Professional Documents
Culture Documents
I. History of Grammar
I. History of Grammar
Uploaded by
Isse Nvrro0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesThe document discusses the history and definitions of grammar. It covers how grammar evolved in the 17th and 19th centuries and how it is defined as the underlying rules of a language. It also defines syntax as the arrangement of words in a sentence. The document then discusses descriptive versus prescriptive grammarians and influential authors on the topic of grammar, style, and word choice. It provides examples of influential musicians, writers, and their approaches to language and expression. Finally, it discusses writing at the word level and choosing words carefully considering denotation and connotation as well as figures of speech.
Original Description:
Original Title
notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the history and definitions of grammar. It covers how grammar evolved in the 17th and 19th centuries and how it is defined as the underlying rules of a language. It also defines syntax as the arrangement of words in a sentence. The document then discusses descriptive versus prescriptive grammarians and influential authors on the topic of grammar, style, and word choice. It provides examples of influential musicians, writers, and their approaches to language and expression. Finally, it discusses writing at the word level and choosing words carefully considering denotation and connotation as well as figures of speech.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesI. History of Grammar
I. History of Grammar
Uploaded by
Isse NvrroThe document discusses the history and definitions of grammar. It covers how grammar evolved in the 17th and 19th centuries and how it is defined as the underlying rules of a language. It also defines syntax as the arrangement of words in a sentence. The document then discusses descriptive versus prescriptive grammarians and influential authors on the topic of grammar, style, and word choice. It provides examples of influential musicians, writers, and their approaches to language and expression. Finally, it discusses writing at the word level and choosing words carefully considering denotation and connotation as well as figures of speech.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
I.
HISTORY OF GRAMMAR
17th century - narrowing of grammar; rules of language
19th century - words went their separate ways
II. DEFINITIONS
Grammar is the underlying system of rules of a language. Is the art of words (by Prof.
D’Agostino)
Syntax is the arrangement and inter-relations among words in a sentence; structure of a
sentence.
“Ya gotta know all the rules and structures inside out before you start to break them —
and make truly great music.” - Charles Mingus, jazz musician
Lingua franca - language used all over the world; it’s english
Grammarians Two Types:
Descriptivist - how people use language
Prescriptivist - how people ought to use language
Prof. Geoffrey Pullum - authority in grammar
“How do I know what I think until I’ve seen what I’ve said?” - E. M. Forster, novelist
The Elements of Style by Strunk and White (book)
. "Vigorous writing is concise. A sentence should contain no unnecessary words,
paragraph no unnecessary sentences, for the same reason that a drawing should
have no unnecessary lines and a machine no unnecessary parts. This requires not
that the writer make all his sentences short, or that he avoid all detail and treat his
subjects only in outline, but that he make every word tell."
.
. “Prose is architecture, not interior decoration” - Ernest Hemingway
.
. Hank Williams - singer/songwriter with good lyrics
. Henry James - writer with simple proses
. Bob Dylan
. Allen Ginsberg
. Walt Whitman
.
. Wayne words - Australian expressions not pronounced correctly
. Strine words - also Australian expressions
.
. le mot juste - French for “exact word” or “right word”
.
. III. WRITING AT THE WORD LEVEL
.
. Fun facts about not so “new” words:
. Selfie - 20 yrs ago in Australia
. Twerking - 20 yrs ago in New Orleans
. OMG - Winston Churchill in 1917
. Unfriend - 1659
.
. Terms:
. Voice - how you talk to the reader
. Tone - effect of your message to the reader
.
. Word Choice:
. a. Choose words carefully
. b. Understand the diff between denotation and connotation
. c. Acquire a rich and ample vocabulary
. d. Use figures of speech such as metaphors and similes
. e. Be aware of the pros and cons of adjectives and adverbs
.
. Avoid these fillers:
. You know
. Like
. Actually
.
.
.
.
You might also like
- SPA RefundDocument1 pageSPA RefundIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- Practical English 1000 Most Effective Words PDFDocument353 pagesPractical English 1000 Most Effective Words PDFJojo Leaon100% (1)
- Group DisscussionDocument4 pagesGroup Disscussionapi-273361600No ratings yet
- LibelDocument2 pagesLibelIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- How To Write With StyleDocument3 pagesHow To Write With StyleIsraelM.PérezNo ratings yet
- Curme: Syntax (1931)Document634 pagesCurme: Syntax (1931)mhc032105636100% (4)
- Gandhi Practice Document This Presentation About Essay Composition College Board RubricDocument3 pagesGandhi Practice Document This Presentation About Essay Composition College Board RubricMandila BudhathokiNo ratings yet
- The Lexicographer's Dilemma: The Evolution of 'Proper' English, from Shakespeare to South ParkFrom EverandThe Lexicographer's Dilemma: The Evolution of 'Proper' English, from Shakespeare to South ParkRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (118)
- 003085041XGrammarStyle PDFDocument290 pages003085041XGrammarStyle PDFVasanthakumar BasavaNo ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument2 pagesAnalysisАлинаNo ratings yet
- Classic Essays On English Prose StyleDocument4 pagesClassic Essays On English Prose StyleIndie BotNo ratings yet
- Traduccion ApuntesDocument22 pagesTraduccion ApuntesAroa Molina LicerasNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Introduction To PoetryDocument17 pagesUnit 1 - Introduction To PoetryAlba Bultó MartíNo ratings yet
- Ru Writing StyleDocument9 pagesRu Writing Stylesomnath76No ratings yet
- StylisticsDocument36 pagesStylisticsliza larinaNo ratings yet
- Shakespeare 2Document3 pagesShakespeare 2Vanessa Bastardo ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Dirty Silence Bill ManhireDocument20 pagesDirty Silence Bill ManhireClare Marcie WilsonNo ratings yet
- Module 3. Modern English PeriodDocument35 pagesModule 3. Modern English PeriodGrigoryNo ratings yet
- How To Become A Good Reader F 08Document3 pagesHow To Become A Good Reader F 08Dee JuzzNo ratings yet
- Roubo OneDocument248 pagesRoubo Onekmarius7100% (2)
- ReviewerDocument13 pagesReviewerAimahr LopezNo ratings yet
- How To Write With StyleDocument5 pagesHow To Write With StyleNoel DallowNo ratings yet
- A Reader in Nineteenth Century Historical Indo-European LinguisticsDocument8 pagesA Reader in Nineteenth Century Historical Indo-European LinguisticsRodol FenixNo ratings yet
- English for Lovers of English: Comments on English Usage for Advanced LearnersFrom EverandEnglish for Lovers of English: Comments on English Usage for Advanced LearnersNo ratings yet
- Summers - Handbook of The Chinese Language (1863)Document428 pagesSummers - Handbook of The Chinese Language (1863)Bertran2100% (1)
- The Esperanto Teacher: A Simple Course For Non-GrammariansDocument148 pagesThe Esperanto Teacher: A Simple Course For Non-Grammariansnorbulinuks100% (1)
- Vonnegut How Towrite With StyleDocument2 pagesVonnegut How Towrite With Styleapi-216459204No ratings yet
- English Poetry For Advanced Level-For Adv Agustus - 2023-January-2024 - Copy (Autosaved) - AcDocument51 pagesEnglish Poetry For Advanced Level-For Adv Agustus - 2023-January-2024 - Copy (Autosaved) - Acfikri zulNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument81 pagesPreviewpdfa.elghachi0204No ratings yet
- The Impact of Shakespeare On The English Language - English ProjectDocument4 pagesThe Impact of Shakespeare On The English Language - English ProjectNatalia RangelNo ratings yet
- Meeting 3 - DictionDocument5 pagesMeeting 3 - DictionGitarevzanii22No ratings yet
- A Semantic Analysis of Nicki Minaj'S Lyrics: A Partial Fulfillment For The Requirement in ENG104 (English Semantics)Document35 pagesA Semantic Analysis of Nicki Minaj'S Lyrics: A Partial Fulfillment For The Requirement in ENG104 (English Semantics)Arleen ColacionNo ratings yet
- File Goc 776127Document240 pagesFile Goc 776127Alexandru Ionut ApostuNo ratings yet
- Unit IntroDocument5 pagesUnit IntroRania AbunijailaNo ratings yet
- Uts Stylistics Arsad-DikonversiDocument2 pagesUts Stylistics Arsad-DikonversiM ArsadNo ratings yet
- Voice in Literature and Creative Writing: A Resource For Teaching A-Level EnglishDocument19 pagesVoice in Literature and Creative Writing: A Resource For Teaching A-Level EnglishM. WilminkNo ratings yet
- Age of JohnsonDocument5 pagesAge of JohnsonJoan Margaret GasatanNo ratings yet
- Esperanto TeacherDocument89 pagesEsperanto TeachereiHossaNo ratings yet
- Interesting Facts of English LanguageDocument3 pagesInteresting Facts of English LanguageeskaysinghNo ratings yet
- Fryerheletext 05 Esptr 10Document89 pagesFryerheletext 05 Esptr 10doncelladelalunanegraNo ratings yet
- Phil Lit Lesson 3 POETRYDocument23 pagesPhil Lit Lesson 3 POETRYKristine RetretaNo ratings yet
- Early Modern English (1500-1700)Document20 pagesEarly Modern English (1500-1700)EwelinaNo ratings yet
- Sign Talk: A Universal Signal Code, Without Apparatus, for Use in the Army, the Navy, Camping, Hunting, and Daily LifeFrom EverandSign Talk: A Universal Signal Code, Without Apparatus, for Use in the Army, the Navy, Camping, Hunting, and Daily LifeNo ratings yet
- Rereading Past WritDocument4 pagesRereading Past WritJoy MontecalvoNo ratings yet
- Writing Scholarly Paper 2018Document59 pagesWriting Scholarly Paper 2018Mario OrtizNo ratings yet
- Practical Task Seminar 5Document7 pagesPractical Task Seminar 5VLAD DRAKULANo ratings yet
- Fun With English by Mikie MetricDocument9 pagesFun With English by Mikie MetricSusila PonnusamyNo ratings yet
- Modern English PresentationDocument18 pagesModern English PresentationSeñor GarbanzoNo ratings yet
- The History of LinguisticsDocument4 pagesThe History of LinguisticsShakar AbdulrahmmanNo ratings yet
- Eng 113 Reviewer For FinalsDocument6 pagesEng 113 Reviewer For FinalsFashiel JuguilonNo ratings yet
- Linguistics Iii: PhonologyDocument10 pagesLinguistics Iii: PhonologyLorenzo VaezNo ratings yet
- Standard Rules - Chapter 16Document1 pageStandard Rules - Chapter 16Nastja VogrincNo ratings yet
- Non-Standard English in WritingDocument3 pagesNon-Standard English in WritingBianca BreșugNo ratings yet
- SyntaxDocument640 pagesSyntaxmartin100% (1)
- A Critical Study of The Essays of Sri Aurobindo GhoshDocument205 pagesA Critical Study of The Essays of Sri Aurobindo Ghoshketan kathane100% (1)
- Shakespeare Age and LanguageDocument8 pagesShakespeare Age and LanguageJoody nananaNo ratings yet
- Borrowings in The English Language - Angela GochevskaDocument7 pagesBorrowings in The English Language - Angela GochevskaGocevska AngelaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Grammar in Early Modern English 1Document4 pagesLesson 7 Grammar in Early Modern English 1YahanieNo ratings yet
- Bertin - Abridged Grammars of The Languages of The Cuneiform Inscriptions (1888)Document138 pagesBertin - Abridged Grammars of The Languages of The Cuneiform Inscriptions (1888)ffphilNo ratings yet
- SPA To Be ApostilledDocument1 pageSPA To Be ApostilledIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- Manifestation and Compliance To OrderDocument2 pagesManifestation and Compliance To OrderIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- Manifestation and Motion For Issuance of Alias SummonsDocument2 pagesManifestation and Motion For Issuance of Alias SummonsIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- Cover For Appellants BriefDocument2 pagesCover For Appellants BriefIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- Cover-Appellee's Brief-PapelleroDocument3 pagesCover-Appellee's Brief-PapelleroIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- ABSCBN Vs ComelecDocument7 pagesABSCBN Vs ComelecIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- Cover-Appellants Brief-Sps NavarroDocument3 pagesCover-Appellants Brief-Sps NavarroIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- State Health OrganizationsDocument10 pagesState Health OrganizationsIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- Epic UGM 2023Document2 pagesEpic UGM 2023Isse NvrroNo ratings yet
- Cybercrime Prevention Act of 2012Document6 pagesCybercrime Prevention Act of 2012Isse NvrroNo ratings yet
- FALSE CAUSE - Is An Argument That Treats As The Cause of A Thing Something That IsDocument2 pagesFALSE CAUSE - Is An Argument That Treats As The Cause of A Thing Something That IsIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
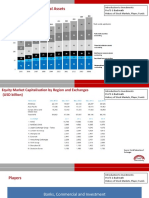
- Asset-V1 IIMBx+FC250x+1T2016+type@asset+block@History of Stock Markets Players Funds HandoutDocument5 pagesAsset-V1 IIMBx+FC250x+1T2016+type@asset+block@History of Stock Markets Players Funds HandoutIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- Estafa JurisprudenceDocument1 pageEstafa JurisprudenceIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- Types of OrdersDocument3 pagesTypes of OrdersIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- Rates of ReturnDocument6 pagesRates of ReturnIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- Asset-V1 IIMBx+FC250x+1T2016+Type@Asset+Block@Real Versus Financial Asset HandoutDocument2 pagesAsset-V1 IIMBx+FC250x+1T2016+Type@Asset+Block@Real Versus Financial Asset HandoutIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysts: Introduction To Investments Prof S G Badrinath Financial AnalystsDocument3 pagesFinancial Analysts: Introduction To Investments Prof S G Badrinath Financial AnalystsIsse Nvrro0% (1)
- Mesuring Expected Returns, Discussing RiskDocument4 pagesMesuring Expected Returns, Discussing RiskIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- I. Understanding Real and Financial Assets: Ii. History of Stock Markets, Players, FundsDocument6 pagesI. Understanding Real and Financial Assets: Ii. History of Stock Markets, Players, FundsIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- Ruth D. Bautista v. CA, Office of The RSP, Region IV, Susan Aloña, GR No. 143375, July 6, 2001Document5 pagesRuth D. Bautista v. CA, Office of The RSP, Region IV, Susan Aloña, GR No. 143375, July 6, 2001Isse NvrroNo ratings yet
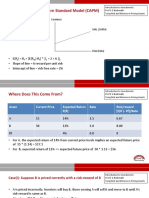
- Risk and Expected Return Standard Model (CAPM)Document6 pagesRisk and Expected Return Standard Model (CAPM)Isse NvrroNo ratings yet
- 2017 Constitutional Law Notes - JudgeSingco 2 PDFDocument158 pages2017 Constitutional Law Notes - JudgeSingco 2 PDFIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- I. Flowchart To Preparing, Delivering, Evaluating SpeechesDocument3 pagesI. Flowchart To Preparing, Delivering, Evaluating SpeechesIsse NvrroNo ratings yet
- LABIAL (Motion To Set Case Hearing Via Video Conference)Document2 pagesLABIAL (Motion To Set Case Hearing Via Video Conference)Isse NvrroNo ratings yet