Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Midterm Exam 1: This Page Is Scratch Paper
Midterm Exam 1: This Page Is Scratch Paper
Uploaded by
Alejandro MiguelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Midterm Exam 1: This Page Is Scratch Paper
Midterm Exam 1: This Page Is Scratch Paper
Uploaded by
Alejandro MiguelCopyright:
Available Formats
Scratch Paper – Page A
Midterm Exam 1
Chem 3B, Fall 2018
Monday, October 1, 2018
7:00 – 9:00 pm
You have 120 minutes to complete this exam.
Please provide all answers in the space provided. Work drawn
in the margins may not be picked up by the scanner and
therefore will not be graded.
Point values are listed within each question. The exam is worth
200 points total.
This Page is Scratch Paper
Please tear this cover page and the next page (amino acid chart) off at the start of the exam. They will not be
collected, scanned, or graded, so make sure your answers are copied into the appropriate location on your exam.
Chemistry 3B Fall 2018 Midterm Exam #1
Scratch Paper – Page B
Chemistry 3B Fall 2018 Midterm Exam #1
Scratch Paper – Page C
Chemistry 3B Fall 2018 Midterm Exam #1
Scratch Paper – Page D
Chemistry 3B Fall 2018 Midterm Exam #1
Name _______________________ SID____________________ Page 1 of 8
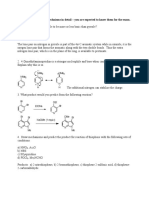
1. Ramipril, pictured below, is medication used to treat high blood pressure.
A. Fill in each box with the name of each circled functional group. (4 x 2 = 8 pt)
amide amine
Ph
N O
N
H
O O O ester
carboxylic acid O
H
Ramipril
(a blood pressure medication)
B. Fill in one multiple-choice circle per row to indicate the hybridization of each lone pair. (8 pt)
s p sp sp2 sp3
s p sp sp2 sp3
Ph
s p sp sp2 N O
sp3 N
H
s p sp sp2 sp3 O O O
O
s p sp sp2 sp3
H
s p sp sp2 sp3
C. Complete the drawings of the predominant protonation state of Ramipril at each pH by adding hydrogens
and charges. (6 pt)
Ph Ph Ph
N O N O N O
N N N
H2 H2 H
O O O O O O O O O
OH O O
protonation state of Ramipril protonation state of Ramipril protonation state of Ramipril
at pH = 1 at pH = 7 at pH = 12
(add hydrogens and charges to finish these structures)
Chemistry 3B Fall 2018 Midterm Exam #1
Name _______________________ SID____________________ Page 2 of 8
D. Heating an acidic aqueous solution of Ramipril causes two sequential hydrolysis reactions. Reaction A
occurs at moderate temperature, while Reaction B requires high temperature and long reaction time. Draw
the product(s) in each box. (10 pt)
Ph Ph
Reaction A
HCl (excess)
N O N OH HO
N N
H H2O (solvent) H2
O O O O O O
OH OH
Product(s) after ONE hydrolysis (ignore stereochemistry)
(hydrolysis of only the more reactive site)
Reaction B
HCl (excess), H2O (solvent)
high temperature, long reaction time
Ph
NH2 HO OH HO
N
H
O O O
OH
Product(s) after TOTAL hydrolysis (ignore stereochemistry)
E. Explain how resonance (conjugation) causes the difference in reactivity demonstrated by Reaction A vs.
Reaction B. (5 pt)
Nitrogen is a stronger resonance electron donor than oxygen (due to the lower electronegativity of
nitrogen than oxygen).
Conjugation between the heteroatom and the carbonyl, as demonstrated by the resonance structures
below, is a stabilizing effect that makes the carbonyl a less reactive electrophile.
O O
(weaker, less stabilizing)
O O
O O
(stronger, more stabilizing)
N N
answer must address "conjugation" or "resonance" to earn full credit.
Chemistry 3B Fall 2018 Midterm Exam #1
Name _______________________ SID____________________ Page 3 of 8
2. Fill in the missing reagents and structures in the following synthesis schemes. Assume that only one major
product forms in each reaction. Do not combine multiple reaction steps in a single box (no numbered steps
within a box). (9 x 5 = 45 pt)
O
S HCl (excess)
Cl Cl 1. Mg
MeOH (solvent)
OH Cl 2.
CO2 O O
O OMe
CrO3 HCl
H2SO4, H2O
MeOH
O O
OH OH OMe
NH2 1.
LiAlH4
O
O + workup
NH 2. H3O
OMe NH2
(+ MeOH)
Chemistry 3B Fall 2018 Midterm Exam #1
Name _______________________ SID____________________ Page 4 of 8
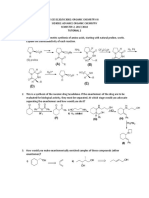
3. Mechanisms, Catalysts, and Equilibirum
A. Draw a curved arrow mechanism for the following reaction. (10 pt)
O O
+ HO NaH (0.10 equiv.) + HS
R R
S O
O
H (regenerated catalyst)
Na H O
pre-catalyst
O O
O H
+ H H R R
S S O
O S
O R
(generated O
catalyst)
B. Explain the following statement regarding the reaction above: “A catalytic amount of NaH is used in
this reaction, and NaH is not the limiting reagent in this reaction. However, NaH is not acting as a
catalyst in this reaction” (5 pt)
A catalytic amount (< 1 equiv.) of NaH is used. The NaH is not a "catalyst" because it does not get
regenerated ever. The actual catalyst in this reaction is EtONa, a catalytic amount of which is made by NaH
deprotonating EtOH at the start of the reaction.
C. Draw a curved arrow mechanism for the following reaction. (10 pt)
O O
+ HS HCl (cat.) + HO
R R
O S
H Cl Cl
H
O
OH
R
R OH OH OH S
O R R H Cl R
O O O
S S S H HO
H
Cl
HS
D. Draw an equilibrium arrow and select the corresponding Keq, and explain which side (if either) is favored
and why: (5 pt)
O O
R + HS R + HO
O S
equilibrium arrow
Which side of this reaction scheme (if either) is favored? Why?
Keq < 1
Left side is favored.
Keq = 1 The sulfur has larger orbitals and therefore worse conjugation (p orbital overlap) with
the carbonyl pi system than oxygen does, so the thioester is less stabilized and is
Keq >1 more reactive than the ester.
(Compare to the explanation for acyl chloride reactivity)
Chemistry 3B Fall 2018 Midterm Exam #1
Name _______________________ SID____________________ Page 5 of 8
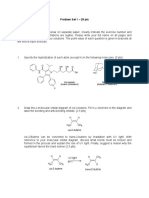
4. Predict the Products
A. Predict the organic product(s) from the following reactions. Where relevant, show all stereoisomers. (3 x
8 = 32 pt)
O O
O D D O H 2N H 2N
O
+ EtO OEt Ph D Ph D
H
N
N O D O
Ph H
EtO OEt
O D O
O
include stereoisomer(s) if relevant N
EtO OEt
H
N
N
Ph D H
O
O O O O O
O +
MgBr
(excess) O O
H
O O N include stereoisomer(s) if relevant
Cy
Boc N
N Cy
H
activated intermediate
Amino group at C terminus is not nucleophilic H 2N
O O
Phe due to amide resonance stabilization Cy
N
C N
H 2N O OH O NH
O O O N O
+ Cy
N O N O N
H H
NH2
O
nucleophilic Pro
site Leu Cy Cy
Boc N N
include stereoisomer(s) if relevant H H
B. Name the peptide product from the reaction above (using 3-letter codes). (hint: use the amino acid chart
handout. Include substituent(s) on the N- and/or C-terminus in the name) (8 pt)
Name the peptide product above (using 3-letter codes) Boc-Leu-Pro-Phe-NH2
Chemistry 3B Fall 2018 Midterm Exam #1
Name _______________________ SID____________________ Page 6 of 8
5. Thionyl Chloride
A. Predict the product of reaction A, and name the new functional group in product A. (5 + 2 = 7 pt)
O O
O Reaction A
OH + Cl
S + SO2 + HCl
Cl Cl
Name of product A functional group acyl chloride
B. Name the new functional group in product B, then draw a curved arrow mechanism for reaction B that
DOES NOT have any intermediates that contain the same functional group as product A. (2 + 10 = 12 pt)
O
O
OH O
+
OH S O + SO2 + HCl
Cl Cl
O O
anhydride Name of product B functional group
Avoid making any intermediates containing the same functional group as product A
OH
O O H O O
Cl
OH
O H O H O
O Cl O O
S O H
O Cl O Cl
O S S Cl
O O O
S
O
Chemistry 3B Fall 2018 Midterm Exam #1
Name _______________________ SID____________________ Page 7 of 8
6. Penicillin and DD-transpeptidase
DD-transpeptidase is an enzyme that catalyzes the crosslinking of peptidoglycan in bacterial cell walls. As
shown in the scheme below, peptidoglycan replaces a D-alanine on a peptide chain.
A. The mechanism includes an acyl enzyme intermediate, using an active site catalytic triad that includes a
base and a nucleophilic serine side chain. Choose the statement that best describes the reaction, then draw
the mechanism in the space below, and circle and label the “acyl enzyme intermediate” (12 pt)
peptidoglycan replaces D-Ala at the amino terminus of the peptide
(choose one)
peptidoglycan replaces D-Ala at the carboxyl terminus of the peptide
R' R'' Enz OH R' R''
O O
H H
Pep N EnzB: Pep N R + H 2N
N O + H 2N R N O
H H
O DD-transpeptidase O
(an enzyme) D-Ala
Pep-D-Ala-D-Ala peptidoglycan Pep-D-Ala-peptidoglycan
- Ignore stereochemistry
- Circle and label portions of the pre-printed structures above to define any abbreviations you use
- Circle and label the "acyl enzyme intermediate" in your mechanism
H H R' H
Enz O Enz O R' N N
R'' R''
Enz O
EnzB: O O
EnzBH
Pep-D-Ala-D-Ala
EnzB H
R O H2
R'
N
H Enz O R' H 2N R''
O H2N R R'' Enz O
N O
H
Enz O R' D-Ala
(see alternatives below) Acyl Enzyme
Intermediate
EnzB:
R R
O NH NH
Pep-D-Ala-peptidoglycan
Enz O Enz O O
R'
R'
EnzB H
Enz OH
EnzB:
EnzB H
R
R R Enz O
EnzB:
H or NH
O N N H O
H O H
Enz O R' Enz O Enz OH R'
R'
EnzB: EnzB: Pep-D-Ala-peptidoglycan
Chemistry 3B Fall 2018 Midterm Exam #1
Name _______________________ SID____________________ Page 8 of 8
B. Penicillins are a class of antibiotics that kill bacteria by inhibiting DD-transpeptidase, leading the cell
walls to weaken and eventually burst open. The penicillin structure mimics the peptide-D-Ala-D-Ala
structure, as demonstrated by the numbering on the structures below.
i. Select the multiple choice options that best describe the nitrogen 4 geometry and lone pair hybridization
in Pep-D-Ala-D-Ala. (4 pt)
ii. Add stereochemistry (wedged or dashed bonds) to the Pep-D-Ala-D-Ala structure above based on the
name “D-Ala”, and add the corresponding stereochemistry to the Penicillin structure, based on the
structure alignment. (6 pt)
linear H 5 H H
Pep N (R) R N S
trigonal planar 1 2 H 1
(R) 5
2
tetrahedral O 3 4
N (R)
8
O 3 4
N (R) 8
6 6
geometry of nitrogen 4 O 7 O 7
OH OH
s p sp sp2 sp3 O O
hybridization of nitrogen 4 lone pair
Pep-D-Ala-D-Ala Penicillin
modify to show stereochemistry modify to show stereochemistry
(make bond(s) wedged or dashed) (make bond(s) wedged or dashed)
based on the name based on comparison to Pep-D-Ala-D-Ala
iii. The nitrogen labeled “4” in the Penicillin structure is forced into a tetrahedral geometry due to ring
strain. How does that affect the reactivity of Penicillin relative to Pep-D-Ala-D-Ala in the enzyme active
site? Explain the relationship between this geometry and reactivity, being specific about the type of
reactivity. (Hint: see mechanism on previous page) (5 pt)
Carbonyl 3 is the electrophilic site in both molecules. The conjugation with nitrogen 4 in the
Pep-D-Ala-D-Ala structure (lone pair in p orbital) stabilizes it and makes it less electrophilic.
The tetrahedral shape in Penicillin prevents conjugation (lone pairs need to be in a p orbital
to participate in resonance) so carbonyl 4 in Penicillin is more electrophilic.
iv. Draw the structure of the inactivated enzyme, which could be described as “the active site serine has
been acylated by penicillin”. (10 pt)
R
H 1
R N 2 5 S O NH
1
3 O 2
O N Enz OH 3
5 S
O 4 6
O HN
OH EnzB: 4 6
O
Enz OH
Penicillin transpeptidase enzyme O
( + EnzB:)
the active site serine has been acylated by penicillin
(ignore stereochemistry)
Chemistry 3B Fall 2018 Midterm Exam #1
You might also like
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Ullmann's Enc. of Industrial ChemistryDocument72 pagesUllmann's Enc. of Industrial ChemistrySlim Toumi50% (2)
- Midterm Exam 1: This Page Is Scratch PaperDocument12 pagesMidterm Exam 1: This Page Is Scratch PaperAlejandro MiguelNo ratings yet
- Molecules 20 03821Document20 pagesMolecules 20 03821putryapurnomo.21No ratings yet
- Journal 2Document6 pagesJournal 2vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Chem-353-Lecture 2Document10 pagesChem-353-Lecture 2Caleb AsharleyNo ratings yet
- V1 JEE Advanced 2024 Chemistry With Solution Paper-1Document17 pagesV1 JEE Advanced 2024 Chemistry With Solution Paper-1Sandeep JainNo ratings yet
- Journal 3Document5 pagesJournal 3vidhyaNo ratings yet
- JURNAL Sintesis Semi KarbazoneDocument5 pagesJURNAL Sintesis Semi Karbazoneluluatul maghfirohNo ratings yet
- A Novel Route Towards Cycle-Tail Peptides Using Oxime Resin: Teaching An Old Dog A New TrickDocument13 pagesA Novel Route Towards Cycle-Tail Peptides Using Oxime Resin: Teaching An Old Dog A New Tricksyed aftab hussainNo ratings yet
- Heterocycle AnswersDocument6 pagesHeterocycle AnswersChris WongNo ratings yet
- Antisense Oligonucleotide Biotechnology, Applications and FutureDocument29 pagesAntisense Oligonucleotide Biotechnology, Applications and FuturesurojitarpitaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Novel Azo Dyes Derived From 8hydroxyquinoline 1Document7 pagesSynthesis of Novel Azo Dyes Derived From 8hydroxyquinoline 1Darian HerascuNo ratings yet
- Matheus Síntese de Produto Natural 439Document4 pagesMatheus Síntese de Produto Natural 439MATHEUS PHILYPI ALVES VAZNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SynopsisDocument7 pagesChemistry SynopsisDr Prashant Shihora100% (1)
- Asymmetric SynthesisDocument25 pagesAsymmetric SynthesisHimanshu Kumar bharti 375 ctcpNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity of Semicarbazone DerivativesDocument5 pagesSynthesis and Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity of Semicarbazone DerivativesWalid EbaiedNo ratings yet
- Unsual Mecanismo DFT Arcilla LeerDocument7 pagesUnsual Mecanismo DFT Arcilla LeerJosé Guadalupe García EstradaNo ratings yet
- 2023-03-24 Printed As PDF Presi Pt06Document3 pages2023-03-24 Printed As PDF Presi Pt06sauronsauronNo ratings yet
- On The Electrophilic Reactivities of Acarbonyl Heterocylces and ArenesDocument7 pagesOn The Electrophilic Reactivities of Acarbonyl Heterocylces and ArenesFinn NelsonNo ratings yet
- Expt. 5 Determination of PK of An Indicator Using SpectrophotometryDocument13 pagesExpt. 5 Determination of PK of An Indicator Using SpectrophotometryjepglNo ratings yet
- 2006-CHM6108 - L5L6 SlidesDocument52 pages2006-CHM6108 - L5L6 Slidesaidar.seralinNo ratings yet
- Phosphonate Prodrugs: An Overview and Recent Advances: ReviewDocument20 pagesPhosphonate Prodrugs: An Overview and Recent Advances: ReviewJairo CariñoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2Marlinda Marcus LundangNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological and Synthetic Profile of Benzothiazepine: A ReviewDocument9 pagesPharmacological and Synthetic Profile of Benzothiazepine: A ReviewRao Zikar IslamNo ratings yet
- Benzodiazepines andDocument49 pagesBenzodiazepines andryrahulyadav4No ratings yet
- 31p NMRDocument17 pages31p NMRperulageaNo ratings yet
- 8 tRNA Synthetase Genetic Code and Anticodon Relation FinalsDocument29 pages8 tRNA Synthetase Genetic Code and Anticodon Relation Finalsbushra vainceNo ratings yet
- 5 Lec HeterocyclicDocument19 pages5 Lec HeterocyclicCM DianaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Amino Acids PDFDocument56 pagesChemistry Amino Acids PDFChitrasen GuptaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document3 pagesProblem Set 1Ajj JajNo ratings yet
- N-Demethylation of AlkaloidsDocument13 pagesN-Demethylation of AlkaloidsPhuongNo ratings yet
- L1 SlidesDocument13 pagesL1 SlidesAakash LawaNo ratings yet
- Answers ch10Document6 pagesAnswers ch10김아진No ratings yet
- Practical FCHG412 Prodrugs: Module Outcomes For The PracticalDocument14 pagesPractical FCHG412 Prodrugs: Module Outcomes For The PracticalGreg RalphNo ratings yet
- Chemdraw Kimia MedisinalDocument6 pagesChemdraw Kimia MedisinalRisky DaniarNo ratings yet
- Panel 2.05bDocument1 pagePanel 2.05bchinurathoreNo ratings yet
- Karboksilne Kisline: Analiza in Nadzor Zdravil Fakulteta Za Farmacijo Oktober 2009Document57 pagesKarboksilne Kisline: Analiza in Nadzor Zdravil Fakulteta Za Farmacijo Oktober 2009api-3814389No ratings yet
- FF - MC LECTURE PPT 2Document18 pagesFF - MC LECTURE PPT 2Dila AprilliaNo ratings yet
- Harigopal S Sawarkar 2020 SYNTHESIS AND ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITIES OF NOVEL 1,3,4-THIADIAZOLE BEARING CARBOXAMIDES DERIVATIVESDocument10 pagesHarigopal S Sawarkar 2020 SYNTHESIS AND ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITIES OF NOVEL 1,3,4-THIADIAZOLE BEARING CARBOXAMIDES DERIVATIVESshubha shrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Hetero AromaticsDocument139 pagesChemistry of Hetero Aromaticslalitarun100% (1)
- 10 1016@j BMCL 2019 126712Document10 pages10 1016@j BMCL 2019 126712Omar Nassir MoftahNo ratings yet
- 2023-03-24 Printed As PDF Presi Pt03Document2 pages2023-03-24 Printed As PDF Presi Pt03sauronsauronNo ratings yet
- Diels-Alder ExperimentDocument7 pagesDiels-Alder ExperimentSimranjit Kaur100% (3)
- Addition To CCDocument17 pagesAddition To CCHadiNo ratings yet
- Halogen DerivativeDocument32 pagesHalogen Derivativesachin pantNo ratings yet
- Synthesis, in Silico and in Vitro Anti-Proliferative Studies of Some Novel Benzamido Substituted IMIDAZO (1,2-b) PYRIDAZIN-2-ONESDocument17 pagesSynthesis, in Silico and in Vitro Anti-Proliferative Studies of Some Novel Benzamido Substituted IMIDAZO (1,2-b) PYRIDAZIN-2-ONESQuty Papa KannaNo ratings yet
- 3,5-Bis (2-Indolyl) Pyridine and 3 - ( (2-Indolyl) - 5-Phenyl) Pyrid PDFDocument22 pages3,5-Bis (2-Indolyl) Pyridine and 3 - ( (2-Indolyl) - 5-Phenyl) Pyrid PDFpaiaravindNo ratings yet
- WittigDocument22 pagesWittigMusic Generation AT -No ratings yet
- Functional Group Reactions: C Synthesis Strategies, Chem 315/316 / Beauchamp 1Document19 pagesFunctional Group Reactions: C Synthesis Strategies, Chem 315/316 / Beauchamp 1Zia urRehman100% (1)
- 9-Carbonyl 2019 PDFDocument1 page9-Carbonyl 2019 PDFNoel SibyNo ratings yet
- DasjkfjdsfjdslDocument9 pagesDasjkfjdsfjdslRhyme CakesNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument20 pagesDNA ReplicationFrie An PanteNo ratings yet
- Alkaloid S1Document142 pagesAlkaloid S1Faisal MNo ratings yet
- CH 25Document18 pagesCH 25Srnsoumya NathNo ratings yet
- Organometallic ChemDocument22 pagesOrganometallic ChemaltyeizNo ratings yet
- 2016 Delt Paper Revision Accepted SupplementaryDocument11 pages2016 Delt Paper Revision Accepted SupplementarypufuNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of β: Chemistry Centre, School of Sciences, University of Minho e-mail: amcampos@quimica.uminho.ptDocument10 pagesSynthesis of β: Chemistry Centre, School of Sciences, University of Minho e-mail: amcampos@quimica.uminho.ptAnonymous lsnDTjvNo ratings yet
- StereochemistryDocument31 pagesStereochemistryAnonymous TCbZigVqNo ratings yet
- Kap 12,13,17, IIDocument12 pagesKap 12,13,17, IImuraliNo ratings yet
- Chapt16 LectureDocument85 pagesChapt16 LectureArief BudhyantoroNo ratings yet
- Current Progress of Pt-Based ORR Electrocatalysts For PEMFCs An Integrated View Combining Theory and ExperimentDocument16 pagesCurrent Progress of Pt-Based ORR Electrocatalysts For PEMFCs An Integrated View Combining Theory and ExperimentadarshNo ratings yet
- Sulfur-Doped Graphene As An EfficientDocument7 pagesSulfur-Doped Graphene As An EfficientJorge VazquezNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Calorific Value of Natural Gas by Different MethodsDocument9 pagesDetermination of The Calorific Value of Natural Gas by Different MethodsMichael Castro AbuduNo ratings yet
- An Industrial Perspective On Catalysts For Low-Temperature CO2 ElectrolysisDocument11 pagesAn Industrial Perspective On Catalysts For Low-Temperature CO2 ElectrolysisHarth SolawNo ratings yet
- Four Challenges For Nickel Steam-Reforming CatalystsDocument8 pagesFour Challenges For Nickel Steam-Reforming CatalystsReza Rhi100% (2)
- G22 Serapion-Module 9 EnzymesDocument3 pagesG22 Serapion-Module 9 Enzymestherese angelieNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Bioprocess PDFDocument137 pagesUnit1 Bioprocess PDFChris PenielNo ratings yet
- Ytterbium Triflate Catalyzed Synthesis oDocument42 pagesYtterbium Triflate Catalyzed Synthesis oElisabeta StamateNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument41 pagesIntroductionابوالنور عمارNo ratings yet
- 2021 Fast Hydropyrolysis of Biomass ConversionDocument11 pages2021 Fast Hydropyrolysis of Biomass ConversionLiliana Ale RuizNo ratings yet
- Catalysis PDFDocument23 pagesCatalysis PDFGoutam Giri100% (1)
- A Kinetic Model For Methanol-To-Propylene Process in The Presence of Co-FeedDocument50 pagesA Kinetic Model For Methanol-To-Propylene Process in The Presence of Co-FeedAdi permadiNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Studies of Ketazine Formation PDFDocument6 pagesKinetic Studies of Ketazine Formation PDFkamesh_che009100% (1)
- Kinetic and Mechanistic Aspects For CO2 Reforming of Methane Over Ni Based CatalystDocument17 pagesKinetic and Mechanistic Aspects For CO2 Reforming of Methane Over Ni Based CatalystMarcus NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process: Phenol Plant Process DiagramDocument6 pagesManufacturing Process: Phenol Plant Process DiagramshisokarNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (191: Yamamoto, Shibukawa SyukiDocument6 pagesUnited States Patent (191: Yamamoto, Shibukawa SyukiUntung SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Ethylene and Acetylene PlantDocument405 pagesEthylene and Acetylene Plantkatamani temple75% (4)
- Computational Modeling of Homogeneous Catalysis - Feliu MaserasDocument375 pagesComputational Modeling of Homogeneous Catalysis - Feliu MaserasPatrașcu IulianNo ratings yet
- Reactor TypesDocument81 pagesReactor Typesshiel175No ratings yet
- Enzyme Commission Number (EC Number)Document1 pageEnzyme Commission Number (EC Number)Sunil BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Piazzesi, PHD Thesis, ETH Zurich, 2006Document164 pagesPiazzesi, PHD Thesis, ETH Zurich, 2006Alfin AdiNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument2 pagesEnzymessimplyshriyaNo ratings yet
- Catalyst DefinitionDocument17 pagesCatalyst DefinitionTRIBRATA BASKORONo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document12 pagesChapter 11anilkumarappapurapu100% (2)
- Experimental Methods in Catalytic KineticsDocument13 pagesExperimental Methods in Catalytic Kineticsmarcos carrilloNo ratings yet
- Effect of Temperature On Enzyme Kinetics StudyDocument7 pagesEffect of Temperature On Enzyme Kinetics StudyYvonne MunNo ratings yet
- Potassium Capture by Kaolin and Coal Fly Ash DTUDocument178 pagesPotassium Capture by Kaolin and Coal Fly Ash DTUPrakash WarrierNo ratings yet
- MSC in Chemical and Bioengineering Study Plan ETH ZurichDocument1 pageMSC in Chemical and Bioengineering Study Plan ETH ZurichMohammed SaifNo ratings yet