Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Futuro Perfeccto
Futuro Perfeccto
Uploaded by
Confecciones ColombiaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Futuro Perfeccto
Futuro Perfeccto
Uploaded by
Confecciones ColombiaCopyright:
Available Formats
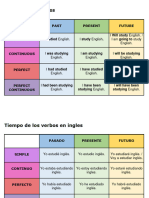
Future perfect and future perfect continuous
Future perfect:
Use the future perfect to emphasize that something will be completed or
achieved by a particular point in the future.
The grammar rules are:
Affirmative
subject + will have + verb (past participe)
Negative
subject + won’t have + verb (past participe)
Interrogative
will + subject + have + verb (past participe) + ?
For example:
Affirmative
He will have written his book in one month.
Negative
He won’t have written his book in one month.
Interrogative
Will he have written his book in one month ?
The future perfect is always accompanied by a specific moment.
Future perfect continuous
Use the future perfect continuous to emphasize the duration of an activity in
progress at a particular point in the future.
The grammar rules are:
Affirmative
subject + will have been + verb (-ing)
Negative
subject + won’t have been + verb (-ing)
Interrogative
will + subject + have been + verb (-ing) + ?
For example:
Affirmative
By this time tomorrow, Joon will have been traveling for 24 hours.
Negative
By this time tomorrow, Joon won’t have been traveling for 24 hours.
Interrogative
Will Joon have been traveling for 24 hours by this time tomorrow ?
You might also like
- The English Tenses - Practical Grammar Guide PDFDocument4 pagesThe English Tenses - Practical Grammar Guide PDFcharliie estradaNo ratings yet
- Summarizing Anisa Yuniar Safira 20059198 Review of TensesDocument5 pagesSummarizing Anisa Yuniar Safira 20059198 Review of TensesAlifiany MardhiahNo ratings yet
- Perfect TenseDocument18 pagesPerfect TenseBiancaNo ratings yet
- Tenses 2Document12 pagesTenses 2nurmaulia sukmaNo ratings yet
- Progressive and Future Tense Group 4Document9 pagesProgressive and Future Tense Group 4Daffa YusufNo ratings yet
- Future Perfect Continuous.Document1 pageFuture Perfect Continuous.Diseño RepsNo ratings yet
- FUTURE TENSES IN ENGLISH FinalDocument3 pagesFUTURE TENSES IN ENGLISH FinalTaehyung KimNo ratings yet
- Cute Little Notes SlidesMania - DocsDocument38 pagesCute Little Notes SlidesMania - Docsdebasissahu09471No ratings yet
- Future Perfect TenseDocument3 pagesFuture Perfect TenseDost JanNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument3 pagesFuture TensesMatheus GuilhermeNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense: Usually, SeldomDocument6 pagesSimple Present Tense: Usually, Seldomrara wiladhatikaNo ratings yet
- 'Lesson' Future Perfect Vs Future Simple-1Document4 pages'Lesson' Future Perfect Vs Future Simple-1salmafrkoussNo ratings yet
- Tense Definition Structure ExampleDocument6 pagesTense Definition Structure Exampleshazzadbd1No ratings yet
- Group 4purposive CommunicationDocument19 pagesGroup 4purposive Communicationbmiranda.stiNo ratings yet
- Company. Not Work Hard For This Company. This Company?: Simple Present TenseDocument5 pagesCompany. Not Work Hard For This Company. This Company?: Simple Present Tensemaulana iqbalNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Written ReportDocument12 pagesGroup 2 Written ReportPRECIOUS KAYE MARIE BANTIGUENo ratings yet
- Future Tense: By: Nurmi Yanti Prima 2010070120026 Mutia Angraini 2010070120019Document9 pagesFuture Tense: By: Nurmi Yanti Prima 2010070120026 Mutia Angraini 2010070120019Nurmi Yanti PrimaNo ratings yet
- 16 Tenses in English and Part of SpeechDocument10 pages16 Tenses in English and Part of SpeechFarhan Maulana HajNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense: Company. Not Work Hard For This Company. For This Company?Document5 pagesSimple Present Tense: Company. Not Work Hard For This Company. For This Company?Nayanika GamingNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect TenseDocument11 pagesPresent Perfect TenseAgusRivaiAnwarAriefrsNo ratings yet
- A. Understanding TenseDocument4 pagesA. Understanding TenseNovi LusianaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense: Seldom This CompanyDocument13 pagesSimple Present Tense: Seldom This CompanySkinsa BeautyNo ratings yet
- Future Progressive TenseDocument6 pagesFuture Progressive TenseBrenda Ting StNo ratings yet
- Future TenseDocument3 pagesFuture TenseBlue EagleNo ratings yet
- Wendy Vanegas Reina: Decimo 2018Document7 pagesWendy Vanegas Reina: Decimo 2018Cristian ReinaNo ratings yet
- Kel 2Document15 pagesKel 2ricoalvayotobingNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument20 pagesInglesJesús RamsésNo ratings yet
- Future Perfect Tense & Future Perfect Continous TenseDocument6 pagesFuture Perfect Tense & Future Perfect Continous TenseKintan Budi Kresnanda100% (1)
- Uses of TensesDocument17 pagesUses of TensesMsPushpanjali PatilNo ratings yet
- 16 Tenses Dalam Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pages16 Tenses Dalam Bahasa InggrisJonash C. Murdiny TulisNo ratings yet
- 12 Tenses in EnglishDocument5 pages12 Tenses in EnglishEvelin CastroNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument7 pagesSimple Present TenseRini NgidihoNo ratings yet
- Instructions or Directions:: For Repeated Actions or EventsDocument3 pagesInstructions or Directions:: For Repeated Actions or EventsAvon Gaming DextinNo ratings yet
- Aspects of VerbsDocument77 pagesAspects of VerbsnonNo ratings yet
- Simple Past and Present PerfectDocument4 pagesSimple Past and Present PerfectGilder Franz Inga CalcinaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Kel9Document8 pagesTugas Kel9pingkananggun19No ratings yet
- 16 TensesDocument10 pages16 TensesOscariza AristyasNo ratings yet
- Tiempos Verbales & Sus UsosDocument5 pagesTiempos Verbales & Sus UsosAllan BertrandNo ratings yet
- ProgressiveDocument5 pagesProgressiveDaisylineCaleonCruzNo ratings yet
- 4 Future TenseDocument3 pages4 Future TenseitsTecthyNo ratings yet
- 16 Tenses Bahasa Inggris: Digunakan Untuk Menunjukkan Fakta, Kebiasaan, Dan Keadaan Umum Yang Terjadi Pada Saat IniDocument8 pages16 Tenses Bahasa Inggris: Digunakan Untuk Menunjukkan Fakta, Kebiasaan, Dan Keadaan Umum Yang Terjadi Pada Saat Inismk Syamsul ArifinNo ratings yet
- 16 Simple Pas TenseDocument7 pages16 Simple Pas TenseBrow Nies ParlayNo ratings yet
- Ketentuan Pemakaian TensesDocument8 pagesKetentuan Pemakaian TensesNovilia FriskaNo ratings yet
- Tiempos Verbales InglesDocument5 pagesTiempos Verbales InglesMarta XxNo ratings yet
- TensisDocument16 pagesTensisPuja Nurmala100% (1)
- Makalah B. Inggris UbisDocument6 pagesMakalah B. Inggris UbisUbis LandriNo ratings yet
- Marshanda Callysta F.S (001) Nur Muthahirah M.R (019) Fina Hilwatul Quthroh (086) M. Fikri Hanif (101) Zahara Aghnia MDocument23 pagesMarshanda Callysta F.S (001) Nur Muthahirah M.R (019) Fina Hilwatul Quthroh (086) M. Fikri Hanif (101) Zahara Aghnia MNadia Ananda PutriNo ratings yet
- Sesion 11Document20 pagesSesion 11Luigi RecuayNo ratings yet
- English PresentationDocument21 pagesEnglish PresentationTharindu DilshanNo ratings yet
- Cours Anglais Général 01Document17 pagesCours Anglais Général 01AmoyeNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument7 pagesTensesSdkanisius WatuagungNo ratings yet
- Rumus TensesDocument17 pagesRumus TensesRizal MuhaiminNo ratings yet
- 16 Tenses in EnglishDocument8 pages16 Tenses in EnglishNovaSoniaChuaNo ratings yet
- 44 All TensesDocument3 pages44 All TensesjeikodelarosaNo ratings yet
- Bhs Inggris Session 3Document11 pagesBhs Inggris Session 3Nina EmanuelaNo ratings yet
- 16 Tenses Bahasa InggrisDocument7 pages16 Tenses Bahasa InggrisFajar PambudiNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument20 pagesTensesLucila RoifeNo ratings yet
- SIMPLE PRESENT-1 SusiDocument3 pagesSIMPLE PRESENT-1 SusiUulAmrelNo ratings yet