Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assessing The Pregnant Woman Presumptive (Subjective) Symptoms
Assessing The Pregnant Woman Presumptive (Subjective) Symptoms
Uploaded by
Myfanway Am-isCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Physiology of Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDocument2 pagesPhysiology of Normal Spontaneous DeliverySummer Rain100% (2)
- OB 1st PNCUDocument8 pagesOB 1st PNCUAngelo Erispe100% (1)
- CaseanalysisDocument2 pagesCaseanalysisChrislyn Dian Pene100% (1)
- Patho Physiology Ovarian CystDocument3 pagesPatho Physiology Ovarian CystSig Deliso100% (1)
- Chapter 15 - Labor and Birth: Ob LectureDocument15 pagesChapter 15 - Labor and Birth: Ob LectureMARIA PEARLITA TANNo ratings yet
- 05.fisiologi KehamilanDocument40 pages05.fisiologi KehamilanYunan Syahban MaskatNo ratings yet
- MCN Lec MidtermDocument29 pagesMCN Lec Midtermnaomie manaliliNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cyst PathophysiologyDocument1 pageOvarian Cyst PathophysiologyShamsa Afdal100% (2)
- Pregnancy Group 15Document31 pagesPregnancy Group 15Aeron Jay GalagateNo ratings yet
- Patho of OCDocument1 pagePatho of OCOrrin D. BarbaNo ratings yet
- Case PresDocument22 pagesCase Presandrei jinNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 MidtermsDocument21 pagesNCM 107 MidtermsMA. ALTHEA LOUISE SALVACIONNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa Abruptio Placenta Placenta Location: During PregnancyDocument3 pagesPlacenta Previa Abruptio Placenta Placenta Location: During PregnancyBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- TM 1 - Perubahan Fisik Selama KehamilanDocument28 pagesTM 1 - Perubahan Fisik Selama Kehamilanarda mega mNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics (Tra Intl)Document10 pagesObstetrics (Tra Intl)Cess MarigondonNo ratings yet
- Lp1 ReviewerDocument19 pagesLp1 ReviewerNiña Ricci MtflcoNo ratings yet
- The Discomforts Pregnancy: Deborah Davis, CRNPDocument9 pagesThe Discomforts Pregnancy: Deborah Davis, CRNPRiska Noor Fauziah MadjiidNo ratings yet
- Proses Persalinan Dan Konsep DasarDocument31 pagesProses Persalinan Dan Konsep DasarShella Ramashanti100% (1)
- Lp1 ReviewerDocument17 pagesLp1 ReviewerNiña Ricci MtflcoNo ratings yet
- Physiologic Changes in Pregnancy: 1. UterusDocument14 pagesPhysiologic Changes in Pregnancy: 1. UterusNiña Ricci MtflcoNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy 66Document64 pagesPregnancy 66Mohnnad Hmood AlgaraybhNo ratings yet
- Labor and Birth Process and NURSING MANAGEMENT (Chapter 13 and 14) False Labor Factors That Affect LaborDocument7 pagesLabor and Birth Process and NURSING MANAGEMENT (Chapter 13 and 14) False Labor Factors That Affect LaborSHARLAIN GAIL V. MELECIONo ratings yet
- Positive Pregnancy Test-Presence of HCG in The 5. BallottmentDocument8 pagesPositive Pregnancy Test-Presence of HCG in The 5. BallottmentVince Matt BaguioNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and ChildbirthDocument14 pagesPregnancy and ChildbirthNataly Aponte CruzadoNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Pregnant Woman ReviewerDocument8 pagesAssessment of The Pregnant Woman ReviewerVince Matt BaguioNo ratings yet
- Intrartum/Intrapartal Period: Phenomena and Process of Labor and Delivery I. Onset of LaborDocument14 pagesIntrartum/Intrapartal Period: Phenomena and Process of Labor and Delivery I. Onset of Laborclaireaongchua1275No ratings yet
- Ovarian Cysts 101Document4 pagesOvarian Cysts 101sonnymorenteNo ratings yet
- Montano Case AnalysisDocument12 pagesMontano Case Analysiskarl montanoNo ratings yet
- PBL and NDXDocument15 pagesPBL and NDXJasmin AdoraNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Chronic Hypertension With Superimposed Preeclampsia (Obstetrical Complex)Document13 pagesCase Study of Chronic Hypertension With Superimposed Preeclampsia (Obstetrical Complex)Ivan Laurentine AceretNo ratings yet
- Maternity Nursing NotesDocument7 pagesMaternity Nursing NotesazitaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Concept of Pregnancy Final NCM 107 07172019Document6 pagesConcept of Pregnancy Final NCM 107 07172019Jarod Hembrador100% (1)
- W3case Objectives and Learning ObjectivesDocument14 pagesW3case Objectives and Learning ObjectivesGabriella TjondroNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of PregnancyDocument63 pagesDiagnosis of Pregnancyindri febiyanNo ratings yet
- The Confirmation of Pregnancy, Psychological and Physiological Changes of PregnancyDocument37 pagesThe Confirmation of Pregnancy, Psychological and Physiological Changes of Pregnancyana aurea aquino de leonNo ratings yet
- NUR 1025 Exam 1 NotesDocument3 pagesNUR 1025 Exam 1 NotesfpltdcNo ratings yet
- (ObstetricsA) Prenatal Care - Dr. San Jose (Lea Pacis)Document12 pages(ObstetricsA) Prenatal Care - Dr. San Jose (Lea Pacis)Karen EstavilloNo ratings yet
- PBL 3 KLP 10Document45 pagesPBL 3 KLP 10Ana Abadi Al IndNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Care 101 OrientationDocument42 pagesAntepartum Care 101 OrientationJoahneNo ratings yet
- Maternal Physiological and Psychological Adaptations To PregnancyDocument62 pagesMaternal Physiological and Psychological Adaptations To PregnancySuad jakalatNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care SessionDocument35 pagesAntenatal Care Sessionbintehawaarain98No ratings yet
- Normal Labor and DeliveryDocument142 pagesNormal Labor and DeliveryRosalie RoselloNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1Document100 pagesNCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1marilexdomagsangNo ratings yet
- Lecture On PregnancyDocument40 pagesLecture On PregnancyMarc Jamel ROdriguezNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 RLE NotesDocument40 pagesNCM 107 RLE NotesPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Case 01 - Maternal PhysiologyDocument5 pagesCase 01 - Maternal PhysiologyRem AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Early Pregnancy ComplicationsDocument38 pagesEarly Pregnancy ComplicationsAzim Syahmi Abd RazakNo ratings yet
- CMCP M1Document312 pagesCMCP M1evangdelacruz1010No ratings yet
- MATERNAL NleDocument8 pagesMATERNAL NleMary Danielle SaludarioNo ratings yet
- Prenatal CareDocument77 pagesPrenatal Caredavidbuena0920No ratings yet
- Antepartum PeriodDocument20 pagesAntepartum PeriodMary Joy FrancoNo ratings yet
- Refreshing Inersia UteriDocument31 pagesRefreshing Inersia UteriDera Seta SaputriNo ratings yet
- Excitement Phase 4 WeeksDocument4 pagesExcitement Phase 4 WeekshahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- The Child Bearing StageDocument130 pagesThe Child Bearing StageSheenaGuinoCullaNo ratings yet
- OB BessDocument4 pagesOB BessKate SantosNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgBadmrbzR Zbaf9LIsgA4xz3BXrf4T JrmRyxu5 5bkJFOaK1lMBnJ2 AUVEbPfI17GyIzBlEKvmA QY2 MBlLC8PHYkavITBEfKLN2rz Ns UV ETHtZJ3GVrlvuohWjtap7LzQ0YgxbfDocument37 pagesACFrOgBadmrbzR Zbaf9LIsgA4xz3BXrf4T JrmRyxu5 5bkJFOaK1lMBnJ2 AUVEbPfI17GyIzBlEKvmA QY2 MBlLC8PHYkavITBEfKLN2rz Ns UV ETHtZJ3GVrlvuohWjtap7LzQ0YgxbfBiraito TakanaNo ratings yet
- Maternal & Newborn 1Document133 pagesMaternal & Newborn 1Philip Gene II MalacasNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Kehamilan-1Document34 pagesFisiologi Kehamilan-1Igus UlfayazeNo ratings yet
- Pre Natal Care Book BasedDocument9 pagesPre Natal Care Book BasedAngelaTrinidadNo ratings yet
- Bladder IrrigationDocument3 pagesBladder IrrigationMyfanway Am-isNo ratings yet
- IV CannulationDocument4 pagesIV CannulationMyfanway Am-isNo ratings yet
- A2 Concept MapDocument1 pageA2 Concept MapMyfanway Am-isNo ratings yet
- Assessment: NCM 33 - Leclab Perineal Care, Hot Sitz Bath and Heat Lamp TreatmentDocument2 pagesAssessment: NCM 33 - Leclab Perineal Care, Hot Sitz Bath and Heat Lamp TreatmentMyfanway Am-isNo ratings yet
- POCQI-Slides For Lead Facilitator Ver-3Document62 pagesPOCQI-Slides For Lead Facilitator Ver-3muna WarohNo ratings yet
- Is, Am, Are,: Was, WereDocument2 pagesIs, Am, Are,: Was, WereAsma noviyantiNo ratings yet
- Tugas Elearning Pertemuan Ke - 13 - Asdiana Meliani (F0G020054)Document9 pagesTugas Elearning Pertemuan Ke - 13 - Asdiana Meliani (F0G020054)ANdri FauziNo ratings yet
- Endometrial Hyperplasia Management G40 v4Document12 pagesEndometrial Hyperplasia Management G40 v4sulaimanakramzai123No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan of Preparation of Parenthood and Child BiethDocument7 pagesLesson Plan of Preparation of Parenthood and Child Biethsuman guptaNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Early PregnancyDocument7 pagesTerm Paper Early Pregnancyaehupavkg100% (1)
- Final ReportDocument175 pagesFinal ReportAmogh SanikopNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step 3 CCS StrategiesDocument6 pagesUSMLE Step 3 CCS StrategiesDuncan Jackson100% (1)
- Endocrine Pharma 1Document3 pagesEndocrine Pharma 1Vaishali PrasharNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument25 pagesEndocrinologyMaryam ShahzadiNo ratings yet
- Ob Post TestDocument11 pagesOb Post TestAlexNo ratings yet
- Invitation To Health Live It Now Brief Edition 9th Edition Dianne Hales Test BankDocument22 pagesInvitation To Health Live It Now Brief Edition 9th Edition Dianne Hales Test Bankcomplinofficialjasms100% (32)
- Objectives and PoaDocument2 pagesObjectives and PoaALIZA BAKILNo ratings yet
- Respondent 3Document6 pagesRespondent 3Giezell Kenette KallosNo ratings yet
- Statistics Learning From Data 1st Edition Roxy Peck Test BankDocument25 pagesStatistics Learning From Data 1st Edition Roxy Peck Test BankTracySnydereigtc100% (41)
- Presentation On AnaemiaDocument19 pagesPresentation On AnaemiaAnkit MalikNo ratings yet
- 2009 - Analysis of Overall Kinematics and Abdominal Response of PregnantDocument10 pages2009 - Analysis of Overall Kinematics and Abdominal Response of PregnantGuilherme AugustoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyClau MagahisNo ratings yet
- Ryan Robinson WritingDocument2 pagesRyan Robinson WritinggliftanNo ratings yet
- Occipitoposterior PositionsDocument49 pagesOccipitoposterior PositionsBharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- The Penis: - Phimosis: Scarring of The Prepuce Which Will Not Retract Without FissuringDocument20 pagesThe Penis: - Phimosis: Scarring of The Prepuce Which Will Not Retract Without FissuringWorku KifleNo ratings yet
- Family Health Book (English)Document66 pagesFamily Health Book (English)Jane Rojas FortunaNo ratings yet
- Test ISSUEm 3 Q 3Document2 pagesTest ISSUEm 3 Q 3May KopsNo ratings yet
- Nausea and Vomiting of PregnancyDocument8 pagesNausea and Vomiting of PregnancycintacitraNo ratings yet
- Literature Review MatrixDocument2 pagesLiterature Review MatrixRonamae LintagNo ratings yet
- Section A. Family Planning Services For Women of Reproductive AgeDocument27 pagesSection A. Family Planning Services For Women of Reproductive AgeMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Effects of Hormonal Changes Throughout The Menstrual Cycle On JoiDocument131 pagesEffects of Hormonal Changes Throughout The Menstrual Cycle On JoiAhamadulla hil GalebNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingDocument6 pagesThe Endocrine System Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingWai KikiNo ratings yet
- 6 - Physiology MCQ of General PhysiologyDocument20 pages6 - Physiology MCQ of General PhysiologymohammedNo ratings yet
Assessing The Pregnant Woman Presumptive (Subjective) Symptoms
Assessing The Pregnant Woman Presumptive (Subjective) Symptoms
Uploaded by
Myfanway Am-isOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessing The Pregnant Woman Presumptive (Subjective) Symptoms
Assessing The Pregnant Woman Presumptive (Subjective) Symptoms
Uploaded by
Myfanway Am-isCopyright:
Available Formats
ASSESSING THE PREGNANT WOMAN
Presumptive (Subjective) Symptoms
which could easily indicate other conditions
taken as single entities
Breast changes – feelings of tenderness, fullness, tingling, enlargement and darkening of the areola
Nausea, vomiting
o arising when fatigued
o known as morning sickness as levels of hCG and progesterone begin to rise
Amenorrhea – absence of menstruation
Frequent urination – sense of having to void more often
Fatigue – general feeling of tiredness
Uterine enlargement – uterus can be palpated over symphysis pubis
Quickening – fetal movement felt by woman
Linea nigra – line of dark pigment forms on the abdomen
Melasma – dark pigment for on face
Striae gravidarum – stretch mark form on abdomen
Probable (Objective) Symptoms
can be verified by an examiner
Maternal serum test – a venipuncture of blood serum reveals the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin
hormone
Chadwick’s sign – color change of the vagina from pink to violet
Goodell’s sign – softening of the cervix
Hegar’s sign – softening of the lower uterine segment
Sonography evidence of gestational sac – characteristic ring is evident
Ballottement – when lower uterine segment is tapped on a bimanual examination, the fetus can be felt to rise
against the abdominal wall
Braxton Hicks contractions – periodic uterine tightening occurs
Fetal outline felt by examiner – fetal outline can be palpated through abdomen
Laboratory Tests
the use of a venipuncture or a urine specimen to detect the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
hCG
a hormone created by the chorionic villi of the placenta, in the urine or blood serum of the pregnant woman
only 95% to 98% accurate so results are considered as probable rather than positive
In non-pregnant woman, no units of hCG will be detectable because there are no trophoblast cells producing hCG.
In pregnant woman, trace amounts of hCG will appear in her serum as early as 24 to 48 hours after implantation and
reach a measurable level.
Positive Finding
Sonographic evidence of fetal outline
o fetal outline can be seen and measured by sonogram
Fetal heart audible
o doppler ultrasound reveals heartbeat
Fetal movement felt by examiner
o fetal movement can be palpated through abdomen
Positive Signs of Pregnancy
1. demonstration of a fetal heart separate from the mother’s
o fetal heart cannot be heard through an ordinary stethoscope until 18 to 20 weeks
o an echocardiography can demonstrate a heartbeat as early as 5 weeks
o an ultrasound can reveal a beating fetal heart as early as 6 th to 7th week of pregnancy
o doppler instrumentation (converts ultrasonic frequencies to audible frequencies) is able to detect fetal
heart sounds as early as the 10th to 12th week of gestation
o normal fetal heart rate – 120-60 bpm
o polyhydramnios – a larger-than-normal amount of amniotic fluid present
2. fetal movements felt by an examiner
o fetal movements may be felt by a woman as early as 16 to 20 weeks
o objective examiner can discern fetal movements at about 20 th to 40th week of pregnancy
3. visualization of the fetus by ultrasound
o ultrasound – the most common method for confirmation of pregnancy today
o if a woman is pregnant, a characteristic ring (indicating the gestational sac), will be revealed on an
oscilloscope screen as early as the 4th to 6th week of pregnancy
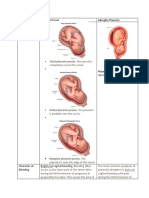
Physiologic Changes of Pregnancy
Location of Change First Trimester Second Trimester Third Trimester
Cardiovascular blood volume blood pressure slightly blood pressure returns to
increasing decreased prepregnancy levels
pseudoanemia may
occur
clotting factors
increasing
Ovarian uterine corpus luteum corpus luteum steady increased growth
active fading
steady increased placenta producing
growth estrogen and
progesterone,
steady increased
growth of ovarian
uterine
Cervix softening begins softening increases “ripe”
Vagina white discharge present increasing in amount
Musculoskeletal progressive
cartilage softening
lordosis increasing
progressively
increasing
Pigmentation progressively possible back or pelvic
increasing girdle pain
Kidney maternal
glomerular
filtration rate
increasing
glycosuria begins
and increases
aldosterone
increased, aiding
retention of sodium
and fluid
Gastrointestinal slowed peristalsis
Thyroid increased metabolic rate
You might also like
- Physiology of Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDocument2 pagesPhysiology of Normal Spontaneous DeliverySummer Rain100% (2)
- OB 1st PNCUDocument8 pagesOB 1st PNCUAngelo Erispe100% (1)
- CaseanalysisDocument2 pagesCaseanalysisChrislyn Dian Pene100% (1)
- Patho Physiology Ovarian CystDocument3 pagesPatho Physiology Ovarian CystSig Deliso100% (1)
- Chapter 15 - Labor and Birth: Ob LectureDocument15 pagesChapter 15 - Labor and Birth: Ob LectureMARIA PEARLITA TANNo ratings yet
- 05.fisiologi KehamilanDocument40 pages05.fisiologi KehamilanYunan Syahban MaskatNo ratings yet
- MCN Lec MidtermDocument29 pagesMCN Lec Midtermnaomie manaliliNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cyst PathophysiologyDocument1 pageOvarian Cyst PathophysiologyShamsa Afdal100% (2)
- Pregnancy Group 15Document31 pagesPregnancy Group 15Aeron Jay GalagateNo ratings yet
- Patho of OCDocument1 pagePatho of OCOrrin D. BarbaNo ratings yet
- Case PresDocument22 pagesCase Presandrei jinNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 MidtermsDocument21 pagesNCM 107 MidtermsMA. ALTHEA LOUISE SALVACIONNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa Abruptio Placenta Placenta Location: During PregnancyDocument3 pagesPlacenta Previa Abruptio Placenta Placenta Location: During PregnancyBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- TM 1 - Perubahan Fisik Selama KehamilanDocument28 pagesTM 1 - Perubahan Fisik Selama Kehamilanarda mega mNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics (Tra Intl)Document10 pagesObstetrics (Tra Intl)Cess MarigondonNo ratings yet
- Lp1 ReviewerDocument19 pagesLp1 ReviewerNiña Ricci MtflcoNo ratings yet
- The Discomforts Pregnancy: Deborah Davis, CRNPDocument9 pagesThe Discomforts Pregnancy: Deborah Davis, CRNPRiska Noor Fauziah MadjiidNo ratings yet
- Proses Persalinan Dan Konsep DasarDocument31 pagesProses Persalinan Dan Konsep DasarShella Ramashanti100% (1)
- Lp1 ReviewerDocument17 pagesLp1 ReviewerNiña Ricci MtflcoNo ratings yet
- Physiologic Changes in Pregnancy: 1. UterusDocument14 pagesPhysiologic Changes in Pregnancy: 1. UterusNiña Ricci MtflcoNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy 66Document64 pagesPregnancy 66Mohnnad Hmood AlgaraybhNo ratings yet
- Labor and Birth Process and NURSING MANAGEMENT (Chapter 13 and 14) False Labor Factors That Affect LaborDocument7 pagesLabor and Birth Process and NURSING MANAGEMENT (Chapter 13 and 14) False Labor Factors That Affect LaborSHARLAIN GAIL V. MELECIONo ratings yet
- Positive Pregnancy Test-Presence of HCG in The 5. BallottmentDocument8 pagesPositive Pregnancy Test-Presence of HCG in The 5. BallottmentVince Matt BaguioNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and ChildbirthDocument14 pagesPregnancy and ChildbirthNataly Aponte CruzadoNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Pregnant Woman ReviewerDocument8 pagesAssessment of The Pregnant Woman ReviewerVince Matt BaguioNo ratings yet
- Intrartum/Intrapartal Period: Phenomena and Process of Labor and Delivery I. Onset of LaborDocument14 pagesIntrartum/Intrapartal Period: Phenomena and Process of Labor and Delivery I. Onset of Laborclaireaongchua1275No ratings yet
- Ovarian Cysts 101Document4 pagesOvarian Cysts 101sonnymorenteNo ratings yet
- Montano Case AnalysisDocument12 pagesMontano Case Analysiskarl montanoNo ratings yet
- PBL and NDXDocument15 pagesPBL and NDXJasmin AdoraNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Chronic Hypertension With Superimposed Preeclampsia (Obstetrical Complex)Document13 pagesCase Study of Chronic Hypertension With Superimposed Preeclampsia (Obstetrical Complex)Ivan Laurentine AceretNo ratings yet
- Maternity Nursing NotesDocument7 pagesMaternity Nursing NotesazitaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Concept of Pregnancy Final NCM 107 07172019Document6 pagesConcept of Pregnancy Final NCM 107 07172019Jarod Hembrador100% (1)
- W3case Objectives and Learning ObjectivesDocument14 pagesW3case Objectives and Learning ObjectivesGabriella TjondroNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of PregnancyDocument63 pagesDiagnosis of Pregnancyindri febiyanNo ratings yet
- The Confirmation of Pregnancy, Psychological and Physiological Changes of PregnancyDocument37 pagesThe Confirmation of Pregnancy, Psychological and Physiological Changes of Pregnancyana aurea aquino de leonNo ratings yet
- NUR 1025 Exam 1 NotesDocument3 pagesNUR 1025 Exam 1 NotesfpltdcNo ratings yet
- (ObstetricsA) Prenatal Care - Dr. San Jose (Lea Pacis)Document12 pages(ObstetricsA) Prenatal Care - Dr. San Jose (Lea Pacis)Karen EstavilloNo ratings yet
- PBL 3 KLP 10Document45 pagesPBL 3 KLP 10Ana Abadi Al IndNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Care 101 OrientationDocument42 pagesAntepartum Care 101 OrientationJoahneNo ratings yet
- Maternal Physiological and Psychological Adaptations To PregnancyDocument62 pagesMaternal Physiological and Psychological Adaptations To PregnancySuad jakalatNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care SessionDocument35 pagesAntenatal Care Sessionbintehawaarain98No ratings yet
- Normal Labor and DeliveryDocument142 pagesNormal Labor and DeliveryRosalie RoselloNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1Document100 pagesNCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1marilexdomagsangNo ratings yet
- Lecture On PregnancyDocument40 pagesLecture On PregnancyMarc Jamel ROdriguezNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 RLE NotesDocument40 pagesNCM 107 RLE NotesPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Case 01 - Maternal PhysiologyDocument5 pagesCase 01 - Maternal PhysiologyRem AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Early Pregnancy ComplicationsDocument38 pagesEarly Pregnancy ComplicationsAzim Syahmi Abd RazakNo ratings yet
- CMCP M1Document312 pagesCMCP M1evangdelacruz1010No ratings yet
- MATERNAL NleDocument8 pagesMATERNAL NleMary Danielle SaludarioNo ratings yet
- Prenatal CareDocument77 pagesPrenatal Caredavidbuena0920No ratings yet
- Antepartum PeriodDocument20 pagesAntepartum PeriodMary Joy FrancoNo ratings yet
- Refreshing Inersia UteriDocument31 pagesRefreshing Inersia UteriDera Seta SaputriNo ratings yet
- Excitement Phase 4 WeeksDocument4 pagesExcitement Phase 4 WeekshahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- The Child Bearing StageDocument130 pagesThe Child Bearing StageSheenaGuinoCullaNo ratings yet
- OB BessDocument4 pagesOB BessKate SantosNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgBadmrbzR Zbaf9LIsgA4xz3BXrf4T JrmRyxu5 5bkJFOaK1lMBnJ2 AUVEbPfI17GyIzBlEKvmA QY2 MBlLC8PHYkavITBEfKLN2rz Ns UV ETHtZJ3GVrlvuohWjtap7LzQ0YgxbfDocument37 pagesACFrOgBadmrbzR Zbaf9LIsgA4xz3BXrf4T JrmRyxu5 5bkJFOaK1lMBnJ2 AUVEbPfI17GyIzBlEKvmA QY2 MBlLC8PHYkavITBEfKLN2rz Ns UV ETHtZJ3GVrlvuohWjtap7LzQ0YgxbfBiraito TakanaNo ratings yet
- Maternal & Newborn 1Document133 pagesMaternal & Newborn 1Philip Gene II MalacasNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Kehamilan-1Document34 pagesFisiologi Kehamilan-1Igus UlfayazeNo ratings yet
- Pre Natal Care Book BasedDocument9 pagesPre Natal Care Book BasedAngelaTrinidadNo ratings yet
- Bladder IrrigationDocument3 pagesBladder IrrigationMyfanway Am-isNo ratings yet
- IV CannulationDocument4 pagesIV CannulationMyfanway Am-isNo ratings yet
- A2 Concept MapDocument1 pageA2 Concept MapMyfanway Am-isNo ratings yet
- Assessment: NCM 33 - Leclab Perineal Care, Hot Sitz Bath and Heat Lamp TreatmentDocument2 pagesAssessment: NCM 33 - Leclab Perineal Care, Hot Sitz Bath and Heat Lamp TreatmentMyfanway Am-isNo ratings yet
- POCQI-Slides For Lead Facilitator Ver-3Document62 pagesPOCQI-Slides For Lead Facilitator Ver-3muna WarohNo ratings yet
- Is, Am, Are,: Was, WereDocument2 pagesIs, Am, Are,: Was, WereAsma noviyantiNo ratings yet
- Tugas Elearning Pertemuan Ke - 13 - Asdiana Meliani (F0G020054)Document9 pagesTugas Elearning Pertemuan Ke - 13 - Asdiana Meliani (F0G020054)ANdri FauziNo ratings yet
- Endometrial Hyperplasia Management G40 v4Document12 pagesEndometrial Hyperplasia Management G40 v4sulaimanakramzai123No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan of Preparation of Parenthood and Child BiethDocument7 pagesLesson Plan of Preparation of Parenthood and Child Biethsuman guptaNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Early PregnancyDocument7 pagesTerm Paper Early Pregnancyaehupavkg100% (1)
- Final ReportDocument175 pagesFinal ReportAmogh SanikopNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step 3 CCS StrategiesDocument6 pagesUSMLE Step 3 CCS StrategiesDuncan Jackson100% (1)
- Endocrine Pharma 1Document3 pagesEndocrine Pharma 1Vaishali PrasharNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument25 pagesEndocrinologyMaryam ShahzadiNo ratings yet
- Ob Post TestDocument11 pagesOb Post TestAlexNo ratings yet
- Invitation To Health Live It Now Brief Edition 9th Edition Dianne Hales Test BankDocument22 pagesInvitation To Health Live It Now Brief Edition 9th Edition Dianne Hales Test Bankcomplinofficialjasms100% (32)
- Objectives and PoaDocument2 pagesObjectives and PoaALIZA BAKILNo ratings yet
- Respondent 3Document6 pagesRespondent 3Giezell Kenette KallosNo ratings yet
- Statistics Learning From Data 1st Edition Roxy Peck Test BankDocument25 pagesStatistics Learning From Data 1st Edition Roxy Peck Test BankTracySnydereigtc100% (41)
- Presentation On AnaemiaDocument19 pagesPresentation On AnaemiaAnkit MalikNo ratings yet
- 2009 - Analysis of Overall Kinematics and Abdominal Response of PregnantDocument10 pages2009 - Analysis of Overall Kinematics and Abdominal Response of PregnantGuilherme AugustoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyClau MagahisNo ratings yet
- Ryan Robinson WritingDocument2 pagesRyan Robinson WritinggliftanNo ratings yet
- Occipitoposterior PositionsDocument49 pagesOccipitoposterior PositionsBharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- The Penis: - Phimosis: Scarring of The Prepuce Which Will Not Retract Without FissuringDocument20 pagesThe Penis: - Phimosis: Scarring of The Prepuce Which Will Not Retract Without FissuringWorku KifleNo ratings yet
- Family Health Book (English)Document66 pagesFamily Health Book (English)Jane Rojas FortunaNo ratings yet
- Test ISSUEm 3 Q 3Document2 pagesTest ISSUEm 3 Q 3May KopsNo ratings yet
- Nausea and Vomiting of PregnancyDocument8 pagesNausea and Vomiting of PregnancycintacitraNo ratings yet
- Literature Review MatrixDocument2 pagesLiterature Review MatrixRonamae LintagNo ratings yet
- Section A. Family Planning Services For Women of Reproductive AgeDocument27 pagesSection A. Family Planning Services For Women of Reproductive AgeMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Effects of Hormonal Changes Throughout The Menstrual Cycle On JoiDocument131 pagesEffects of Hormonal Changes Throughout The Menstrual Cycle On JoiAhamadulla hil GalebNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingDocument6 pagesThe Endocrine System Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingWai KikiNo ratings yet
- 6 - Physiology MCQ of General PhysiologyDocument20 pages6 - Physiology MCQ of General PhysiologymohammedNo ratings yet