Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stresses and Strains
Stresses and Strains
Uploaded by
MiraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stresses and Strains
Stresses and Strains
Uploaded by
MiraCopyright:
Available Formats
Stresses and strains
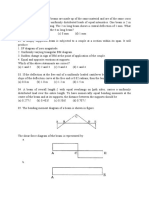
7.4 A cylindrical soil, 75 mm in diameter and 150 mm long, is axially compressed. The length decreases
to 147 mm and the radius increases by 0.3 mm.
Calculate: (a) The axial and radial strains (b) The volumetric strains (c) Poisson’s ratio
7.5 A cylindrical soil, 75 mm in diameter and 150 mm long, is radially compressed. The length increases
to 153 mm and the radius decreases to 37.2 mm.
Calculate: (a) The axial and radial strains (b) The volumetric strains
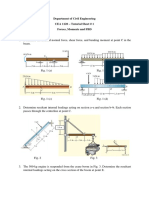
7.6 A soil, 100 mm 3 150 mm 3 20 mm high, is subjected to simple shear deformation (see Figure 7.3).
The normal force in the Z direction is 1 kN and the shear force is 0.5 kN. The displacements at the top of
the soil in the X and Z directions are Dx 5 1 mm and Dz 5 1 mm.
Calculate: (a) The shear and normal stresses (b) The axial and shear strain
You might also like
- PROBLEMAS Torsion Mechanics of Materials 24 Resolver Multiplos de TresDocument24 pagesPROBLEMAS Torsion Mechanics of Materials 24 Resolver Multiplos de Treslhhortuah100% (2)
- Column SplicingDocument31 pagesColumn Splicingprabhu8150% (4)
- Gear PrimeDocument7 pagesGear PrimeEjNo ratings yet
- Production Question Set 2Document70 pagesProduction Question Set 2ErKRGautamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheets SOMDocument20 pagesTutorial Sheets SOMPriyanshu Sharma100% (1)
- Som MCQDocument14 pagesSom MCQVignesh Vicky0% (2)
- CH 12 Areas Related To Circles WorksheetDocument3 pagesCH 12 Areas Related To Circles WorksheetRuzal AnandNo ratings yet
- ME 361 Dynamics of Machinery Mech. Dept./ IDL Knust Assignment I Unit 1Document6 pagesME 361 Dynamics of Machinery Mech. Dept./ IDL Knust Assignment I Unit 1pjrfhn7596No ratings yet
- Practicals Combined Structural Geology 2014Document11 pagesPracticals Combined Structural Geology 2014PaulaNo ratings yet
- MET 302 (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2Document17 pagesMET 302 (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2BF3nobelNo ratings yet
- 7 Design of One Way Slabs5b16145dDocument7 pages7 Design of One Way Slabs5b16145dClarisse DoriaNo ratings yet
- Jsce Past QuestionsDocument2 pagesJsce Past QuestionsJuddy ScienceNo ratings yet
- XC Cs 37 T 5 P Xosy E85 UgupDocument5 pagesXC Cs 37 T 5 P Xosy E85 Ugupshanmuga Priya (Shan)No ratings yet
- Area of Plane FiguresDocument4 pagesArea of Plane FiguresvishyacharyaNo ratings yet
- Som 02 StrainDocument12 pagesSom 02 StrainSatish DhanyamrajuNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Questions of Chapter 3Document2 pagesMultiple-Choice Questions of Chapter 3Lennie ManaloNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument34 pagesStrength of Materialssatish44850% (2)
- Chapter Nineteen Base Plate: 19.1 Base Plates For Axially Loaded ColumnsDocument76 pagesChapter Nineteen Base Plate: 19.1 Base Plates For Axially Loaded ColumnsTatingJainarNo ratings yet
- MATH Fundamentals of Structural Steel deDocument76 pagesMATH Fundamentals of Structural Steel deKevin Miscala MelendresNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document2 pagesTutorial 5Amos YapNo ratings yet
- TOM Question BankDocument10 pagesTOM Question BankMadhan Kumar GovindarajuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8Document5 pagesAssignment 8Mohammed Junaid ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volume (Assignment-1)Document2 pagesSurface Area and Volume (Assignment-1)wordsandherrNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids: Shear Stresses in Beams and Related ProblemsDocument37 pagesMechanics of Solids: Shear Stresses in Beams and Related ProblemsrpsirNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets - FinalDocument6 pagesProblem Sets - FinalRuth LauronNo ratings yet
- 37 To 48 MSQDocument100 pages37 To 48 MSQTarun RathoreNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Classwork - Student-1Document4 pagesMensuration Classwork - Student-1Priyanka KengarNo ratings yet
- Buckling of Thin Metal Shells 90Document1 pageBuckling of Thin Metal Shells 90pawkomNo ratings yet
- CVG2140 - Assignment 3 (2016) - SolutionDocument6 pagesCVG2140 - Assignment 3 (2016) - SolutionFadey FaridNo ratings yet
- Ch.1 Reinforcement Details for Flat Slab 5 필기Document3 pagesCh.1 Reinforcement Details for Flat Slab 5 필기sunnyhijjNo ratings yet
- Ch.1 Reinforcement Details For Flat Slab 5Document3 pagesCh.1 Reinforcement Details For Flat Slab 5sunnyhijjNo ratings yet
- SFD, BMD and Deflection of Beams Question SheetDocument4 pagesSFD, BMD and Deflection of Beams Question SheetSai Krishna SKNo ratings yet
- Senior One End of Term One Examinations, 2015 Technical Drawing 735/1 Time: 2 Hours' InstructionsDocument1 pageSenior One End of Term One Examinations, 2015 Technical Drawing 735/1 Time: 2 Hours' InstructionsEremu ThomasNo ratings yet
- Stress TransformationsDocument4 pagesStress TransformationsNitin BuZzNo ratings yet
- QUIZ Without AnswersDocument24 pagesQUIZ Without AnswersSanjay TiwariNo ratings yet
- Drawing Exam PaperDocument2 pagesDrawing Exam Papermeeravali_7No ratings yet
- FRANSCISCO-Sept 2012Document9 pagesFRANSCISCO-Sept 2012Arnz BibosoNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsBhavesh PipaliyaNo ratings yet
- H. Ord T. ENG. (CEI), MI. PLANT E., FIED., ARAeS., CERT. ED. (Auth.) - General Engineering Drawing Examples (1973, Macmillan Education UK)Document64 pagesH. Ord T. ENG. (CEI), MI. PLANT E., FIED., ARAeS., CERT. ED. (Auth.) - General Engineering Drawing Examples (1973, Macmillan Education UK)Giovanni MedranoNo ratings yet
- Herons Formula TestDocument8 pagesHerons Formula Testpranav ranjanNo ratings yet
- Group 16Document10 pagesGroup 16Benj FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - StrainDocument18 pagesChapter 2 - StrainACC SHNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Questions PDFDocument5 pagesMachine Design Questions PDFrajibNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volume FormulasDocument7 pagesSurface Area and Volume FormulasshruthimNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion QDocument9 pagesRotational Motion QRamchandra MurthyNo ratings yet
- Mom - AssignmentDocument2 pagesMom - Assignmentsatishkumarkolluru9809No ratings yet
- Mechanical Eng Ses Main 2016 First PDFDocument8 pagesMechanical Eng Ses Main 2016 First PDFSumeet TiwariNo ratings yet
- Milling Machine StudyDocument10 pagesMilling Machine StudyshNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 4 TextDocument18 pagesChapter4 4 TextFidan DaskalovNo ratings yet
- Maths 10 ProjectDocument23 pagesMaths 10 ProjectRAVIOOO7No ratings yet
- Problem Set-Md 2Document11 pagesProblem Set-Md 2kim dianonNo ratings yet
- Angles MeasurementDocument60 pagesAngles Measurementsitaram_akella_1No ratings yet
- Ese Som Pyq Chapter 1Document38 pagesEse Som Pyq Chapter 1Krishna GovindNo ratings yet
- Mod-3B-Helical GearDocument2 pagesMod-3B-Helical GearSharthak GhoshNo ratings yet
- 14 - F2 Circles (Circumference, Area)Document4 pages14 - F2 Circles (Circumference, Area)jaycieNo ratings yet
- GEO 201 - Structural Geology - Answers - Test 2 - Sem. 1 - 10.11.2022Document7 pagesGEO 201 - Structural Geology - Answers - Test 2 - Sem. 1 - 10.11.2022barekie86No ratings yet
- Stress in ASME Pressure Vessels, Boilers, and Nuclear ComponentsFrom EverandStress in ASME Pressure Vessels, Boilers, and Nuclear ComponentsNo ratings yet
- Album of Dated Latin Inscriptions, Part II, Plates: Rome and the Neighborhood, A.D. 100-199From EverandAlbum of Dated Latin Inscriptions, Part II, Plates: Rome and the Neighborhood, A.D. 100-199No ratings yet
- SADSFDGHFRJTKYLUKJNHBDocument4 pagesSADSFDGHFRJTKYLUKJNHBMiraNo ratings yet
- KJFVGBHNJKLDocument3 pagesKJFVGBHNJKLMiraNo ratings yet
- Dfgrthyjku, LmnbdgsvfaegrhtjDocument2 pagesDfgrthyjku, LmnbdgsvfaegrhtjMiraNo ratings yet
- Ass 21Document1 pageAss 21MiraNo ratings yet
- Presentation 3Document3 pagesPresentation 3MiraNo ratings yet
- RtuiljhDocument3 pagesRtuiljhMiraNo ratings yet
- LJGFHDG 456789098765 TRDocument3 pagesLJGFHDG 456789098765 TRMiraNo ratings yet
- Mep Ce 2016 PDFDocument2 pagesMep Ce 2016 PDFMiraNo ratings yet
- Oiuytrdessxdcfvgb HNJMK, LKJHCVDocument4 pagesOiuytrdessxdcfvgb HNJMK, LKJHCVMiraNo ratings yet
- InfiltrationDocument11 pagesInfiltrationMiraNo ratings yet
- FINALDocument32 pagesFINALMiraNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems For Advanced Engineering Mathematics: April 2019Document103 pagesPractice Problems For Advanced Engineering Mathematics: April 2019MiraNo ratings yet