Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hematuria
Hematuria
Uploaded by
Vivek0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views13 pagesA 67-year-old male presented with blood in his urine. His history and examination were consistent with benign prostatic hyperplasia, a benign enlargement of the prostate gland which can cause hematuria and urinary symptoms. Further investigations and referral to a urologist were recommended to confirm the diagnosis. Differential diagnoses included infections, stones, tumors, and prior procedures but were deemed less likely based on the history provided.
Original Description:
Original Title
hematuria
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA 67-year-old male presented with blood in his urine. His history and examination were consistent with benign prostatic hyperplasia, a benign enlargement of the prostate gland which can cause hematuria and urinary symptoms. Further investigations and referral to a urologist were recommended to confirm the diagnosis. Differential diagnoses included infections, stones, tumors, and prior procedures but were deemed less likely based on the history provided.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views13 pagesHematuria
Hematuria
Uploaded by
VivekA 67-year-old male presented with blood in his urine. His history and examination were consistent with benign prostatic hyperplasia, a benign enlargement of the prostate gland which can cause hematuria and urinary symptoms. Further investigations and referral to a urologist were recommended to confirm the diagnosis. Differential diagnoses included infections, stones, tumors, and prior procedures but were deemed less likely based on the history provided.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 13
HEMATURIA
You are a GP, your next patient is a 67 year old male
who comes in complaining of blood in urine.
Tasks
History
Physical Finding from the examiner
Diagnosis and Differentials
Management
History
For how many episodes? What colour have you noticed(frank blood or
cloudy brown), any clots?
During passage of urine, does this happen at the beginning or at the
end? (initial-urethtral origin, terminal-bladder or prostate origin)
Do you have frequency of urination? How many times during the day
and how many times during the night
difficulties urinating, such as trouble starting the flow of urine?
the urge to urinate often, particularly at night?
Any problem with the stream, any dribbling afterwards?
feeling as though the bladder can't be fully emptied?
Any pain or burning sensation on passing urine? Fever with chills or
rigor? any loin pain or loin to groin pain?
Have you noticed any changes in weight recently? Any change
in your appetite? Backache?
Any smptoms like cough, sob, chest pain, palpitations,
headache? Any lumps or bumps around the body
Have you had any large amounts of beetroot, berries?
(pseudohematuria)
Any recent trauma
SADMA : Known hypertensive.Are you on any medications?
any blood thinners?( patient’s taking aspirin)
Any family history of bleeding disorders or cancers?
Any previous instrumentation or surgery in the urinary
tract?(stricture)
Physical Examination
General Appearance: BMI, Pallour, lymphadenopathy
Vital signs: BP with postural drop, pulse with rate and rhythm,
temperature
Abdomen Examination: tenderness, any mass or organomegaly
percussion of the bladder wall (after the patient has voided)
DRE * Size and consistency of the prostate? Surface Nodularity? Is
the median sulcus palpable? Mobility or the attachment of the rectal
mucosa to underlying gland? (consistnecy firm but not hard, no
induration, moderate enlargement, mobile, surface-smooth)
Neurological examination of upper and lower limb
Respiratory and CVS examination
Office test : urine dipstick test, BSL
INVESTIGATIONS
FBE, ESR & CRP
Renal function tests (s. Creatinine, eGFR)
Serum electrolyte level, blood glucose level
PSA
Urine MC & S, urine cytology
XRAY KUB (for assessing radio opaque renal, ureteric stones,
sensitivity 60%)
USG KUB
Non contrast CT of KUB
CT intravenous pyelogram/ CT urogram By urologist
Cystoscopy
Transrectal USG with biopsy(if needed)
Diagnosis and Management
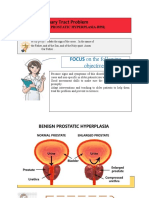
From history and examination, most likely you have a
condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia, which a benign
enlargement of the prostate gland. This gland is a small gland
located at the base of the bladder, function is to form some part
of semen. Sometimes this gland enlarges with increased
vasculatrity leading to blood in urine, also partial blockage of the
tubes (urethra)that passes through the prostate gives rise to
symptoms like frequency, weak stream, hesitency with initiating
urination
I would have to further (aformentioned) investigations and refer
you to the specialist/urologist to review and confirm
There are multiple causes of hematuria/blood in urine.
Infection in the tract can cause hematuria but you don’t have any
burning sesnation or fever
Infection of the kidneys (pyelonephritis) but you don’t have any
fever with chills or rigor
Stone in urinary tracts (ureter, bladder) can lead to blood in urine
but you don’t have severe loin to groin pain
In suspicious lesions or tumor of the urinary tract and prsotate,
hematuria can occur, but there would be weight loss, backache
Due to previous instrumentation or any surgery of the urinary tract,
blood in urine can occur
Also no history of trauma noted
(This case can come with problems with ‘urinary symptoms’ other
than hematuria)
Handbook case- condition 67- urinary symptoms with tiredness due
to hydrochlorthiazide
CASE: You have a 33 year old male coming to
your GP practice with 1-day history of
hematuria. He had an episode of URTI 2 days
ago. On examination his BP is 160/90,
generalized edema, urine dipstick Blood and
protein ++
History
Management
History
I can understand you had sore throat 2 days back, did you take any medications for it?
For how many episodes? What colour have you noticed(frank blood or cloudy
brown), any clots?
Any pain or burning sensation on passing urine? Fever with chills o rigor? any loin
pain or loin to groin pain?
Do you have frequency or urgency of urination? How many times during the day
and how many times during the night
During passage of urine, does this happen at the beginning or at the end? (initial-
urethtral origin, terminal-bladder or prostate origin)
Any trouble with the flow of the urine? Any puffiness of the face? Or legs?
Are you sexually active? If you don’t mind me asking, could it be sexually acquired?
Any hx of STD?
Do you engage in vigorous sports or physical acivities? Have you noticed bleeding
from anywhere else? Nosebleeds or easy bruising?
Have you had any large amounts of beetroots, berries or lollies?
SADMA
Positive here: history of sore throat a day ago, high blood
pressure,
Differentials in this scenario/age:
IgA nephropathy
PSGN
Basement membrane disease,
Polycystic kidney disease,
Stone in urinary tract/ stricture
March hemoglobinuria
Investigations: CBC, ESR, RFTs, ASO titre, complement level,
Urine MCS(RBC casts and RBC-indicates glomerula injury)
Urine culture, 24 hour urinary protein, USG, Non contrast CT (if
stone is suspected)
Most likely you have a condition called IgA nephropathy.
Because of the recent upper resp tract infection, the body
produced some antibodies towards bugs and these antibodies
deposited in the kidney’s filtering system, glomerulous
resulting in blood in urine.
You require admission, where will be assessed by a
nephrologist.
They will do the required investigations
High blood pressure medications.
Taking angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or
angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) can lower your blood
pressure and reduce protein loss.
Immunosuppressant- corticosteroids
Diuretics
You might also like
- Coding BreakdownDocument2 pagesCoding BreakdownAlex SouzaNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document30 pagesCH 10Narendran KumaravelNo ratings yet
- SWX315 Commander - Shuttlewagon Mobile Railcar MoversDocument54 pagesSWX315 Commander - Shuttlewagon Mobile Railcar MoversJesús Palomares100% (1)
- CRPC Project Sem 8thDocument11 pagesCRPC Project Sem 8thAbhay TiwariNo ratings yet
- Earthing Design CalculationsDocument7 pagesEarthing Design CalculationsVamsiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3 2D Shape With ReflectionDocument7 pagesLesson Plan 3 2D Shape With ReflectionfatimaNo ratings yet
- Urology HX and ExamDocument31 pagesUrology HX and ExamMisbah KaleemNo ratings yet
- Urethrolithiasis - EditDocument37 pagesUrethrolithiasis - EditShabrina Sari MedinaNo ratings yet
- Parade Bedah Urology-1Document22 pagesParade Bedah Urology-1Ide Yudis TiyoNo ratings yet
- Bladder Outlet Obstruction & Obstructive Uropathy BPHDocument73 pagesBladder Outlet Obstruction & Obstructive Uropathy BPHSisay FentaNo ratings yet
- Surgery ClerkingDocument24 pagesSurgery ClerkingSomto NwabuezeNo ratings yet
- Hematuria Passage of RBC in The Urine. We Have To Distinguish It From Other Causes ofDocument16 pagesHematuria Passage of RBC in The Urine. We Have To Distinguish It From Other Causes ofBuydh BfdsfsNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Renal and Urinary Tract FunctionDocument40 pagesAssessment of Renal and Urinary Tract FunctionBjorn Francisco100% (1)
- Renal and Urinary DisordersDocument134 pagesRenal and Urinary Disordersmirmodepon05100% (1)
- CRS: Hematuria: Group 3Document44 pagesCRS: Hematuria: Group 3Bazlie MifzalNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Anatomy Slides FINALDocument36 pagesPelvic Anatomy Slides FINALRajashekharNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument24 pagesHistoryAmin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Dysuria: Name: Chathiya Banu M/Num: MBBS 1608-7368Document39 pagesDysuria: Name: Chathiya Banu M/Num: MBBS 1608-7368Chathiya Banu KrishenanNo ratings yet
- Renal Disorders 1Document73 pagesRenal Disorders 1Kyla PamaNo ratings yet
- Icu Case Presentation: Group 1BDocument57 pagesIcu Case Presentation: Group 1Bjay kusainNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Patient With HaematuriaDocument21 pagesApproach To A Patient With HaematuriaMisbah KaleemNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Urine Retention Et Causa Benign Hyperplasia ProstatDocument37 pagesCase Report: Urine Retention Et Causa Benign Hyperplasia ProstatKania A BustamNo ratings yet
- Pap SmearDocument75 pagesPap SmearRaine BowNo ratings yet
- Abdominalpain 130214101728 Phpapp01Document78 pagesAbdominalpain 130214101728 Phpapp01Riddhisundar SamantaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection: DR Humna Najeeb KhanDocument28 pagesUrinary Tract Infection: DR Humna Najeeb KhanSaliha AkramNo ratings yet
- These Are Hospital PresentationsDocument73 pagesThese Are Hospital PresentationsMahmoud AjinehNo ratings yet
- Hematuria: Blood in The Urine Bladder Is Super Vascular and Prone To IrritationDocument4 pagesHematuria: Blood in The Urine Bladder Is Super Vascular and Prone To IrritationCarissa CorraroNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Renal & Genitourinary DisordersDocument72 pagesPediatric Renal & Genitourinary DisordersMarie Angelique Cruz CrestaniNo ratings yet
- A Guide To House Officers in Surgery Casualty ReceptionDocument19 pagesA Guide To House Officers in Surgery Casualty ReceptionVinicio LabanoNo ratings yet
- History/Physical and Symptoms and Signs of Different Diseases in UrologyDocument25 pagesHistory/Physical and Symptoms and Signs of Different Diseases in UrologyPatrascu CristiNo ratings yet
- History/Physical and Symptoms and Signs of Different Diseases in UrologyDocument26 pagesHistory/Physical and Symptoms and Signs of Different Diseases in UrologyDr. NasrumminallahNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain: Kerut SuardanaDocument48 pagesAbdominal Pain: Kerut SuardanaDiah SandiNo ratings yet
- Managing Urinary Tract Problem: FOCUS On The FollowingDocument11 pagesManaging Urinary Tract Problem: FOCUS On The FollowingLovely DaroleNo ratings yet
- Frequent Urination - What Causes A Frequent Urge To PeeDocument11 pagesFrequent Urination - What Causes A Frequent Urge To PeeJimmy GillNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy FINALDocument32 pagesEctopic Pregnancy FINALZak KazNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain: LSU Medical Student Clerkship, New Orleans, LADocument48 pagesAbdominal Pain: LSU Medical Student Clerkship, New Orleans, LALeonardo Adi BestNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive DisordersDocument5 pagesMale Reproductive DisorderslordwinjohnbernardoNo ratings yet
- Querol, Zachary Ivan G. - EAMC OB-GYNE CASE WRITE-UP 3Document8 pagesQuerol, Zachary Ivan G. - EAMC OB-GYNE CASE WRITE-UP 3zachary.ivan.querolNo ratings yet
- Urologic Emergencies: Hakan Koyuncu MD Associate Professor Yeditepe University Medical Faculty Department of UrologyDocument62 pagesUrologic Emergencies: Hakan Koyuncu MD Associate Professor Yeditepe University Medical Faculty Department of UrologycoassrunNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)Document5 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)Suneel Kumar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain: LSU Medical Student Clerkship, New Orleans, LADocument48 pagesAbdominal Pain: LSU Medical Student Clerkship, New Orleans, LAAmd SolihinNo ratings yet
- Urinary Disorders 2Document19 pagesUrinary Disorders 2ula mdiNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Bladder Outlet Obstruction (BOO)Document73 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Bladder Outlet Obstruction (BOO)Swe Zin NaingNo ratings yet
- CRT Acute AbdomenDocument73 pagesCRT Acute AbdomenNATTAPAT SANGKAKUL100% (1)
- Badan Sekejap. Kalau Ada Sakit, Sila Bagi Tahu.: Abdomen ExaminationDocument3 pagesBadan Sekejap. Kalau Ada Sakit, Sila Bagi Tahu.: Abdomen ExaminationHeavens SakeNo ratings yet
- Alteration in Urinary System - ppt22222Document117 pagesAlteration in Urinary System - ppt22222yen1988No ratings yet
- Ms Reviewer Renal UrinaryDocument5 pagesMs Reviewer Renal UrinaryAlyssa Nicole CajayonNo ratings yet
- Acute Abdomen and PeritonitisDocument17 pagesAcute Abdomen and PeritonitisAsuri KrishnaNo ratings yet
- UtiDocument23 pagesUtiShamila KaruthuNo ratings yet
- HX Taking Reproductive SystemDocument78 pagesHX Taking Reproductive SystemMuskaan ZaharaNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument7 pagesLiver CirrhosisJohn Yves B. SantosNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Fisik Sistem Renal Pada Pediatric: Oleh: Ns. Evy Marlinda, M.Kep, SP - Kep.AnDocument12 pagesPemeriksaan Fisik Sistem Renal Pada Pediatric: Oleh: Ns. Evy Marlinda, M.Kep, SP - Kep.AnJians FaujiansNo ratings yet
- Abdomen - Case Sheet - FinalDocument8 pagesAbdomen - Case Sheet - FinalHengkai NeoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Retention 2Document3 pagesUrinary Retention 2Agli AdhityaNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument9 pagesBenign Prostatic HyperplasiaElizabeth Mapa100% (1)
- Abdome AgudoDocument63 pagesAbdome AgudoAnne Caroline De Morais AlvesNo ratings yet
- Ruq Abdominal Pain: Steven B. Goldin, MD, PHD University of South Florida Dimitrios Stefanidis, MD, PHDDocument55 pagesRuq Abdominal Pain: Steven B. Goldin, MD, PHD University of South Florida Dimitrios Stefanidis, MD, PHDAndrei LucaNo ratings yet
- Div. of Urology, Dept. Surgery Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera UtaraDocument54 pagesDiv. of Urology, Dept. Surgery Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera UtaraMuhammad Mahadi HasibuanNo ratings yet
- Key Urological SymptomsDocument25 pagesKey Urological SymptomsStella Agatha WidjajaNo ratings yet
- Dela Torre Case Presentation South GenDocument44 pagesDela Torre Case Presentation South GenRalph Dale Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Storing A Urine SampleDocument8 pagesStoring A Urine SampleMarz DempseyNo ratings yet
- Prostae UroDocument43 pagesProstae UroShidevNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Prostate: Dr.M.Galuh Richata, SpuDocument9 pagesDisorders of The Prostate: Dr.M.Galuh Richata, SpuAndika TansirNo ratings yet
- Urology Clerking Difficulty in UrinationDocument11 pagesUrology Clerking Difficulty in Urinationmacdominic22No ratings yet
- 4 Examining Gastrointestinal SystemDocument75 pages4 Examining Gastrointestinal SystemSafi MohammedNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Patients Knowledge, Self-Care ManagementDocument10 pagesHypertensive Patients Knowledge, Self-Care ManagementLilian ArthoNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Ch13.4 TBDocument5 pagesGr10 Ch13.4 TBnr46jpdxbpNo ratings yet
- Modern Business Statistics With Microsoft Office Excel 4Th Edition Anderson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument47 pagesModern Business Statistics With Microsoft Office Excel 4Th Edition Anderson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFjerryholdengewmqtspaj100% (11)
- 50 HaazinuDocument6 pages50 HaazinuTheodore James TurnerNo ratings yet
- Parbrahm CharitraDocument96 pagesParbrahm CharitraGhanshyam1414No ratings yet
- Genesis g16Document2 pagesGenesis g16Krist UtamaNo ratings yet
- Shakila L Green ResumeDocument4 pagesShakila L Green Resumeapi-275476844No ratings yet
- Full Research Terrarium in A BottleDocument28 pagesFull Research Terrarium in A BottleBethzaida Jean RamirezNo ratings yet
- TESDA Circular No. 065 A 2021 Ammendments To The Guidelines Conduct of PNSCDocument17 pagesTESDA Circular No. 065 A 2021 Ammendments To The Guidelines Conduct of PNSCtracert_atanNo ratings yet
- Indirani College of Nursing: Level of Student - B.SC (N) Ii Yrs TractionDocument7 pagesIndirani College of Nursing: Level of Student - B.SC (N) Ii Yrs TractiondhanasundariNo ratings yet
- Adobe Photoshop CS6 Exam SimulationDocument6 pagesAdobe Photoshop CS6 Exam SimulationMuhammad NadhirNo ratings yet
- Documentation FlutterDocument12 pagesDocumentation FlutterIvhan SalazarNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning in GeoscienceDocument22 pagesMachine Learning in GeoscienceAde PrayudaNo ratings yet
- VR-Research Paper: August 2021Document66 pagesVR-Research Paper: August 2021Shashank YadavNo ratings yet
- Journaling PDFDocument1 pageJournaling PDFMargarita Maria Botero PerezNo ratings yet
- SIP Presentation On MSMEDocument15 pagesSIP Presentation On MSMEShradha KhandareNo ratings yet
- New TIP Course 1 DepEd Teacher PDFDocument89 pagesNew TIP Course 1 DepEd Teacher PDFLenie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Glaciers Notes Part 1Document6 pagesGlaciers Notes Part 1David ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Honeywell Actuator M7410EDocument6 pagesHoneywell Actuator M7410EFrinaru CiprianNo ratings yet
- Assignment 9-Ra 9184 (Ce Laws, Ethics, and Contracts)Document4 pagesAssignment 9-Ra 9184 (Ce Laws, Ethics, and Contracts)Luke MoraledaNo ratings yet
- TLC Online Learning Pack ContentDocument15 pagesTLC Online Learning Pack ContentjennoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae (CV) : Data PribadiDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae (CV) : Data Pribadingurah.gde.ariNo ratings yet
- Audit UNIT 4Document14 pagesAudit UNIT 4Nigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Objective of ECO401 (1 22) Short NotesDocument11 pagesObjective of ECO401 (1 22) Short Notesmuhammad jamilNo ratings yet