Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Procedures Rationale
Procedures Rationale
Uploaded by
Jamaica Leslie Noveno0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views3 pages1. The document outlines the procedure for incorporating a medication into an IV fluid bag or bottle, including verifying the order, explaining the procedure to the patient, preparing materials, adding the medication aseptically, mixing, observing the patient, and documenting.
2. Key steps include checking the right patient, drug, dose, route, time and documenting properly to ensure medication safety, as well as explaining the procedure to the patient, preparing equipment aseptically, adding and mixing the drug, observing for interactions, and properly disposing of medical waste.
3. Proper hand hygiene, aseptic technique when handling medications and medical equipment, and close monitoring of the patient after administration are emphasized to deliver safe and
Original Description:
Original Title
IV
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document outlines the procedure for incorporating a medication into an IV fluid bag or bottle, including verifying the order, explaining the procedure to the patient, preparing materials, adding the medication aseptically, mixing, observing the patient, and documenting.
2. Key steps include checking the right patient, drug, dose, route, time and documenting properly to ensure medication safety, as well as explaining the procedure to the patient, preparing equipment aseptically, adding and mixing the drug, observing for interactions, and properly disposing of medical waste.
3. Proper hand hygiene, aseptic technique when handling medications and medical equipment, and close monitoring of the patient after administration are emphasized to deliver safe and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views3 pagesProcedures Rationale
Procedures Rationale
Uploaded by
Jamaica Leslie Noveno1. The document outlines the procedure for incorporating a medication into an IV fluid bag or bottle, including verifying the order, explaining the procedure to the patient, preparing materials, adding the medication aseptically, mixing, observing the patient, and documenting.
2. Key steps include checking the right patient, drug, dose, route, time and documenting properly to ensure medication safety, as well as explaining the procedure to the patient, preparing equipment aseptically, adding and mixing the drug, observing for interactions, and properly disposing of medical waste.
3. Proper hand hygiene, aseptic technique when handling medications and medical equipment, and close monitoring of the patient after administration are emphasized to deliver safe and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
IV.
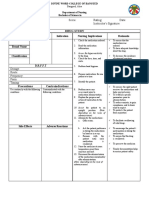
MEDICATION INCORPORATION OF DRUG INTO IVF BOTTLE/BAG
Procedures Rationale
1. Verify the written medication card against Checking ensures that patient receives the
the doctor's order. correct ordered IV solution and medication.
2. Observe 10 Rs when preparing and Right Drug.
administering medication The first right of drug administration is to
check and verify if it’s the right name and
form. Beware of look-alike and sound-alike
medication names. Misreading medication
names that look similar is a common
mistake.
Right Patient.
Ask the name of the client and check his/her
ID band before giving the medication. Even
if you know that patient’s name, you still
need to ask just to verify.
Right Dose.
Check the medication sheet and the doctor’s
order before medicating. Be aware of the
difference between an adult and a pediatric
dose.
Right Route.
Check the order if it’s oral, IV, SQ, IM, etc.
Right Time and Frequency.
Check the order for when it would be given
and when was the last time it was given..
Right Documentation.
Make sure to write the time and any remarks
on the chart correctly.
Right History and Assessment.
Secure a copy of the client’s history to drug
interactions and allergies.
Drug approach and Right to Refuse.
Give the client enough autonomy to refuse
the medication after thoroughly explaining
the effects.
Right Drug-Drug Interaction and
Evaluation.
Review any medications previously given or
the diet of the patient that can yield a bad
interaction to the drug to be given. Check
also the expiry date of the medication being
given.
Right Education and Information.
Provide enough knowledge to the patient of
what drug he/she would be taking and what
are the expected therapeutic and side effects.
NEVER document that you have given a
medication until you have actually
administered it.
3. Explains procedure (medication and Explanations allays anxiety
action) to reassure patient and significant
others and check patency of IV site
4.Verify for skin test of drug for IV Skin tests are usually well tolerated, in rare
incorporation (if skin testing is necessary). instances they can cause a more serious
allergic reaction.
5. Wash hands before and after the Hand hygiene deters the spread of
procedures microorganims.
6. Prepare the necessary materials needed Having equipment available saves time and
for the procedures such as: injection tray, facilitates accomplishment of task.
syringes needed, right drug to be
incorporated either in ampule or vial.
7. Disinfect injection port of the vial and the Wipe the top of the vial with 60–
ampule before breaking then aspirate the 70% alcohol (isopropyl alcohol or ethanol)
right dose aseptically. using a swab or cotton-wool ball; open the
package in front of the patient to reassure
them that the syringe and needle have not
been used previously
8. Remove the cover of the administration This removes air from tubing; in larger
set, maintain sterility and incorporate amounts, air can act as an embolus.
prepared drug into the airway aseptically. Recapping maintains the sterility of the
Recap airway after. NOTE: If the setup. Labeling ensures accurate
administration set, has no airway, pull out continuation and administration of correct IV
the set and incorporate prepared set to the solution.
bottle drug and re-spike the IVF set to the
bottle then place the label.
9.Swirl the bottle to mix the drug with IVF Diluting them can reduce their efficacy and
and regulate the flow rate accordingly. introduce the risk of medication errors and
contamination of sterile I.V. medications
10. Observe for 5-10 minutes for any drug Observations provide additional safety
interaction while reassuring the patient; measures, especially for high-alert
monitor VS medications. IV medications act rapidly.
11. Document the procedure done on the Nursing documentation is essential for good
patient’s chart. clinical communication.
Appropriate documentation provides an
accurate reflection of nursing assessments,
changes in clinical state, care provided and
pertinent patient information to support the
multidisciplinary team to deliver great care.
12. Discard sharp and other wastes The main purpose of discarding sharp and
according to the Health Care Waste other wastes is to protect employees
Management from sharps that may carry contagious
diseases
You might also like
- 12 Rights of Drug AdministrationDocument2 pages12 Rights of Drug AdministrationJes Cristy Lindongan75% (4)
- Leadership and Management MCQS With AnswDocument4 pagesLeadership and Management MCQS With AnswEmirates International Institute94% (16)
- PRS Ear Instillation - GlovaDocument3 pagesPRS Ear Instillation - GlovaAndrea Colleen GlovaNo ratings yet
- 10 Rights of Drug Administration With Nursing ImplicationsDocument3 pages10 Rights of Drug Administration With Nursing ImplicationsJet Bautista100% (6)
- 10 Rights of Drug AdministrationDocument11 pages10 Rights of Drug AdministrationAlthea Amor CambarijanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology M1 Post TaskDocument2 pagesPharmacology M1 Post TaskAlex WagnerNo ratings yet
- 12 Rights of Administering Medication PDF Dose (Biochemistry) ChemistryDocument1 page12 Rights of Administering Medication PDF Dose (Biochemistry) ChemistryTina Michelle DazaNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacology 1Document36 pagesBasic Pharmacology 1Marian SuhatNo ratings yet
- NURDR Notes w3Document4 pagesNURDR Notes w3ziarich ayraNo ratings yet
- Prin - of Drug AdministrationDocument4 pagesPrin - of Drug AdministrationAzhly AntenorNo ratings yet
- Right Dosage: Administration AdministrationDocument1 pageRight Dosage: Administration AdministrationChelsea JardelezaNo ratings yet
- Administering Oral Medication (Print)Document5 pagesAdministering Oral Medication (Print)Binoy Serino100% (1)
- 10 Rights of Drug AdministrationDocument1 page10 Rights of Drug AdministrationDoyTanNo ratings yet
- Adding Medication To IV Fluid ContainerDocument14 pagesAdding Medication To IV Fluid Containerjennielunay00No ratings yet
- Right Drug.: List of Look-Alike/sound-Alike DrugsDocument2 pagesRight Drug.: List of Look-Alike/sound-Alike DrugsKaye TenorioNo ratings yet
- Module 3.1 - Safety in Medication AdministrationDocument29 pagesModule 3.1 - Safety in Medication AdministrationAkio OzaragaNo ratings yet
- Module 3.1 - Safety in Medication AdministrationDocument29 pagesModule 3.1 - Safety in Medication AdministrationAkio OzaragaNo ratings yet
- PHARMADocument5 pagesPHARMAJorgie Ann ReyNo ratings yet
- Administration of MedicationDocument10 pagesAdministration of MedicationYeesha Palacio BalmesNo ratings yet
- NCM 0106 - Handout No.3. Rights For Medication Administration PDFDocument3 pagesNCM 0106 - Handout No.3. Rights For Medication Administration PDFKristine KimNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ortega ST., Iriga City, Philippines: University of Saint Anthony (Dr. Santiago G. Ortega Memorial)Document3 pagesDr. Ortega ST., Iriga City, Philippines: University of Saint Anthony (Dr. Santiago G. Ortega Memorial)Wilma BeraldeNo ratings yet
- Skill 3 Administering Intravenous MedicationDocument6 pagesSkill 3 Administering Intravenous MedicationDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities For Medication AdministrationDocument1 pageNursing Responsibilities For Medication Administrationmagicrjay26No ratings yet
- Nebulization TherapyDocument14 pagesNebulization TherapyCnette S. LumboNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NCP Template 2Document2 pagesDrug Study NCP Template 2Janico Lanz BernalNo ratings yet
- Nur 1208 2021 Prep of MedsDocument38 pagesNur 1208 2021 Prep of MedsDannielle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Guide To Good Dispensing PracticeDocument7 pagesGuide To Good Dispensing PracticeGizelle Mae Pasiol-MacayanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 3Document2 pagesPharmacology 3Mharlynne Nezlou L. PoliranNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Nursing Process and Administration-PharmaDocument13 pagesModule 4 - Nursing Process and Administration-PharmaKelsey MacaraigNo ratings yet
- "Five-Plus-Five" Rights of Medication Administration: Right PatientDocument9 pages"Five-Plus-Five" Rights of Medication Administration: Right PatientAlex BasadaNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Principles of Pharmacology To Ensure Safe and Proper Use of DrugsDocument21 pagesConcepts and Principles of Pharmacology To Ensure Safe and Proper Use of DrugsBea Bianca CruzNo ratings yet
- Medication Administration ReviewerDocument5 pagesMedication Administration ReviewerprincessdyrianeNo ratings yet
- Procedure Checklist Oral Medication AdministrationDocument4 pagesProcedure Checklist Oral Medication AdministrationRochel HatagueNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Zamboanga CityDocument12 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Zamboanga CityChristine Joy MolinaNo ratings yet
- IthinkaboutyoualotDocument5 pagesIthinkaboutyoualotpgumbanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Medication AdministrationDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - Medication AdministrationYvonne SeraspeNo ratings yet
- Assignment #2 Administration of Drugs: C. Single Order-Some Medications To Be Given Only Once and Are OrderedDocument5 pagesAssignment #2 Administration of Drugs: C. Single Order-Some Medications To Be Given Only Once and Are OrderedIsmael JaaniNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document18 pagesCH 03Emmanuel GaliciaNo ratings yet
- 12 Rights in Administering MedicationDocument3 pages12 Rights in Administering MedicationCassandra ArroganciaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Part 3Document6 pagesPharma Part 3Bee LeriosNo ratings yet
- Funda. RleDocument4 pagesFunda. Rleyassermacacunapundugar08092002No ratings yet
- Administration of Therapeutic AgentsDocument16 pagesAdministration of Therapeutic AgentscolendresjonnaNo ratings yet
- Disp Intro To Dispensing 0 PC 2Document32 pagesDisp Intro To Dispensing 0 PC 29s6fgyzyr6No ratings yet
- Pharmacology (DNPC 4122) : Nur Adilah Rasyadah Binti Suhaimi 3042191093Document12 pagesPharmacology (DNPC 4122) : Nur Adilah Rasyadah Binti Suhaimi 3042191093Suhaimi ShafieNo ratings yet
- Safety and QualityDocument24 pagesSafety and QualityPaula Janine BarrogaNo ratings yet
- Rights in Drug Administration and Medication ErrorsDocument12 pagesRights in Drug Administration and Medication ErrorsLumina lNo ratings yet
- 7) Unit Drug Dispensing and InjectionsDocument24 pages7) Unit Drug Dispensing and InjectionsShankar MurariNo ratings yet
- The 10 Rights of Medications AdministrationDocument2 pagesThe 10 Rights of Medications AdministrationSistine Rose LabajoNo ratings yet
- Administration of Oral Medication: Practical ProceduresDocument2 pagesAdministration of Oral Medication: Practical ProceduresNom NomNo ratings yet
- The 10 Rights of Medications AdministrationDocument3 pagesThe 10 Rights of Medications AdministrationJacklyn PacibleNo ratings yet
- Drug AdministrationDocument30 pagesDrug AdministrationandreabreeNo ratings yet
- Administering Nasal MedicationsDocument4 pagesAdministering Nasal MedicationsNessy Nicholle SatruionNo ratings yet
- Medications OSCE Criteria 2011-12Document3 pagesMedications OSCE Criteria 2011-12Kim GuevarraNo ratings yet
- 1-Guidelines For Safe Medication Adminstration (Non Parentral Medication Adminstration)Document6 pages1-Guidelines For Safe Medication Adminstration (Non Parentral Medication Adminstration)onco learnNo ratings yet
- The Ten Rights of Drug AdministrationDocument2 pagesThe Ten Rights of Drug AdministrationMike CalipayanNo ratings yet
- 2018 Pharm Good-Prescribing-PracticeDocument4 pages2018 Pharm Good-Prescribing-PracticeOlivia StevensNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Pharma Safety and Quality of Drug Administration Final PDFDocument10 pagesModule 3 Pharma Safety and Quality of Drug Administration Final PDFMichelle HutamaresNo ratings yet
- Rights of Drug AdministrationDocument4 pagesRights of Drug AdministrationAnusha VergheseNo ratings yet
- Clinical Skills For Pharmacists A Patient Focused Approach PDF 17420717Document14 pagesClinical Skills For Pharmacists A Patient Focused Approach PDF 17420717John LópezNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Medication Adherence: A practical approach to optimizing medication useFrom EverandFast Facts: Medication Adherence: A practical approach to optimizing medication useNo ratings yet
- Intensive Care Unit Orientation: Prof. Precy P. LantinDocument17 pagesIntensive Care Unit Orientation: Prof. Precy P. LantinJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- CA PostTest Grp2Document12 pagesCA PostTest Grp2Jamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Day 2-Case Study (Grp.3)Document1 pageDay 2-Case Study (Grp.3)Jamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- (Atherosclerosis) - Accumulated PlaquesDocument7 pages(Atherosclerosis) - Accumulated PlaquesJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- FCL700 - Outreach ProgramDocument124 pagesFCL700 - Outreach ProgramJamaica Leslie Noveno100% (2)
- This Study Resource Was: Running Head: CULTURAL DIVERSITY 1Document7 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Running Head: CULTURAL DIVERSITY 1Jamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- (Sep. 6) CPR RationalizationDocument21 pages(Sep. 6) CPR RationalizationJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- NCM 120 LecDocument4 pagesNCM 120 LecJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 RizalDocument38 pagesLesson 4 RizalJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- The Yonsei Lifestyle Profile: . Physical ActivityDocument9 pagesThe Yonsei Lifestyle Profile: . Physical ActivityJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- At The End of The Lesson, Students Should Be Able To.: Learning OutcomesDocument4 pagesAt The End of The Lesson, Students Should Be Able To.: Learning OutcomesJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- "Quality Function Deployment Gurus": STI College SouthwoodsDocument10 pages"Quality Function Deployment Gurus": STI College SouthwoodsJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Uph - Medical University Sto. Nino, Binan City, Laguna 1st SemDocument2 pagesUph - Medical University Sto. Nino, Binan City, Laguna 1st SemJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- New Syllabus - Ca1Document8 pagesNew Syllabus - Ca1Jamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- HRMEVNT - Events Management Midterm Analysis of Clients and CompetitorsDocument9 pagesHRMEVNT - Events Management Midterm Analysis of Clients and CompetitorsJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Nahnah Mandarin Colors.Document5 pagesNahnah Mandarin Colors.Jamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- "Mandarin Colors": STI College SouthwoodsDocument5 pages"Mandarin Colors": STI College SouthwoodsJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: The Road Less TravelledDocument4 pagesWorksheet: The Road Less TravelledLauraNo ratings yet
- Objective of Concrete Mix DesignDocument10 pagesObjective of Concrete Mix Designutachi93No ratings yet
- Tandberg En8040-UserGuideDocument38 pagesTandberg En8040-UserGuideMikhil0% (1)
- Assignment On Smart City PDFDocument8 pagesAssignment On Smart City PDFzazaNo ratings yet
- Final 2Document72 pagesFinal 2VM MittalNo ratings yet
- Park Et Al., 2021Document11 pagesPark Et Al., 2021madelineNo ratings yet
- Mortgage Loan Disclosure Statement - GFEDocument3 pagesMortgage Loan Disclosure Statement - GFEafncorpNo ratings yet
- Marketing of PencilDocument11 pagesMarketing of PencilMokshika KocharNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Strategic Management Text and Cases 7th Edition Dess Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Strategic Management Text and Cases 7th Edition Dess Solutions Manual PDFsaucerbield61wpyn100% (13)
- Ipr Q&aDocument31 pagesIpr Q&aSumit BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Revised-Manuscript (Sec 1 and 2) Plant DesignDocument332 pagesRevised-Manuscript (Sec 1 and 2) Plant DesignJose Daniel AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Traffic Theory - Wireless Communication SystemsDocument25 pagesTraffic Theory - Wireless Communication SystemsMuhammad Zaka Ur Rehman100% (1)
- ChevyDocument3 pagesChevysecretNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus in Accounting For Refresher 2Document8 pagesCourse Syllabus in Accounting For Refresher 2Sharon AnchetaNo ratings yet
- ShockLog Essentials v10 4Document79 pagesShockLog Essentials v10 4William Rubio AvilaNo ratings yet
- Thursday, August 27, 2015 EditionDocument14 pagesThursday, August 27, 2015 EditionFrontPageAfricaNo ratings yet
- WFA103759 (WPA3 Update)Document4 pagesWFA103759 (WPA3 Update)PiotrNo ratings yet
- 102 - Nitin Kalburgi (Internship Report)Document23 pages102 - Nitin Kalburgi (Internship Report)Akash SajjanNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Sub Process: Perception, Cognition and EmotionDocument4 pagesNegotiation Sub Process: Perception, Cognition and EmotionArti Das100% (1)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of ComputersDocument5 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of ComputersAlfred AtikaNo ratings yet
- Soundproof GeneratorDocument1 pageSoundproof Generatorprasadi.ariyadasaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Introduction To CompilationDocument13 pages2 - Introduction To CompilationShaddyNo ratings yet
- CounterACT Switch Commands in Use by The Switch Plugin v8.9.4Document798 pagesCounterACT Switch Commands in Use by The Switch Plugin v8.9.4Thiên HoàngNo ratings yet
- BH42SH60 0854PL 46kgcmDocument1 pageBH42SH60 0854PL 46kgcmYash PanchalNo ratings yet
- 4th Computer Hardware ServicingDocument25 pages4th Computer Hardware ServicingShabby Gay Malala TroganiNo ratings yet
- Total Dynamic Head - TDHDocument37 pagesTotal Dynamic Head - TDHs pNo ratings yet
- Last Minute Revison - Law of Evidence - 19.05.2022Document5 pagesLast Minute Revison - Law of Evidence - 19.05.2022gajendraburagaNo ratings yet
- Resume Samuel Sauvage AuDocument1 pageResume Samuel Sauvage AuRupinder JeetNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Design, Operation and Maint. Proc. ManualDocument87 pagesPipeline Design, Operation and Maint. Proc. ManualImanPapalala100% (3)
- Lab 4 Problem Set KeyDocument4 pagesLab 4 Problem Set KeyHirajNo ratings yet