Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Lab #4
Chemistry Lab #4
Uploaded by
shantal grantOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Lab #4
Chemistry Lab #4
Uploaded by
shantal grantCopyright:
Available Formats
Damelia Coleman Chemistry February 4, 2019
LAB #: 4
TITLE: Bonding
TOPIC: Ionic and Covalent Compounds
AIM: To distinguish between ionic and covalent compounds
APPARATUS/ MATERIALS: Sucrose, sodium chloride, naphthalene, magnesium sulphate,
copper sulphate, potassium nitrate, electrolytic cell, beakers, Bunsen burner.
METHOD:
1. The sodium chloride was heated and observed for one minute.
2. Step one (1) was repeated using the five compounds.
3. The solubility of each of the compounds were tested in water.
4. The electrolytic cell was used to test the conductivity of the compounds in their solution
state.
5. The results obtained were tabulated.
DIAGRAMS:
TITLE: DIAGRAM OF AN ELECTROLYTIC CELL
Damelia Coleman Chemistry February 4, 2019
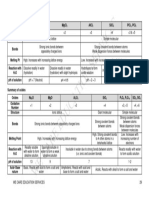
RESULTS:
TITLE: TABLE SHOWING THE PROPERTIES OF EACH COMPOUNDS
COMPOUNDS HEATING SOLUBILITY IN ELETRICAL
WATER CONDUCTIVITY
SODIUM CHLORIDE When it was being heated the Due to its ionic bond There are free ions
sodium chloride did not Sodium Chloride is moving in the solution,
change due to its strong ionic soluble in water. therefore it is an ionic
electrostatic bond causing the compound which
substance to have a high allows electricity to
melting point, therefore it conduct.
remained as white solid
crystals.
COPPER SULPHATE The blue crystals began to Copper Sulphate is Due to the free ions in
turn pale to white powder soluble in water its solution it is an
while it was being heated. because of its ionic ionic compound
During the change it shows bond, so it is able to therefore electricity is
that this compound has a low dissolve in polar able to conduct.
melting point. substances such as
water.
NAPHTHALENE The substance was heated Because of its non- Does not conduct any
rapidly resulting in a polar covalent bond electrical charge
colourless liquid, due to its Naphthalene is because it has no free
low melting point. While this insoluble in water. ions, therefore it is a
substance was burning, it Non-polar substances non-polar covalent
released a similar scent of cannot dissolve in compound.
camphor balls. polar substances.
POTASSIUM NITRATE The white salt crystals melted Because of its ionic This ionic compound
into a brown liquid during the bond, Potassium contains free ions
heating process. Nitrate is soluble in which allows the
water. solution to conduct
electrical charge.
MAGNESIUM During the heating process, Magnesium Sulphate is In this solution it
SULPHATE melting, the substance dried able to dissolve in contained free ions
into white powdered solid water due to its ionic moving around which
substance. Much changes did bond. results in electrical
not took place. charge. Hence it is an
ionic compound.
SUCROSE This compound was heated Sucrose is soluble in Because of its polar
rapidly resulting in a black water because it is a covalent bond it is able
liquid, which shows that this polar covalent to dissolve in water. It
compound has a low melting compound. has no free ions
point. Therefore it is a therefore it cannot
covalent compound. conduct electricity.
Damelia Coleman Chemistry February 4, 2019
DISCUSSION:
Ionic compound is a chemical compound that is composed of metal and non-metal atoms which
are held together by an electrostatic force due to ionic bonding.
Covalent compound is a molecule that is made up of two non-metal atoms which are formed by
covalent bonding, hence they share one or more pairs of valence electrons.
The results shown in the table above represents the occurrence of each compounds and how they
reacted. The various compounds were tested in the given state, by heating, solubility in water
and electrical conductivity in their aqueous state. The results showed how each compound
reacted to the different test.
CONCLUSION:
It can concluded that the ionic compounds were found to be Sodium Chloride, Potassium
Nitrate, Copper Sulphate and Magnesium Sulphate. The covalent compounds that were found
are Sucrose and Naphthalene.
You might also like
- Larkin Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLarkin Lab ReportChristopherAguilar33% (3)
- Experiment 5 Properties of Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument5 pagesExperiment 5 Properties of Ionic and Covalent CompoundsAbdul Rahman Abdul Najib100% (1)
- Exp 6 Sodium Fusion PDFDocument4 pagesExp 6 Sodium Fusion PDFJessica Margaux Mercado0% (1)
- Chemical Bond (ContDocument18 pagesChemical Bond (ContJachinta JuliusNo ratings yet
- The Properties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds: Experiment 4Document5 pagesThe Properties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds: Experiment 4MUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibirium in SolutionsDocument4 pagesIonic Equilibirium in SolutionsshaudtddydkNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 (Chemistry)Document7 pagesExperiment 3 (Chemistry)Nur DiyanahNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent BondsDocument4 pagesIonic and Covalent BondsericaNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab Report 7Document5 pagesChem Lab Report 7Nor Ashikin Ismail67% (3)
- Covalent Compound PropertiesDocument31 pagesCovalent Compound PropertiesApril Mae BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Quiz Discussion Organic Chemistry Act.Document4 pagesQuiz Discussion Organic Chemistry Act.quirenicoleNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and Liquids Activity 1: Color DropDocument12 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Solids and Liquids Activity 1: Color DropElaine Mae G. EsqueroNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and Liquids Activity 1: Color DropDocument12 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Solids and Liquids Activity 1: Color DropElaine Mae G. EsqueroNo ratings yet
- Too Share or Not To ShareDocument6 pagesToo Share or Not To ShareSpencer JorgensenNo ratings yet
- Ibanez, Ivan David S Module # 01 Answer To The Activities and Exercises Bsed-Science-2bDocument10 pagesIbanez, Ivan David S Module # 01 Answer To The Activities and Exercises Bsed-Science-2bAlvin Andante IbañezNo ratings yet
- Comparing AciditiesDocument2 pagesComparing AciditiesKim ThaiNo ratings yet
- X Chem Master Key Differences 22 - 23Document30 pagesX Chem Master Key Differences 22 - 23Prerna JainNo ratings yet
- BRYANDocument2 pagesBRYANSeb AcabaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Conductivity Laboratory ReportDocument7 pagesElectrical Conductivity Laboratory ReportSteven LeeNo ratings yet
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationLeslieNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Properties of Ionic Compounds - KeyDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Properties of Ionic Compounds - Keyrandomlol7777No ratings yet
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationIngridNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Dissimilarity Between Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument5 pagesExperiment 5 Dissimilarity Between Ionic and Covalent CompoundsNurasyilah YakubNo ratings yet
- Ionic v. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument3 pagesIonic v. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationJackelineNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 6 Dissimilarity Between LECTROVALENT AND COVALENT BONDDocument7 pagesEXPERIMENT 6 Dissimilarity Between LECTROVALENT AND COVALENT BONDMuhamad Faris88% (8)
- EmiraldszzzsDocument24 pagesEmiraldszzzsgacokicarolNo ratings yet
- Reaction of Period III Oxides and Chlorides With WaterDocument2 pagesReaction of Period III Oxides and Chlorides With WaterNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- LAB #2-Ionic and CovalentDocument3 pagesLAB #2-Ionic and CovalentshadowNo ratings yet
- Bonding Prelab Answer KeyDocument1 pageBonding Prelab Answer KeyRosebud ThiriNo ratings yet
- Fat Molecules: Key Concepts Critical Thinking ChallengeDocument1 pageFat Molecules: Key Concepts Critical Thinking ChallengerainNo ratings yet
- Properties of Ionic and CovalentDocument1 pageProperties of Ionic and CovalentJoselyn Villena MarquezNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte and Redox: Chemistry ReportDocument7 pagesElectrolyte and Redox: Chemistry ReportGrace KahonoNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 5Document25 pagesPDF Document 5miriam harriottNo ratings yet
- The Name's Bonds, Breaking BondsDocument6 pagesThe Name's Bonds, Breaking Bondsapi-348321624No ratings yet
- Chem Lab ReviewerDocument2 pagesChem Lab ReviewerMaria Angelica PescadorNo ratings yet
- Katia Medina Larkin 2Document3 pagesKatia Medina Larkin 2kmedina2014No ratings yet
- 4.5 Physical Properties: Syllabus StatementsDocument1 page4.5 Physical Properties: Syllabus StatementsBreeSchuchNo ratings yet
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument4 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationAngelicaNo ratings yet
- Science Fair Project: Type Your Project Title Here Your Name Your Teacher's Name Your SchoolDocument290 pagesScience Fair Project: Type Your Project Title Here Your Name Your Teacher's Name Your SchoolmanueveredNo ratings yet
- Orgchem Lab Midterm ReviewerDocument8 pagesOrgchem Lab Midterm ReviewerJana PaduaNo ratings yet
- Al Ittihad Private School Jumeira Science Department 2021/2022Document4 pagesAl Ittihad Private School Jumeira Science Department 2021/2022budoorNo ratings yet
- Covalent Network MoleculesDocument1 pageCovalent Network MoleculesGill CraigNo ratings yet
- X Chem Master Key Differences 23 - 24Document35 pagesX Chem Master Key Differences 23 - 24zilkag47No ratings yet
- Chemistry Experiment #2Document3 pagesChemistry Experiment #2Grace JosephNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis:: Compounds To Be Tested Ionic or Covalent High or Low Melting Point? Electricity?Document3 pagesHypothesis:: Compounds To Be Tested Ionic or Covalent High or Low Melting Point? Electricity?LeslieNo ratings yet
- Christian Lara Lab ReportDocument3 pagesChristian Lara Lab ReportLeslieNo ratings yet
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab Investigation: HypothesesDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab Investigation: HypothesesLeslieNo ratings yet
- 5.4 (A) Ionic and Covalent Compounds PropertiesDocument12 pages5.4 (A) Ionic and Covalent Compounds PropertiesFidree AzizNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis 1 TEDocument5 pagesElectrolysis 1 TETom TommmaNo ratings yet
- Module-Ii Chemical Bonding: General Chemistry CHEM-1001Document193 pagesModule-Ii Chemical Bonding: General Chemistry CHEM-1001Shivansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 LabrepDocument4 pagesExperiment 5 LabrepDI LacsonNo ratings yet
- Water Unit 1Document2 pagesWater Unit 1Alice.in.spaceNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsDocument36 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsYard BirdNo ratings yet
- S - Block Elements, Class 11Document13 pagesS - Block Elements, Class 11Ashish kumarNo ratings yet
- Group 14Document2 pagesGroup 14fiqaNo ratings yet
- Harcourt Essen ReactionDocument2 pagesHarcourt Essen ReactionMohammed Saqlain100% (2)
- Experiment 6 - Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument5 pagesExperiment 6 - Aromatic HydrocarbonsKaye SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Periodicity Notes - Docx-29Document1 pagePeriodicity Notes - Docx-29Kiều TrangNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 The S Block Elements - 0Document21 pagesNcert Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 The S Block Elements - 0Raghav VermaNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- How to Do Chemical Tricks: Containing Over One Hundred Highly Amusing and Instructive Tricks With ChemicalsFrom EverandHow to Do Chemical Tricks: Containing Over One Hundred Highly Amusing and Instructive Tricks With ChemicalsNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry - Unit - I (Water Treatment)Document23 pagesEngineering Chemistry - Unit - I (Water Treatment)sivabharathamurthy92% (97)
- Exercise No. 09 - Vit. B Complex SyrupDocument5 pagesExercise No. 09 - Vit. B Complex Syruppharmaebooks50% (2)
- Mil STD 202gDocument193 pagesMil STD 202gR&D SANPARNo ratings yet
- Cause and Prevention For Steam Turbine Blade Scaling FoulingDocument10 pagesCause and Prevention For Steam Turbine Blade Scaling Foulingrajgadge777829100% (1)
- Training Cooling Tower Treatment ChemicalsDocument127 pagesTraining Cooling Tower Treatment ChemicalsparagNo ratings yet
- S No Unit Portion To Be Reduced: CHEMISTRY (043) Class XIDocument2 pagesS No Unit Portion To Be Reduced: CHEMISTRY (043) Class XIDivyansh BishtNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ, S) : Subject: ChemistryDocument6 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQ, S) : Subject: ChemistryNaveed Ahmed ButtNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Jun 2010 Actual Exam Paper Unit 6Document16 pagesChemistry Jun 2010 Actual Exam Paper Unit 6dylandonNo ratings yet
- Exercise 12Document19 pagesExercise 12AkashGauravNo ratings yet
- BrineDocument2 pagesBrinemkgchemNo ratings yet
- Senior General Chemistry 1 Q1 - M2 For PrintingDocument22 pagesSenior General Chemistry 1 Q1 - M2 For PrintingJiltonNo ratings yet
- Dektol KodakD72Document3 pagesDektol KodakD72haryantoNo ratings yet
- Solvent DryingDocument10 pagesSolvent DryingEvs GoudNo ratings yet
- Lab Shopping ListDocument3 pagesLab Shopping ListDoug McCaughanNo ratings yet
- Practical SyllabusDocument4 pagesPractical SyllabusOmSilence2651No ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering Environmental Engineering Laboratory Chemical List Practical I&IIDocument8 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering Environmental Engineering Laboratory Chemical List Practical I&IISureshSawantNo ratings yet
- As 2503.1-2006 Refractories and Refractory Materials - Chemical Analysis Silica RefractoriesDocument7 pagesAs 2503.1-2006 Refractories and Refractory Materials - Chemical Analysis Silica RefractoriesSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen, Nitrate (Colorimetric, Brucine)Document4 pagesNitrogen, Nitrate (Colorimetric, Brucine)envirocompNo ratings yet
- Fatty Alcohol Flow DiagramDocument10 pagesFatty Alcohol Flow DiagramGoklas WinnerNo ratings yet
- Handout of S & P Block Elements (PMDC)Document6 pagesHandout of S & P Block Elements (PMDC)mahnoors571No ratings yet
- Vaccine IngredientsDocument4 pagesVaccine IngredientsJulie BinghamNo ratings yet
- Bath and Shower ProductsDocument26 pagesBath and Shower ProductsPriscilla Alioto100% (2)
- Qualitative-Organic-Analysis PDFDocument37 pagesQualitative-Organic-Analysis PDFrahmahNo ratings yet
- Crystallization 2013Document2 pagesCrystallization 2013Peterter Paul100% (1)
- How To Do Chemistry Labs Using Micro-Chemistry Techniques and RecyclingDocument52 pagesHow To Do Chemistry Labs Using Micro-Chemistry Techniques and RecyclingPaul SchumannNo ratings yet
- 444323735-Chem-Matters-Workbook-2E-Teacher-s-Edn-pdf 27-27Document1 page444323735-Chem-Matters-Workbook-2E-Teacher-s-Edn-pdf 27-27whatisNo ratings yet
- Urine Preservatives 2Document23 pagesUrine Preservatives 2HEMAMALINI RAMASESHAN100% (1)
- Dispersion For CeramicDocument5 pagesDispersion For CeramicThanhNo ratings yet
- 2019 1st Science EnglishDocument16 pages2019 1st Science EnglishAlex HalesNo ratings yet