Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Caroline Tjengdrawira Best Practices Guidelines For EPC and O M PDF
Caroline Tjengdrawira Best Practices Guidelines For EPC and O M PDF
Uploaded by
Venkataramanan SOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Caroline Tjengdrawira Best Practices Guidelines For EPC and O M PDF
Caroline Tjengdrawira Best Practices Guidelines For EPC and O M PDF
Uploaded by
Venkataramanan SCopyright:
Available Formats
Solar Bankability Final Workshop
8th February 2017 – Session 3
Best Practices Guidelines for EPC and O&M
Caroline Tjengdrawira (3E)
Funded by the Horizon 2020
Framework Programme of the
European Union
Presentation Outline
I. Lifecycle costs and related risks in PV investment financial model
II. Gaps in EPC and O&M technical aspects
III. Best-practice guidelines for EPC and O&M contracting
• Solar Bankability Final Workshop | Brussels | 7-8 Feb 2017 • 2
Lifecycle Costs in PV Investment Financial Model
EPC and O&M are Influential to CAPEX and OPEX
» CAPEX is dominant in » Majority of CAPEX is » Wide O&M range in
lifecycle costs EPC OPEX
(75-90%) (70-90%) (30-70%)
Data from surveys of
• 18 PV financial models (ground-mounted plants, FR-UK-DE-IT, 2011-2015)
• 8 EPC and O&M contracts (ground-mounted and rooftop plants, FR-UK-IT-NL, 2014-2016)
• 7 yield reports and scientific literature
• Solar Bankability Final Workshop | Brussels | 7-8 Feb 2017 • 3
Technical Inputs in EPC, O&M and Yield Estimation
Gaps Analysis in Technical Assumptions
Risk Phase/field Identified critical technical gaps
Year-0 Procurement/ 1. Insufficient EPC technical specifications to ensure that selected components
product selection are suitable for use in the specific PV plant environment of application.
and testing 2. Inadequate component testing to check for product manufacturing
deviations.
3. Absence of adequate independent product delivery acceptance test and
criteria.
Planning/ 4. The effect of long-term trends in the solar resource is not fully accounted
lifetime energy
yield estimation 5.
for.
Exceedance probabilities (e.g. P90) are often calculated for risk assessment
» Gaps exist across all
assuming a normal distribution for all elements contributing to the overall
uncertainty.
project phases
6. Incorrect degradation rate and behavior over time assumed in the yield
estimation.
7. Incorrect availability assumption to calculate the initial yield for project
investment financial model (vs O&M plant availability guarantee).
Transportation 8. Absence of standardized transportation and handling protocol.
Installation/ 9. Inadequate quality procedures in component un-packaging and handling
construction during construction by workers.
10. Missing intermediate construction monitoring.
Installation/ 11. Inadequate protocol or equipment for plant acceptance visual inspection.
provisional and 12. Missing short-term performance (e.g. PR) check at provisional acceptance
final acceptance test, including proper correction for temperature and other losses.
13. Missing final performance check and guaranteed performance.
14. Incorrect or missing specification for collecting data for PR or availability
evaluations: incorrect measurement sensor specification, incorrect
irradiance threshold to define time window of PV operation for
Data from surveys of
PR/availability calculation. • 18 PV financial models (ground-mounted plants,
Risks Operation 15. Selected monitoring system is not capable of advanced fault detection and FR-UK-DE-IT, 2011-2015)
during identification.
operation 16. Inadequate or absence of devices for visual inspection to catch invisible • 8 EPC and O&M contracts (ground-mounted and
defects/faults. rooftop plants, FR-UK-IT-NL, 2014-2016)
17. Missing guaranteed key performance indicators (PR, availability or energy
yield). • 7 yield reports and scientific literature
18. Incorrect or missing specification for collecting data for PR or availability
evaluations: incorrect measurement sensor specification, incorrect
irradiance threshold to define time window of PV operation for
PR/availability calculation.
Maintenance 19. Missing or inadequate maintenance of the monitoring system.
20. Module cleaning missing or frequency too low.
• Solar Bankability Final Workshop | Brussels | 7-8 Feb 2017 • 4
Gaps in EPC Contracting
Year-0 Risks
Procurement, Product Selection and Testing
• Insufficient EPC technical specifications for major plant components
• Inadequate component testing
• Absence of product acceptance
Transportation
• Absent standard protocol for transport and handling
Construction
• Inadequate protocol for component handling by workers
• Missing construction monitoring
• Solar Bankability Final Workshop | Brussels | 7-8 Feb 2017 • 5
Gaps in EPC Contracting
Year-0 Risks
Provisional and final acceptance
• Inadequate visual inspection protocol
• Missing/incorrect short-term performance check at provisional acceptance
• Missing/incorrect final performance check
• Absence of guaranteed performance
• Missing/incorrect:
– Assumptions in performance calculation
– Measurement sensor specification
– Irradiance threshold
• Solar Bankability Final Workshop | Brussels | 7-8 Feb 2017 • 6
Gaps in O&M Contracting
Risks During Operation
Operation
• Inadequate monitoring system for advanced fault detection and
identification
• Inadequate visual inspection protocol
• Absence of guaranteed performance
• Missing/incorrect:
– Assumptions in performance calculation
– Measurement sensor specification
– Irradiance threshold
Maintenance
• Missing/inadequate monitoring system maintenance
• Module cleaning missing or frequency too low
• Solar Bankability Final Workshop | Brussels | 7-8 Feb 2017 • 7
PV Financial Model – Technical Risks
Gaps in Technical Assumptions Leading to Technical Risks Impacting PV
Investment Costs
GAPS RISKS LCOE
• Incorrect set-ups of • Type 1 risks • Increase costs
EPC and O&M influence plant (CAPEX or OPEX)
• Incorrect yield performance and • Over- or under-
estimation yield estimation of yield
• Type 2 risks cause
partial or overall
plant outage
lowering plant
availability and yield
• Solar Bankability Final Workshop | Brussels | 7-8 Feb 2017 • 8
Managing PV Technical Risks
Technical Aspects in EPC and O&M Contracts
» Are important since they affect CAPEX, OPEX or yield.
» Need to be set up properly to minimize technical risks.
EPC O&M
• Solar Bankability Final Workshop | Brussels | 7-8 Feb 2017 • 9
Best Practice Checklists
Tools to Minimize Technical Risks by Proper EPC and O&M Contracting and
Yield Estimation
Three main checklists are:
1. Best Practice Checklist for EPC Technical Aspects
2. Best Practice Checklist for O&M Technical Aspects
3. Best Practice Checklist for Long-Term Yield Assessment
Three supplementary checklists are:
4. Checklist for As-Build Documents – Type and Details
5. Checklist for Record Control
6. Checklist for Reporting Indicators
• Solar Bankability Final Workshop | Brussels | 7-8 Feb 2017 • 10
Best-Practice for EPC and O&M Contracting
Technical Aspects & What to Look for in The Contracts
EPC contract
A Definitions, interpretation
B Contractual commitments
C Scope of works – engineering
D Scope of works – procurement
E Scope of works – construction
F Scope of works – administrative and others
G Manufacturer warranties
H EPC warranty and Defect Liability Period (DLP)
I Key performance indicators (KPIs) and guarantees
J Commissioning and acceptance
O&M contract
A Definitions, interpretation
B Purpose and responsibilities
C Scope of works – environmental, health and safety
D Scope of works – operations
E Scope of works – maintenance
F Scope of works – data and monitoring
G Scope of works – spare parts management
H Scope of works – plant security
I Key performance indicators (KPIs)
J Contractual commitments
• Solar Bankability Final Workshop | Brussels | 7-8 Feb 2017 • 11
Best Practice Checklists
Online at www.solarbankability.eu
• Solar Bankability Final Workshop | Brussels | 7-8 Feb 2017 • 12
Technical Risk Flash Cards
Online at www.solarbankability.eu
Categorization based on:
• Risk impacts CAPEX/OPEX/yield
• Risk mitigation impacts on CAPEX/OPEX/yield
Risk 1. Insufficient EPC technical specifications to ensure Phase of risk occurrence
that selected components are suitable for use in the
Risk 1. Insufficient EPC technical Phase of risk occurrence
ofspecifications
application to ensure
Procurement Planning
specific PV plant environment
that selected components are suitable for use in the
Risk 1. Insufficient EPC technical Phase of risk occurrence
ofspecifications
application to ensure
Procurement Planning
specific PV plant environment
that selected components are suitable for use in the
O&M Construction
Procurement Planning
specific PV plant environment of application
O&M Construction
Key takeaway PV plant component specification and requirement in the EPC contract should be as detail as
O&M Construction
possible to ensure that the components procured are suited for the intended PV installation
Key takeaway specific PV application,
plant component specification
site and environmentand requirement in the EPC contract should be as detail as
possible to ensure that the components procured are suited for the intended PV installation
Risk flash cards with following info: Key takeaway specific
Impact of risk
PV application,
LCOE variables
plant component
impacted
possible to ensure
specification
site and
by that
environment
this risk:
and requirement
CAPEXin the EPC OPEX contract should Yield
be as detail as
the components procured are suited for the intended PV installation
specific application, site and environment CAPEX OPEX Yield
Impact of risk LCOE variables impacted by this risk:
•
Mitigations Component testing When specifying the technical requirements for PV
Description of the risk, Impact of
Mitigations
risk DesignLCOE variables
review +
Component testing
impactedplant components
by this
When
risk:
specifying the
CAPEX
technical
OPEX
in the EPC contract, in addition to
requirements
the component type and quantity, the specifications for PV
Yield
construction monitoring
plant
alsocomponents in the EPC contract, in addition to
•
Design review + should include:
Phase at which the risk occurs, EPC qualification
Mitigations
Advanced
Component testing
construction monitoring
Design
monitoring
review + Allshould
When
plant
specifying the
certifications
alsocomponents
include:
technical
andEPC
in the
requirements
the component type and quantity, the specifications
applicable conformances
for
(e.g.
contract, in addition
PV
to
EPC qualification IEC61215, IEC61730, type
the component IEC61701, IEC62804,
and quantity, theIEC61716
specifications
construction monitoring
•
Basic monitoring modules;
All applicable certifications and conformances (e.g.
Key takeaway of the risk, Advanced monitoring
Advanced EPC qualification
inspection
Basic monitoring
for
markIEC61215,
IEC62109,
should also include:
IEC61730,
of compliance
modules;
All applicable
IEC61000
for allIEC61701,
for inverters;
electrical IEC62804,
certifications
components)
and
CE
IEC61716
Visual Advanced monitoring
inspection for IEC62109, IEC61000 forconformances
inverters; CE (e.g.
Advanced inspection The environmental
IEC61215, condition
IEC61730, the components
IEC61701, will IEC61716
IEC62804,
• Mitigations, Basic monitoring
Yield/performance
Visual inspection
test
Advanced inspection The
snow
mark
be installed
of compliance
for in (temperature,
modules;
environmental
load, anyof
mark special
for all
IEC62109,
condition
chemical
compliance
electrical
humidity,
IEC61000
the
forexposure,
all
components)
wind forand
components
electrical
inverters; CE
will
components)
Yield/performance test be installed
corrosion risk etc.) in (temperature, humidity, wind and
Visual inspection
• Risk and mitigation impacts on LCOE For PV
Yield/performance test
The environmental condition the components will
snow load, any special chemical exposure,
modules, module
be installed
corrosion risk component bill
in (temperature,
etc.) of
humidity, wind and
materialssnow
and the proof
load, any of IEC certification
special chemical exposure,
For PV
documents modules,
for these
corrosion module
etc.) component bill of
materials
risk
materials and the proof of IEC certification
For PVCAPEX
documents modules, module
OPEXcomponent
for these materials bill of
Yield
Impact of LCOE variables impacted by the risk
mitigation mitigations:
materials and the proof of IEC certification
Impact of LCOE variables impacted by the risk documentsCAPEXfor these materials
OPEX Yield
mitigation mitigations:
Impact of LCOE variables impacted by the risk CAPEX OPEX Yield
mitigation mitigations:
• Solar Bankability Final Workshop | Brussels | 7-8 Feb 2017 • 13
Reports
Online at www.solarbankability.eu
Deliverable D3.1 report
• “Review and Gap Analyses of Technical Assumptions in PV
Electricity Cost – Report on Current Practices in How Technical
Assumptions are Accounted in PV Investment Cost Calculation”
Deliverable D3.2 report
• “Best Practice Guidelines for PV Cost Calculation – Accounting
for Technical Risks and Assumptions in PV LCOE”
• Solar Bankability Final Workshop | Brussels | 7-8 Feb 2017 • 14
Thank you
PRESENTED BY
Caroline Tjengdrawira
ctj@3e.eu
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 649997.
The content of this report reflects only the author’s view and the Commission is not responsible for any use that may be made of the information it contains
Funded by the Horizon 2020
Framework Programme of the
European Union
You might also like
- Solar Project Example - FINAL - FINALDocument19 pagesSolar Project Example - FINAL - FINALYassine Iferden TorssanovskiNo ratings yet
- MBA Project On Employee Welfare MeasuresDocument92 pagesMBA Project On Employee Welfare MeasuresJebin Jacob93% (15)
- WBS For Wedding ProjectDocument1 pageWBS For Wedding ProjectKhushboo Katyayan50% (2)
- First Solar AnswerDocument1 pageFirst Solar AnswerEleonora SalvagnoNo ratings yet
- LBP Iaccess Enrollment FormDocument4 pagesLBP Iaccess Enrollment FormKlEər Oblimar0% (1)
- PV Value v1 1 User ManualDocument23 pagesPV Value v1 1 User ManualGanesh AyerNo ratings yet
- Iec TR 61000-5-6-2002Document52 pagesIec TR 61000-5-6-2002Venkataramanan S100% (1)
- Iec 61000-4-15-2010 Ish1-2017Document1 pageIec 61000-4-15-2010 Ish1-2017Venkataramanan S100% (1)
- Iec 61000-4-12-2017Document100 pagesIec 61000-4-12-2017Venkataramanan S100% (1)
- 4MW RTS Project Initiated by GEDCOL, OdishaDocument29 pages4MW RTS Project Initiated by GEDCOL, Odishamailnehru8955No ratings yet
- Global Technology Trends in Solar PV Power: R&D and CommercialDocument35 pagesGlobal Technology Trends in Solar PV Power: R&D and CommercialSurya Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Islands Microgrid Profiles Islands Global Remote Communities CaseStudy 2015Document32 pagesIslands Microgrid Profiles Islands Global Remote Communities CaseStudy 2015oidaadmNo ratings yet
- Design Document v2Document17 pagesDesign Document v2api-533235687No ratings yet
- Africa Energy Review 2021Document37 pagesAfrica Energy Review 2021Jedson SilvaNo ratings yet
- Thomas Jakobsen - RE Investment Strategies in VietnamDocument14 pagesThomas Jakobsen - RE Investment Strategies in VietnamAsia Clean Energy ForumNo ratings yet
- Solar Power Procurement Related Issues Order-TNERC-16-10-2020Document47 pagesSolar Power Procurement Related Issues Order-TNERC-16-10-2020SRINIVASAN TNo ratings yet
- Ulrike Jahn Mitigating The Technical Risks in Project LifetimeDocument16 pagesUlrike Jahn Mitigating The Technical Risks in Project LifetimeVenkataramanan SNo ratings yet
- GCF Concept Note TemplateDocument7 pagesGCF Concept Note TemplateNGO GDNNo ratings yet
- Best Practice Guidelines For PV Cost CalculationDocument72 pagesBest Practice Guidelines For PV Cost CalculationDoan Anh TuanNo ratings yet
- World Bank PDFDocument18 pagesWorld Bank PDFshiintuNo ratings yet
- Summer Industrial Training ReportDocument26 pagesSummer Industrial Training ReportAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- LOI For RVA Solar Fund PPA.2018.Nonprofit - FillableDocument19 pagesLOI For RVA Solar Fund PPA.2018.Nonprofit - FillableRichard LucasNo ratings yet
- 01 - Wind Solar PV (Draft)Document30 pages01 - Wind Solar PV (Draft)Chiaoyin ChengNo ratings yet
- Plant Engineering: Medium Voltage Cable Failure Mechanism Update 3Document60 pagesPlant Engineering: Medium Voltage Cable Failure Mechanism Update 3Dedit Gunarso PutroNo ratings yet
- GIZ RTS Investment Guidelines EN FinalDocument71 pagesGIZ RTS Investment Guidelines EN FinalDieuhoang NgoNo ratings yet
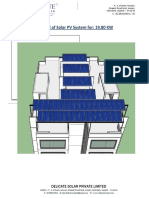
- Proposal of Solar: PV System For: 19.80 KWDocument4 pagesProposal of Solar: PV System For: 19.80 KWGajju Gulsher BhaiNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of An Independent Renewable Energy Source (5kva Solar Powered Inverter)Document17 pagesDesign and Implementation of An Independent Renewable Energy Source (5kva Solar Powered Inverter)BayeNo ratings yet
- Solar Bankability - d1.1 - d2.1 - Technical Risks in PV Projects PDFDocument139 pagesSolar Bankability - d1.1 - d2.1 - Technical Risks in PV Projects PDFSyed Furqan RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Solar Power SystemDocument4 pagesSolar Power SystemSmartBrainsNo ratings yet
- Solar Power Industry - Nguyen Dinh Quynh KhaDocument21 pagesSolar Power Industry - Nguyen Dinh Quynh KhaQuynh Kha Nguyen DinhNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric Storage Solutions - 20160627Document23 pagesSchneider Electric Storage Solutions - 20160627Azree Mohd NoorNo ratings yet
- Solar Floating at EGAT 'S ProjectDocument41 pagesSolar Floating at EGAT 'S ProjectChong Jiazhen50% (2)
- Transient Stability Assessment of Power System With Large Amount of Wind Power Penetration The Danish Case StudyDocument8 pagesTransient Stability Assessment of Power System With Large Amount of Wind Power Penetration The Danish Case StudyThức VõNo ratings yet
- ASEAN Power Updates 2021 (R27092021)Document16 pagesASEAN Power Updates 2021 (R27092021)PamudjiNo ratings yet
- Microgrid Architectures For Low Voltage Distributed GenerationDocument10 pagesMicrogrid Architectures For Low Voltage Distributed Generationhafiz858No ratings yet
- Report Batteries Solar Photovoltaic ApplicationsDocument87 pagesReport Batteries Solar Photovoltaic ApplicationsMohd Zulfika AbdolkaderNo ratings yet
- WTMR Final For Posting 8-9-19Document103 pagesWTMR Final For Posting 8-9-19Balaji_Rajaman_2280No ratings yet
- Electrical MetodologyDocument40 pagesElectrical MetodologyrasoolNo ratings yet
- Microgrids Smart Grids and Energy Storage SolutionsDocument28 pagesMicrogrids Smart Grids and Energy Storage SolutionsDGGNo ratings yet
- BYD Battery-Box Operating Manual LVL 15.4: PremiumDocument37 pagesBYD Battery-Box Operating Manual LVL 15.4: PremiumDINONo ratings yet
- Horizontal Stability Check by P-Y AnalysisDocument21 pagesHorizontal Stability Check by P-Y AnalysisOanh PhanNo ratings yet
- Asset ManagementDocument4 pagesAsset ManagementJohan TadlasNo ratings yet
- Factsheet-Kaxu Solar PowerDocument2 pagesFactsheet-Kaxu Solar PowerudelmarkNo ratings yet
- RatedPower PvDesign Energy Methodology ReportDocument111 pagesRatedPower PvDesign Energy Methodology Reportlos_erizosNo ratings yet
- PVTRIN Training Course: Troubleshooting GuideDocument20 pagesPVTRIN Training Course: Troubleshooting GuideBeni Saputra100% (1)
- First Solar 2014 Annual Report Bookmark - FinalDocument188 pagesFirst Solar 2014 Annual Report Bookmark - FinalFabián OrccónNo ratings yet
- SPV Planning ChecklistDocument74 pagesSPV Planning ChecklistJunel Lawrence IndiongcoNo ratings yet
- Performance RatioDocument9 pagesPerformance RatioShaileshnartiNo ratings yet
- Best Practices Handbook-NREL15Document255 pagesBest Practices Handbook-NREL15aitormrNo ratings yet
- Masterthesis Wietse Kruijsse Digital VersionDocument103 pagesMasterthesis Wietse Kruijsse Digital Versionkristinadodi1No ratings yet
- Offshore Wind in IndiaDocument10 pagesOffshore Wind in IndiaVenkatasubramanian IyerNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Single Axis Solar Tracker Using Arduino ApproachDocument8 pagesHorizontal Single Axis Solar Tracker Using Arduino ApproachKenan KenobeNo ratings yet
- Solar Photovoltaic Output Smoothing Using Battery Energy Storage SystemDocument4 pagesSolar Photovoltaic Output Smoothing Using Battery Energy Storage SystemAlif Imran MohamedNo ratings yet
- Rajasthan Solar ParksDocument20 pagesRajasthan Solar ParksRamaiah KumarNo ratings yet
- Solar PV Asset Management Trends Update - AlectrisDocument15 pagesSolar PV Asset Management Trends Update - AlectrisalvarovergaraNo ratings yet
- Solar Storage Solution20180709 V3Document12 pagesSolar Storage Solution20180709 V3SathishNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation and Optimization of Wind-Solar PV Hybrid Electricity Generation and Application To Electric VehicleDocument17 pagesPerformance Evaluation and Optimization of Wind-Solar PV Hybrid Electricity Generation and Application To Electric VehicleIJMTST-Online JournalNo ratings yet
- A 470036Document113 pagesA 470036Mamoona BashirNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power Based LCOE Analysis - SgurrEnergyDocument8 pagesReactive Power Based LCOE Analysis - SgurrEnergySgurr EnergyNo ratings yet
- Enabling Floating Solar Photovoltaic (FPV) Deployment: Review of Barriers To FPV Deployment in Southeast AsiaDocument36 pagesEnabling Floating Solar Photovoltaic (FPV) Deployment: Review of Barriers To FPV Deployment in Southeast AsiaNam Hoai LeNo ratings yet
- Market Assessment For Promoting Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Investment in Brazil Through Local Financial InstitutionsDocument201 pagesMarket Assessment For Promoting Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Investment in Brazil Through Local Financial Institutionsalan_douglas_pooleNo ratings yet
- Return On Investment of Solar PPVDocument2 pagesReturn On Investment of Solar PPVPramod DevalNo ratings yet
- SG II QUALITY Annex 24.12.2015Document89 pagesSG II QUALITY Annex 24.12.2015parthaNo ratings yet
- IEC 61010-1-2010 Amd1-2016 Cor1-2019Document4 pagesIEC 61010-1-2010 Amd1-2016 Cor1-2019Venkataramanan SNo ratings yet
- Iec 61005-2014Document108 pagesIec 61005-2014Venkataramanan SNo ratings yet
- Iec TS 61000-5-10-2017Document58 pagesIec TS 61000-5-10-2017Venkataramanan S50% (2)
- Iec 61000-4-8-2009Document70 pagesIec 61000-4-8-2009Venkataramanan SNo ratings yet
- Iec TS 61000-5-9-2009Document70 pagesIec TS 61000-5-9-2009Venkataramanan SNo ratings yet
- Iec TS 61000-5-8-2009Document32 pagesIec TS 61000-5-8-2009Venkataramanan SNo ratings yet
- IRENA - Renewable Energy Project FacilitationDocument64 pagesIRENA - Renewable Energy Project FacilitationVenkataramanan SNo ratings yet
- Connections - and - Connectors - Best PracticesDocument4 pagesConnections - and - Connectors - Best PracticesVenkataramanan SNo ratings yet
- Methods of Earth Resistance Testing (Part-2) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument8 pagesMethods of Earth Resistance Testing (Part-2) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesVenkataramanan SNo ratings yet
- Methods of Earth Resistance Testing (Part-1) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument5 pagesMethods of Earth Resistance Testing (Part-1) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesVenkataramanan SNo ratings yet
- In MF Monthly Portfolio Axismf Nov 2020Document215 pagesIn MF Monthly Portfolio Axismf Nov 2020Venkataramanan SNo ratings yet
- Ready For Mass Deployment: Bifacial PV TechnologyDocument9 pagesReady For Mass Deployment: Bifacial PV TechnologyVenkataramanan SNo ratings yet
- STUDY GUIDE Part 3 ProblemsDocument2 pagesSTUDY GUIDE Part 3 ProblemsBaylon RachelNo ratings yet
- Automation PresentationDocument32 pagesAutomation PresentationAman Sharma100% (1)
- CEODocument2 pagesCEOSheheryar ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Police CompetencyDocument10 pagesPolice CompetencyJushua PatulotNo ratings yet
- Effect of Advertisement On ConsumersDocument59 pagesEffect of Advertisement On Consumersvishal394% (49)
- SHARES - EXERCISES - KopiaDocument6 pagesSHARES - EXERCISES - KopiaOla KrupaNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management in Brief: Medhi CahyonoDocument7 pagesSupply Chain Management in Brief: Medhi CahyonoSetio TanoeNo ratings yet
- Sustainability and Asset Pricing ModelsDocument11 pagesSustainability and Asset Pricing ModelsMarisa LaokulrachNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 Protocol and Its Impact On The Construction Industry in AustraliaDocument61 pagesCovid-19 Protocol and Its Impact On The Construction Industry in Australiafaza izbikNo ratings yet
- Final Ko Ni Final 1234Document53 pagesFinal Ko Ni Final 1234Prajwol TamangNo ratings yet
- Datastream - How To Search For ESG Data - July 2022Document17 pagesDatastream - How To Search For ESG Data - July 202224a4010600No ratings yet
- Kalkidan Melaku Assignment 2Document5 pagesKalkidan Melaku Assignment 2KalkidanNo ratings yet
- Adsense Tips: (Collection of Adsense Tips and How To Articles) This Book Is Compiled byDocument46 pagesAdsense Tips: (Collection of Adsense Tips and How To Articles) This Book Is Compiled byJ.Ulrich Mamphayssou N'GUESSANNo ratings yet
- RP Assigment (Report)Document62 pagesRP Assigment (Report)Kithmina ThilakarathneNo ratings yet
- MS Adj 001Document1 pageMS Adj 001Manish ChandNo ratings yet
- Terex Simplicity Vibrating Feeders: Terex Minerals Processing SystemsDocument6 pagesTerex Simplicity Vibrating Feeders: Terex Minerals Processing Systemsestramilsolution100% (1)
- Notes On Business Law Regulation 202: Hand Out No. 01 By: Atty. Reinier John G. BrofarDocument6 pagesNotes On Business Law Regulation 202: Hand Out No. 01 By: Atty. Reinier John G. BrofarJamila MendozaNo ratings yet
- KH Concept Catalogue Sep 2023Document39 pagesKH Concept Catalogue Sep 2023Jus StreamingNo ratings yet
- 2044 6175 2 RVDocument12 pages2044 6175 2 RVBambang HaryadiNo ratings yet
- Oct 21 Time TableDocument112 pagesOct 21 Time TableChai ChaiNo ratings yet
- Esewa Final Project 1Document31 pagesEsewa Final Project 1spikerohit44No ratings yet
- Case Study Champions League FinalDocument14 pagesCase Study Champions League FinalRakeem DavidsonNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 3Document2 pagesProblem Set 3Omar SrourNo ratings yet
- Successful Legacy Systems Modernization Insurance White Paper 2489Document12 pagesSuccessful Legacy Systems Modernization Insurance White Paper 2489Avinash DNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management Nust RevisedDocument133 pagesPrinciples of Management Nust RevisedCharlesTichavavamweNo ratings yet
- Pmi ProcedureDocument6 pagesPmi ProcedureKetan GavadeNo ratings yet
- Order of Payment: CNC Online Application SystemDocument1 pageOrder of Payment: CNC Online Application SystemEva MarquezNo ratings yet