Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jyoti - A00206469 - Module 01 QA (1) .Asd
Jyoti - A00206469 - Module 01 QA (1) .Asd
Uploaded by
JYOTI SHARMAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Jyoti - A00206469 - Module 01 QA (1) .Asd
Jyoti - A00206469 - Module 01 QA (1) .Asd
Uploaded by
JYOTI SHARMACopyright:
Available Formats
Connecting Networks Q&A
Introduction, Chapters 1.1 – 1.3
Chapter 1 Question Answer
1. Is a WAN owned by the company or an Yes WAN is owned by a company.
external entity?
2. Why is a WAN necessary? Use a wide vriety of transmission media, allow access to
branch office, custmoers, remote workers.
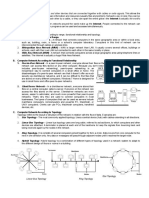
3. What are common WAN topologies and a Point to point – use a point to point circuit between two
summary of the topology’s traits? end points.
Packets are sent in both directions.
Hub and spoke – known as a “star” or “point-to-
multipoint”
Shared by all spoke circuits.
Full mesh – use virtual circuit, but we need to
configure and maintain a large number of virtual circuits.
Dual homed – provide reduncy and load balancing
Require additional networking hardware to implement
4. Outline a common evolution of a network as a It enables the computers to share the documents and
company expands? informations and also the equipment assets. So it makes
the company easier to work easier.
5. Where does a WAN operate in the OSI model? WAN generally operate at the lower three layer of OSI
model, and that layers are physical layer, data link layer
and network layer.
6. Explain the common WAN terminology. A WAN uses data links provided by carrier services to
access the Internet and connect different locations of an
organization to each other.
7. Describe common WAN devices. CSU/DSU – (channel service unit) provide termination
for digital signals and ensure connection entegrnity.
(data service unit) converts the line frames into frames
that the LAN can interpret and vice versa.
Access Server – it concentrate dial in and dial out user
communications. It may have a mixtures of analog and
digital interfaces.
Dialup modems – the modems modulate the computers
digital signals into voice frequencies and transmits it.
Broadband modems – it used high speed DSL or cable
network serive.
Chapter 1 Question Answer
It use high broadband frequencies.
WAN switch – it is multipoint interworking device used
in carrier network
Core routers – it is the backbone of WAN.
8. Discuss circuit-switching technology and Circuit-switching – it establishes a dedicated circuit or
identify common types. channel between nodes and terminals.
Example – PSTN (Public switched telephone
network)and ISDN (integrated services digital network)
9. Discuss packet-switching technology and Packet- switching – it sperate traffic data into packets.
identify common types. It routed over a shared network.
10. Outline common WAN access options. We have two type of WAN access option
Private WAN infrastructure – it includes point-to-point,
leased lines, circuit switched links and packet switched
links.
Public WAN infrastructure – service providers may offer
broadband internet using DSL, cable or a satellite. Data
travels between cooperate sites over public WAN.
11. Describe a common IP infrastructure. The IP infrastructure represents a key
boundary between a communications medium and the
applications that are built upon this medium. It allows
two different marketplace to operate on their own
terms.
12. Discuss leased line topology and the pros and It leased from a service provider. It depends on price
cons. depending on bandwith and distance.
Pros – it contains less expertise to install
Its quality is good that removes all latency and jitter
between end points
It prvide dedicated connection that’s stay forever.
Cons -- its very expensive
It have limited flexibility.
13. Where might dialup be a viable option?
Outline the option.
14. What are types of ISDN? Is it used very much? ISDN integrated service digital network, it changes the
internal connection of PSTN from analog to time
divioson multiplexed (TDM ). TDM that allow two or
more signals to transfer as subchannel over one
channel.
15. Describe the Frame Relay capability. A non-broadcast multiaccess technology.
It used to connect multi sites using PVcs, that’s carry
both voice and data traffic.
It supports data rates up to 4+ Mb/s.
16. Explain ATM topology. Asynchronous Transfer Mode is a cell based not frame
based.
Cells are length of 53bytes
5 byte header with 48 bytes of payload.
It support link speed of t1/E1 to OC-12 and faster
17. How has Ethernet Wan evolved and what are It includes fibre optics makes WAN processor easier.
its benefits?
Chapter 1 Question Answer
18. Where is MPLS used? What types of WAN Multiprotocol label switching it is used to direct the
technologies are supported? data from one router to the next.
Its multiprotocol high performance WAN technology
and it is a service provider technology.
19. Explain a VSAT topology. Very small aperture terminal, it creates private WAN
using satellite communications.
It create private WAN while providing connectivity to
remote locations.
20. Discuss DSL. Digital subscriber line, it uses twisted pair telephone
lines to transport high bandwith data
It change the ethernet signal to digital signal
21. Outline the components of a Cable topology. It is used in urban areas to seprate television
What can happen if many users join the signals. It provide always on connections and simple
network? installations.
22. Outline Wireless WAN options including Cellular version is in high popularity. It connect users
cellular versions. and their locations.
23. What does a VPN provide users? VPN is used make a secure connection between
private network over a public network.
We have two types of VPN site to site VPN or
remote access VPN.
24. Outline the considerations when selecting When we select WAN access we have to tell why we
WAN access. are using it , we have to tell about the requirements
and the geographic scope
You might also like
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksFrom EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Get Strong in 3 Days A WeekDocument6 pagesGet Strong in 3 Days A Weekmohamed aliNo ratings yet
- Digital Banking - HDFC BankDocument79 pagesDigital Banking - HDFC BankÂShu KaLrà80% (5)
- Ccna Exploration Accessing The Wan Study Guide: Chapter 2: PPPDocument9 pagesCcna Exploration Accessing The Wan Study Guide: Chapter 2: PPPMatthew RilleyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7: Bmit3094 Advanced Computer NetworksDocument4 pagesTutorial 7: Bmit3094 Advanced Computer Networksterence yapNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and NetworkingDocument5 pagesData Communication and Networkingmahnoor khanNo ratings yet
- Ec 8702 Ad Hoc and Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument33 pagesEc 8702 Ad Hoc and Wireless Sensor NetworksParanthaman GNo ratings yet
- Local Area Network (LAN)Document15 pagesLocal Area Network (LAN)vaibhav1211No ratings yet
- WAN Technologies PDFDocument132 pagesWAN Technologies PDFAsifNo ratings yet
- AWSN Q.B-DR - SRKDocument34 pagesAWSN Q.B-DR - SRKMithraNo ratings yet
- Ccna Final Project File To B PrintedDocument82 pagesCcna Final Project File To B Printedvarun jain100% (5)
- Module 5Document58 pagesModule 5Ankit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- WAN - Internet - PPPoEDocument46 pagesWAN - Internet - PPPoEblue.jupiter9x154No ratings yet
- Wan ConceptDocument27 pagesWan ConceptVichheka SouenNo ratings yet
- Computer Network: Wide Area Network (WAN)Document30 pagesComputer Network: Wide Area Network (WAN)Emad Samir FarahatNo ratings yet
- CNCTC Network and Administration.2Document187 pagesCNCTC Network and Administration.2masterwi.mwNo ratings yet
- CNCTC Network and Administration.1Document54 pagesCNCTC Network and Administration.1masterwi.mwNo ratings yet
- Ccna4e Ch1 Study Guide KeyDocument11 pagesCcna4e Ch1 Study Guide Keyjdr114No ratings yet
- Wide Area NetworksDocument77 pagesWide Area NetworksXuan Lich LeNo ratings yet
- Network HardwareDocument27 pagesNetwork HardwareAsim AwadNo ratings yet
- Tle-Ict Computer Systems Servicing: Quarter 1 - Module 4Document10 pagesTle-Ict Computer Systems Servicing: Quarter 1 - Module 4Jeo MillanoNo ratings yet
- Chap Quizzes Ccna4 PDFDocument16 pagesChap Quizzes Ccna4 PDFzero shinkiroNo ratings yet
- ICT 8 - Q3 (Network and Network Devices)Document4 pagesICT 8 - Q3 (Network and Network Devices)Glaiza HigoNo ratings yet
- Network Essentials OverviewDocument23 pagesNetwork Essentials OverviewVimala ElumalaiNo ratings yet
- SDH HCIA LectureDocument53 pagesSDH HCIA LectureSayed Rahim NaderiNo ratings yet
- Seminar ON Cisco Certified Networking Associate (CCNA)Document29 pagesSeminar ON Cisco Certified Networking Associate (CCNA)jain2102No ratings yet
- Repeater - Current Wireless Network TechnologyDocument6 pagesRepeater - Current Wireless Network TechnologyGodwin OanesNo ratings yet
- Instructor Materials Chapter 1: WAN Concepts: CCNA Routing and Switching Connecting NetworksDocument30 pagesInstructor Materials Chapter 1: WAN Concepts: CCNA Routing and Switching Connecting NetworksJude Allan UrmenetaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 s1, s2Document39 pagesUnit 1 s1, s2krithigaNo ratings yet
- CN (Network Categories)Document11 pagesCN (Network Categories)Pradyumn Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: LAN: Local Area Network MAN: Metropolitan Area NetworkDocument19 pagesPresentation On: LAN: Local Area Network MAN: Metropolitan Area Networkktkalai selviNo ratings yet
- Q3 Module1 G11 CSS-NCII Sison-Central-IsDocument10 pagesQ3 Module1 G11 CSS-NCII Sison-Central-IsxzainahanielmartinezNo ratings yet
- Shared LANDocument10 pagesShared LANapi-26570979No ratings yet
- 1 - Network DevicesDocument2 pages1 - Network DevicesDarlin DountsNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - The Basic of Computer NetworkingDocument5 pagesModule 5 - The Basic of Computer NetworkingErichelle EspineliNo ratings yet
- WAN Technologies and Components: H A P T E RDocument39 pagesWAN Technologies and Components: H A P T E RRohit AroraNo ratings yet
- Networking Fundamentals: A. Computer Network According To RangeDocument5 pagesNetworking Fundamentals: A. Computer Network According To RangeJohnArgielLaurenteVictorNo ratings yet
- Networks: An Interconnected WorldDocument23 pagesNetworks: An Interconnected WorldDAR HDGNo ratings yet
- 03 - Network Components and DevicesDocument3 pages03 - Network Components and DevicesBanjo De los SantosNo ratings yet
- Instructor Materials Chapter 1: WAN Concepts: CCNA Routing and Switching Connecting NetworksDocument29 pagesInstructor Materials Chapter 1: WAN Concepts: CCNA Routing and Switching Connecting NetworksAsy LpanNo ratings yet
- D Evice - To - D Evice C Ommunication U Nderlaying C Onverged H Eterogeneous N EtworksDocument10 pagesD Evice - To - D Evice C Ommunication U Nderlaying C Onverged H Eterogeneous N EtworksBaidalKochamNo ratings yet
- WAN Technologies AssignmentDocument13 pagesWAN Technologies AssignmentDavid Cleary100% (1)
- Chapter4-Networking - Term2Document12 pagesChapter4-Networking - Term2Mohammad MoosaNo ratings yet
- Partea2 Cap6 PDFDocument28 pagesPartea2 Cap6 PDFCristian M. VăduvaNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 Comms 3Document26 pagesMod 2 Comms 3Chester AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- COMP 202 ReviewerDocument3 pagesCOMP 202 ReviewerbarreraarielleannjNo ratings yet
- MaNET ReportDocument32 pagesMaNET Reportkhandelwalalok92% (13)
- From Ad Hoc To ICEBERG: Differences in Two Wireless Network EnvironmentsDocument28 pagesFrom Ad Hoc To ICEBERG: Differences in Two Wireless Network EnvironmentsPreet ChahalNo ratings yet
- Netacad and Quizlet CCNA4 Chapter 1 4Document107 pagesNetacad and Quizlet CCNA4 Chapter 1 4ChoyNo ratings yet
- Assignment IT LEcDocument12 pagesAssignment IT LEcgestebautistaNo ratings yet
- CPE 313-Data - and - Digital - Communication - Module-2Document20 pagesCPE 313-Data - and - Digital - Communication - Module-2RichardsNo ratings yet
- NetworkDocument14 pagesNetworkAmit ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- MIS3200 Class 2Document23 pagesMIS3200 Class 2Thái TrầnNo ratings yet
- Pranali D AWNDocument28 pagesPranali D AWNSivakamasundari PilaiporuthanNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Cables Carry Information Using - of Light and Designed For Long Distance Network Communications. (Pulses) 8Document4 pagesFiber Optic Cables Carry Information Using - of Light and Designed For Long Distance Network Communications. (Pulses) 8didie7950% (2)
- DCCCONNECTINGDEVICEDocument27 pagesDCCCONNECTINGDEVICEgaikwadsamruddhi240206No ratings yet
- Instructor Materials Chapter 1: WAN Concepts: CCNA Routing and Switching Connecting NetworksDocument29 pagesInstructor Materials Chapter 1: WAN Concepts: CCNA Routing and Switching Connecting NetworksRichard CheccaNo ratings yet
- 02 SDH PrinciplesDocument63 pages02 SDH Principlesajith9997No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Point-to-Point Connections: CCNA Routing and Switching Connecting Networks v6.0Document52 pagesChapter 2: Point-to-Point Connections: CCNA Routing and Switching Connecting Networks v6.0Thorn SithaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Networks Session 1Document50 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networks Session 1Msambili NdagaNo ratings yet
- Review of The Emotional Feature Extraction and Classification Using EEG SignalsDocument12 pagesReview of The Emotional Feature Extraction and Classification Using EEG Signalsforooz davoodzadehNo ratings yet
- UN Supplier Negotiation UNDP-NGA-00260,1 EnglishDocument13 pagesUN Supplier Negotiation UNDP-NGA-00260,1 EnglishclementNo ratings yet
- Literature Review: Bab 2 LiteraturDocument17 pagesLiterature Review: Bab 2 LiteraturAINA ZAWAWINo ratings yet
- Sans Icsps Ics418 0923 WebDocument2 pagesSans Icsps Ics418 0923 WebAjmul IndiaNo ratings yet
- BOOK AGILE 60-Questions-New-Scrum-Master-v1Document20 pagesBOOK AGILE 60-Questions-New-Scrum-Master-v1Julian de las CasasNo ratings yet
- ADA CSE - IT (3rd Year) Engg. Lecture Notes, Ebook PDF Download PART1Document82 pagesADA CSE - IT (3rd Year) Engg. Lecture Notes, Ebook PDF Download PART1Raja SekharNo ratings yet
- Arch Linux: A Simple, Lightweight Distribution For 32-Bit CpusDocument3 pagesArch Linux: A Simple, Lightweight Distribution For 32-Bit CpusManuel ReyNo ratings yet
- 9.CoCU Contact Hour - Network - L3Document2 pages9.CoCU Contact Hour - Network - L3محمدجوزيايNo ratings yet
- Internet and Cyber Security PresentationDocument13 pagesInternet and Cyber Security PresentationNihariNo ratings yet
- IPTV UK M3U Playlist Updated November 2022Document2 pagesIPTV UK M3U Playlist Updated November 2022Anderson Fernando33% (3)
- AWS SES 50K LIMIT (Demo)Document10 pagesAWS SES 50K LIMIT (Demo)Máy Chiết Rót Hữu ThànhNo ratings yet
- Desafios BackendDocument7 pagesDesafios BackendJean RosaNo ratings yet
- AZ-303 Exam - Free Actual Q&as, Page 1 - ExamTopicsDocument5 pagesAZ-303 Exam - Free Actual Q&as, Page 1 - ExamTopicsJosé Omar Atayde0% (1)
- Equationsb YcmaDocument10 pagesEquationsb YcmaAnan LeeNo ratings yet
- M Tech ITDocument61 pagesM Tech ITPoornima.BNo ratings yet
- 5 MICROPROCESSOR 8086 Branching InstructionDocument30 pages5 MICROPROCESSOR 8086 Branching InstructionMunazza FatmaNo ratings yet
- Harshit Sharma: House Keeping SystemDocument2 pagesHarshit Sharma: House Keeping SystemshadowNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Nagpur University LLMDocument94 pagesSyllabus of Nagpur University LLMHariomMaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Acceptance of The Terms of ServiceDocument150 pagesAcceptance of The Terms of ServiceANKIT VERMA CLCNo ratings yet
- 3 Lab ManualDocument124 pages3 Lab ManualSejal SitaniNo ratings yet
- Congestion Control and Quality of ServiceDocument27 pagesCongestion Control and Quality of ServiceFarhan TariqNo ratings yet
- AutoMobile Service STNDocument74 pagesAutoMobile Service STNAswin PrasannanNo ratings yet
- Oracle Database Upgrade MethodsDocument20 pagesOracle Database Upgrade MethodshassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter8 - VHDL - Sequential CircuitsDocument64 pagesChapter8 - VHDL - Sequential CircuitsRagheb IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Sbest PracticesDocument36 pagesSbest PracticesMarlene BraidsNo ratings yet
- 808D OP Turning 0113 en PDFDocument118 pages808D OP Turning 0113 en PDFemir_delic2810100% (1)
- ACBS Chapter ManualDocument12 pagesACBS Chapter ManualJon100% (2)
- Evo Ma10: Scanning Electron MicroscopeDocument14 pagesEvo Ma10: Scanning Electron MicroscopeVidas Makarevicius100% (1)