Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PSY Midterm Modules
PSY Midterm Modules
Uploaded by
James BarzoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CASE3Document5 pagesCASE3romelynNo ratings yet
- The Western and Eastern Concepts of SelfDocument18 pagesThe Western and Eastern Concepts of SelfYeji BabeNo ratings yet
- InventoriesDocument10 pagesInventoriesJames BarzoNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsDocument15 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsAtteya Mogote Abdullah86% (28)
- UTS LessonsDocument20 pagesUTS LessonsSara AlbinaNo ratings yet
- PSY Reviewer MidtermsDocument29 pagesPSY Reviewer MidtermsSara AlbinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsDocument19 pagesLesson 4 The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsOlivares Chesanna Denise T.No ratings yet
- UTSDocument11 pagesUTSernest empuertoNo ratings yet
- Uts Midterm ReviewerDocument21 pagesUts Midterm ReviewerVanessa VillaramNo ratings yet
- 7self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsDocument4 pages7self in Western and Eastern Thoughtsruth san joseNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtDocument12 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern Thoughtbalucosgeave18No ratings yet
- Week 5 Self in Western and Oriental or Eastern Thought 20230927100800Document16 pagesWeek 5 Self in Western and Oriental or Eastern Thought 20230927100800azimgaming080805No ratings yet
- The Western and Eastern Concepts of SelfDocument37 pagesThe Western and Eastern Concepts of SelfElleNo ratings yet
- The Western and Eastern Concepts of SelfDocument17 pagesThe Western and Eastern Concepts of SelfAngeloseNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - LESSON 5 - Eastern and Western ConceptDocument14 pagesMODULE 1 - LESSON 5 - Eastern and Western ConceptBaniel, Chester Leo P.No ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsDocument2 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsyimlurimlaNo ratings yet
- Eastern and Western Thought - Lesson 4Document14 pagesEastern and Western Thought - Lesson 4Mary Grace Alipayo SambajonNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtDocument12 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtMarthy DayagNo ratings yet
- Module One - Chapter FourDocument2 pagesModule One - Chapter FourJohn Lloyd Artuz EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document16 pagesChapter 5Samantha EllaineNo ratings yet
- The Western and Eastern Concepts of Self: Don Honorio Ventura State UniversityDocument13 pagesThe Western and Eastern Concepts of Self: Don Honorio Ventura State UniversityKenneth CanceranNo ratings yet
- Eastern PhilosophyDocument2 pagesEastern PhilosophyDan Lhery Susano Gregorious100% (1)
- Week 7 Self in Eastern and Western ThoughtsDocument8 pagesWeek 7 Self in Eastern and Western Thoughtsguzman.justinemark.academicNo ratings yet
- Module 4 (Autosaved)Document14 pagesModule 4 (Autosaved)Argie GallazaNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern Thoughts5Document10 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern Thoughts5Penelope GarciaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Topic 4Document3 pagesModule 1 Topic 4Lord GrimNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtDocument17 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtLionel Palacio Canoy100% (1)
- Lecture Notes 8 The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtDocument23 pagesLecture Notes 8 The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtAeleu JoverzNo ratings yet
- Topic 5Document7 pagesTopic 5Marg'riette PascuaNo ratings yet
- UTSDocument3 pagesUTSmmoirajadeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - Lesson 4Document28 pagesCHAPTER 1 - Lesson 4Sontosidad, Febie Jynn A.No ratings yet
- Eastern and Western PerspectiveDocument17 pagesEastern and Western PerspectiverlcasinilloNo ratings yet
- Eastern and Western Thought: Individualistic Versus CollectiveDocument15 pagesEastern and Western Thought: Individualistic Versus Collectivenan nanNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self 3Document32 pagesUnderstanding The Self 3Darylle Mae AñascoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document23 pagesChapter 5Laarni De VeraNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Module For MidtermsDocument6 pagesUnderstanding The Self Module For Midtermsfrederick liponNo ratings yet
- 1 Module 1 - Concept and Nature of Self: Who Am I?Document13 pages1 Module 1 - Concept and Nature of Self: Who Am I?John MichaelNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Oriental/ Eastern ThoughtDocument16 pagesThe Self in Western and Oriental/ Eastern ThoughtEXCALIBURNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern Thought Lesson 4Document1 pageThe Self in Western and Eastern Thought Lesson 4Cj DagpinNo ratings yet
- UTS - Chapter 1, Lesson 4Document2 pagesUTS - Chapter 1, Lesson 4Krishna Faith P. DelaraNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self 3Document32 pagesUnderstanding The Self 3Christian Adaoag75% (4)
- Understanding The SelfDocument3 pagesUnderstanding The SelfKatherine ManaloNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern Thoughts: Learning Experiences & Self-Assessment Activities (Saa)Document7 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern Thoughts: Learning Experiences & Self-Assessment Activities (Saa)Jeremias De la CruzNo ratings yet
- The Eastern and Western View of SelfDocument2 pagesThe Eastern and Western View of SelfNombre Princess AliyahNo ratings yet
- 1cec - Module 1 Lesson 4 Group 3 - The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsDocument2 pages1cec - Module 1 Lesson 4 Group 3 - The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsGerrylie GallardoNo ratings yet
- Eastern Perspectives On Positive Psychology: Name: Harshita KapoorDocument23 pagesEastern Perspectives On Positive Psychology: Name: Harshita KapoorHarshita Kapoor100% (1)
- Module 2 The Western and Eastern ThoughtsDocument12 pagesModule 2 The Western and Eastern ThoughtsCristine BalocaNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western Eastern ThoughtDocument22 pagesThe Self in Western Eastern ThoughtAngelynne Villapando DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Essentialist ModelDocument3 pagesEssentialist ModelGerard Byron JacildoNo ratings yet
- 15.2 Introduction in World ReligionDocument6 pages15.2 Introduction in World ReligionKurt Russel LeonemNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsDocument14 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsJustien BautistaNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document6 pagesModule 5Jared TeneberNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsDocument50 pagesLesson 5: The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsMary Jane Nabo MurilloNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument33 pagesUnderstanding The SelfJhen Mary Rose Bandojo100% (1)
- Chapter III Philosophies Movement in Education (Final) - 075235Document57 pagesChapter III Philosophies Movement in Education (Final) - 075235John Robert BagalayNo ratings yet
- Uts ProjecgDocument7 pagesUts ProjecgJamie Lynn Lee AbanillaNo ratings yet
- Gec1 Lesson5Document11 pagesGec1 Lesson5Ray Niel Liquisen ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Self and Its Relevance For Self Management - (Autosaved)Document37 pagesUnderstanding Self and Its Relevance For Self Management - (Autosaved)Subhash chandra ghoshNo ratings yet
- The Western and Eastern Concepts of SelfDocument13 pagesThe Western and Eastern Concepts of SelfJhal Mark Le VillarealNo ratings yet
- Psychological Views of SelfDocument38 pagesPsychological Views of SelfGNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Power: Teachings from Ancient Thinkers: Power Games: A Motivational Guide, #6From EverandPhilosophy of Power: Teachings from Ancient Thinkers: Power Games: A Motivational Guide, #6No ratings yet
- Why It Is Good to Be Good: Ethics, Kohut's Self Psychology, and Modern SocietyFrom EverandWhy It Is Good to Be Good: Ethics, Kohut's Self Psychology, and Modern SocietyRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (1)
- Problem 2Document1 pageProblem 2James BarzoNo ratings yet
- A. Definition and Concept of Taxation B. Nature of TaxationDocument1 pageA. Definition and Concept of Taxation B. Nature of TaxationJames BarzoNo ratings yet
- Necessity Theory 2. Benefits-Protection Theory (Symbiotic Relationship) 3. Jurisdiction Over Subject and ObjectsDocument2 pagesNecessity Theory 2. Benefits-Protection Theory (Symbiotic Relationship) 3. Jurisdiction Over Subject and ObjectsJames BarzoNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument1 pageThesisJames BarzoNo ratings yet
- CH 07Document33 pagesCH 07James BarzoNo ratings yet
- CH 07Document33 pagesCH 07James BarzoNo ratings yet
- The Weighted Average Method of Process Costing Computes The Cost Per Equivalent Unit Based Solely OnDocument106 pagesThe Weighted Average Method of Process Costing Computes The Cost Per Equivalent Unit Based Solely OnJames BarzoNo ratings yet
- If Department Q Uses 60 000 of Direct Materials and Department T Uses 15 000 ofDocument160 pagesIf Department Q Uses 60 000 of Direct Materials and Department T Uses 15 000 ofJames BarzoNo ratings yet
- Suppl Problems Process Costing 08Document5 pagesSuppl Problems Process Costing 08James BarzoNo ratings yet
- AIS-Revenue CycleDocument67 pagesAIS-Revenue CycleJames Barzo100% (2)
- Expenditure CycleDocument5 pagesExpenditure CycleJames BarzoNo ratings yet
- CSE - SDO Pampanga - Sexual and Reproductive Health 4th Revised 2Document32 pagesCSE - SDO Pampanga - Sexual and Reproductive Health 4th Revised 2Ma Concepcion Adriano GuansingNo ratings yet
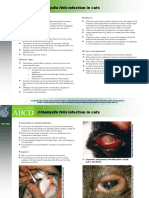
- Chlamydia Felis: Infection in CatsDocument2 pagesChlamydia Felis: Infection in CatsPetrisor GheorghiuNo ratings yet
- Guide To Path Tests Aclmar BF Nat 00059Document4 pagesGuide To Path Tests Aclmar BF Nat 00059Faraz MahboobNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases in MalesDocument15 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases in MalesSam Raven AndresNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Gynecology and Infertility. Factors Associated With Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument16 pagesKeywords: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Gynecology and Infertility. Factors Associated With Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Uts Chapter 2 Lesson 1Document29 pagesUts Chapter 2 Lesson 1John Jerome GironellaNo ratings yet
- Conjunctiva: Fourth Year Omar Al-Mukhtar Univercity 2019-2020Document55 pagesConjunctiva: Fourth Year Omar Al-Mukhtar Univercity 2019-2020Helene AlawamiNo ratings yet
- Symptom Flow Chart: Vaginal DischargeDocument2 pagesSymptom Flow Chart: Vaginal DischargeJeff ZhouNo ratings yet
- PHAR 233 - Pathophysiology of Infectious DiseasesDocument89 pagesPHAR 233 - Pathophysiology of Infectious DiseasesLina RamojNo ratings yet
- Nami - ChlamydiaDocument32 pagesNami - ChlamydiaNami ArthisariNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Nelia B. Perez RN, MSN Class 2015Document94 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases: Nelia B. Perez RN, MSN Class 2015Mariana CreciunNo ratings yet
- Question Booklet Series - : Time Allowed: 2 Hrs. Questions: 1-200Document13 pagesQuestion Booklet Series - : Time Allowed: 2 Hrs. Questions: 1-200WickyNo ratings yet
- Proposed Regional Genitourinary Center: in CalabarzonDocument45 pagesProposed Regional Genitourinary Center: in Calabarzonallyssa monica duNo ratings yet
- Could It Be An STI?: DR Neelam DoshiDocument67 pagesCould It Be An STI?: DR Neelam Doshijoee ahmedNo ratings yet
- Rd-15 Bartholin Cyst and Abscess 10-12Document2 pagesRd-15 Bartholin Cyst and Abscess 10-12Chong Hui ChekNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitte D Infections: Keeshia Anna Zerrudo Clinical Clerk Iloilo Doctors' Hospital Inc. August 18, 2020Document117 pagesSexually Transmitte D Infections: Keeshia Anna Zerrudo Clinical Clerk Iloilo Doctors' Hospital Inc. August 18, 2020Angela SaldajenoNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument15 pagesWeek 11 Sexually Transmitted DiseaseAngel Alexa Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document98 pagesLesson 2Maira Garcia C.No ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Prevention and ControlDocument197 pagesCommunicable Disease Prevention and Controldennisjamesbartz100% (1)
- FCM 3 - 3A Group 8 - National AIDS STI Prevention and Control ProgramDocument184 pagesFCM 3 - 3A Group 8 - National AIDS STI Prevention and Control ProgramRenz Francis SasaNo ratings yet
- PGI MANIMTIM - CPG - BF Screening Guidelines For PediatricsDocument42 pagesPGI MANIMTIM - CPG - BF Screening Guidelines For PediatricsKim Adarem Joy ManimtimNo ratings yet
- Gynae & Obs Bcqs BookletDocument58 pagesGynae & Obs Bcqs BookletKiran Ayub100% (1)
- PID LectureDocument41 pagesPID LectureHarold Gabriel Sanchez DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Koala Book KGDocument15 pagesKoala Book KGozuchanNo ratings yet
- The Gynecologic History and Pelvic Examination Up To Date 2016Document14 pagesThe Gynecologic History and Pelvic Examination Up To Date 2016Mateo GlNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Xii 2024 - Siswa-1Document17 pagesLatihan Soal Xii 2024 - Siswa-1aqilahpramesti65No ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Summary of CDC Treatment GuidelinesDocument3 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases: Summary of CDC Treatment GuidelinesbenzveewitNo ratings yet
- U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations For Contraceptive Use, 2016 MMWRDocument60 pagesU.S. Selected Practice Recommendations For Contraceptive Use, 2016 MMWRhectorNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument24 pagesResearch ProposalLorraine ZarateNo ratings yet
PSY Midterm Modules
PSY Midterm Modules
Uploaded by
James BarzoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PSY Midterm Modules
PSY Midterm Modules
Uploaded by
James BarzoCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 6: The Western and Eastern Perspective: • Eastern Philosophy preferred to generalize the
How it Relates to Self ideas and show how they’ll reflect the same
truths.
How is Eastern different from Western Thoughts?
• Western philosophy focuses on the finding the
• Impact of Culture on Self
differences in ideas while Eastern philosophy
Culture and society are also a primeval force which focuses on the similarities.
somehow has a great impact on the formation of the self.
• The Tao Te Ching written by Lao-Tzu contains all
Mainly because, every individual life in a certain time and
five main Western philosophy categories in a
culture.
small book, you can find passages and verses
The influences of one’s culture and the pertaining beliefs epistemological, ethical, political and aesthetic
that goes with it can be a crucial factor in the individual’s natures but these ideas are not specifically
adaptation of self-concepts, self-realization, and concepts defined but rather they are revealed.
related to it such as personality traits and behaviors.
Eastern Philosophies
Those who live in a particular culture or context, form
• The eastern philosophies consider the self as
their own worldviews thereby shaping a person’s reality.
secondary to its community and relationship with
These worldviews are used by people as guidelines for
others. It views the self as interconnected and
organizing once life and believing in certain concepts.
indistinct. It puts much value in man’s
We also use worldviews to process information based on relationship with others, and his identity in
a particular culture, value and custom (Clark 2002 as cited relation to others whom comes in contact with.
in Alata,Caslib, Jr., Serafica, and Pawilen, 2018).
Meaning to say, the culture of a person where she/he Confucianism
lives affect the formation of the self through these
worldviews.
There are two worldviews can be also called perspectives Buddhism Taoism
or philosophies which varies in terms of self-
understanding;
• Currently, the two main philosophies dividing the
CONFUCIANISM
world are the eastern and western philosophy. • The religious beliefs of
Eastern Philosophy Confucianism points man as
• Eastern Philosophy (mostly China and India) also having virtues and moral existence
explored the five main categories, but they didn’t (Alata, Caslib, Jr., Serafica, and
really make a distinction between certain Pawilen, 2018). Meaning to say,
categories. they live according to codes of ethical conduct
• They didn’t really make a distinction on: where behaviors are highly connected to one’s
- Metaphysics and Epistemology social life or community living.
- Philosophy and Religion • An individual’s identity is highly related according
• Although Western Philosophy tends to focus on to his status in the community or culture that he
the parts in an idea, the Eastern Philosophers lives with.
focus to look at the idea as a whole, rather than
breaking down ideas and concepts into • Confucian followers consider the good of many
categories. first before upholding one’s personal interest.
• This belief upholds the social order and balance in
society (Ho, 1995).
• Subduing oneself and living a virtuous life is an • A Buddhist believes that “there is no self”
important goal in life. (O’Brien, 2018). It is more concerned with the
irrationality and transcendence of the self.
Care about what others think and you will be a prisoner. –
Lao Tzu • The self is seen as an illusion, it is something to
hold and control things, or human centered (Ho,
TAOISM 1995). The Buddhists would renounce self in
• Taoism came originally from terms of its cravings or attachments of the world
China 2,500 years ago (Craig, 2007). because it is the source of suffering.
• Its primary teacher, Lao Tzu, • The self in Buddhism would instead achieve
believes that there are universal enlightenment by attaining the state of Nirvana.
principles that govern the nature of reality. Overview of the Eastern Philosophy
• Man, therefore uses the elements of the universe • The Self in Eastern Philosophy does not focus
in order to achieve balance and unity. A Taoist much on being an individual person. Rather, he is
considers it important to observe nature, its laws a collectivist by nature.
and live with the principles of reality.
• A collectivist person strives to become better not
• The self in Taoism is part of the universe and not for his individual success but to the betterment of
just part of the community. his community.
• A Taoist considers it important to be selfless but • An Eastern believer sees value in dignity and
balanced with society and nature stands for. sense of pride which comes from his very standing
• He is open to ideas and accepting of change and and relationship with the community or the
does not promote prejudices and egocentricism. universe he/she belongs with. He would rather
choose interconnectedness rather than
• Balance and Harmony of everything is sought. individuality.
• A Taoist, in order to cultivate the self must
The Self in Western Thought
practice moral values and virtues in his daily life.
This person is more concerned with living • Western Philosophy (Ancient Greeks, Europeans
according to nature. and Americans) usually focused on five categories
• One way of doing this by controlling one’s body 1. Metaphysics – the study of existence
and mind. Other practices involved is meditation, 2. Epistemology – the study of knowledge
and qigong. 3. Ethics – the study of action
4. Politics – the study of force
• Taoist also adapt a free flowing, relative and
5. Aesthetics – the study of art
unitary view of everything.
BUDDHISM Western Philosophy
• Buddhism is a philosophy more geared • In western philosophy the philosophers tend to
towards the formation and function of the use a lot of logic, reasoning and categorization.
self. According to Buddhism, there are five
• They tend to break down the ideas as much as
physical and mental components of the
they could.
self.
• They also focused on the ideas in parts rather
• There are five physical and mental components of
than the whole idea.
the self. These are form (rapa), feeling (verdana),
perception or conception (sanjna) and
consciousness (vijnana) (Five Skandhas, 2017).
• The self in the western part of the world began • Collectivism and connected is more apparent, a
during the seventeenth and eighteenth century political or economic theory advocating collective
where the Enlightenment Period sprang. control especially over production and
distribution.
• During this period, the focus of man is to search
for truth and meaning through the tools of Fragmentary Vs Holistic
science and reason with man as the prime mover
• In Western philosophy they see things like the
(King 2013, as cited in Kim, 2014).
brain and the body as separate identities, rather
• Man appears to be the main focus and than viewing the two parts as equal; the mentality
individualism is much highlighted. has now been passed on into politics and even in
religion.
• Individualism emphasizes the importance of
person’s abilities, qualities, needs and wants. • In Eastern philosophy people are like to look at
Thus, it is important to discover factors which issues at a whole scale.
would help understand the nature of man/self.
• Chinese and Indian philosophers believed that
• Western culture sees individuals to be possessing their teachings are not meant to take you to
traits and abilities that can drive them to succeed. separate truths but the parts would eventually
lead to one truth.
• It values competition, assertiveness, and equality
among men. Fairness in competition and equality • The social media, migration and intermarriages,
of rights is upheld in here. variety between the Western and Asian
perceptions may either be blurred or highlighted;
• In terms of relationships, man would likely call
conflict is inevitable in diversity; peace is also
their superiors/boss, family or relatives in their
possible through the understanding of where
first names, in recognition of respect and equality
each of us is coming from.
(Alata, Caslib, Jr., Serafica, Pawilen, 2018).
Module 7: The Physical and Sexual Self
Conflict and Harmony
Characteristics of Adolescence
• Western philosophy was built on the idea of
differences and separation so they will not try and Adolescents tend to be age-segregated. They interact
settle for common ground; they will use heavy mostly with their own age group, rather than with
debate to try to convince the audience which younger children and older adults. This may be largely
opinion is superior. dictated by the organization of our educational system
into ‘grades’. Although adolescents may prefer to spend
• Eastern will usually find common group, a perfect
their time with others of the same age proximity, it does
example of this is the Yin and Yang.
limit their ability to guide younger people and learn from
• Yin symbolizes feminine, dark, cold, and yielding older ones.
while Yang symbolizes masculine, bright and
Jobs held by teens may give them an opportunity to spend
advancing.
time with other age groups: babysitting or working at a
• These might be separate ideas in Western but in daycare OR working in a retail store or fast-food
the Eastern equal amounts of both ideas are of restaurant.
importance, together created a whole.
An older child, still accepting financial support, will also
Individualism & Collectivism have to accept the continuing control of the parents. Why
wouldn’t a parent who is providing money to the child,
• Individualism is highly praised in the West, the
still want to control how that money is spent?
belief that the needs of each person are more
important than the needs of the whole society or If the older child is still living in the parent’s home, why
group. wouldn’t they still have to live by the parent’s rules about
curfews, getting a job, keeping their room clean, or The heart, lungs, prostate gland, and seminal vesicles also
helping with household chores? increase in size; boys produce more red blood cells than
girls. These changes normally begin to occur between the
This economic dependency may extend the period of
ages of 9-14 years and are completed between ages 12
adolescence for years… as long as age 24 or even 30.
and 16 years.
Adolescents are heavily targeted and influenced by mass
During adolescence, the testes in males start producing
media. With rapidly developing physical and cognitive
more androgens. The primary one is called testosterone.
capacities, they are especially vulnerable to the
This affects the development of primary sex
counterculture aspects of media programming. They seek
characteristics for boys, which include the enlargement of
excessive stimulation, as they are bombarded with images
the testes and scrotum, followed about a year later by
and sounds of tragedy, sexuality, and brutality via
growth of the penis. The first ejaculation, (emission of
magazines, the internet, TV, video games, loud music.
semen) may be the result of masturbation or occurs
Physical Growth during sleep (wet dream). These first emissions usually do
not contain fertile sperm.
Unlike children, however, adolescents monitor their
development carefully. They constantly compare At the beginning of the adolescent period, the ovaries in
themselves with ideal standards or images, becoming females produce more estrogens. The primary one is
embarrassed, fascinated or insecure. They then revise called progesterone. This affects the development of
their self-image. How they and their parents deal with the primary sex characteristics for girls, which include the
rapid changes of adolescence will impact their overall enlargement of the labia and clitoris, as well as the
adjustment. development of the uterus and vagina. The first
menstrual cycle, or menarche occurs at the age of 12 – 12
The rapid changes of adolescent physical growth rival the ½. The first ovulation of an egg occurs a year or more later.
rate of changes found in prenatal development and
infancy. Secondary sex characteristics also develop during
adolescence. These are physical changes that do not
The hypothalamus is the part of the brain that controls the directly affect reproduction, but are associated with
pituitary gland; the pituitary gland is the master gland of sexual maturation.
the body.
Secondary sex characteristics in males include pubic,
underarm, and facial hair growth, deepening of the voice,
and the ability to increased muscular development.
Secondary sex characteristics in females include fat
deposits on breasts and hips, a widening of the pelvic
bowl, and growth of underarm and pubic hair.
Sexual development is biological, but sexual behavior is
social and emotional as well as biological. Teens struggle
with their gender identity… dealing with their sexual
urges, but also with the culture’s expectations to exercise
restraint. The media, parents, schools, and religious
groups may present various attitudes toward sexual
behavior.
Since birth, the body of each individual has been
Sexual behavior may fall within different realms:
producing hormones from endocrine glands. Hormones
romantic (loving and/or leading toward marriage), casual
are biochemical substances that are secreted into the
(no special relationships established before having sex),
bloodstream. Each body, both male and female, have
manipulative (sex is offered to get what something you
been producing hormones called androgens and
estrogens.
want), teasing (flirting with no intentions to have a sexual activity associated with more drug use and
relationship or sex), and exploratory (experimentation). delinquency than later sexual activity.
Many adolescents choose to delay sexual relationships, Abnormalities and Diseases Related to the Physical Body
and practice abstinence. and Sexual Hormones
Physical Growth, and Psychosexual Development In the Early Stages
During adolescence, the individual enters into the final - The gonads (reproductive glands that produce
stage of Freud’s Theory of Psychosexual Development: the gametes; testis or ovary) (1-8 weeks of
embryonic development)
1. Oral stage
2. Anal stage - embryonic reproductive structures of males and
3. Phallic stage females are alike and are said to be in the
4. Latency stage indifferent stage.
5. Genital stage
During the genital stage, sexual urges are once
again awakened.
Attitudes toward sexual behavior in the United States
have varied over the last 50 years. During the 1950’s and
60’s, most young people felt pre-marital sex was immoral.
There was some peer pressure that compelled adolescent
boys to have sexual experience before marriage, while
girls were to remain chaste (virgins). This was the basis of
the popular ‘double standard’.
By the 1970’s sexual attitudes had changed, which might
have been the result of the widespread distribution of
reliable birth control pills, and partly because of the sexual
revolution of the 1960’s. Attitudes were more accepting
of casual sex, and same-sex orientation… sexual attraction
toward members of one’s own sex.
By the 1980’s, attitudes toward sexual behavior in
America returned to more conservative values. This may
have been influenced by rising numbers of STD’s…
sexually transmitted diseases. Although instances of - formation of male or female structures depends
adolescent sexual activity stayed high, sex was less casual. on the presence of testosterone
Facts: Since the year 2000, about 60% of white males and - If embryonic testes release testosterone, then the
females engage in sexual intercourse by the age of 18. duct system and external genitalia follows.
Black and Hispanic males report sexual activity at earlier
ages. Hispanic girls delay sexual activity more than other - Female embryos that form ovaries will cause the
groups. Adolescent boys and girls from two-parent development of the female ducts and external
families have less and later sexual experience than those genitalia since testosterone hormone is not
from single-parent families; overly restrictive and overly produced.
permissive parenting are associated with earlier sexual
activity in adolescents; good academic students delay
sexual activity more than poorer academic students; early
- Escherichia coli which spread through the
digestive tract; the sexually transmitted
microorganisms such as syphilis, gonorrhea, and
herpes virus; and yeast (a type of fungus)
In Females:
- Painful or abnormal menses may also be due to
infection or hormone imbalance.
- Tumors of the breast and cervix are the most
common reproductive cancers in adult females.
In Males:
- Common inflammatory conditions are prostatitis,
urethritis, and epididymitis, all of which may
follow sexual contacts in which sexually
transmitted disease (STD) microorganisms are
transmitted.
- Orchiditis, or inflammation of the testes, can
cause sterility and most commonly follows
mumps in an adult male.
In Males:
- Prostate cancer (a common sequel to prostatic
hypertrophy) is a widespread problem in adult
males.
Abnormalities Sex hormone production - Although aging men show a steady decline in
Pseudohermaphrodites are formed who are individuals testosterone secretion, their reproductive
having accessory reproductive structures that do not capability seems unending.
“match” their gonads;
Module 8: Human Sexual Behavior and STDs
Hermaphrodites are individuals who possess both ovarian
• Erogenous Zones
and testicular tissues but this condition is rare in nature.
parts of the body receptive to and increase sexual
- Puberty is the period of life when the arousal when touched in a sexual manner
reproductive organs grow to their adult size and This can be:
become functional under the influence of rising mouth,
levels of gonadal hormones (testosterone in
breasts,
males and estrogen in females).
genitals, and
Diseases Associated with the Reproductive System anus;
other common areas of the body that can be
In Females, vaginal Infections are:
aroused easily may include the neck, thighs,
- Young, elderly women and low diseases abdomen, and feet. (lips, scalp, palm of hands,
resistances fingertips, behind the knee, inner thighs, toes)
- If untreated, may spread throughout the female Human Sexual Behavior - any activity—
reproductive tract and may cause pelvic solitary, between two persons, or in a
inflammatory disease and sterility. group—that induces sexual arousal.
2 Major factors that determine human
Excitement
sexual behavior:
- Inherited sexual response patterns that
have evolved as a means of ensuring
reproduction Resolution Plateau
- Degree of restraint or other types of
influence exerted on the individual by
Sexual
society in the expression of his/her sexuality. Climax
Types of Behavior
• Physiology of Human Sexual Response
1. Solitary Behavior
1. Excitement phase. There is increase in
- Self-gratification means self-stimulation that
pulse and blood pressure, and skin
leads to sexual arousal and generally, sexual
temperature. Flushing and swelling of all
climax; most self-gratification takes place in distensible body parts are also
private as an end in itself. experienced. Symptoms of arousal
- most frequent in unmarried eventually increase to a near maximal
- more males vs. females physiological level that leads to the next
- less frequent or is abandoned when stage.
sociosexual activity is available. 2. Plateau phase. It is generally of brief
2. Sociosexual Behavior duration. If stimulation is continued,
- Heterosexual = male and female (greatest) orgasm usually occurs.
3. Sexual climax. It is marked by a feeling of
- occurs in childhood; may be motivated by
abrupt, intense pleasure.
curiosity, such as showing or examining
4. Resolution phase. It is the last stage that
genitalia.
refers to the return to a normal or
- Physical contact involving necking or petting subnormal physiologic state.
is considered as an ingredient of the learning
process. • Nervous System Factors
- Petting differs from hugging, kissing, and - autonomic system ----- controls involuntary
generalized caresses of the clothed body to responses.
practice involving stimulation of the - hypothalamus and the limbic system -------
genitals. responsible for regulating the sexual response.
- Coitus, the insertion of the male - lower spinal cord leads to erection and
ejaculation for male
reproductive structure into the female
- Stimulation of vaginal genital and perineal areas -
reproductive organ, is viewed by society
----discharges and lubrication for female
quite differently depending upon the marital
status of the individuals. • Sexual Problems
- Physiological problems.
Diseases 2ndary to abnormal development of the
genitalia or that part of the neurophysiology controlling
sexual response;
Physiology of Human Sexual Response - Psychological problems.
socially induced inhibitions,
maladaptive attitudes,
ignorance, and sexual myths held by society;
• Sexual Problems - It spreads easily and can lead to infertility in both
- Premature emission of semen is a common men and women, if untreated. Antibiotics stop
problem, especially for young males; the infection.
- Erectile impotence is almost always of Symptoms: Common symptoms are burning during
psychological origin in males under 40; in older urination and discharge, but often there are no early
males, physical causes are more often involved; symptoms. Later, the infection may cause skin rashes or
- Ejaculatory impotence, which results from the spread the joints and blood.
inability to ejaculate in coitus, is uncommon and
is usually of psychogenic origin. In men: Discharge from the penis, swollen testicles.
- Vaginismus is a strong spasm of the pelvic In women: Vaginal discharge, pelvic pain, spotting.
musculature constricting the female reproductive Symptoms may be mild and are easily confused with a
organ so that penetration is painful or impossible. urinary tract or vaginal infection.
• Sexually Transmitted Diseases 3. Syphilis
These are bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections Syphilis: First Stage
transmitted from an infected person to an • Primary Stage
uninfected person through sexual contact. • During the first (primary) stage of syphilis, you
1. Chlamydia may notice a single sore or multiple sore. The sore
2. Gonorrhea is the location where syphilis entered your body.
3. Syphilis Sores are usually (but not always) firm, round, and
4. Chancroid painless.
5. Human Papillomavirus • The sore usually lasts 3 to 6 weeks and heals
6. Herpes Simplex Virus regardless of whether or not you receive
7. Trichomonas Vaginalis treatment. Even after the sore goes away, you
1. Chlamydia must still receive treatment.
- caused by bacteria called Chlamydia trachomatis.
- can infect both sexes. Syphilis: Secondary Stage
- Women can get chlamydia in the cervix, rectum, • During the secondary stage, you may have skin
or throat. rashes and/or mucous membrane lesions.
- Men can get chlamydia in the urethra (inside the Mucous membrane lesions are sores in your
penis), rectum, or throat. mouth, vagina, or anus.
• Around 70 – 80 % of women with chlamydia • Starts with rash on one or more areas of your
don’t notice any symptoms. body.
• If you get signs and symptoms, these usually • rash can show up when your primary sore is
appear between one and three weeks after healing or several weeks after the sore has
having unprotected sex with an infected healed.
person. • rash can look like rough, red, or reddish-brown
The most common symptoms: spots on the palms of your hands and/or the
• Pain when urinating bottoms of your feet. ---usually won’t itch and it
• Discharge is sometimes so faint that you won’t notice it.
• Pain in the lower abdomen • fever, swollen lymph glands, sore throat, patchy
• Bleeding hair loss, headaches, weight loss, muscle aches,
• Pain in the testicles and fatigue (feeling very tired).
• Fever, nausea and pain during sex • The symptoms from this stage will go away
whether or not you receive treatment.
2. Gonorrhea: The Clap • Without the right treatment, your infection will
move to the latent and possibly tertiary stages of
syphilis.
Syphilis: Latent Stage • 79 million Americans, most in their late teens and
• The latent stage of syphilis is a period of time early 20s, are infected
when there are no visible signs or symptoms of • many different types of HPV.
syphilis. If you do not receive treatment, you can • can cause health problems including genital warts
continue to have syphilis in your body for years and cancers.
without any signs or symptoms. • vaccines can stop these
Syphilis: Tertiary Stage
• Most people with untreated syphilis do not 6. Herpes Simplex Virus
develop tertiary syphilis. However, when it does Two types: Herpes type 1 & type 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2)
happen it can affect many different organ • Herpes type 1 (oral)
systems. • causes sores around the mouth and lips
• The heart and blood vessels, and the brain and (sometimes called fever blisters or cold sores).
nervous system are affected. • Herpes type 2 (genital)
• Tertiary syphilis is very serious and would occur • infected person may have sores around the
10–30 years after your infection began. In genitals or rectum
tertiary syphilis, the disease damages your • Can have periods of being dormant,
internal organs and can result in death. • Attacks (or outbreaks) can be brought on by the
following conditions:
4. Chancroid • General illness (from mild illnesses to
- More commonly seen in men than women, serious conditions)
particularly uncircumcised males. • Fatigue
- Spread by having unprotected, vaginal or oral sex. • Physical or emotional stress
- Contagious as long as the person as open sores. • Immunosuppression due to AIDS or
The open sores contain bacteria and any contact such medications as chemotherapy
with these sores can result in infection. or steroids
- May be treated with certain antibiotics. The • Trauma to the affected area, including
ulcers generally heal with 2 to 3 weeks. sexual activity
Some symptoms include: • Menstruation
- Sores or raised bumps on the genitals which
eventually if untreated, becomes filled with pus 7. Trichomonas Vaginalis
and eventually ruptures leaving a painful • The most common symptoms among women are:
sore/ulcer. • vaginal discharge, which can be white, gray,
- The bacterial may also infect the lymph glands in yellow, or green, and usually frothy with an
the groin. These glands may become enlarged, unpleasant smell
hard and painful. • vaginal spotting or bleeding
- In women, ulcers appear on the genitals, painful • genital burning or itching
urination and painful intercourse. • genital redness or swelling
• frequent urge to urinate
5. Human Papillomavirus • pain during urination or sexual intercourse
How is HPV spread? • The most common symptoms in men are:
• having vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone • discharge from the urethra
who has the virus. • burning during urination or after ejaculation
• can be passed even when an infected person • an urge to urinate frequently
has no signs or symptoms.
• can develop symptoms years after you
have sex with someone who is infected. Natural and Artificial Methods of Contraception
• What is HPV? Natural Method
The natural family planning methods do not involve any In many ways, our spiritual self is influenced
chemical or foreign body introduction into the human by the religious teachings, practices and
body. beliefs of our time. Our moral uprightness
a. Abstinence and sensibility as well as our conscience is
b. Calendar Method
shaped by the religious rituals, traditions,
c. Basal Body Temperature
and ceremonies we are exposed to.
d. Cervical Mucus Method
e. Symptothermal Method
Our understanding of these concepts
f. Ovulation Detection broadens our view of our self and would
g. Coitus Interruptus help us understand some of the motivating
Artificial Methods: force for our actions and decisions in life.
a. Oral Contraceptives Thus, helping us be more enlightened and be
b. Transdermal Patch aware of an aspect of our inner self.
c. Vaginal Ring From this, we now delve into various
d. Subdermal Implants concepts related to the discovery of one’s
e. Hormonal Injections spiritual self. These are various Religions,
f. Intrauterine Device
Rituals, Customs, Practices and Beliefs. And
g. Chemical Barriers
on the last part, a discussion on how a
h. Diaphragm
i. Cervical Cap
person may be able to find his/her meaning
j. Male Condoms and purpose in life.
k. Female Condoms
l. Surgical Methods Religion is known as a set of personal or
organized belief, customs and practice in relation
Module 9: The Spiritual Self to faith and the object/s of faith of person.
Introduction - It is also considered as devotion to or
Our life is made up of more than the physical commitment to a God or supernatural being
things. We can touch, see, hear and feel in which a person believes in.
things but our total experience is not just Population by Religion
made up of what is material. That is why we Christianity: 1.9 billion people
need to understand our self, in relation to Islam: 1.1 billion
our spiritual aspect. Hinduism: 800 million
According to William James (1890), the Buddhism: 325 million
spiritual self is one aspect of the self that is Judaism: 13 million
considered to the most intimate, and
belonging to the inner subjective part of the Ritual
self. According to Penner (2017 as cited in Alata,
Other definitions of the spiritual self is to Caslib Jr., Serafica and Pawilen, 2018), the
view it as a part of you that provides insight, three fundamental characteristics of rituals
intuition, and other ways of knowing what to are:
do or move in a certain direction beyond 1) an emotional feeling of respect, awe,
what our senses tell us. This helps us decide fascination or dread in relation to the sacred,
in what direction to take when it comes to 2) dependence upon a belief system usually
our moral responsibility, sense of right and expressed in the language of myth and
wrong or even our conscience. 3) symbolic in relation to its reference.
Rituals is referring to the ceremonial rites of 8. Do not steal.
a religions practice. 9. Do not lie.
It is about the social customs and protocols 10. Do not covet.
an individual practice in adherence to a Important Days
Ash Wednesday-Lent
certain religion or religious practice.
Palm Sunday
Rituals acts of faith in practice of their
Maundy Thursday
religious practice and it is a way of defining Good Friday
or describing human behavior. Easter
Ascension
MOST PREVALENT RELIGIONS, RITUALS, AND Pentecost
PRACTICES AS IT RELATES TO SPIRITUALITY Advent
Christmas
Epiphany
JUDAISM
Is a monotheistic religion
Judaism is the oldest and smallest of the
world's five great religions
Being a part of a Jewish community and
living one's life according to Jewish law and
traditions is very important.
The fundamental beliefs of Judaism are:
-There is a single, all-powerful God
who created the universe and
Christianity
everything in it.
Based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ
- God has a special relationship with the
Originated in Palestine in the 1st century AD
Jewish people due to covenant that God made
Believe that Jesus was the son of God who came
with Moses on Mount Sinai, 3500 years ago.
and died for people’s sins and then rose so that all
people could be saved
Rambam’s 13 Principles of Faith
Believe in one God(monotheistic) who created
1. G-d exists
the universe and all things in it
2. G-d is one and unique
Christianity originally developed as a part of
3. G-d is incorporeal
Judaism
4. G-d is eternal
Christian Way of Life
5. Prayer is to be directed to G-d alone and to no
Fellowship with God
other
Our relationships with others
6. The words of the prophets are true
Obedience to God's commands
7. Moses’ prophecies are true, and Moses was the
Discipline
greatest of the prophets
8. The Written Torah (first 5 books of the Bible) and
God:
Oral Torah were given to Moses
1. Do not worship any other gods.
9. There will be no other Torah
2. Do not make any idols.
10. G-d knows the thoughts and deeds of men
3. Do not misuse the name of God.
11. G-d will reward the good and punish the wicked
4. Keep the Sabbath holy.
12. The Messiah will come
Man:
13. The dead will be resurrected
5. Honor your father and mother.
• 613 Mitzvot
6. Do not murder.
7. Do not commit adultery.
Foods are kosher when they meet all criteria that
Jewish law applies to food
Characteristics that make a food non-kosher:
the mixture of meat and milk
the use of cooking utensils which had
previously been used for non-kosher food
The type of animal it is
Leviticus 11:3 says that Jews may eat all animals
The Jewish place of worship is called a Synagogue that have cloven hooves and chew their cud
The religious leader of a Jewish community is Leviticus 11:4 explicitly prohibited the
called a Rabbi consumption of animals that do not have these
Unlike leaders in many other faiths, a rabbi is not characteristics designating them "unclean to
a priest and has no special religious status you."
The Jewish holy day, or Sabbath (Shabbat), starts Six mammals are specifically not allowed:
at sunset on Friday and continues until sunset on The camel
Saturday The hyrax
During the Sabbath, Jews do not work (drive, The hare
cook, etc) The pig
7 Holy Days Whales and dolphins
Rosh Hashanah-Jewish New Year Kosher animals are as follows:
Yom Kippur-A day of fasting and praying which Cows, goats, sheep, antelope, deer,
occurs 10 days after the first day of Rosh giraffes, okapis and pronghorns
Hashanah. The holiest day in the year Most fish (excluding shellfish, sharks,
Sukkot-8-day festival of thanksgiving octopus, eels and squid)
Hanukkah - The Feast of Lights is an 8-day Feast of Chicken, duck, turkey
Dedication. It recalls the war fought by the Milk and cheese are kosher but cannot be
Maccabees in the cause of religious freedom eaten with meat or mixed with meat.
Purim-The Feast of Lots recalls the defeat by Preparation
Queen Esther of the plan to slaughter all of the the slaughter of animals is designed to
Persian Jews, circa 400 BC minimize the pain—usually done by a
Pesa(Passover)-The 8 day festival recalls the slice across the throat
exodus of the Israelites from slavery in Egypt circa this eliminates the practice of hunting for
1300 BCE. A holiday meal, the Seder, is held at food unless it can be captured alive and
home ritually slaughtered.
Shavouth-Pentecost recalls God's revelation of All blood and veins must be removed
the Torah to the Jewish people from meat (salting and broiling are
Menorah -It is a symbol of the nation of Israel common methods)
and a mission to be "a light unto the nations.
ISLAM
Yarmulke is worn during prayer to • Islam is the world's second most followed religion
show respect to G_d • It began around 1400 years ago in Arabia, but
swiftly become a world faith, and now has around
The Star of David is the 1.2 billion people
international symbol of Judaism • "Islam" is an Arabic word which means
“surrendering oneself to the will of God”
• One will achieve peace and security by doing so
• A person surrenders to the will of Allah by living
Kosher Foods and thinking in the way Allah has instructed.
• Islam is more than a system of beliefs. The faith • Ramadan is the holiest day for Islam. It
provides a social and legal system and governs marks when Muhammad had the Qur-an
things like family life, law and order, ethics, dress, revealed to him
and cleanliness, as well as religious ritual and • Sawm is usually described as fasting, but
observance—Islamic Republic it actually involves abstaining from all
Islam is practiced: bodily pleasures between dawn and
• The countries with the largest Islamic populations sunset
are not in the Middle East as most would think • Not only is food forbidden, but also things
• The largest are Indonesia (170 million), Pakistan like smoking, chewing gum, negative
(136 million), Bangladesh (105 million), and India thoughts and sexual activity
(103 million) 4. Zakat(almsgiving) is giving alms to the poor
• Islam's three holiest places, the cities of Mecca, • This is a compulsory gift of 2.5 % of one's savings
Medina and Jerusalem, are all in the Middle East each year
• Giving in this way is intended to free Muslims
• The present form of Islam began in Arabia in 622 from the love of money
AD • It reminds them that everything they have really
• It is based on the ministry of a man named belongs to God.
Muhammad and, on the words, that Allah gave to 5. Hajj is the pilgrimage to Mecca that all
the world through him physically/financially able Muslims should make
• Muhammad did not found Islam. Islam was at least once in their life
created by Allah at the beginning of time, and in • Mecca is the most holy place for Muslims
fact Muslims regard Adam as the first Muslim • Takes place during days 8-13 of the 12th month of
• Muhammad was the final messenger through the Islamic Lunar calendar
whom Allah revealed the faith to the world • They circle the Kaaba seven times on three
• There had been earlier messengers, among them occasions, say prayers, drink from a holy spring,
Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses and Jesus. walk to Mount Arafat to pray, feast, cast stones at
three pillars (to fight Satan’s temptations), shave
5 Pillars of Islam hair, run seven times between some hills
1. Shahada (witness) is the Muslim profession of
faith The Kaaba - It is the most sacred site in Islam. It is
- "I witness that there is no god but Allah, and considered by Muslims to be the Bayt Allāh(Arabic: َبيْت
that Muhammad is the prophet of Allah" للا, "House of God"), and has a similar role to
the Tabernacle and Holy of Holies in Judaism.
• Muslims say this when they wake up in the
morning and just before they go to sleep at Other Info
night.
2. Salat (daily prayer) is a prayer ritual performed 5 The Qur’an is the Islamic holy book
times a day by all Muslims over the age of 10 The Qur'an is the actual word of God, and
• Between first light and sunrise contains the fundamental beliefs of Islam
Mecca, Medina and Jerusalem are holy cities
• After the sun has passed the middle of the sky
According to tradition, the Qur'an was dictated to
• Between mid-afternoon and sunset
Muhammad
• Between sunset and the last light of the day
Two major sects
• Between darkness and dawn
Sunni-920 million people(everywhere
3. Sawm(fasting) is abstaining each day during
else)
Ramadan
Shiite-120 million people(Iran)
• Sawm helps Muslims develop self-
Comparing the Sunni and Shiite branches
control, gain a better understanding of
of Islam
God's gifts and greater compassion
towards the deprived.
Hindus believe the universe doesn't have a
Islamic Law beginning and an end. It's a cyclical pattern, so
The Sharia outlines all of the laws (comes from the once it ends, it begins again.
Koran) One attains Moksha when one has "overcome
5 Major Crimes: ignorance" and no longer desires anything at all
theft, highway robbery, intoxication, (and yes, that includes the desire for Moksha)
adultery and falsely accusing another of Hindu Beliefs
adultery All good things in life are gifts from
Food Laws God
Very similar laws to the Jewish kosher foods
No alcohol, pork, blood, no pork fat products, Finding out what your life’s calling is as
scavenger animals Dharma suggest/requires is a very
important goal
Food must be prepared similarly to the Jews
Slice to the jugular
Being a fair and decent person is very
Drain blood important
HINDUISM
Hinduism includes a very wide range of beliefs
Wealth, power and material
and practices, so there aren't many things that belongings are good goals as long as
are common to all Hindu groups they don’t become all important
Hinduism has no founder, no single book of faith,
no creed, and no single source of authority (such Moksha is the ultimate goal; freedom
as Jesus) from life and death
Hinduism is very individualistic but a big part of a
person’s everyday life Four Stages of Life
There are 750 million Hindus in the world, mostly
in India • Ages 12-24 you get educated and trained
For many Hindus, religion is a matter of practice • Ages 24-48 you get married, raise a family, make
rather than of beliefs. It's more what you do than money, get involved in many things
what you believe. • Ages 48-72 you become a mentor to a young
Behind Hindu practice is the belief that every soul person and start isolating themselves from the
is trapped in a cycle of birth-death- outside world
rebirth(reincarnation). Every Hindu wants to • At age 72 you end ties to the outside world and
escape from this cycle. get rid of your worldly possessions. Prayer and
Hindus aim to live in a way that will cause each of devotion become very important.
their lives to be better than the life before. • Mostly aimed at men and is not followed as much
Whether one is reborn into a better life, a worse as it used to be
life, or even to live as an animal, depends on
Hindu Gods
Karma, which is the value of a soul's good and bad
deeds. • One would think Hinduism is polytheistic.
Dharma is a “cosmic natural law” that forms the Most Hindus would say they worship one
basis for Hindu philosophies, beliefs and practices God.
and holds everything together • There is only one ultimate God, Brahman, but
People that live in harmony with Dharma proceed shows itself in many forms
more quickly toward Moksha • The gods Brahma, Vishnu and Shiva, for example,
Hindus ultimate aim is escape from the life cycle are different aspects of Brahman:
altogether and achieve the ultimate liberation— • Brahma reflects God's divine work of
Moksha creating the universe
• Vishnu reflects God's work in keeping the Do not harm yourself or others, do not
universe in existence steal, and no sexual misconduct
• Shiva reflects God's work in destroying it 5. Right Livelihood
No jobs dealing in weapons, in living
BUDDHISM beings (including raising animals for
Founded in India around 500 BC by Siddhartha slaughter as well as slave trade and
Gautama prostitution), working in meat production
and butchery, and selling alcohol and
Became Buddha, the Enlightened One, when he drugs
was 29 6. Right Effort
He was trying to find the true meaning of life and Give 100% effort in what you do
eventually, through four trance-like stages of 7. Right Mindfulness
meditation, he was enlightened to the Buddhist Having the power to control our thought
was of life process and see the truth behind things
8. Right Concentration
His main teachings were to eliminate human Ability to have deep concentration and
wants as they are the cause of suffering in the ability to focus on wholesome thoughts
world and actions
OVERVIEW
Buddhism has no unique creed, no single
In addition, a person might believe in a greater,
authority and no single sacred book
supernatural, higher being usually termed as God,
Buddhism focuses on each individual seeking to while others may believe in deep teachings of
attain enlightenment religion which seems to govern.
Some religious practices, belief, customs and
Key beliefs and values are contained in "The Four
tradition presented by the different religions may
Noble Truths “
have some similarity or contrasting differences.
1. Life means suffering Some believes in the concept of the afterlife or in
2. The origin of suffering is attachment to worldly learning virtues which are essential to one’s life. n
things their way of life.
3. The end to suffering is attainable through Lastly, the making of a spiritual self is not only
eliminating physical wants/needs found in the practice of religion and its beliefs.
Eventually can achieve Nirvana (no wind) Spirituality is connected with our deep concern
Nirvana means freedom from all worries with our soul and not just the physical or material
and troubles self. It is concerned with the exercise of morals,
4. The path to the end suffering and conscience and deep understanding of God and
achieve Nirvana is to follow the Eight-Fold Path how we are connected to the greater schemes of
Eight Fold Path life.
1. Right View A person’s spiritual self can be understood and is
To see and view things as they really are often manifested in accordance with his or her
Attained true wisdom religion, rituals, practices and customs related
2. Right Intention with it.
Think and do the right things at all times The religious beliefs that he or she adheres to and
3. Right Speech its way of expression is an essential component of
Do not lie, curse, slander, or gossip his or her spiritual self. This can shape the way he
or she lives life, be shaped, molded and form
habits which are necessary to understand this
4. Right Action aspect of the self.
Module 10: The Political Self and its Relation to the culture. Having a full grasp of it will help us in
Filipino Identity understanding who is the “Filipino Identity”.
- Before discussing the Filipino Identity, let us first
• The word politics comes from the “political”. It define who is the “Filipino”.
means the activities associated with the - The 1987 Philippine Constitution states that
governance of a country or other area, especially Filipino citizens are: “…those whose fathers
the debate or conflict among individuals or or mothers are citizens of the Philippines, those
parties having or hoping to achieve power. born before January 17, 1973, of Filipino
• Politics is the activities involved in running a mothers, who elect Philippine citizenship upon
governmental entity or state. reaching the age of majority, and those who are
Importance of Politics naturalized in accordance with law.”
• They decide how much money the state will take - While the definition of the Constitution is
from people in the form of taxes to spend on binding, reality points that those who were not
public projects such as healthcare, education, or born in the country but grew up in the same
defense. culture develop and share common personality
• Political decisions also make the laws that affect traits and values with those who were natural
people's lives. born Filipino. Thus, citizenship is not just the only
• In short, those who run the politics, also have a gauge of being a Filipino.
direct and indirect hand in the affairs of the
people living within that country. Political What makes a “Filipino Identity”?
decisions, especially by those in government Filipino Values and Traits
power affect lives. • Values are defined as a person's principles or
standards of behavior; one's judgment of what is
• Politics take place within a nation’s context, important in life.
culture and environment. Before it actually • In many ways, it signifies a degree of importance
begun, what really helped shape politics in the of some thing or action, with the goal of knowing
country is the identity of those that surround it. actions that are best to do or what way is best to
• In reality, politics is influenced by the culture, live, or to describe the significance of different
values, traits of the individuals living in a actions.
particular country or nation. • Traits are a distinguishing quality or
• To understand, the politics and activities of the characteristic, typically one belonging to a
people, we must learn to understand its identity. person.
• Thus, to understand the politics and activities of • Combined together, the Filipino Identity has a
the Filipino, we must identify with what shapes unique set of values and traits that helps him
its identity. stand apart from the others.
The Filipino Identity
- The first colonizers to influence the Philippines were • Filipino Hospitality
the Spaniards who made its way here in 1890’s; One of the unique ways to welcome guests and tourists
- Then Japanese forces took their place in 1946. here in the Philippines is by treating them nicely and
- Afterwards, the American forces helped in the warmly as if they are their own brothers and sisters.
liberation of the Philippines which eventually paved Treating the guests with Filipino Hospitality means that
the way for us to become an independent nation. the guests feel at home, offering them something to eat,
- In reality, foreign culture, beliefs, language, and or even a place to stay.
religion have made a huge impact on our own by • Respect for Elders
setting a foundation to the contemporary Filipino - In the Philippines, especially in parts of Luzon,
identity and culture. elders are greeted by kissing their hand while
- As such, the Filipino of today may have traces of saying “Mano po!”. and constantly using “po”
various values and practices coming from different and “opo” in conversations.
- We also use specific “references” that show • “Bahala Na” Attitude
respect towards elder. A wide array of - The phrase is said to have originated from
references to elder people such as ate for older “Bathala na,” where Bathala means God, and
sister; kuya for older brother; tito and tita for the phrase meaning leaving everything into
uncle and aunt; lolo and lola for grandfather and God’s hands. Saying Bahala Na also means that
grandmother; and manong and aling for older we leave the control and the outcome of things
people outside the family. in the hands of God.
• Close Family Ties • Palabra de Honor
- Filipinos are also known to keep relational ties - A Spanish term which means Word of Honor
with their families very close. Occasions, such as - A verbal commitment by one person to another
family reunions during birthdays, holidays, or agreeing to do (or not to do) something in the
fiestas year-round are most of the time shared future.
within the family. • Colonial Mentality
- Some Filipino families choose to live together. It is regarded as the lack of patriotism and the attitude
This might mean that some parents still allow where Filipinos favor foreign products more than their
their children to live under their roof even if they own; This stems from the belief that foreign goods are of
are married and have kids. Parents on the other better quality than those made in the country. To some,
hand, are seldom placed in nursing homes but it is also the desire to look more foreign than local and
are taken care of by family members. keep up with foreign beauty trends.
• Cheerful Personality • “Mañana” Habit
Filipinos are also known to be smiling, or sharing a laugh Filipino term for procrastination; derived from a Filipino
with others and this is known as the cheerful personality. phrase called “Mamaya na” meaning dawdling things,
Sometimes, they even smile towards strangers as a way which could have been done at an earlier time.
to show warmth. But, sometimes, Filipinos also smile • “Ningas Kugon”
when they are happy, or even when they are sad or - “Ningas” is a Filipino term for flame and “kugon”
angry. This seems to be coping strategy for many is a Filipino term for Cogon grass that easily
Filipinos especially during trying times and calamities. burns out after it is put into flames. A man who
• Self-sacrifice is referred to as Ningas Cogon has an attitude of
- Filipinos tend to put others well-being first eagerly starting things but quickly losing
before. This may mean that one would go out his eagerness soon after experiencing difficulty.
way in order to carry the burden of taking care • Pride
or extending help to their friends, families, and Pride is an attitude where an individual puts more value
loved ones. They would be willing to give up on ego, reputation or having a “good face” in other
their time, dreams, and personal ambitions. people’s eyes. Most Filipinos hold on to their pride as if
- One good example is an Overseas Filipino they are more precious than keeping a good relationship
Workers (OFWs). The OFW sacrifices a lot by with family and loved ones.
leaving their homes and families in order to earn • Crab Mentality
higher and send money to their families. For this It is an attitude where an individual resents the
reason, the OFW seems to be a hero. achievement of another due to envy or jealous, instead
• Bayanihan of feeling happy for that person. The person with crab
- It is a trait of the Filipino where helping, mentality tends to gain satisfaction in pulling a person
cooperation is extended to a neighbor or any down or looks for a person to fall from grace.
part of one’s to signify unity. This may also mean • Filipino Time
that a person lends a helping hand to another Filipinos have this common attitude of arriving late at
person within the community without asking for commitments, dinner, or parties especially if they are
anything in return. meeting someone close to them.
Filipino Markers
1. Proverbs or Salawikain
a. proverbs expressing a general attitude
toward life and the laws that govern life
b. ethical proverbs recommending certain
virtues and condemning certain vices
c. proverbs expressing a system of values
d. proverbs expressing general truths and
observations about life and human
nature
e. humorous proverbs
f. miscellaneous proverbs
2. Superstitions
Filipinos’ set of superstitions passed down from
generation to generation
Some of these may be influenced by beliefs from other
cultures, but Filipinos have retold these superstitions
according to their own experiences.
3. Myths and Legends
Due to the Philippines’s rich culture and history,
numerous myths and legends have sprung.
These stories are aimed to explain the origin of things, at
the same time, teach a valuable lesson.
4. Heroes and Icons
Heroes serve as a reminder of true patriotism and
nationalism as they have sacrificed their lives for the
sake of their country’s freedom and progress.
Famous Filipino icons such as Lea Salonga, Manny
Pacquiao, and our very own national hero, Jose Rizal,
have made the Filipino name more pronounced
worldwide through their own expertise.
How to Be A Good Filipino
1. Be an active Filipino citizen.
2. Study the Philippine history.
3. Support local products.
4. Speak the Filipino language.
5. Do not spread fake news and be democratic in
engaging with dissent.
You might also like
- CASE3Document5 pagesCASE3romelynNo ratings yet
- The Western and Eastern Concepts of SelfDocument18 pagesThe Western and Eastern Concepts of SelfYeji BabeNo ratings yet
- InventoriesDocument10 pagesInventoriesJames BarzoNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsDocument15 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsAtteya Mogote Abdullah86% (28)
- UTS LessonsDocument20 pagesUTS LessonsSara AlbinaNo ratings yet
- PSY Reviewer MidtermsDocument29 pagesPSY Reviewer MidtermsSara AlbinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsDocument19 pagesLesson 4 The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsOlivares Chesanna Denise T.No ratings yet
- UTSDocument11 pagesUTSernest empuertoNo ratings yet
- Uts Midterm ReviewerDocument21 pagesUts Midterm ReviewerVanessa VillaramNo ratings yet
- 7self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsDocument4 pages7self in Western and Eastern Thoughtsruth san joseNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtDocument12 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern Thoughtbalucosgeave18No ratings yet
- Week 5 Self in Western and Oriental or Eastern Thought 20230927100800Document16 pagesWeek 5 Self in Western and Oriental or Eastern Thought 20230927100800azimgaming080805No ratings yet
- The Western and Eastern Concepts of SelfDocument37 pagesThe Western and Eastern Concepts of SelfElleNo ratings yet
- The Western and Eastern Concepts of SelfDocument17 pagesThe Western and Eastern Concepts of SelfAngeloseNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - LESSON 5 - Eastern and Western ConceptDocument14 pagesMODULE 1 - LESSON 5 - Eastern and Western ConceptBaniel, Chester Leo P.No ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsDocument2 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsyimlurimlaNo ratings yet
- Eastern and Western Thought - Lesson 4Document14 pagesEastern and Western Thought - Lesson 4Mary Grace Alipayo SambajonNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtDocument12 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtMarthy DayagNo ratings yet
- Module One - Chapter FourDocument2 pagesModule One - Chapter FourJohn Lloyd Artuz EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document16 pagesChapter 5Samantha EllaineNo ratings yet
- The Western and Eastern Concepts of Self: Don Honorio Ventura State UniversityDocument13 pagesThe Western and Eastern Concepts of Self: Don Honorio Ventura State UniversityKenneth CanceranNo ratings yet
- Eastern PhilosophyDocument2 pagesEastern PhilosophyDan Lhery Susano Gregorious100% (1)
- Week 7 Self in Eastern and Western ThoughtsDocument8 pagesWeek 7 Self in Eastern and Western Thoughtsguzman.justinemark.academicNo ratings yet
- Module 4 (Autosaved)Document14 pagesModule 4 (Autosaved)Argie GallazaNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern Thoughts5Document10 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern Thoughts5Penelope GarciaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Topic 4Document3 pagesModule 1 Topic 4Lord GrimNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtDocument17 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtLionel Palacio Canoy100% (1)
- Lecture Notes 8 The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtDocument23 pagesLecture Notes 8 The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtAeleu JoverzNo ratings yet
- Topic 5Document7 pagesTopic 5Marg'riette PascuaNo ratings yet
- UTSDocument3 pagesUTSmmoirajadeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - Lesson 4Document28 pagesCHAPTER 1 - Lesson 4Sontosidad, Febie Jynn A.No ratings yet
- Eastern and Western PerspectiveDocument17 pagesEastern and Western PerspectiverlcasinilloNo ratings yet
- Eastern and Western Thought: Individualistic Versus CollectiveDocument15 pagesEastern and Western Thought: Individualistic Versus Collectivenan nanNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self 3Document32 pagesUnderstanding The Self 3Darylle Mae AñascoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document23 pagesChapter 5Laarni De VeraNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Module For MidtermsDocument6 pagesUnderstanding The Self Module For Midtermsfrederick liponNo ratings yet
- 1 Module 1 - Concept and Nature of Self: Who Am I?Document13 pages1 Module 1 - Concept and Nature of Self: Who Am I?John MichaelNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Oriental/ Eastern ThoughtDocument16 pagesThe Self in Western and Oriental/ Eastern ThoughtEXCALIBURNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern Thought Lesson 4Document1 pageThe Self in Western and Eastern Thought Lesson 4Cj DagpinNo ratings yet
- UTS - Chapter 1, Lesson 4Document2 pagesUTS - Chapter 1, Lesson 4Krishna Faith P. DelaraNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self 3Document32 pagesUnderstanding The Self 3Christian Adaoag75% (4)
- Understanding The SelfDocument3 pagesUnderstanding The SelfKatherine ManaloNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern Thoughts: Learning Experiences & Self-Assessment Activities (Saa)Document7 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern Thoughts: Learning Experiences & Self-Assessment Activities (Saa)Jeremias De la CruzNo ratings yet
- The Eastern and Western View of SelfDocument2 pagesThe Eastern and Western View of SelfNombre Princess AliyahNo ratings yet
- 1cec - Module 1 Lesson 4 Group 3 - The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsDocument2 pages1cec - Module 1 Lesson 4 Group 3 - The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsGerrylie GallardoNo ratings yet
- Eastern Perspectives On Positive Psychology: Name: Harshita KapoorDocument23 pagesEastern Perspectives On Positive Psychology: Name: Harshita KapoorHarshita Kapoor100% (1)
- Module 2 The Western and Eastern ThoughtsDocument12 pagesModule 2 The Western and Eastern ThoughtsCristine BalocaNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western Eastern ThoughtDocument22 pagesThe Self in Western Eastern ThoughtAngelynne Villapando DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Essentialist ModelDocument3 pagesEssentialist ModelGerard Byron JacildoNo ratings yet
- 15.2 Introduction in World ReligionDocument6 pages15.2 Introduction in World ReligionKurt Russel LeonemNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsDocument14 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsJustien BautistaNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document6 pagesModule 5Jared TeneberNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsDocument50 pagesLesson 5: The Self in Western and Eastern ThoughtsMary Jane Nabo MurilloNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument33 pagesUnderstanding The SelfJhen Mary Rose Bandojo100% (1)
- Chapter III Philosophies Movement in Education (Final) - 075235Document57 pagesChapter III Philosophies Movement in Education (Final) - 075235John Robert BagalayNo ratings yet
- Uts ProjecgDocument7 pagesUts ProjecgJamie Lynn Lee AbanillaNo ratings yet
- Gec1 Lesson5Document11 pagesGec1 Lesson5Ray Niel Liquisen ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Self and Its Relevance For Self Management - (Autosaved)Document37 pagesUnderstanding Self and Its Relevance For Self Management - (Autosaved)Subhash chandra ghoshNo ratings yet
- The Western and Eastern Concepts of SelfDocument13 pagesThe Western and Eastern Concepts of SelfJhal Mark Le VillarealNo ratings yet
- Psychological Views of SelfDocument38 pagesPsychological Views of SelfGNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Power: Teachings from Ancient Thinkers: Power Games: A Motivational Guide, #6From EverandPhilosophy of Power: Teachings from Ancient Thinkers: Power Games: A Motivational Guide, #6No ratings yet
- Why It Is Good to Be Good: Ethics, Kohut's Self Psychology, and Modern SocietyFrom EverandWhy It Is Good to Be Good: Ethics, Kohut's Self Psychology, and Modern SocietyRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (1)
- Problem 2Document1 pageProblem 2James BarzoNo ratings yet
- A. Definition and Concept of Taxation B. Nature of TaxationDocument1 pageA. Definition and Concept of Taxation B. Nature of TaxationJames BarzoNo ratings yet
- Necessity Theory 2. Benefits-Protection Theory (Symbiotic Relationship) 3. Jurisdiction Over Subject and ObjectsDocument2 pagesNecessity Theory 2. Benefits-Protection Theory (Symbiotic Relationship) 3. Jurisdiction Over Subject and ObjectsJames BarzoNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument1 pageThesisJames BarzoNo ratings yet
- CH 07Document33 pagesCH 07James BarzoNo ratings yet
- CH 07Document33 pagesCH 07James BarzoNo ratings yet
- The Weighted Average Method of Process Costing Computes The Cost Per Equivalent Unit Based Solely OnDocument106 pagesThe Weighted Average Method of Process Costing Computes The Cost Per Equivalent Unit Based Solely OnJames BarzoNo ratings yet
- If Department Q Uses 60 000 of Direct Materials and Department T Uses 15 000 ofDocument160 pagesIf Department Q Uses 60 000 of Direct Materials and Department T Uses 15 000 ofJames BarzoNo ratings yet
- Suppl Problems Process Costing 08Document5 pagesSuppl Problems Process Costing 08James BarzoNo ratings yet
- AIS-Revenue CycleDocument67 pagesAIS-Revenue CycleJames Barzo100% (2)
- Expenditure CycleDocument5 pagesExpenditure CycleJames BarzoNo ratings yet
- CSE - SDO Pampanga - Sexual and Reproductive Health 4th Revised 2Document32 pagesCSE - SDO Pampanga - Sexual and Reproductive Health 4th Revised 2Ma Concepcion Adriano GuansingNo ratings yet
- Chlamydia Felis: Infection in CatsDocument2 pagesChlamydia Felis: Infection in CatsPetrisor GheorghiuNo ratings yet
- Guide To Path Tests Aclmar BF Nat 00059Document4 pagesGuide To Path Tests Aclmar BF Nat 00059Faraz MahboobNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases in MalesDocument15 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases in MalesSam Raven AndresNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Gynecology and Infertility. Factors Associated With Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument16 pagesKeywords: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Gynecology and Infertility. Factors Associated With Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Uts Chapter 2 Lesson 1Document29 pagesUts Chapter 2 Lesson 1John Jerome GironellaNo ratings yet
- Conjunctiva: Fourth Year Omar Al-Mukhtar Univercity 2019-2020Document55 pagesConjunctiva: Fourth Year Omar Al-Mukhtar Univercity 2019-2020Helene AlawamiNo ratings yet
- Symptom Flow Chart: Vaginal DischargeDocument2 pagesSymptom Flow Chart: Vaginal DischargeJeff ZhouNo ratings yet
- PHAR 233 - Pathophysiology of Infectious DiseasesDocument89 pagesPHAR 233 - Pathophysiology of Infectious DiseasesLina RamojNo ratings yet
- Nami - ChlamydiaDocument32 pagesNami - ChlamydiaNami ArthisariNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Nelia B. Perez RN, MSN Class 2015Document94 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases: Nelia B. Perez RN, MSN Class 2015Mariana CreciunNo ratings yet
- Question Booklet Series - : Time Allowed: 2 Hrs. Questions: 1-200Document13 pagesQuestion Booklet Series - : Time Allowed: 2 Hrs. Questions: 1-200WickyNo ratings yet
- Proposed Regional Genitourinary Center: in CalabarzonDocument45 pagesProposed Regional Genitourinary Center: in Calabarzonallyssa monica duNo ratings yet
- Could It Be An STI?: DR Neelam DoshiDocument67 pagesCould It Be An STI?: DR Neelam Doshijoee ahmedNo ratings yet
- Rd-15 Bartholin Cyst and Abscess 10-12Document2 pagesRd-15 Bartholin Cyst and Abscess 10-12Chong Hui ChekNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitte D Infections: Keeshia Anna Zerrudo Clinical Clerk Iloilo Doctors' Hospital Inc. August 18, 2020Document117 pagesSexually Transmitte D Infections: Keeshia Anna Zerrudo Clinical Clerk Iloilo Doctors' Hospital Inc. August 18, 2020Angela SaldajenoNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument15 pagesWeek 11 Sexually Transmitted DiseaseAngel Alexa Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document98 pagesLesson 2Maira Garcia C.No ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Prevention and ControlDocument197 pagesCommunicable Disease Prevention and Controldennisjamesbartz100% (1)
- FCM 3 - 3A Group 8 - National AIDS STI Prevention and Control ProgramDocument184 pagesFCM 3 - 3A Group 8 - National AIDS STI Prevention and Control ProgramRenz Francis SasaNo ratings yet
- PGI MANIMTIM - CPG - BF Screening Guidelines For PediatricsDocument42 pagesPGI MANIMTIM - CPG - BF Screening Guidelines For PediatricsKim Adarem Joy ManimtimNo ratings yet
- Gynae & Obs Bcqs BookletDocument58 pagesGynae & Obs Bcqs BookletKiran Ayub100% (1)
- PID LectureDocument41 pagesPID LectureHarold Gabriel Sanchez DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Koala Book KGDocument15 pagesKoala Book KGozuchanNo ratings yet
- The Gynecologic History and Pelvic Examination Up To Date 2016Document14 pagesThe Gynecologic History and Pelvic Examination Up To Date 2016Mateo GlNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Xii 2024 - Siswa-1Document17 pagesLatihan Soal Xii 2024 - Siswa-1aqilahpramesti65No ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Summary of CDC Treatment GuidelinesDocument3 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases: Summary of CDC Treatment GuidelinesbenzveewitNo ratings yet
- U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations For Contraceptive Use, 2016 MMWRDocument60 pagesU.S. Selected Practice Recommendations For Contraceptive Use, 2016 MMWRhectorNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument24 pagesResearch ProposalLorraine ZarateNo ratings yet