia patient’s BP
Back or leg closely to
50 mg P.O evaluate.
daily pain
RATIONALE
RESPIRATORY: To evaluate the
Increased to effectiveness of the
100 mg therapy.
based on BP Cough
4. Monitor
response URI
elderly
patients who
OTHER:
are also
taking
Angioedema diuretics.
RATIONALE
Patient with For symptomatic
nephropathy hypotension.
5. Regularly
CNS: assess
Asthenia elderly
Fatigue patients with
Fever renal function
Hypoesthesia (via
creatinine
CV: and BUN
Chest pain levels)
Hypotension
Orthostatic RATIONALE
hypotension To evaluate kidney
and renal function
EENT: respectively.
Cataract
Sinusitis 6. Tell the
elderly
GI: patient to
Diarrhea avoid salt
Dyspepsia substitutes.
Gastritis RATIONALE
To avoid
Nausea
hypernatremia
because it can
GU:
cause high
UTI
potassium level in
patients taking
HEMATOLOGIC:
losartan.
Anemia 7. Advise
elderly
METABOLIC: patient or
caregiver to
Hyperkalemia
report all
Hypoglycaemia
adverse
Hyponatremia
reactions to
Weight gain the medical
provider such
as swelling of
face, eyes,
MUSCULOSKELETAL
lips, or
tongue or
Back pain
breathing
Leg or knee
difficulty.
pain
Muscle RATIONALE
weakness To avoid further
RESPIRATORY: complications and to
treat the adverse
Cough reactions
Bronchitis immediately.
8. Put the
SKIN: medicine in a
bottle and
Cellulitis label it
correctly to
avoid error in
taking
prescribed
medicines.
RATIONALE
This is for the
elderly patient to
correctly take
medications
particularly those
patients who are
taking multiple
prescribed
medications
(polypharmacy).
You might also like
- PCAP Pediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPCAP Pediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYCHRISTIE MONTANO25% (4)
- Autism For DummiesDocument11 pagesAutism For Dummiesgocyndigo72yahoocomNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesMultiple Sclerosis Nursing Care PlanCHRISTIE MONTANONo ratings yet
- NCP. MOuth SoreDocument1 pageNCP. MOuth SoreChriszanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Ertapenem (Invanz)Document1 pageErtapenem (Invanz)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyArnel MacabalitaoNo ratings yet
- Aspirin Drug SummDocument2 pagesAspirin Drug SummWarren0% (1)
- Final Magnesium SulfateDocument3 pagesFinal Magnesium SulfateGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- FebuxostatDocument5 pagesFebuxostatadzmir hunainNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Meclizine Is An Antagonist atDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Meclizine Is An Antagonist atJayson Ray AbellarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Vitamin C + ZincDocument2 pagesDrug Study Vitamin C + ZincKrizzia FosterNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Document2 pagesDrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AtropineDocument3 pagesDrug Study AtropineAerron Severus Secano ShuldbergNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- Verapamil HCLDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dosa Ge Mechanis Mof Action Indicatio N Contraindic Ation Adverse/Side Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument14 pagesDrug Name Dosa Ge Mechanis Mof Action Indicatio N Contraindic Ation Adverse/Side Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoNo ratings yet
- Fluvastatin - Drug StudyDocument1 pageFluvastatin - Drug StudyKevin H. MilanesNo ratings yet
- LOVASTATINDocument2 pagesLOVASTATINAngel CatalanNo ratings yet
- JM DrugDocument3 pagesJM DrugVerdie B. NgayanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEChezka Orton Swift BolintiamNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyMarychen Cabunas100% (1)
- DS LosartanDocument1 pageDS LosartanYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- Vit K Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVit K Drug StudyKrisha AristonNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesMinaNo ratings yet
- Drug NystatinDocument1 pageDrug NystatinSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Healthcare - Drug Study Worksheet - Penicillin G SodiumDocument2 pagesHealthcare - Drug Study Worksheet - Penicillin G SodiumBenjamin CañalitaNo ratings yet
- CefadroxilDocument2 pagesCefadroxilArvie AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PantoprazoleDocument3 pagesDrug Study PantoprazoleIRISH CACAYANNo ratings yet
- Ds Pedia WardDocument2 pagesDs Pedia WardRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Aspirin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAspirin Drug StudyIRISH CACAYANNo ratings yet
- Pravastatin SodiumDocument3 pagesPravastatin Sodiumapi-3797941No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY AtorvastatinDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY AtorvastatinKyla BeconiaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNemo Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- AzithromycinDocument1 pageAzithromycinGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Celecoxib CelebrexDocument1 pageCelecoxib CelebrexBeverly Ann de LeonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: MethyldopaDocument1 pageDrug Study: MethyldopaTempoNo ratings yet
- Caltrate PlusDocument3 pagesCaltrate PlusLanzen Dragneel100% (1)
- Drug Study HepatitisDocument7 pagesDrug Study HepatitisKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- Ceftaroline Teflaro CefotaximeDocument3 pagesCeftaroline Teflaro CefotaximeKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Sennosides (Senokot)Document1 pageSennosides (Senokot)E100% (1)
- OmeprazoleDocument2 pagesOmeprazoleKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyAldrin Ian Oraza AlpeNo ratings yet
- Betadine GargleDocument1 pageBetadine GargleReemALMousawiNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityChelsea WuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyGrace CadawasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyDavid RefuncionNo ratings yet
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 pageLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Administration Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Mechanism of Action Administration Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesIvan Liquiran AvenadoNo ratings yet
- GENTIMICINDocument1 pageGENTIMICINVinzNo ratings yet
- Leoprolide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLeoprolide Drug Studyhappymee927No ratings yet
- Clindamycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesClindamycin Drug StudyArthur Christopher CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AMIODARONE & PROPOFOLDocument3 pagesDrug Study AMIODARONE & PROPOFOLNIKKI CARYL ZAFRANo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityShiva TorinsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ferrous Sulfate + FADocument3 pagesDrug Study Ferrous Sulfate + FAKristine ChampnessNo ratings yet
- PantoprazoleDocument1 pagePantoprazolehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- CoversylDocument3 pagesCoversylianecunarNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY OmeprazoleDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY OmeprazoleBRYCE WILLIAM GONo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolKay MirandaNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyDiothelli Mae BokingoNo ratings yet
- Albuterol DsDocument2 pagesAlbuterol DsCalvin Keith YadaoNo ratings yet
- IbuprofenDocument2 pagesIbuprofenKim Glaidyl Bontuyan100% (2)
- Vehicular Accident (VA) Manifesting Hypovolemic Shock NCPDocument6 pagesVehicular Accident (VA) Manifesting Hypovolemic Shock NCPCHRISTIE MONTANONo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Patient With PNEUMONIA (Geriatrics)Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patient With PNEUMONIA (Geriatrics)CHRISTIE MONTANO0% (1)
- Respiratory Acidosis and AlkalosisDocument2 pagesRespiratory Acidosis and AlkalosisCHRISTIE MONTANONo ratings yet
- Raynauds and Buerguers DiseaseDocument3 pagesRaynauds and Buerguers DiseaseCHRISTIE MONTANO100% (2)
- Types of AnemiaDocument11 pagesTypes of AnemiaCHRISTIE MONTANO50% (2)
- Antilipemic Agents - ATORVASTATIN CALCIUM (Lipitor)Document5 pagesAntilipemic Agents - ATORVASTATIN CALCIUM (Lipitor)CHRISTIE MONTANONo ratings yet
- Arteriosclerosis vs. AtherosclerosisDocument3 pagesArteriosclerosis vs. AtherosclerosisCHRISTIE MONTANONo ratings yet
- CHN - COPAR Family Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesCHN - COPAR Family Nursing Care PlanCHRISTIE MONTANO100% (2)
- BACILLUS CALMETTE - GUERIN (BCG) Drug StudyDocument2 pagesBACILLUS CALMETTE - GUERIN (BCG) Drug StudyCHRISTIE MONTANO100% (2)
- MATERNAL and CHILD SUMMARY Chapters 26 - 29 (Adelle Pillitteri)Document87 pagesMATERNAL and CHILD SUMMARY Chapters 26 - 29 (Adelle Pillitteri)CHRISTIE MONTANO100% (8)
- MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSING SUMMARY Chapter 30-34 (Adelle Pillitteri)Document134 pagesMATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSING SUMMARY Chapter 30-34 (Adelle Pillitteri)CHRISTIE MONTANO100% (6)
- Case Analysis On Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument29 pagesCase Analysis On Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceCHRISTIE MONTANO100% (1)
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionDocument9 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract InfectionCHRISTIE MONTANO100% (1)
- Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument19 pagesLower Respiratory Tract InfectionsCHRISTIE MONTANO100% (1)
- 3340-Sds-Petromin Atf Dexron Ii e V#2Document6 pages3340-Sds-Petromin Atf Dexron Ii e V#2SICIM SAUDI ARABIANo ratings yet
- Manifesting Generators - Resources For LifeDocument3 pagesManifesting Generators - Resources For LifeIrem YitmenNo ratings yet
- Position Paper ZABATEDocument20 pagesPosition Paper ZABATEAtty. Emmanuel SandichoNo ratings yet
- 1574-Article Text-2641-1-10-20181107Document5 pages1574-Article Text-2641-1-10-20181107Faraz HaiderNo ratings yet
- Anna Garcia Death Timeline 1Document19 pagesAnna Garcia Death Timeline 1api-245176779No ratings yet
- FA1 Mini Operation ManualDocument7 pagesFA1 Mini Operation ManualJuan Angel Martinez RamirezNo ratings yet
- June 2008Document17 pagesJune 2008proxy1589No ratings yet
- Blood Bank EquipmentsDocument12 pagesBlood Bank EquipmentsJomar100% (1)
- HackerRank - India Benefits and PerksDocument5 pagesHackerRank - India Benefits and PerksNacturNo ratings yet
- Knowledge ManagementDocument63 pagesKnowledge Managementrahul-singh-6592No ratings yet
- Kit For Human Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (HTSH) : Irmak-9Document2 pagesKit For Human Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (HTSH) : Irmak-9micky mouseNo ratings yet
- HOLANDA ALEX CFE103 Module4 ContextEngageActivitiesDocument4 pagesHOLANDA ALEX CFE103 Module4 ContextEngageActivitiesAsus LaptopNo ratings yet
- Deep Fat FryingDocument2 pagesDeep Fat FryingalinawidagdoNo ratings yet
- BP ProcedureDocument2 pagesBP Procedureflomar22No ratings yet
- CSQ Nap4 FullDocument219 pagesCSQ Nap4 FullJeisson FarroNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Centre: Assignment - 3Document12 pagesDialysis Centre: Assignment - 3grvoneandonlyNo ratings yet
- JSP 403 Vol 2 Chapter 2Document61 pagesJSP 403 Vol 2 Chapter 2SOOD ASSOCIATES GOANo ratings yet
- ELIGIBILITY BKPDocument1 pageELIGIBILITY BKPLydia FrederickNo ratings yet
- Ultrarunning MagDocument60 pagesUltrarunning MagLynseyNo ratings yet
- Anthropometry For ElderlyDocument20 pagesAnthropometry For ElderlyjarvantaraNo ratings yet
- Chris Hemsworth's God-Like Thor WorkoutDocument8 pagesChris Hemsworth's God-Like Thor WorkoutmarticarrerasNo ratings yet
- ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4 Edition - Ning PDFDocument112 pagesACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4 Edition - Ning PDFbasuthker raviNo ratings yet
- Administrative Assistant or Office Assistant or SecretaryDocument2 pagesAdministrative Assistant or Office Assistant or Secretaryapi-121408530No ratings yet
- New Lipid PowerpointDocument113 pagesNew Lipid PowerpointMadane Jamila Amerol SaminNo ratings yet
- Shiva LatestDocument3 pagesShiva LatestToby JordanNo ratings yet
- Kiran Raju - Techversant PayslipDocument3 pagesKiran Raju - Techversant PayslipCap RJNo ratings yet
- Managing Our Waste: Powerpoint Slides Prepared by Stephen TurnbullDocument59 pagesManaging Our Waste: Powerpoint Slides Prepared by Stephen TurnbullJulia HartNo ratings yet
- Celebrating Worthing College 2012 SpeadsDocument9 pagesCelebrating Worthing College 2012 SpeadsWorthing College-SportNo ratings yet
- Injury Biomechanics: AAMIR SOHAIL - Student ID 163101039 - December 16, 2016Document12 pagesInjury Biomechanics: AAMIR SOHAIL - Student ID 163101039 - December 16, 2016Aamir SohailNo ratings yet