Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Key Words
Physics Key Words
Uploaded by
Kab Mac0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageThis document provides definitions for key physics terms including acceleration, amplitude, current, dispersion, electricity, electromagnetic spectrum, energy, force, frequency, friction, fusion, gravity, insulation, light, mass, matter, power, radiation, radioactivity, reflection, refraction, resistance, sound, spectrum, speed, static electricity, velocity, voltage, wavelength, weight, and work. Terms are defined concisely with relevant units of measurement where applicable.
Original Description:
Original Title
Physics-Key-Words
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides definitions for key physics terms including acceleration, amplitude, current, dispersion, electricity, electromagnetic spectrum, energy, force, frequency, friction, fusion, gravity, insulation, light, mass, matter, power, radiation, radioactivity, reflection, refraction, resistance, sound, spectrum, speed, static electricity, velocity, voltage, wavelength, weight, and work. Terms are defined concisely with relevant units of measurement where applicable.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pagePhysics Key Words
Physics Key Words
Uploaded by
Kab MacThis document provides definitions for key physics terms including acceleration, amplitude, current, dispersion, electricity, electromagnetic spectrum, energy, force, frequency, friction, fusion, gravity, insulation, light, mass, matter, power, radiation, radioactivity, reflection, refraction, resistance, sound, spectrum, speed, static electricity, velocity, voltage, wavelength, weight, and work. Terms are defined concisely with relevant units of measurement where applicable.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
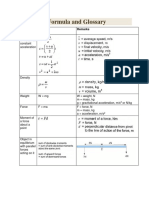
SCIENCE KEY WORDS – PHYSICS
Acceleration Rate of change in velocity. Measured in m/s2.
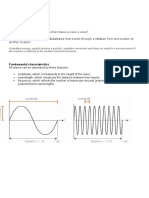
Amplitude The maximum distance that a wave has from its rest position.
Conductor Material through which an electric current or heat will flow through easily.
Electrical current is a flow of charge. In wires, the charges are carried by electrons.
Current
In fluids, the charges are carried by ions. Measured in amperes (A).
Dispersion Splitting up of white light into the colours of the spectrum.
Electricity A form of energy produced by the movement of electrons.
Electromagnetic The range of wavelengths or frequencies over which electromagnetic radiation
spectrum extends.
Energy enables something to do physical work involving the application of a force.
Energy
Measured in Joules (J).
Fission The splitting of an atomic nucleus to produce nuclear energy.
Forces are pushes and pulls that make things move or change shape. Measured in
Force
Newtons (N).
Frequency Number of waves that pass a fixed point per second. Measured in Hertz (Hz).
Friction Friction is a resisting force between two surfaces rubbing against each other.
Fusion The joining of atomic nuclei to produce nuclear energy.
The force that attracts a body toward the centre of the earth, or toward any other
Gravity
physical body having mass.
Insulator Material through which an electric current or heat will not flow through easily.
Light Electromagnetic radiation that has a speed of 299 792 458 metres per second.
Mass A measure of the amount of matter in an object. Measured in kilograms (kg)
Matter Matter is the stuff that everything is made from.
Power The amount of energy transferred per second. Power is measured in watts (W).
The emission of heat energy as electromagnetic waves or as moving subatomic
Radiation
particles.
Radioactivity The emission of particles or electromagnetic waves from the nucleus of an atom.
Reflection Change in direction of a sound or light wave when it hits a surface.
Refraction Bending of light as it passes though materials with different densities.
Resistance is the extent to which a conductor hinders the flow of an electric current.
Resistance
Resistance is measured in ohms (Ώ).
Sound Vibrations that pass through solids, liquids and gases.
A band of colours, as seen in a rainbow, produced by separation of the components
Spectrum
of light by their different degrees of refraction.
Speed is a measure of how quickly something moves through a given distance. It is
Speed measured in metres per second (m/s) and calculated by using the formula speed =
distance ÷ time.
Static Build up of electric charge from friction between insulating materials.
electricity
Velocity Velocity is speed in a stated direction. The unit of velocity is m/s.
Voltage The measure of energy available to drive a current. Measured in volts (V).
The distance between one peak or crest of a wave of light, heat, or other energy
Wavelength
and the next.
The force of gravity on a mass. It is given by the equation weight = mass × gravity
Weight
where, on Earth, gravity = 9.8 N/kg.
Physical work is done when a force makes something move. Work is defined by the
Work
formula work done = force × distance. Measured in newton metres (Nm).
You might also like
- Physics GlossaryDocument21 pagesPhysics GlossaryKing VaibhavNo ratings yet
- Physics HandbookDocument10 pagesPhysics HandbookNational Physical Laboratory100% (1)
- Introduction To Modern Physics-Min PDFDocument47 pagesIntroduction To Modern Physics-Min PDFALURU VAISHNAVI 17BCE0017No ratings yet
- Global Skills of DrawingDocument2 pagesGlobal Skills of DrawingWes ArtNo ratings yet
- GCSC Physics GlossaryDocument8 pagesGCSC Physics GlossarysmeenaNo ratings yet
- Physics A Level DefinitionsDocument12 pagesPhysics A Level DefinitionsNaillah Saba100% (1)
- Electromagnetic - Waves 2 SSCDocument28 pagesElectromagnetic - Waves 2 SSCJuliever EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- HT Lecture Notes - 0Document41 pagesHT Lecture Notes - 0SUPRADEEP GNo ratings yet
- Science VocabularyDocument6 pagesScience Vocabularysamed brionesNo ratings yet
- Glossary A Level PhysicsDocument10 pagesGlossary A Level Physicsdanishali1090No ratings yet
- 68-Radiation Heat Transfer-Terminology and Laws-22-Oct-2019Material - I - 22-Oct-2019 - Radiation PDFDocument48 pages68-Radiation Heat Transfer-Terminology and Laws-22-Oct-2019Material - I - 22-Oct-2019 - Radiation PDFsiva yandraNo ratings yet
- 1 Basic Electrical IdeasDocument19 pages1 Basic Electrical IdeasYeri KimNo ratings yet
- p2 RevisionDocument27 pagesp2 Revisionapi-255043845No ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3RD QTRDocument6 pagesScience Reviewer 3RD QTRElise Emmry R. OchoaNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument213 pagesPhysicsBilal Hussain Shah100% (1)
- Physics 2Document187 pagesPhysics 2Bilal Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - WAVESDocument6 pagesChapter 1 - WAVESSiraf IldaNo ratings yet
- Finals ReviewerDocument3 pagesFinals ReviewerJames MoriartyNo ratings yet
- Rad PhysicsDocument109 pagesRad PhysicsRicardo EdanoNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics Loop CardsDocument1 pageQuantum Physics Loop Cardsderekboyle1973No ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics: Dr. B. M. Krishna MariserlaDocument13 pagesQuantum Mechanics: Dr. B. M. Krishna MariserlaGulzaar ChanniwalaNo ratings yet
- Science VocabularyDocument10 pagesScience VocabularyCandice LuNo ratings yet
- Bus BarDocument11 pagesBus BarDawit Adane KebedeNo ratings yet
- Physics Checkpoint Topics Part 1Document23 pagesPhysics Checkpoint Topics Part 1esteban ferrada silvaNo ratings yet
- Physics Definition List Form 5Document6 pagesPhysics Definition List Form 5Yinxin OngNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Wave PropagationDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic Wave PropagationRacquel Pauline LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Physical Principles of Remote SensingDocument23 pagesPhysical Principles of Remote SensingBernalyn ManaogNo ratings yet
- QuantisationDocument3 pagesQuantisationNarjis FatimaNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave PropagationDocument81 pagesRadio Wave PropagationJoseph JeremyNo ratings yet
- Current?: What Is Electric Current?Document9 pagesCurrent?: What Is Electric Current?NikeyNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic RadiationDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic RadiationSundayNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 - Principles of SpectrosDocument59 pagesChap 2 - Principles of SpectrosRezaul Karim100% (3)
- NEUTRON - The Neutron Is ADocument10 pagesNEUTRON - The Neutron Is AsushreenandaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Live Class-3 Teacher NotesDocument22 pagesAtomic Structure Live Class-3 Teacher Notestarun singhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Radiations: Dr. Mohammad Khairul Azhar Abdul RazabDocument60 pagesIntroduction To Radiations: Dr. Mohammad Khairul Azhar Abdul RazabLailatul KisstinaNo ratings yet
- Factsheet No WaveDocument6 pagesFactsheet No WaveJohn Van Dave TaturoNo ratings yet
- EM WAVE PPT OriginalDocument39 pagesEM WAVE PPT Originalsujithrasuji773No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - WavesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - WavesQiun LeeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Revision (PDFDrive)Document104 pagesAQA GCSE Revision (PDFDrive)ALiNo ratings yet
- Physics HSHSHSHSHDocument7 pagesPhysics HSHSHSHSHdorashreyanshNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Q2Document33 pagesLesson 1 Q2odnimernNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument11 pagesPhysics NotesnadineNo ratings yet
- Stage 7 Physics Strand NotesDocument8 pagesStage 7 Physics Strand NotesMazuba ChibbelaNo ratings yet
- RadiationDocument19 pagesRadiationNajmul Islam ShawonNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Thermal RadiationDocument23 pagesFundamentals of Thermal Radiationverify nameNo ratings yet
- Physics NewDocument5 pagesPhysics Newrosie FerrerNo ratings yet
- Physics: TheoryDocument5 pagesPhysics: TheoryIrshad KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7: Radiation and Matter: Phys 275 Astrophysics I - Planets and Stars Lecture 7 January 25th 2011Document29 pagesLecture 7: Radiation and Matter: Phys 275 Astrophysics I - Planets and Stars Lecture 7 January 25th 2011Nick CoishNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5Document21 pagesChapter - 5BISRAT YIHUNNo ratings yet
- l1 Electromagnetic Radiation-1Document32 pagesl1 Electromagnetic Radiation-1sittiekeharaabutazilNo ratings yet
- Icv 212Document8 pagesIcv 212kkiger1127No ratings yet
- Physics Definitions To Be LearnedDocument4 pagesPhysics Definitions To Be LearnedTshin Qi ZhouNo ratings yet
- Module 20-21 in STM 004Document58 pagesModule 20-21 in STM 004Ivy Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- CHEM 101 - L4 - Atomic Structure and Periodicity of Elements - Part BDocument41 pagesCHEM 101 - L4 - Atomic Structure and Periodicity of Elements - Part BlentlebuisanyangNo ratings yet
- Joshua Nzomo BTEE/217J/2020 Assignment 1Document2 pagesJoshua Nzomo BTEE/217J/2020 Assignment 1JpricarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Particle Properties of WavesDocument9 pagesChapter Two Particle Properties of WavesAmanuel BazeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering For Non-Chemical Engineers - Vol. 02 - DHARMSINH DESAI UNIVERSITYDocument150 pagesChemical Engineering For Non-Chemical Engineers - Vol. 02 - DHARMSINH DESAI UNIVERSITYGustavo Gonzalez ServaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves (EM Waves)Document17 pagesElectromagnetic Waves (EM Waves)Joshdave cuambotNo ratings yet
- Radiation Electromagnetic 20Document23 pagesRadiation Electromagnetic 20KENNYNo ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itFrom EverandELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Physics and Their Applications, and Logical Structure of Quantum Mechanics March 2018 Projects Theoretical PhysicsDocument21 pagesBasic Principles of Physics and Their Applications, and Logical Structure of Quantum Mechanics March 2018 Projects Theoretical PhysicsKab MacNo ratings yet
- Photography For Beginners: A Complete Guide: InfographicDocument19 pagesPhotography For Beginners: A Complete Guide: InfographicKab MacNo ratings yet
- Fiction Practice Question and Creative Writing JDocument6 pagesFiction Practice Question and Creative Writing JKab MacNo ratings yet
- Exam Structure O Level GeoDocument2 pagesExam Structure O Level GeoKab MacNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Miranda Jochebed BSED2bDocument7 pagesLesson Plan - Miranda Jochebed BSED2bJochebed MirandaNo ratings yet
- 0653 w15 QP 32Document28 pages0653 w15 QP 32yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06-Colour Image ProcessingDocument84 pagesChapter 06-Colour Image Processingboddumeghana2220No ratings yet
- Rto Bysavmt Paket1un20182/019Document25 pagesRto Bysavmt Paket1un20182/019Nanda BasNo ratings yet
- Biological Resonance Heals The Wholeness: Similibus Curantur Meaning That Likes Cure Likes) - BasicallyDocument20 pagesBiological Resonance Heals The Wholeness: Similibus Curantur Meaning That Likes Cure Likes) - BasicallyCristiane ccmNo ratings yet
- tmp517C TMPDocument7 pagestmp517C TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Halo Lux Halo ParDocument4 pagesHalo Lux Halo ParMilan MarkićevićNo ratings yet
- Technical Guide For Solar Thermal SystemsDocument197 pagesTechnical Guide For Solar Thermal SystemsArvin ArviniNo ratings yet
- Indoor Omni Ceiling Mounted Antenna: IXD-360VH03NNDocument1 pageIndoor Omni Ceiling Mounted Antenna: IXD-360VH03NNИван КадигробNo ratings yet
- Color SchemesDocument2 pagesColor SchemesphenorenNo ratings yet
- Productsheet DENTLED DL60Document2 pagesProductsheet DENTLED DL60N'DA N'DRI ANGE FABIENNE KONANNo ratings yet
- Pratil MadeDocument2 pagesPratil MadeGajanan TaleNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Grade 10 11th WeekDocument31 pagesDaily Lesson Log Grade 10 11th WeekDENNIS N. MUÑOZ100% (1)
- Nathaniel SlidesCarnivalDocument43 pagesNathaniel SlidesCarnivalPatrícia SodréNo ratings yet
- 6 Jan 2023 Simple Harmonic Motion SHM #BounceBack SprintDocument88 pages6 Jan 2023 Simple Harmonic Motion SHM #BounceBack SprintPrantik RoyNo ratings yet
- EDCh 4 RF IfDocument3 pagesEDCh 4 RF IfsmileyNo ratings yet
- Here Flow ENDocument8 pagesHere Flow ENAhmed KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Catálogo Calvin Klein Men& Women Underwear July, 2010Document124 pagesCatálogo Calvin Klein Men& Women Underwear July, 2010franypabloNo ratings yet
- Talbott - Thunderbolts of The GodsDocument98 pagesTalbott - Thunderbolts of The Godslolas59100% (16)
- Product Specifications: LDX-6516DS-VTMDocument3 pagesProduct Specifications: LDX-6516DS-VTMJura GirskiNo ratings yet
- Linde Service Guide: ArrangementDocument2 pagesLinde Service Guide: ArrangementTrần Đức PhiNo ratings yet
- 1 Communication System Module 1Document13 pages1 Communication System Module 1Anandhu cNo ratings yet
- Osram P-Vip PDFDocument57 pagesOsram P-Vip PDFtantra_lover2005No ratings yet
- HWX-6516DS1-VTM: Electrical SpecificationsDocument3 pagesHWX-6516DS1-VTM: Electrical SpecificationsDavid NigraNo ratings yet
- Wall Sconce WLMS18Document1 pageWall Sconce WLMS18EliasNo ratings yet
- Visual Color Evaluation Metamerism (Based On ASTM D-4086)Document3 pagesVisual Color Evaluation Metamerism (Based On ASTM D-4086)T AaaNo ratings yet
- Digital Infrared Photography ManualDocument352 pagesDigital Infrared Photography ManualOl RebNo ratings yet
- BOL 4.2 Primary ColorsDocument5 pagesBOL 4.2 Primary Colorsceleste c. casinilloNo ratings yet
- Combined Geo-Scientist (P) Examination 2020 Paper-II (Geophysics)Document25 pagesCombined Geo-Scientist (P) Examination 2020 Paper-II (Geophysics)OIL INDIANo ratings yet