Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reading Plan 1. Identifying Cognates 2. Global Reading 3. Glossary 4. Doing A Synoptic Table What Is MRSA?
Reading Plan 1. Identifying Cognates 2. Global Reading 3. Glossary 4. Doing A Synoptic Table What Is MRSA?
Uploaded by
Cami Piña Espinoza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views5 pagesOriginal Title
what is mrsa
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views5 pagesReading Plan 1. Identifying Cognates 2. Global Reading 3. Glossary 4. Doing A Synoptic Table What Is MRSA?
Reading Plan 1. Identifying Cognates 2. Global Reading 3. Glossary 4. Doing A Synoptic Table What Is MRSA?
Uploaded by
Cami Piña EspinozaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
ENGLISH II FOR NURSING MAY 28 -20
Reading plan
1. Identifying cognates
2. Global reading
3. Glossary
4. Doing a synoptic table
What Is MRSA?
Recovered from: WEB MED https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/understanding-mrsa#2
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a bacterium that causes infections
in different parts of the body. It's tougher to treat than most strains of staphylococcus
aureus -- or staph -- because it's resistant to some commonly used antibiotics.
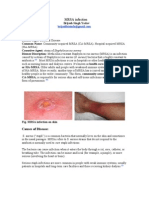
The symptoms of MRSA depend on where you're infected. Most often, it causes mild
infections on the skin, like sores, boils, or abscesses. But it can also cause more serious skin
infections or infect surgical wounds, the bloodstream, the lungs, or the urinary tract.
Though most MRSA infections aren't serious, some can be life-threatening. Many public
health experts are alarmed by the spread of tough strains of MRSA. Because it's hard to
treat, MRSA is sometimes called a "super bug."
What Causes MRSA?
Garden-variety staph are common bacterium that can live in our bodies. Plenty of healthy
people carry staph without being infected by it. In fact, one third of everybody has staph
bacteria in their noses.
CONTINUE READING BELOW
But staph can be a problem if it manages to get into the body, often through a cut. Once
there, it can cause an infection. Staph is one of the most common causes of skin infections
in the U.S. Usually, these are minor and don't need special treatment. Less often, staph can
cause serious problems like infected wounds or pneumonia.
Staph can usually be treated with antibiotics. But over the decades, some strains of staph --
like MRSA -- have become resistant to antibiotics that once destroyed it. MRSA was first
discovered in 1961. It's now resistant to methicillin, amoxicillin, penicillin, oxacillin, and
other common antibiotics known as cephalosporins.
While some antibiotics still work, MRSA is constantly adapting. Researchers developing
new antibiotics are having a tough time keeping up.
Who Gets MRSA?
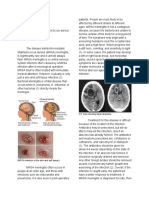
MRSA is spread by contact. So, you could get MRSA by touching another person who has
it on the skin. Or you could get it by touching objects that have the bacteria on them.
MRSA is carried by about 2% of the population (or 2 in 100 people), although most of
them aren't infected.
There are two different populations of people who get MRSA -- one is in decline -- those
who get it in hospitals or other health care environments -- and the other is on the rise --
those who get it in the community. MRSA infections are common among people who have
weak immune systems who are in hospitals, nursing homes, and other health care centers.
Infections can appear around surgical wounds or invasive devices, like catheters or
implanted feeding tubes. According to the CDC, invasive MRSA infections that began in
hospitals declined 8% between 2011 and 2013.
Community-Associated MRSA
MRSA skin infections have been identified among certain populations that share close
quarters or have more skin-to-skin contact. Examples are team athletes, military recruits,
prison inmates, and children in daycare. But more and more CA-MRSA infections are
being seen in the general community, especially in certain geographic regions. MRSA is
also more likely to affect younger people. In a study of Minnesotans published in
TheJournal of the American Medical Association, the average age of people with MRSA in
a hospital or health care facility was 68. But the average age of a person with CA-MRSA
was only 23.
READING PLAN STUDENTS:
1. Identify cognados
Monica Valentina Ruiz Villada 100150302018
Methicillin
María Camila Piña Espinosa 100150632018
bacterium
infections
antibiotics
symptoms
infected
bacteria
treatment
treated
antibiotics
resistant
methicillin
amoxicillin
penicillin
oxacillin
person
hospitals
athletes
military
geographic
2. Global reading
3. Glossary
Strains: Cepas
Sores: llagas
Boils: forúnculos
Abscesses: abscesos
Wounds: heridas
Bloodstream: torrente sangíneo
Staph: estafilococo
4. Doing a synoptic table
Es resistente a algunos
antibióticos de uso común.
Causa infecciones leves en la piel,
como llagas, forúnculos o
abscesos.
El MRSA es una bacteria
Causa infecciones graves
que causa infecciones en
de la piel.
diferentes partes del
cuerpo. La mayoría de las infecciones por
MRSA infecta las heridas MRSA no son graves, algunas
quirúrgicas, el torrente pueden ser potencialmente
sanguíneo, los pulmones o mortales
el tracto urinario.
Las personas sanas portan MRSA fue descubierto por primera
estafilococos sin ser vez en 1961
infectados por esta.
El estafilococo es una Si el estafilococo ingresa al MRSA se ha vuelto resistente a
MRSA cuerpo, puede causar una los antibióticos que una vez lo
bacteria que causa serios
Staphylococcus aureus problemas si es contacto infección. destruyeron.
meticilino resistente con el cuerpo
Puede causar problemas Ahora es resistente a la meticilina,
graves como heridas amoxicilina, penicilina, oxacilina y
infectadas o neumonía. otros antibióticos conocidos como
cefalosporinas.
MRSA es transportado por
aproximadamente el 2% de Las infecciones por MRSA son
la población comunes entre las personas que
tienen un sistema inmunitario débil.
El MRSA se transmite por
Las personas que se MRSA también es más
contacto con una persona u
encuentran en hospitales, probable que afecte a personas
objeto con él.
entornos de atención médica más jóvenes
o en la comunidad contraen
Pueden aparecer infecciones
MRSA
alrededor de heridas quirúrgicas
o dispositivos invasivos.
You might also like
- Gregory Lessing Garrett - Stand or Fall in The COVID 19 Chess GameDocument122 pagesGregory Lessing Garrett - Stand or Fall in The COVID 19 Chess Gamedjv1985100% (3)
- MrsaDocument13 pagesMrsaSadia AkramNo ratings yet
- Pantosti 2009Document7 pagesPantosti 2009phamnguyenthaovy3101No ratings yet
- Bio Holiday HWDocument12 pagesBio Holiday HWAalif AzaNo ratings yet
- MrsaDocument10 pagesMrsaNurul FaizaahNo ratings yet
- MRSA Treasure Hunt WorksheetDocument2 pagesMRSA Treasure Hunt WorksheetNicole SanchezNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Infection (MRSA Infection)Document8 pagesBacterial Infection (MRSA Infection)Brijesh Singh Yadav100% (1)
- How MRSA Works: Bacterium RocketsDocument4 pagesHow MRSA Works: Bacterium RocketsElmerDolendoTorrevillaNo ratings yet
- Colloidal Silver Cures MRSA ReportDocument16 pagesColloidal Silver Cures MRSA ReportGodwinNo ratings yet
- MRSA FinalDocument4 pagesMRSA FinalApril DawnNo ratings yet
- Document About MRSA and DangersDocument6 pagesDocument About MRSA and DangersAcidViperNo ratings yet
- Ca-Mrsa 2Document7 pagesCa-Mrsa 2zakariakeli41No ratings yet
- Disease ReportDocument2 pagesDisease Reportapi-511364141No ratings yet
- Acquired Hospital: InfectionDocument3 pagesAcquired Hospital: Infectionnayem hossainNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease Research MRSADocument2 pagesInfectious Disease Research MRSAKiyo TanNo ratings yet
- Mrsa 2Document7 pagesMrsa 2Ach Ri Fa INo ratings yet
- Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: (MRSA)Document13 pagesMethicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: (MRSA)Adnan JourdanNo ratings yet
- Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) in The Intensive Care UnitDocument8 pagesMethicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) in The Intensive Care UnitMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- MRSA InfectionDocument5 pagesMRSA InfectionHoàng Kiều OanhNo ratings yet
- Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: Signs and SymptomsDocument6 pagesMethicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: Signs and SymptomssujithasNo ratings yet
- MRSA InfectionsDocument32 pagesMRSA InfectionsJenita Magdalena100% (1)
- Empiric Antibiotics For Acute Infections of The HaDocument4 pagesEmpiric Antibiotics For Acute Infections of The HaBrea WilleyNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Aureus Is The Most Common Cause of Skin and Soft-TissueDocument5 pagesStaphylococcus Aureus Is The Most Common Cause of Skin and Soft-Tissuemina .18No ratings yet
- Are You and Your Patients in Safe HandsDocument8 pagesAre You and Your Patients in Safe Handsanis merahNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationDocument10 pagesNew Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationfeldiyannaNo ratings yet
- Mrsa PP Microsoft PP PPT Final Without NCPDocument32 pagesMrsa PP Microsoft PP PPT Final Without NCPapi-355433171No ratings yet
- Cellular Microbiology - 2012 - Otto - MRSA Virulence and SpreadDocument9 pagesCellular Microbiology - 2012 - Otto - MRSA Virulence and Spreadkamelia yolandaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Superbugs CRKPDocument2 pagesAntibiotic Superbugs CRKPRizwan RasheedNo ratings yet
- Skin and Soft-Tissue Infections Caused by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus AureusDocument11 pagesSkin and Soft-Tissue Infections Caused by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus AureusFerdy RamadhanNo ratings yet
- MRSA Brochure Simple EnglishDocument2 pagesMRSA Brochure Simple EnglishYS NateNo ratings yet
- Products & Services: Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th EditionDocument3 pagesProducts & Services: Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th EditionTati MaryatiNo ratings yet
- What Is A Superbug?: Example: MRSADocument1 pageWhat Is A Superbug?: Example: MRSARandom ExplorerNo ratings yet
- Methicillin Resistant (MRSA) : Staphylococcus AureusDocument2 pagesMethicillin Resistant (MRSA) : Staphylococcus AureusdanielaNo ratings yet
- Ijms 24 08182Document3 pagesIjms 24 08182safna mariyamNo ratings yet
- KanafaniDocument13 pagesKanafaniJon SaifuNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin Resistance in Staphylococcus: AureusDocument13 pagesVancomycin Resistance in Staphylococcus: AureusFernando Martínez HiguerasNo ratings yet
- HW Mrsa 4Document2 pagesHW Mrsa 4Anonymous lm3GIU450% (4)
- MSSA Information FactsheetDocument2 pagesMSSA Information FactsheetAlinaNo ratings yet
- General Information About MRSADocument4 pagesGeneral Information About MRSATati MaryatiNo ratings yet
- MrsaDocument1 pageMrsaSmadu AdrianaNo ratings yet
- Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms (Mdros) in Healthcare FacilitiesDocument57 pagesMulti-Drug Resistant Organisms (Mdros) in Healthcare Facilitiesasma .sassiNo ratings yet
- Drug Resistance and Antibiotic PoliciesDocument13 pagesDrug Resistance and Antibiotic PoliciesChinky GalNo ratings yet
- Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) in Developing and Developed Countries: Implications and SolutionsDocument9 pagesMethicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) in Developing and Developed Countries: Implications and SolutionsfebyNo ratings yet
- MDROsDocument94 pagesMDROsRAHULNo ratings yet
- MRSA Special ReportDocument7 pagesMRSA Special ReportFisnik I. MahmutiNo ratings yet
- Methicillinresistant Staphylococcus Aureus A Mini ReviewDocument6 pagesMethicillinresistant Staphylococcus Aureus A Mini ReviewSandhi WiryaNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Aureus Is The Most Common Cause of Skin and Soft-TissueDocument2 pagesStaphylococcus Aureus Is The Most Common Cause of Skin and Soft-Tissuemina .18No ratings yet
- Screening For MRSA by Dr.T.V.Rao MDDocument30 pagesScreening For MRSA by Dr.T.V.Rao MDtummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease PaperDocument4 pagesCommunicable Disease PaperCorrine BlucherNo ratings yet
- BUGS TO SUPER BUGS Emerging Challenges in Health CareDocument2 pagesBUGS TO SUPER BUGS Emerging Challenges in Health Caretummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Current Concepts On The Virulence Mechanisms of Meticillin-Resistant Staphylococcus AureusDocument15 pagesCurrent Concepts On The Virulence Mechanisms of Meticillin-Resistant Staphylococcus AureusSeptiani HasibuanNo ratings yet
- PH ArticleDocument2 pagesPH ArticlepriyankaNo ratings yet
- Ëv Ëv Ëv ËvDocument9 pagesËv Ëv Ëv ËvtacolianaNo ratings yet
- MRSADocument6 pagesMRSAKimberly Clarisse VegaNo ratings yet
- Mrsa 3Document12 pagesMrsa 3Ach Ri Fa INo ratings yet
- Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Tuberculosis: Part 1: Aureus and Multidrug ResistantDocument3 pagesMethicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Tuberculosis: Part 1: Aureus and Multidrug ResistantSukma EffendyNo ratings yet
- 3 - Acute InfectionsDocument44 pages3 - Acute InfectionsAlexa GabrielaNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Hospital Environment in The Healthcare-Associated Infections: A General Review of The LiteratureDocument13 pagesThe Role of The Hospital Environment in The Healthcare-Associated Infections: A General Review of The LiteratureMimi ElagoriNo ratings yet
- Viral Vistas: Insights into Infectious Diseases: The Invisible War: Decoding the Game of Hide and Seek with PathogensFrom EverandViral Vistas: Insights into Infectious Diseases: The Invisible War: Decoding the Game of Hide and Seek with PathogensNo ratings yet
- Historical Profile of Harold G WolffDocument2 pagesHistorical Profile of Harold G WolffBarry BrantonNo ratings yet
- Legal and Ethical Aspects of Critical Care NursingDocument66 pagesLegal and Ethical Aspects of Critical Care NursingJamille Abenir Lopez100% (2)
- Safe and Clean Environment in Hospital 237640255Document38 pagesSafe and Clean Environment in Hospital 237640255Akanksha SinghNo ratings yet
- Client Intake Form: Date Patient Last: First Initial Address City Zip Date of Birth Phone CellDocument6 pagesClient Intake Form: Date Patient Last: First Initial Address City Zip Date of Birth Phone Celljayson_tamayo2No ratings yet
- Cervical Spine Surgery: Arthroplasty Versus Fusion Versus Posterior ForaminotomyDocument10 pagesCervical Spine Surgery: Arthroplasty Versus Fusion Versus Posterior ForaminotomyKyle RobinNo ratings yet
- 418-M3-Cu14 Nursing Care of Clients in Emergency Situations 1 - AbcsDocument9 pages418-M3-Cu14 Nursing Care of Clients in Emergency Situations 1 - AbcsDanica FrancoNo ratings yet
- Untitled DesignDocument10 pagesUntitled DesignPAKK 0617 Lim Pei PeiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory NCLEX Practice Test Part 1: Guillain-Barré SyndromeDocument20 pagesRespiratory NCLEX Practice Test Part 1: Guillain-Barré SyndromeHasan A AsFour100% (2)
- First Aid For Mental Health - Tutor NotesDocument41 pagesFirst Aid For Mental Health - Tutor NotesJASON SANDERS100% (2)
- Cannabidiol CBD - What We Know and What We Don't Harvard Health Blog Harvard Health PublishingDocument9 pagesCannabidiol CBD - What We Know and What We Don't Harvard Health Blog Harvard Health PublishingSantosNo ratings yet
- Vulstan James Shedura-Curriculum Vitae (CV)Document14 pagesVulstan James Shedura-Curriculum Vitae (CV)Vulstan James SheduraNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in MycologyDocument1 pageBasic Concepts in MycologyAngeloMartinNo ratings yet
- REFERENCESDocument2 pagesREFERENCESFarrenheit IsidroNo ratings yet
- CHNDocument6 pagesCHNJilkiah Mae Alfoja Campomanes100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan DiarrheaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan DiarrheaCzarina AeriNo ratings yet
- Father Saturnino Urios College of Sibagat IncDocument10 pagesFather Saturnino Urios College of Sibagat IncJenny Mar CañedaNo ratings yet
- Distribusi Gingivitis Pada Pasien SkizofreniaDocument6 pagesDistribusi Gingivitis Pada Pasien SkizofreniafaniaNo ratings yet
- Policy On HIVAIDS EthiopiaDocument11 pagesPolicy On HIVAIDS EthiopiaSabir Imam100% (1)
- Clinical Outcomes Comparing Two Prosthetic Knee Designs in Individuals With Unilateral Transfemoral Amputation in TurkeyDocument8 pagesClinical Outcomes Comparing Two Prosthetic Knee Designs in Individuals With Unilateral Transfemoral Amputation in TurkeyAlexandru Codrin-IonutNo ratings yet
- Sterile TechDocument85 pagesSterile TechBSN II - Tutor, Rel joshuaNo ratings yet
- DPMU Module PDFDocument315 pagesDPMU Module PDFkeyspNo ratings yet
- Health Statistics and Epidemiology QuestionsDocument2 pagesHealth Statistics and Epidemiology QuestionsCorinneNo ratings yet
- Antithyroid DrugsDocument46 pagesAntithyroid Drugsalhsnym820No ratings yet
- Describe What It Feel Like Living in Kolkata Streets ?Document1 pageDescribe What It Feel Like Living in Kolkata Streets ?madiha katniNo ratings yet
- Systemic Pediatrics: DR Sidharth Sethi MD, Fasn, FiapDocument33 pagesSystemic Pediatrics: DR Sidharth Sethi MD, Fasn, FiapAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Weicheng XuDocument10 pagesWeicheng Xumuhammad hamdanNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Allocation LetterDocument2 pagesVaccine Allocation LetterNEWS CENTER MaineNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Safety in Cemeteries - Andre Van Den BergDocument45 pagesSustainable Safety in Cemeteries - Andre Van Den BergMackoy MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Chang2015 - Effects of An Intervention With Drinking Chamomile Tea On Sleep Quality and DepressionDocument10 pagesChang2015 - Effects of An Intervention With Drinking Chamomile Tea On Sleep Quality and DepressionVinicius LayatteNo ratings yet