Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Handout Dna
Handout Dna
Uploaded by
Emman RevillaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Handout Dna
Handout Dna
Uploaded by
Emman RevillaCopyright:
Available Formats
MOTIVATION
Chat/Messenger codes/abbreviation
Code
1. HAND – have a nice day
2. LMK – let me know
3. IKR – I know right
4. NVM – never mind
5. SLR – Sorry late reply
6. BTW – by the way
7. TIA – thanks in advance
8. TYT – take your time
9. TTYL – talk to you later
10. ROTFL – rolling on the floor laughing
Codes that we usually use daily
But today we will discuss about the most important coded message of all time – the DNA code.
Show picture of chromosome.. identify chromatin
Sections of the chromosome – gene responsible for certain traits.. basic unit of heredity
How is passing of genes allows traits to be passed on from parents to offspring
DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid
Reading Material (30 minutes)
DNA: The Blueprint of Life
All cells require some form of instruction or guideline to
be able to function properly. They need rules or codes
to make materials in the cell. And that code is the DNA.
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid, a double
stranded molecule (see picture at the side) found inside
the nucleus of the cell. It contains the information or
code that determines inherited characteristics. It has
the code for making proteins. The double stranded
structure has repeating sub-units/building blocks called
nucleotides. Therefore, a DNA is a chain of nucleotides.
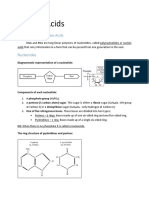
A nucleotide has three important parts: (1) a phosphate group (2) a sugar
and (3) nitrogenous base. In DNA, the sugar is deoxyribose, which is part of
its name. Nitrogenous bases are organic molecules containing nitrogen in
the form of ring structure. There are
four different types of nitrogenous
bases: (1) adenine, (2) thymine, (3) cytosine and (4) guanine.
Adenine and guanine are called Purines with double ring of carbon
and nitrogen atoms while thymine and cytosine are called
Pyrimidine with single ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms. A
phosphate group attaches with a deoxyribose sugar and any one
of these 4 nitrogen bases. With this, there can be four types of
nucleotide.
The slanted shape of the DNA molecule causes it to form a spiral or helix shape. Because it is
double stranded, the term double helix is used to describe its structure. Along the sides of the
structure are backbones made of alternating phosphate and sugar molecules called sugar
phosphate backbone bonded together. On the inside, like the rungs of a ladder are the nitrogen
bases.
The four types of nucleotide containing the different
nitrogen bases join together in a very complex way to form
the double helix structure. The base adenine always pairs
with thymine, while the base cytosine always pairs with
guanine. Adenine and thymine has two hydrogen bonds while
cytosine and guanine has three hydrogen bonds. Strands of
the DNA are said to be complementary to each other. You can
predict one strand if you know the other strand.
It is the order of these four bases of the DNA or the base
sequence that allows your body to create you. This
sequence is the code that controls the production of all the
proteins of an organism. Proteins determine the traits that
will be shown in an individual.
GUIDE QUESTIONS: ANSWERS ONLY!!! (on your notebook)
1. What is a DNA?
2. Enumerate the components of a nucleotide. (3)
3. Enumerate the four nitrogen bases. (4)
4. Describe the structure of the DNA.
5. How do the nitrogen bases pair?
6. Why is the sequence of nucleotide important in determining traits?
Code that makes you, you is found in the four nitrogen bases.
Twisted ladder or double helix structure
Like any good structure, there has to be main support
Sugar and phosphate bond together to form twin backbone
Base pairing
You might also like
- Lesson Plan MathDocument9 pagesLesson Plan MathEmman Revilla87% (23)
- Activity 1 4pics-1 WordDocument1 pageActivity 1 4pics-1 WordEmman Revilla100% (4)
- Nucleic Acid ProjectDocument18 pagesNucleic Acid ProjectPramod Etarvi90% (10)
- Preparing Questions For A Qualitative Research InterviewDocument9 pagesPreparing Questions For A Qualitative Research InterviewEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper: Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument13 pagesResearch Paper: Alzheimer's DiseaseABC Four CornersNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Nucleic AcidDocument33 pagesStructure and Function of Nucleic AcidLaiba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Genetics BS - 6 Semester: Assignment # 1Document20 pagesGenetics BS - 6 Semester: Assignment # 1Hassan JavedNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismDocument41 pagesNucleic Acid MetabolismPavani AkkalaNo ratings yet
- How Your Genes Determine Who You AreDocument12 pagesHow Your Genes Determine Who You Areaerinimmmm3030No ratings yet
- WK 4Document5 pagesWK 4kathleen D.No ratings yet
- Biotechnology: Guided Learning Activity Kit DNA Versus RNADocument20 pagesBiotechnology: Guided Learning Activity Kit DNA Versus RNAKimberly Esmelo100% (1)
- Activity No.1 BSci 101Document3 pagesActivity No.1 BSci 101Shamaica SurigaoNo ratings yet
- Dna - CotDocument39 pagesDna - CotJcob BangcayaNo ratings yet
- Expt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetDocument9 pagesExpt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetMary Ella Mae PilaNo ratings yet
- DNA Components and Structure WSDocument3 pagesDNA Components and Structure WSmoadhmoayedNo ratings yet
- 8 - Genetic MaterialDocument22 pages8 - Genetic MaterialCrisha LimNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument61 pagesDNA Structure and Replicationmanuela pardoNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Material-1Document48 pagesThe Genetic Material-1Windra TrivenNo ratings yet
- Genetic MaterialDocument31 pagesGenetic MaterialANBC- 24- Safa AfreenNo ratings yet
- Om Prakash PPT BiologyDocument11 pagesOm Prakash PPT BiologyOm Prakash100% (1)
- Topic 1 - A1.2 Nucleic AcidsDocument63 pagesTopic 1 - A1.2 Nucleic AcidsOlatundeNo ratings yet
- 5-A1.2 Nucleıc AcidsDocument41 pages5-A1.2 Nucleıc Acidsmakaya02No ratings yet
- Unit-9 Regression AnalysisDocument20 pagesUnit-9 Regression AnalysisPRASANT KUMAR SAMALNo ratings yet
- Dna 053215Document13 pagesDna 053215Baninla NerusNo ratings yet
- 3.5. Nucleic Acids 22-23Document3 pages3.5. Nucleic Acids 22-23SiNo ratings yet
- 8.3 DNA Worksheet StudentDocument4 pages8.3 DNA Worksheet StudentVippo Montecillo0% (1)
- The Story of DNA - Script and Answer KeyDocument3 pagesThe Story of DNA - Script and Answer KeyAdam SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Structure of Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesStructure of Nucleic AcidsHanz Glitzer MosquedaNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna StructureDocument26 pagesDna and Rna StructureVince Lenzer BeliganioNo ratings yet
- 1934 FdocDocument6 pages1934 Fdoctyleryawh2072No ratings yet
- 1 Nucleic AcidsDocument11 pages1 Nucleic AcidsSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication PDFDocument7 pagesDNA Replication PDFPiyush ChandraNo ratings yet
- DNA As Code of Life - Rau's IASDocument5 pagesDNA As Code of Life - Rau's IASClinton AhongshangbamNo ratings yet
- Intro To DNADocument53 pagesIntro To DNAKAREN SALLESNo ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument8 pagesDna ReplicationIrma NeyraNo ratings yet
- Notes - Dna Protein Synthesis - Student 2000Document14 pagesNotes - Dna Protein Synthesis - Student 2000api-270403367No ratings yet
- Me Sci 10 q3 1301 PsDocument27 pagesMe Sci 10 q3 1301 PsCassy Leighz BagonocNo ratings yet
- HeredityDocument24 pagesHeredityvivas.kznne.9No ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument218 pagesGenetic EngineeringSrramNo ratings yet
- DNA and Protein Synthesis - Chapter Notes: "Life Is A Three Letter Word!"Document13 pagesDNA and Protein Synthesis - Chapter Notes: "Life Is A Three Letter Word!"Chan Karlok100% (1)
- Carry Instructions Be Copied Polynucleotides Nucleotides: Adenine Guanine Thymine Uracil CytosineDocument3 pagesCarry Instructions Be Copied Polynucleotides Nucleotides: Adenine Guanine Thymine Uracil Cytosineapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Nucleic-AcidDocument28 pagesNucleic-AcidIvan Jhon AnamNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 5. Molecular Basis of Heredity Structure of The Genetic MaterialDocument3 pagesEXERCISE 5. Molecular Basis of Heredity Structure of The Genetic MaterialMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- q3 DNA RNADocument22 pagesq3 DNA RNADante tuminesNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Nucleic AcidsDocument23 pages1.5 Nucleic AcidsMûhd AïZām ÄhmâdNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q3 Week4Document22 pagesScience10 Q3 Week4Samad Recca T. NatividadNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Introduction To Microbial GeneticsDocument18 pagesLab 1 Introduction To Microbial Genetics1318202128No ratings yet
- (Unit II) Chapter 6: The Structure of DNADocument24 pages(Unit II) Chapter 6: The Structure of DNAswagNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure + Function 12-1Document31 pagesDNA Structure + Function 12-1Jalajarani AridassNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project 2019Document15 pagesChemistry Project 2019Aiasha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribo Nucleic AcidDocument26 pagesDeoxyribo Nucleic AcidJoshua EbenezerNo ratings yet
- HEREDITYDocument23 pagesHEREDITYvivas.kznne.9No ratings yet
- Activity 1 - DNA StructureDocument4 pagesActivity 1 - DNA StructureHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2Document2 pagesAssignment No. 2Jane Valine BalinoNo ratings yet
- Genetic MaterialDocument62 pagesGenetic MaterialFaris ShamimNo ratings yet
- Chem & Import of Nucleotides11Document79 pagesChem & Import of Nucleotides11asaNo ratings yet
- C6 Nucleic AcidsDocument57 pagesC6 Nucleic AcidsSoraya Al-obinayNo ratings yet
- DnapageDocument2 pagesDnapageapi-258322847No ratings yet
- Nucleicacids Dnarna 100618205106 Phpapp01Document40 pagesNucleicacids Dnarna 100618205106 Phpapp01InerTiaOpheliaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1 On Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesAssignment No.1 On Nucleic AcidsRuel John RanayNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA NOTESDocument16 pagesDNA and RNA NOTESTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- REPLICATIONDocument9 pagesREPLICATIONdineshNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 Breathe In, Breathe OutDocument3 pagesActivity 5 Breathe In, Breathe OutEmman Revilla100% (1)
- ACTIVITY 3 What A Bunch of GrapesDocument1 pageACTIVITY 3 What A Bunch of GrapesEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- Directions: Label The Parts and Answer The Questions BelowDocument1 pageDirections: Label The Parts and Answer The Questions BelowEmman Revilla100% (1)
- ACTIVITY 2 Define MeDocument1 pageACTIVITY 2 Define MeEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answer.: Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesInstruction: Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answer.: Respiratory SystemEmman Revilla0% (1)
- Learning Activity Sheet: Pre-Assessment: I. True or FalseDocument2 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: Pre-Assessment: I. True or FalseEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- Tarpapel Element and CompoundDocument3 pagesTarpapel Element and CompoundEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Complete The Crossword Puzzle BelowDocument1 pageSolutions: Complete The Crossword Puzzle BelowEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - How Long Can You Hold Your BreathDocument2 pagesActivity 1 - How Long Can You Hold Your BreathEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
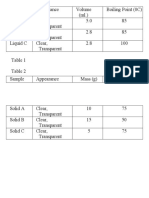
- Sample PropertiesDocument2 pagesSample PropertiesEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- Motivation Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesMotivation Climate ChangeEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- Trachea Nasal Cavity Bronchioles Pharynx Oral Cavity Diaphragm Alveoli Bronchi Lungs LarynxDocument3 pagesTrachea Nasal Cavity Bronchioles Pharynx Oral Cavity Diaphragm Alveoli Bronchi Lungs LarynxEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- Entrep ComputationDocument18 pagesEntrep ComputationEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- Form Carbohydrate That Is Usable by The BodyDocument5 pagesForm Carbohydrate That Is Usable by The BodyEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 7 Intro ClimateDocument1 pageACTIVITY 7 Intro ClimateEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- SHS Math and Science Instructor STI College San Pablo: (Current Accepted Model On The Formation of The Universe)Document9 pagesSHS Math and Science Instructor STI College San Pablo: (Current Accepted Model On The Formation of The Universe)Emman RevillaNo ratings yet
- UranusDocument4 pagesUranusEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- Dispersion of LightDocument2 pagesDispersion of LightEmman Revilla100% (1)
- Quiz in Projectile MotionDocument1 pageQuiz in Projectile MotionEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and MechanicsDocument7 pagesThermodynamics and MechanicsEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
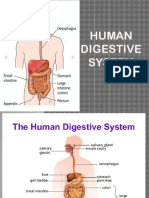
- Digestive-System-2 Grade 8Document39 pagesDigestive-System-2 Grade 8Joshua Muego100% (2)
- Bethesda System For ThyroidDocument61 pagesBethesda System For ThyroidAkanksha KushwahNo ratings yet
- Brachionus CalyciflorusDocument10 pagesBrachionus CalyciflorusÉrica OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Meselson and Stahl's ExperimentDocument3 pagesMeselson and Stahl's ExperimentChristina PatrNo ratings yet
- MD AnatomyDocument16 pagesMD AnatomyJaydenNo ratings yet
- Ignou Physical Anthropology-1Document470 pagesIgnou Physical Anthropology-1Komal50% (2)
- Daftar Pustaka: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas AndalasDocument3 pagesDaftar Pustaka: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas AndalasFaizal DzikrullahNo ratings yet
- Aakash Test PaperDocument12 pagesAakash Test Paperajitha67% (3)
- Haemophilus DucreyiDocument15 pagesHaemophilus DucreyiDesti Ratna Putri100% (1)
- Impact of Plant Breeding On The Genetic Diversity of Cultivated Strawberry As Revealed by Expressed Sequence Tag-Derived Simple Sequence Repeat MarkersDocument12 pagesImpact of Plant Breeding On The Genetic Diversity of Cultivated Strawberry As Revealed by Expressed Sequence Tag-Derived Simple Sequence Repeat MarkersJuan Diego DuqueNo ratings yet
- Biology 102 - Chapter 1Document6 pagesBiology 102 - Chapter 1Lucy KillackyNo ratings yet
- Silk'n Lipo - Clinical OverviewDocument10 pagesSilk'n Lipo - Clinical OverviewFit BoxxNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 6 Studyguide360Document19 pagesClass 10 Science Notes Chapter 6 Studyguide360fraeric05No ratings yet
- CH 15Document54 pagesCH 15mariamNo ratings yet
- New Genetic ProblemsDocument8 pagesNew Genetic Problemsmzunl25476No ratings yet
- From Compartmental Models To Point NeuronsDocument43 pagesFrom Compartmental Models To Point NeuronsAkshay PatharkarNo ratings yet
- 11 Homeostasis Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Document13 pages11 Homeostasis Biology Notes IGCSE 2014sabah8800100% (2)
- TaqMan Universal PCR ProtocolDocument60 pagesTaqMan Universal PCR Protocolkrista_jw9525No ratings yet
- PTH Calset: English Intended UseDocument2 pagesPTH Calset: English Intended UseJimboreanu György PaulaNo ratings yet
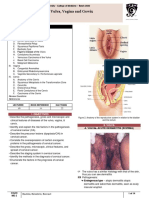
- B14PathologyL1 - Diseases of The Vulva, Vaginal, and CervixDocument14 pagesB14PathologyL1 - Diseases of The Vulva, Vaginal, and CervixBarda GulanNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument102 pagesThyroidfadoNo ratings yet
- James Perloff - Tornado in A Junkyard (Condensed)Document24 pagesJames Perloff - Tornado in A Junkyard (Condensed)mcdozer100% (1)
- Check MAIT: References Cites 53 ArticlesDocument7 pagesCheck MAIT: References Cites 53 ArticlesJános JuhászNo ratings yet
- Bovine BabesiosisDocument6 pagesBovine BabesiosisPawan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders Project Rubric 17-18Document3 pagesGenetic Disorders Project Rubric 17-18api-394564312No ratings yet
- Building Blocks of Life Student Edition CIBT Zl8a60Document15 pagesBuilding Blocks of Life Student Edition CIBT Zl8a60Jcob SntosNo ratings yet
- AyaBringaraj KalpamDocument7 pagesAyaBringaraj KalpamChintamani VeerrajuNo ratings yet
- Algues A4Document4 pagesAlgues A4Pascal MetaisNo ratings yet
- Immunohematology PDFDocument126 pagesImmunohematology PDFNicole Tan Calayca100% (1)