Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Semantic Web: Textbook: Introduction To The Semantic
Semantic Web: Textbook: Introduction To The Semantic
Uploaded by
Shaiju Paul0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views19 pagesThe document introduces the concept of the semantic web and metadata. It defines the semantic web as linked data that allows machines to understand the meaning behind information on the web. It describes how metadata, or data about data, can be used to systematically describe resources in a way that machines can process. It provides Dublin Core as an example of a metadata schema and shows how metadata can be embedded in web pages or added later using metadata tools.
Original Description:
Semantic Web Intorductio
Original Title
SW_mod1_partA
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document introduces the concept of the semantic web and metadata. It defines the semantic web as linked data that allows machines to understand the meaning behind information on the web. It describes how metadata, or data about data, can be used to systematically describe resources in a way that machines can process. It provides Dublin Core as an example of a metadata schema and shows how metadata can be embedded in web pages or added later using metadata tools.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views19 pagesSemantic Web: Textbook: Introduction To The Semantic
Semantic Web: Textbook: Introduction To The Semantic
Uploaded by
Shaiju PaulThe document introduces the concept of the semantic web and metadata. It defines the semantic web as linked data that allows machines to understand the meaning behind information on the web. It describes how metadata, or data about data, can be used to systematically describe resources in a way that machines can process. It provides Dublin Core as an example of a metadata schema and shows how metadata can be embedded in web pages or added later using metadata tools.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 19
Semantic Web
TEXTBOOK : INTRODUCTION TO THE SEMANTIC
WEB AND SEMANTIC WEB SERVICES BY LIYANG
YU
Module 1
Introduction to Semantic Web Technology
From Traditional Web to Semantic Web
An Introduction to Metadata
Search Engines in Both Traditional and Semantic
Web Environments
* TextBook : Part -1 (Chapter 1 & 2)
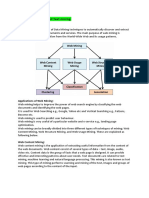
From Traditional Web to Semantic Web
What is WWW?
How are we using the Internet?
search
Integration
Web mining
DEFINITION of SEMANTIC WEB
Semantic Web
AN INTRODUCTION TO METADATA
is defined as “data about data”
it is data that describes information resources
metadata is structured data that machines can read
and understand
a key idea in the vision of the Semantic Web
“metadata is a systematic method for describing
resources and thereby improving their access “
Metadata from the Web world
The Web is made up of many Web documents. Based
on its definition, the metadata of a given Web
document is the data used to describe the document
It may include the title of the document, the author
of the document, and the date this document was
created
The metadata of each Web document has its own
unique structure, and it is simply not possible for an
automated agent to process these metadata in a
uniform and global way
Metadata Schema
To ensure metadata can be automatically processed
by machines, some metadata standard is needed
Such a standard is a set of agreed-on criteria for
describing data
a standard may specify that each metadata record
should consist of a number of predefined elements
representing some specific attributes of a resource
(in this case, the Web document), and each element
can have one or more values. This kind of standard is
called a metadata schema
Dublin Core (DC)
Dublin Core (DC) is a metadata standard
It was developed in the March 1995 Metadata
Workshop sponsored by the Online Computer
Library Center (OCLC) and the National Center for
Supercomputing Applications (NCSA)
It has 13 elements (subsequently increased to 15),
which are called Dublin Core Metadata Element Set
(DCMES)
Dublin Core (DC)
It is proposed as the minimum number of metadata
elements required to facilitate the discovery of
document-like objects in a networked environment
such as the Internet
a HTML <meta> tag is where an item of metadata
about a Web page is stored
A given Web document may contain many <meta>
tags to represent any number of metadata items
Normally, these metadata are not displayed by the
Web browser. They are mainly intended to be read
by automated agents or tools
Dublin Core (DC) Tags
An example of using DC
Let us summarize
METADATA Considerations
1) Embedding the Metadata in Your Page
The easiest thing to do is to embed the metadata
directly in your page when you create it — just use
the <meta> tag in the <head> section
This is indeed a good practice that one should follow
when publishing on the Web
Also, the added metadata should be prepared with
the following assumption in mind: there might exist
some automated agents or tools that can do
something useful with the added metadata
METADATA Considerations
2) Using Metadata Tools to Add Metadata to
Existing Pages
Another choice is to use a metadata tool to create
metadata for an existing Web page. For example, you
can find such a tool at:
http://www.ukoln.ac.uk/metadata/dcdot/
It will read the page you submit and automatically
generate DC metadata for you
DCdot can be used to generate DC metadata
The DC metadata generated by DCdot
METADATA Considerations
3) Using a Text-Parsing Crawler to Create
Metadata
Once the crawler reaches a page and finds that it
does not have any metadata, it attempts to discover
some meaningful information by scanning through
the text and creates some metadata for the page
For instance, the crawler may have a special table
containing all the important keywords that it is
looking for and on finding these words in the current
page, the crawler starts to learn something about the
page, and it writes what it learns into the metadata
Search Engines
You might also like
- Ch02 Data Models Ed7Document35 pagesCh02 Data Models Ed7Mohammed Adams67% (3)
- Semantic Web (CS1145) : Department Elective (Final Year) Department of Computer Science & EngineeringDocument36 pagesSemantic Web (CS1145) : Department Elective (Final Year) Department of Computer Science & Engineeringqwerty uNo ratings yet
- Metadata: Towards Machine-Enabled IntelligenceDocument10 pagesMetadata: Towards Machine-Enabled IntelligenceijwestNo ratings yet
- Metadata: Towards Machine-Enabled IntelligenceDocument10 pagesMetadata: Towards Machine-Enabled IntelligenceijwestNo ratings yet
- Metadata Interoperability HarmonizationDocument11 pagesMetadata Interoperability HarmonizationSamarendra DashNo ratings yet
- Semantic Web TechDocument35 pagesSemantic Web TechNaglaa FathyNo ratings yet
- Metadata: Information Engineering Information Engineering 2009-2010Document32 pagesMetadata: Information Engineering Information Engineering 2009-2010Edwin Walfre Osorio CruzNo ratings yet
- Web Mining: Day-Today: International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)Document4 pagesWeb Mining: Day-Today: International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Template Extraction From Heterogeneous Web Pages Using Text ClusteringDocument6 pagesTemplate Extraction From Heterogeneous Web Pages Using Text Clusteringsurendiran123No ratings yet
- 1.1 Web ScrapingDocument34 pages1.1 Web ScrapinginesNo ratings yet
- Semantic Web Unit - 1 & 2Document16 pagesSemantic Web Unit - 1 & 2pavanpk0812No ratings yet
- CS8080 Irt Unit 4 23 24Document36 pagesCS8080 Irt Unit 4 23 24swarnaas2124No ratings yet
- Semantic Web FinalDocument14 pagesSemantic Web FinalsuperanisNo ratings yet
- Nayak (2022) - A Study On Web ScrapingDocument3 pagesNayak (2022) - A Study On Web ScrapingJoséNo ratings yet
- DWM Assignment 1: 1. Write Detailed Notes On The Following: - A. Web Content MiningDocument10 pagesDWM Assignment 1: 1. Write Detailed Notes On The Following: - A. Web Content MiningKillerbeeNo ratings yet
- Online Banking Loan Services: International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & Management (IJAIEM)Document5 pagesOnline Banking Loan Services: International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & Management (IJAIEM)International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Search Engine 1. ObjectiveDocument63 pagesChapter 1 Search Engine 1. ObjectiveKumar BhupendraNo ratings yet
- Semantic Web Technologies in Data ManagementDocument4 pagesSemantic Web Technologies in Data ManagementTheodore CacciolaNo ratings yet
- Towards Automatic Incorporation of Search Engines Into ADocument19 pagesTowards Automatic Incorporation of Search Engines Into ARobert PerezNo ratings yet
- WEB 3.0 Sreevidhya@StudentsDocument13 pagesWEB 3.0 Sreevidhya@StudentsYogesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Cse-2012 13 Even-III Cse-2 Marks-It63 WT 2marksDocument15 pagesCse-2012 13 Even-III Cse-2 Marks-It63 WT 2marksGeethaa MohanNo ratings yet
- What Is MS Access?Document6 pagesWhat Is MS Access?Rommel LicerioNo ratings yet
- Web Data ScrapingDocument5 pagesWeb Data ScrapingMunawir MunawirNo ratings yet
- Semantc Web and Social NetworksDocument63 pagesSemantc Web and Social NetworksANCY THOMASNo ratings yet
- Bb-Mastering Structured Data On The Semantic WebDocument244 pagesBb-Mastering Structured Data On The Semantic WebMilan TrninićNo ratings yet
- CCS 215 Web Design and Development NOTESDocument69 pagesCCS 215 Web Design and Development NOTESwannabedaniel77No ratings yet
- Web Data Extraction Using The Approach of Segmentation and ParsingDocument7 pagesWeb Data Extraction Using The Approach of Segmentation and ParsingseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- MetadataDocument1 pageMetadatax3phyr_hunt3rNo ratings yet
- 1st Facilitating Document Annotation Using Content and Querying ValueDocument4 pages1st Facilitating Document Annotation Using Content and Querying Valuesonaiya software solutionsNo ratings yet
- 43.v. Bharanipriya1 & v. Kamakshi Prasad2Document6 pages43.v. Bharanipriya1 & v. Kamakshi Prasad2Isabelle-Lynn CoNo ratings yet
- Nama:Fayyadh Syafiq Rabbani Kelas: 2IA15 NPM: 52418630Document6 pagesNama:Fayyadh Syafiq Rabbani Kelas: 2IA15 NPM: 52418630fayyadh syafiqNo ratings yet
- MS Project ReportDocument26 pagesMS Project ReportvirubhauNo ratings yet
- Online Banking Loan Services: International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & Management (IJAIEM)Document4 pagesOnline Banking Loan Services: International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & Management (IJAIEM)International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Web 1Document10 pagesWeb 1Zain Alabeeden AlarejiNo ratings yet
- Web Data Extraction and Alignment: International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), India Online ISSN: 2319 7064Document4 pagesWeb Data Extraction and Alignment: International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), India Online ISSN: 2319 7064Umamageswari KumaresanNo ratings yet
- 3.Eng-A Survey On Web MiningDocument8 pages3.Eng-A Survey On Web MiningImpact JournalsNo ratings yet
- IM Ch15 DB Connectivity Web Technologies Ed12Document26 pagesIM Ch15 DB Connectivity Web Technologies Ed12MohsinNo ratings yet
- World Wide WebDocument8 pagesWorld Wide WebJoseph MungaiNo ratings yet
- Search Engine With Web CrawlerDocument23 pagesSearch Engine With Web CrawlerNithinNo ratings yet
- IJARCCE 67 Project Research PaperDocument3 pagesIJARCCE 67 Project Research PaperShaguftaNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument4 pagesResearch PaperpremacuteNo ratings yet
- Resource Capability Discovery and Description Management System For Bioinformatics Data and Service Integration - An Experiment With Gene Regulatory NetworksDocument6 pagesResource Capability Discovery and Description Management System For Bioinformatics Data and Service Integration - An Experiment With Gene Regulatory Networksmindvision25No ratings yet
- Web Databases: Deepen The Web: Thanaa Ghanem Walid ArefDocument5 pagesWeb Databases: Deepen The Web: Thanaa Ghanem Walid ArefVijay AnandhNo ratings yet
- Search Engine SeminarDocument17 pagesSearch Engine SeminarsidgrabNo ratings yet
- SCBDBDocument2 pagesSCBDBnanoscribdloginNo ratings yet
- Computer Project PDFDocument23 pagesComputer Project PDFSurya MaharaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Search Results From Web DatabasesDocument5 pagesAutomatic Search Results From Web DatabasesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Web Mining and Text MiningDocument13 pagesUnit 7: Web Mining and Text MiningAshitosh GhatuleNo ratings yet
- P S T U: Submitted ToDocument19 pagesP S T U: Submitted Torahman simantoNo ratings yet
- Sync Kit: A Persistent Client-Side Database Caching Toolkit For Data Intensive WebsitesDocument11 pagesSync Kit: A Persistent Client-Side Database Caching Toolkit For Data Intensive Websitesdavid toheaNo ratings yet
- Working With The Database Management SystemDocument15 pagesWorking With The Database Management SystemCresanelle PoloNo ratings yet
- Intro To HTMLDocument29 pagesIntro To HTMLJoyce Ann NunezNo ratings yet
- Delhi Technological University Presentation Subject: Web Technology Mc-320 Topic: Web Mining FrameworkDocument16 pagesDelhi Technological University Presentation Subject: Web Technology Mc-320 Topic: Web Mining FrameworkJim AbwaoNo ratings yet
- Internet & SecurityDocument36 pagesInternet & SecurityVinky BhatiaNo ratings yet
- SEMANTIC WEB ReportDocument22 pagesSEMANTIC WEB ReportAland MediaNo ratings yet
- Web MiningDocument13 pagesWeb Miningdhruu2503No ratings yet
- Metadata Concepts To Support A Net-Centric Data Environment: January 2006Document27 pagesMetadata Concepts To Support A Net-Centric Data Environment: January 2006home cecNo ratings yet
- Lit SurveyDocument11 pagesLit SurveyShalini MuthukumarNo ratings yet
- IT63 Web Technology 2& 16marks Question and AnswerDocument21 pagesIT63 Web Technology 2& 16marks Question and AnswerPremanandhjNo ratings yet
- Web Programming with HTML, CSS, Bootstrap, JavaScript, React.JS, PHP, and MySQL Fourth EditionFrom EverandWeb Programming with HTML, CSS, Bootstrap, JavaScript, React.JS, PHP, and MySQL Fourth EditionNo ratings yet
- SW Mod1 PartBDocument33 pagesSW Mod1 PartBShaiju PaulNo ratings yet
- System Software TutorialDocument1 pageSystem Software TutorialShaiju PaulNo ratings yet
- SS T1 21-8-2019 PDFDocument1 pageSS T1 21-8-2019 PDFShaiju PaulNo ratings yet
- s2 C Programming KTU 2019 SyllabusDocument9 pagess2 C Programming KTU 2019 SyllabusShaiju PaulNo ratings yet
- Remote Method Invocation Tutorial in JavaDocument10 pagesRemote Method Invocation Tutorial in JavaShaiju PaulNo ratings yet
- Install GCC Download & Install Geany Compile C Programs Using Command Mode (CMD) or Geany IDEDocument11 pagesInstall GCC Download & Install Geany Compile C Programs Using Command Mode (CMD) or Geany IDEShaiju PaulNo ratings yet
- AHMED HASSAN - Computer Science Week 4 H.W June 22 TH Till 26th JuneDocument3 pagesAHMED HASSAN - Computer Science Week 4 H.W June 22 TH Till 26th JuneAhmed HassanNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems (R16 Iii B.Tech I Sem) Unit - VIDocument13 pagesOperating Systems (R16 Iii B.Tech I Sem) Unit - VIRajeswaranaidu DarsiNo ratings yet
- Planning For Information NetworkDocument32 pagesPlanning For Information NetworkChandraAdsenubiiNo ratings yet
- Data DictionaryDocument4 pagesData DictionaryCamille Lucelo100% (1)
- D STR Gci.01 2021 PDF eDocument172 pagesD STR Gci.01 2021 PDF eBENTRIA maamarNo ratings yet
- Database Programming With SQL 1-2: Relational Database Technology Practice ActivitiesDocument2 pagesDatabase Programming With SQL 1-2: Relational Database Technology Practice ActivitiesradebpNo ratings yet
- Netapp Is Best For Flash: 7 Reasons WhyDocument1 pageNetapp Is Best For Flash: 7 Reasons WhyHtet Ko Ko LinNo ratings yet
- Swift Microgateway Service Description 0Document20 pagesSwift Microgateway Service Description 0masoud.sharafi1970.09No ratings yet
- The Adapter Architecture For Distributed Web Services Using XML ComponentsDocument8 pagesThe Adapter Architecture For Distributed Web Services Using XML ComponentsA.suresh KumarNo ratings yet
- ACME Command Line Interface TrainingDocument70 pagesACME Command Line Interface Trainingakira_jNo ratings yet
- Pemanfaatan Media Komunikasi Dan Informasi Dalam Perwujudan Pembangunan NasionalDocument11 pagesPemanfaatan Media Komunikasi Dan Informasi Dalam Perwujudan Pembangunan Nasionalros dolorosaNo ratings yet
- Midterm AssignmentDocument2 pagesMidterm AssignmentKey Amor OlivarNo ratings yet
- Governance and Security Essentials in AWS: Telefonica - Eleven PathsDocument37 pagesGovernance and Security Essentials in AWS: Telefonica - Eleven PathspablogarlandeiraNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Technical Report: Tools Used: Wireshark, Snort OS: Ubuntu 18.04Document17 pagesLab 3 Technical Report: Tools Used: Wireshark, Snort OS: Ubuntu 18.04Roger ZhangNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Background of The Study: Chapter OneDocument5 pages1.0 Background of The Study: Chapter OneDamilola AdegbemileNo ratings yet
- EUC1502 Module5 Big-DataDocument46 pagesEUC1502 Module5 Big-DataРадомир МутабџијаNo ratings yet
- Analitik Dan Visualisasi Data - Pengenalan Data Analitik Dan VisualisasiDocument18 pagesAnalitik Dan Visualisasi Data - Pengenalan Data Analitik Dan VisualisasiChom JrNo ratings yet
- MinfinalDocument26 pagesMinfinalPranaydavathNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of Brocade Gen 5 Fibre Channel: White PaperDocument11 pagesThe Benefits of Brocade Gen 5 Fibre Channel: White Paperpriv1234No ratings yet
- DB Lab ManualDocument13 pagesDB Lab ManualABUBAKAR MUJAHIDNo ratings yet
- Manual For BIND DNS Server On CentOSDocument9 pagesManual For BIND DNS Server On CentOSzainabNo ratings yet
- Systems Engineer With Experience in DevelopingDocument3 pagesSystems Engineer With Experience in DevelopingAlexis Guzman ValverdeNo ratings yet
- 03 US Case Study Nestle Waters 20210616Document7 pages03 US Case Study Nestle Waters 20210616Sudipta MishraNo ratings yet
- Parvind - Singh - Mainframe DeveloperDocument4 pagesParvind - Singh - Mainframe Developershobit poojaNo ratings yet
- ACR Pics SIPDocument5 pagesACR Pics SIPGuia Marie Diaz BriginoNo ratings yet
- ERP For Midsized and Smaller CompaniesDocument26 pagesERP For Midsized and Smaller CompaniesRuth SamperNo ratings yet
- 6.1 GCP - Cloud - Bigtable PDFDocument18 pages6.1 GCP - Cloud - Bigtable PDFgauravecec1980No ratings yet
- 10-FDs & Normalization in DBMS - Print - QuizizzDocument5 pages10-FDs & Normalization in DBMS - Print - QuizizzVijayNo ratings yet
- 2017-01-28-Traffic-Analysis-Exercise-Answers PDFDocument12 pages2017-01-28-Traffic-Analysis-Exercise-Answers PDFXCORPSNo ratings yet