Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Free Radical Scavenging Activity: 1. Results and Discussion
Free Radical Scavenging Activity: 1. Results and Discussion
Uploaded by
Afrah MOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Free Radical Scavenging Activity: 1. Results and Discussion
Free Radical Scavenging Activity: 1. Results and Discussion
Uploaded by
Afrah MCopyright:
Available Formats
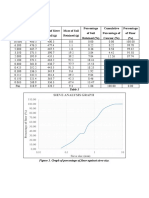
Table 1
Phytochemical screening of plant extract and synthesized nanoparticles.
S. no. Chemical constituents Screening
Plant extract AgNps
1 Alkaloids + –
2 Tannins + +
3 Carbohydrates + +
4 Ascorbic acid + +
5 Proteins + +
Free radical scavenging activity
1 ml of each of different concentrations (100–500 µg
in ethanol) of the synthesized silver nanoparticles and
standard (gallic acid) was added to 2.5 ml of 0.3 mM
DPPH in ethanol solution. The mixture was shaken
vigorously and allowed to stand at room temperature in
dark for 30 min. The absorbance was measured at 517
nm.
1. Results and discussion
When the leaf extract of A. sessilis was mixed with
AgNO3 solu- tion, the pale yellow colour of aqueous
extract changed to brownish colour immediately within
10 min, indicating the formation of sil- ver
nanoparticles (Fig. 1).
Phytochemical screening of A. sessilis leaf extract
shows the presence of alkaloids, tannins, carbohydrates,
proteins, ascorbic acid and synthesized AgNPs shows
the presence of tannins, car- bohydrates, proteins and
ascorbic acid (Table 1). These secondary
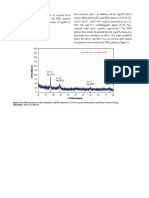
DOI: 10.3109/1040841X.2014.912200 Silver nanoparticles 2
290 K.L. Niraimathi et al. / Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 102 (2013) 288–291
75.00
74.5
74.0
1864.11
2261.41 719.87493.99
3855.98 73.5 2381.972141.92 710.51
3729.72 2369.65 616.68 456.92
3710.08 2343.49
2324.82
3006.13 2300.57
2989.15
73.0
2892.78 1623.04
2855.69 1384.46
72.5
3423.57
%T 2926.69
72.0 1033.37
71.5
71.0
70.5
70.00
4000.0 3000 2000 1500 1000 413.0
cm-1
Fig. 3. FT-IR absorption spectra of bio-moieties with synthesized AgNPs.
You might also like
- 2018 Cambridge Lower Second Progression Test Science Stage 9 QP Paper 1 - tcm143-430411Document16 pages2018 Cambridge Lower Second Progression Test Science Stage 9 QP Paper 1 - tcm143-430411SOFÍA CARO MORENO100% (4)
- (Science) Grade-6-SLM - Q1 - Module - 1A - Lesson1and2 - FINALwithposttestandASDocument28 pages(Science) Grade-6-SLM - Q1 - Module - 1A - Lesson1and2 - FINALwithposttestandASRestie Jade Barlaan100% (3)
- Analytical Chemistry Notes, Problems PDFDocument32 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Notes, Problems PDFKuo Sarong100% (1)
- Encyclopedia of Practical Receipts & Processes by DickrichDocument618 pagesEncyclopedia of Practical Receipts & Processes by DickrichProfessor100% (10)
- Results and Discussion: Free Radical Scavenging ActivityDocument2 pagesResults and Discussion: Free Radical Scavenging ActivityAfrah MNo ratings yet
- HKBK College of EngineeringDocument51 pagesHKBK College of EngineeringkarthikNo ratings yet
- Article On 8TH Sem ProjectDocument46 pagesArticle On 8TH Sem ProjectSHAIK AHMED JAWADNo ratings yet
- Lampiran Glukosa DarahDocument4 pagesLampiran Glukosa DarahefendiNo ratings yet
- Non Electrolyte Solutes From Surface Tension ChangeDocument6 pagesNon Electrolyte Solutes From Surface Tension ChangethikamenituyeniNo ratings yet
- Ms (%) Ed (Kcal/Kg) PC (%) Proteina Animapd (%) FC (%) Ee (%)Document20 pagesMs (%) Ed (Kcal/Kg) PC (%) Proteina Animapd (%) FC (%) Ee (%)JUAN FERNANDO SEGURA CASTRONo ratings yet
- Excel HysysDocument11 pagesExcel HysysAndrie Kurniawan IndraNo ratings yet
- Plan Direccional Re EntryDocument4 pagesPlan Direccional Re EntryMiguel Chavez CocaNo ratings yet
- p2 Reporte Practica 8Document22 pagesp2 Reporte Practica 8LAURA STEFANNY CRUZ OLAYANo ratings yet
- Equity Summary DetailsDocument5 pagesEquity Summary DetailsNadeem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Optimized Conversions Using RSMDocument3 pagesOptimized Conversions Using RSMSudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- Proximate Analysis: DescriptivesDocument10 pagesProximate Analysis: DescriptivesAkpan EkomNo ratings yet
- IRMAWATI 1814241012 NTP (Tugas INTU Nyusun Ransum)Document7 pagesIRMAWATI 1814241012 NTP (Tugas INTU Nyusun Ransum)Ratu Haulah Kholillah YusufNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Components: Appendix GDocument6 pagesPhysical Properties of Components: Appendix GMAIMUNATUN NAWAR MOHD YAZANNo ratings yet
- ) of Pure Sucrose Solutions) of Impure Sucrose Solutions: DS DSDocument23 pages) of Pure Sucrose Solutions) of Impure Sucrose Solutions: DS DSSamuel GermatusNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Sucrose SolutionDocument23 pagesPhysical Properties of Sucrose Solutionbùi tuấn tùngNo ratings yet
- CL351: Chemical Engineering Lab-II Semester 1, 2014-2015 IIT GandhinagarDocument6 pagesCL351: Chemical Engineering Lab-II Semester 1, 2014-2015 IIT GandhinagarPradeep DiwakarNo ratings yet
- Indonusa Yudha Perwita - 1657545381823Document8 pagesIndonusa Yudha Perwita - 1657545381823laboNo ratings yet
- Cernica VerificationDocument5 pagesCernica VerificationlouispriceNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Effi Ciency Vs Overall Pressure RatioDocument2 pagesNozzle Effi Ciency Vs Overall Pressure Ratioyoga satoeNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Cardanol AcetateDocument9 pagesSynthesis of Cardanol AcetateHa LeeNo ratings yet
- Echantillon Nom MK5: Weight of SievesDocument3 pagesEchantillon Nom MK5: Weight of SieveselNo ratings yet
- TEC Testing Sheets - Tracker 100716Document10 pagesTEC Testing Sheets - Tracker 100716pradeepreddycvNo ratings yet
- Bahan Baku (Raw Material Feed)Document6 pagesBahan Baku (Raw Material Feed)MFajar FahmiNo ratings yet
- Match! Phase Analysis Report: Sample: BM-Root PartDocument2 pagesMatch! Phase Analysis Report: Sample: BM-Root PartZead Ali AdalNo ratings yet
- Aditya Surya Pratama 36B - Tugas StatistikDocument22 pagesAditya Surya Pratama 36B - Tugas Statistikaditya surya pratamaNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment With 47.6% Calcium Hypochlorite Pool ShockerDocument4 pagesWater Treatment With 47.6% Calcium Hypochlorite Pool ShockerMyrtle.QuakerNo ratings yet
- Appendix A End BookDocument18 pagesAppendix A End BookAloisio NunesNo ratings yet
- Photos of SetupDocument6 pagesPhotos of SetupJebone Stein Web JuarbalNo ratings yet
- Supporting Information For: Characterization of Crude Oil by Real-Component SurrogatesDocument15 pagesSupporting Information For: Characterization of Crude Oil by Real-Component SurrogatesHarmanNo ratings yet
- Mixit PonedorasDocument48 pagesMixit PonedorasFlores Lopez Alexis HernanNo ratings yet
- Programas de Fertilización Uva 513-514Document4 pagesProgramas de Fertilización Uva 513-514Brahian Carranza PalominoNo ratings yet
- Binary System Thermo DyncamixDocument19 pagesBinary System Thermo DyncamixJohn Fritz FestejoNo ratings yet
- 05 Chapter3 ResultsDocument6 pages05 Chapter3 ResultsEmãd MõĥãmêdNo ratings yet
- Direct ShearDocument1 pageDirect Shearyakob mesheshaNo ratings yet
- 4769 10 LedDocument3 pages4769 10 LedAlejandro Paez DiazNo ratings yet
- Bond Work Index Test Report Example 1Document5 pagesBond Work Index Test Report Example 1alinoriNo ratings yet
- Mencari %mole Methanol UapDocument3 pagesMencari %mole Methanol UapChoiriah EBNo ratings yet
- Echantillon Nom MK8: Weight of SievesDocument3 pagesEchantillon Nom MK8: Weight of SieveselNo ratings yet
- CGT21027 BIDM Individual AssignmentDocument7 pagesCGT21027 BIDM Individual AssignmentBhargav Sri DhavalaNo ratings yet
- Total Mass of Soil 500.2 G: Results and CalculationDocument1 pageTotal Mass of Soil 500.2 G: Results and CalculationMEN CHONG YONGNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document1 pageTutorial 5SHOURYA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Engg.: Kinetic Analysis of EnzymeDocument5 pagesEnzyme Engg.: Kinetic Analysis of Enzymeutk335No ratings yet
- 1 Balance MetalurgicoDocument15 pages1 Balance MetalurgicoMAYERNo ratings yet
- 6MWT Distance Conversion TableDocument2 pages6MWT Distance Conversion TablemirnaNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Assignment Correlation AnalysisDocument14 pagesCost Accounting Assignment Correlation Analysisreagan blaireNo ratings yet
- Isobaric Vapor Liquid Equilibria of The Water 1-Propanol System at 30, 60, and 100 KpaDocument5 pagesIsobaric Vapor Liquid Equilibria of The Water 1-Propanol System at 30, 60, and 100 KpaRafael HenriqueNo ratings yet
- 24 - Phan Khánh Ly - 20070745 Problem 2Document8 pages24 - Phan Khánh Ly - 20070745 Problem 2Khánh LyNo ratings yet
- Conductivity AcidsDocument19 pagesConductivity AcidsLuca PataunerNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0301420723004051 mmc1Document25 pages1 s2.0 S0301420723004051 mmc1gbamhurbainNo ratings yet
- Global Synfuels Case StudyDocument26 pagesGlobal Synfuels Case StudyRuchi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Statistic ADocument9 pagesStatistic ACosmin VoicuNo ratings yet
- Camden Electronics CaseDocument2 pagesCamden Electronics CaseTăng QuânNo ratings yet
- This Is Dumb 2Document3 pagesThis Is Dumb 2Jacob ForscytheNo ratings yet
- Echantillon Nom MK14: Weight of SievesDocument3 pagesEchantillon Nom MK14: Weight of SieveselNo ratings yet
- Dia 1Document24 pagesDia 1Manuel SofmetNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 and SIEVE ANALYSIS TESTDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 3 and SIEVE ANALYSIS TESTSiti Nurulsyazni RusliNo ratings yet
- Advanced Dairy Science and TechnologyFrom EverandAdvanced Dairy Science and TechnologyTrevor BritzNo ratings yet
- 4green SynthesisDocument2 pages4green SynthesisAfrah MNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Aureus (Gram-Posi-Tive) by Disc DiffusionDocument1 pageStaphylococcus Aureus (Gram-Posi-Tive) by Disc DiffusionAfrah MNo ratings yet
- Results and Discussion: Silver Nanoparticles CharacterizationDocument1 pageResults and Discussion: Silver Nanoparticles CharacterizationAfrah MNo ratings yet
- C. Longa Compounds (Figure 7B) .: Physicochem Probl Miner Process. 2010 45:85-98Document2 pagesC. Longa Compounds (Figure 7B) .: Physicochem Probl Miner Process. 2010 45:85-98Afrah MNo ratings yet
- 1department of Medical NanotechnologyDocument2 pages1department of Medical NanotechnologyAfrah MNo ratings yet
- FT-IR Chemical AnalysisDocument1 pageFT-IR Chemical AnalysisAfrah MNo ratings yet
- Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Plant ExtractsDocument2 pagesGreen Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Plant ExtractsAfrah MNo ratings yet
- 1department of Medical NanotechnologyDocument3 pages1department of Medical NanotechnologyAfrah MNo ratings yet
- 1department of Medical NanotechnologyDocument2 pages1department of Medical NanotechnologyAfrah MNo ratings yet
- 4green SynthesisDocument2 pages4green SynthesisAfrah MNo ratings yet
- 5the Bioreduction of The AgDocument2 pages5the Bioreduction of The AgAfrah MNo ratings yet
- Morphology Study: BiosynthesisDocument2 pagesMorphology Study: BiosynthesisAfrah MNo ratings yet
- Conclusion: C. Longa Compounds (Figure 7B)Document2 pagesConclusion: C. Longa Compounds (Figure 7B)Afrah MNo ratings yet
- Figure 6: XRD Pattern of Silver Nanoparticles: Angle (2 )Document2 pagesFigure 6: XRD Pattern of Silver Nanoparticles: Angle (2 )Afrah MNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Ag/C. Longa Emulsion: Extraction PreparationDocument4 pagesSynthesis of Ag/C. Longa Emulsion: Extraction PreparationAfrah MNo ratings yet
- Abstract: Green: Curcuma LongaDocument1 pageAbstract: Green: Curcuma LongaAfrah MNo ratings yet
- 5the Bioreduction of The AgDocument3 pages5the Bioreduction of The AgAfrah MNo ratings yet
- Figure 2: UV-Vis Spectra Recorded As A Function of Reaction Time of Silver NanoparticlesDocument1 pageFigure 2: UV-Vis Spectra Recorded As A Function of Reaction Time of Silver NanoparticlesAfrah MNo ratings yet
- 2 ChengDocument2 pages2 ChengAfrah MNo ratings yet
- 5the Bioreduction of The AgDocument2 pages5the Bioreduction of The AgAfrah MNo ratings yet
- 3physical ApproachesDocument3 pages3physical ApproachesAfrah MNo ratings yet
- Geissus Latifolia) and Its Biological Activity. Org Med Chem LettDocument1 pageGeissus Latifolia) and Its Biological Activity. Org Med Chem LettAfrah MNo ratings yet
- Polygonum Glabrum Willd. Leaf Extract Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Assessment of Antimicrobial ActivityDocument1 pagePolygonum Glabrum Willd. Leaf Extract Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Assessment of Antimicrobial ActivityAfrah MNo ratings yet
- 1department of Medical NanotechnologyDocument1 page1department of Medical NanotechnologyAfrah MNo ratings yet
- Caulerpa Racemosa Var. Cylin-Dracea. J Hazard MaterDocument3 pagesCaulerpa Racemosa Var. Cylin-Dracea. J Hazard MaterAfrah MNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Activity 2Document8 pagesChemistry Activity 2Nemalnath reddy KasarapuNo ratings yet
- Barium Chloride 2h2o LRG MsdsDocument3 pagesBarium Chloride 2h2o LRG MsdsAnas GiselNo ratings yet
- Typical Conversion of Lignocellulosic Biomass Into Reducing Sugars Using Dilute Acid Hydrolysis and Alkaline PretreatmentDocument30 pagesTypical Conversion of Lignocellulosic Biomass Into Reducing Sugars Using Dilute Acid Hydrolysis and Alkaline PretreatmentSagar DhuriNo ratings yet
- Nghi SơnDocument33 pagesNghi Sơnminh nguyenNo ratings yet
- Bio-Fuel PosterDocument1 pageBio-Fuel PosterElyssa Michelle Caringas MicuaNo ratings yet
- L7 - BRG - Sources and Types of Air PollutantsDocument53 pagesL7 - BRG - Sources and Types of Air PollutantsIV YEAR CIVILNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument66 pagesChemical EquilibriumalinNo ratings yet
- Construction Chemicals and AdditivesDocument39 pagesConstruction Chemicals and Additivesdharshini deivasigamani100% (2)
- Valency: Combining Power of AtomsDocument56 pagesValency: Combining Power of AtomsDaniel PalmerNo ratings yet
- Casquillos INADocument55 pagesCasquillos INAFrancisco PalomeroNo ratings yet
- Pcs Puls Controlled Spray Arc enDocument22 pagesPcs Puls Controlled Spray Arc enTh NattapongNo ratings yet
- Chemical ApplicationsDocument4 pagesChemical ApplicationsBinit DuttNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document9 pagesExperiment 1Anonymous Osp8BbYEyNo ratings yet
- Wfra - Me: PBR To RepulsionDocument24 pagesWfra - Me: PBR To RepulsionShreyas PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Calcium Nitrate BrochureDocument3 pagesCalcium Nitrate BrochuremanojbanNo ratings yet
- Dye - Classification of Dye According To ApplicationDocument3 pagesDye - Classification of Dye According To ApplicationIrfan AliNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chemistry in Everyday Life Questions Answers PDFDocument14 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chemistry in Everyday Life Questions Answers PDFPraveen Malik100% (1)
- Electrochemical Properties of The Platinum Metals: by M. Muylder N. deDocument7 pagesElectrochemical Properties of The Platinum Metals: by M. Muylder N. deLeopoldo CZNo ratings yet
- Barauni Refinery Unit CapacitiesDocument8 pagesBarauni Refinery Unit Capacitiesrishika sharmaNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen NotesDocument37 pagesHydrogen NotesPrakharNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1 - TQDocument12 pagesGen Chem 1 - TQBlack WhiteNo ratings yet
- Gaseous FuelDocument20 pagesGaseous FuelCaguioa Mark Anthony G.100% (3)
- Li2014 ReviewDocument30 pagesLi2014 ReviewPablo Romo ValdesNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 6Document148 pagesEdexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 6AbdulRahman MustafaNo ratings yet
- Oral Osmotic Drug Delivery System: An UpdateDocument12 pagesOral Osmotic Drug Delivery System: An Updatelaurik1315No ratings yet
- Forging PDF NotesDocument51 pagesForging PDF Notesaman prasadNo ratings yet