Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acids Bases and Salts Igcse Only Complete 2014 Marking Scheme Theory Mcqs PDF
Acids Bases and Salts Igcse Only Complete 2014 Marking Scheme Theory Mcqs PDF
Uploaded by
Ali Ashraf0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
98 views10 pagesThis document provides information about acid-base chemistry concepts and experiments.
1) It matches pH values to solutions, identifying dilute hydrochloric acid as the strongest acid with a pH of 1, and aqueous sodium hydroxide as the strongest base with a pH of 13.
2) Procedures are given for crystallizing a salt from a solution and obtaining anhydrous crystals.
3) Methods are described to compare the properties of strong and weak acids, such as their electrical conductivity, reaction rates with metals, and color with universal indicator. Hydrochloric acid is identified as the stronger acid based on these tests.
Original Description:
Original Title
Acids-Bases-and-Salts-igcse-only-complete-2014-marking-scheme-theory-mcqs.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information about acid-base chemistry concepts and experiments.
1) It matches pH values to solutions, identifying dilute hydrochloric acid as the strongest acid with a pH of 1, and aqueous sodium hydroxide as the strongest base with a pH of 13.
2) Procedures are given for crystallizing a salt from a solution and obtaining anhydrous crystals.
3) Methods are described to compare the properties of strong and weak acids, such as their electrical conductivity, reaction rates with metals, and color with universal indicator. Hydrochloric acid is identified as the stronger acid based on these tests.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
98 views10 pagesAcids Bases and Salts Igcse Only Complete 2014 Marking Scheme Theory Mcqs PDF
Acids Bases and Salts Igcse Only Complete 2014 Marking Scheme Theory Mcqs PDF
Uploaded by
Ali AshrafThis document provides information about acid-base chemistry concepts and experiments.
1) It matches pH values to solutions, identifying dilute hydrochloric acid as the strongest acid with a pH of 1, and aqueous sodium hydroxide as the strongest base with a pH of 13.
2) Procedures are given for crystallizing a salt from a solution and obtaining anhydrous crystals.
3) Methods are described to compare the properties of strong and weak acids, such as their electrical conductivity, reaction rates with metals, and color with universal indicator. Hydrochloric acid is identified as the stronger acid based on these tests.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 10
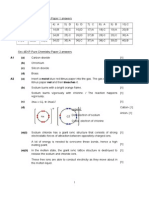
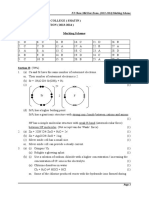
PAGE 68 1 (a) Match the following pH values to the
solutions given below.
8 (a) (changes from) blue (1) to pink (1) 1 3 7 10 13
[2] The solutions all have the same
(b) no more (solid) dissolves or no more concentration.
cobalt(II) carbonate dissolves or no more solution pH
effervescence or bubbling or fizzing [1] aqueous ammonia, weak base 10
filter(residue)/centrifuge/decant [1] dilute hydrochloric acid, a strong acid 1
evaporate/heat/warm/boil/leave in sun aqueous sodium hydroxide, a strong base
AND until most of the water has 13
gone/some water is left/until it is aqueous sodium chloride, a salt 7
concentrated/saturation dilute ethanoic acid, a weak acid 3 [5]
(point)/crystallisation (b) Hydrochloric acid strong acid or
point/crystals form on glass rod or ethanoic acid weak acid [1]
microscope slide/crystals start to form OR: hydrochloric acid completely ionised
[1] or ethanoic acid
Leave/allow to cool/allow to partially ionised
crystallise/filter (off hydrochloric acid greater concentration
crystals)/wash(with distilled of/more H+ ions (than ethanoic acid) [1]
water)/dry crystals with filter paper/dry (c) Rate of reaction with Ca, Mg, Zn, Fe
crystals in warm place or dry in oven or [1]
dry on windowsill [1] Strong (hydrochloric) acid bubbles faster
or more bubbles or dissolves faster [1]
PAGE 69
OR: rate of reaction with (metal)
6 (a) Rb loses 1 electron/1 electron in carbonate [1]
outer shell/1 valency or valence electron strong (hydrochloric) acid faster or more
[1] bubbles or dissolves faster (only if
Sr loses 2 electrons/2 electrons in outer carbonate insoluble) [1]
shell/2 valency or valence electrons [1] OR: electrical conductivity [1]
(b) (i) (mix solutions of) rubidium strong (hydrochloric) acid better
carbonate/Rb2CO3 [1] conductor [1]
strontium chloride/SrCl2 or strontium [Total: 9]
nitrate/Sr(NO3)2 or strontium
PAGE 71
sulfate/SrSO4 or strontium
hydroxide/Sr(OH)2 [1] (b) Ba(C6H13SO3)2 / (C6H13SO3)2Ba [1]
COND (on two correct reactants) filter (c) (i) _ magnesium hexanesulfonate +
or centrifuge or decant (the residue) [1] hydrogen [1]
wash with water and dry/press between (ii) _ calcium hexanesulfonate + water [1]
filter paper/put in (low) oven/put on a (iii) 2C6H13SO3H + Na2CO3 _ 2C6H13SO3Na +
(sunny) windowsill/put in sun/heat [1] CO2 + H2O
C6H13SO3Na = (1) [1]
remaining species correct and equation
(c) (i) nitric acid or nitric(V) acid or
balanced = (1) [1]
HNO3 [1]
(ii) 2KNO3 = 2KNO2 + O2 [2] (d) (i) measure pH / add universal indicator [1]
Species (1) both acids have a low value / pH 0–2 / same
Balance (1) colour / red [1]
or
PAGE 70 measure rate with named reactive metal, Mg,
Zn (1)
both fast reactions (1)
or
measure rate using piece of insoluble water, calcium carbonate and sodium
carbonate, CaCO3 (1) carbonate [2]
both fast reactions (1) ACCEPT: sodium bicarbonate
NOTE: must be insoluble for first mark
or PAGE 74
measure electrical conductivity (1)
both good conductors (1) (b) (i) heat with carbon or coke or carbon
(ii) to have same concentration of H+ / one acid monoxide; [1]
is H2SO4, the other is C6H13SO3H / sulfuric (ii) ZnO + H2SO4 _ ZnSO4 + H2O [2]
acid is dibasic, hexanesulfonic is monobasic [1] for correct reactants [1]for correct products
[1]
(iii) a strong acid is completely ionised, [1] (iii) zinc (not: ions) more reactive than silver
a weak acid is partially ionised [1] and lead; [1]
zinc displaces both metals / silver and lead
produced / ions become atoms / zinc
reduces silver ions and lead ions; [1]
PAGE 72 (silver and lead) can be removed by filtering /
centrifugation / decanting; [1]
an ionic equation; i.e.
Zn + 2 Ag+ _ Zn2+ + 2Ag or Zn + Pb2+ _ Zn2+ +
Pb [1]
allow: any two correct half equations
PAGE 75
(b) (i) strontium carbonate does not
dissolve / no effervescence; [1]
5 (a) because they have more than one
note: not just reaction is complete
oxidation state or valency / form ions with
different (ii) to remove excess / unreacted /
charges [1] undissolved strontium carbonate; [1]
there are two iron oxides (iron(III) oxide and (iii) water of crystallisation needed / 6H2O
iron(II) oxide) / iron forms Fe2+ and Fe3+ in crystals / would get anhydrous salt /
compounds / iron forms iron(II) and iron(III) would not get hydrated salt / crystals
compounds [1] dehydrate; [1]
(b) (i) to remove the precipitate / remove the not: just to obtain crystals
silver(I) chromate(VI) / remove the residue [1]
(ii) to remove soluble impurities / remove
named soluble salt e.g. potassium nitrate / PAGE 76
remove
reactants [1] (b) (i) strontium carbonate does not
(iii) to dry solid / to remove water [1] dissolve / no effervescence; [1]
(c) (i) need one mole of potassium note: not just reaction is complete
chromate(VI) for two moles of silver(I) nitrate / (ii) to remove excess / unreacted /
correct undissolved strontium carbonate; [1]
references to mole ratio [1] (iii) water of crystallisation needed / 6H2O
in crystals / would get anhydrous salt /
PAGE 73
would not get hydrated salt / crystals
(b) (i) anhydrous cobalt chloride becomes dehydrate; [1]
hydrated [1] not: just to obtain crystals
ACCEPT: hydrous
(ii) carbon dioxide is acidic [1] PAGE 77
sodium hydroxide and calcium oxide are bases
/ alkalis [1] 7 (a) (i) add carbon / animal charcoal [1]
(iii) Any two of: filter [1]
OR
repeat experiment without indicator [1] silver(I) nitrate / ethanoate / sulfate;
using same quantity / volume of acid [1] [1]
(ii) add magnesium metal / carbonate / oxide / must be soluble silver salt not silver oxide /
hydroxide carbonate
to (hot) (hydrochloric) acid [1] zinc(II) sulfate [1]
cond: until in excess or no more dissolves or
reacts [1] (b) (i) Ag+(aq) + Cl
–(aq) → AgCl(s) [2]
cond: filter (to remove unreacted solid) [1]
equation correct state symbols missing
PAGE 78 [1]
6 (a) (i) proton or H+ acceptor [1] (ii) ZnCO3 + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + CO2 + H2O [2]
(ii) (measure) pH or (use) UI indicator [1] correct formula for zinc sulfate = 1
note: can be implied need not be explicit [Total: 10]
sodium hydroxide has higher pH /
ammonia(aq) has lower pH [1] PAGE 80
(this sentence would score 2 marks)
or (b) (i) PCl3 + 3H2O → 3HCl + H3PO3 [1]
appropriate colours with UI / appropriate
(ii) acid solutions same concentration [1]
numerical values [1]
measure pH/pH paper/Universal indicator [1]
ammonia is closer to green, blue-green,
hydrochloric acid lower pH [1]
turquoise or lighter blue
colours of Universal indicator can be given as
sodium hydroxide is darker blue / purple /
red<orange<yellow
violet [1]
ignore precise pH values as long as HCl is
or
lower than H3PO3
measure electrical conductivity [1]
OR Acid solutions same concentration [1]
can be implied need not be explicit
add magnesium or any named metal above
ammonia (aq) is the poorer conductor/ sodium
Hydrogen in reactivity series but not above
hydroxide is the better conductor [1] magnesium
calcium carbonate or any insoluble carbonate
(e) (i) pH increases [1] [1]
(ii) oxygen needed for rusting / removes hydrochloric acid react faster/shorter time [1]
oxygen / reacts with oxygen [1] OR acid solutions same concentration [1]
measure electrical conductivity [1]
hydrochloric acid better conductor/bulb brighter
[1]
(b) experiment 1 Ca2+ + CO2 + H2O OR acid solutions same concentration [1]
add sodium thiosulphate [1]
hydrochloric acid forms precipitate faster/less
time [1]
PAGE 79 (iii) sodium hydroxide/sodium carbonate [1]
(e) it would react with/dissolves in a named titration cond on correct reagent [1]
strong acid [1] second mark scores for mention of titration
it would react with/dissolves in a named alkali /burette/pipette/indicator.
[1] experimental detail not required
it shows both basic and acid properties =1 [1] any named soluble calcium salt e.g. calcium
it reacts with both acids and bases/alkalis =1 chloride/nitrate/hydroxide [1]
[1] precipitation/filter/decant/centrifuge [1]
[max 2]
PAGE 81
2 (a) nitric acid; [1]
sodium hydroxide / carbonate / hydrogen 5 (a) (i) 2Li + 2HI → 2LiI + H2 [1]
carbonate; [1] (ii) zinc carbonate + hydriodic acid → zinc
copper(II) oxide / hydroxide / carbonate; iodide + carbon dioxide + water [1]
[1] (iii) MgO + 2HI → MgI2 + H2O [1]
any named soluble chloride; [1] (b) reaction 1 is redox / Li/2HI reaction [1]
accept: hydrochloric acid / hydrogen chloride
cond reason either oxidation number/state / any two [2]
electron transfer [1]
PAGE 85
(d) (i) the reaction is exothermic / reaction
produces heat/energy [1] (b) (i) because it accepts a proton [2]
all the sodium hydroxide used up/neutralised / accepts hydrogen ion or H+ ONLY [1]
reaction has stopped [1] proton and H+ [2]
(ii) adding colder acid / no more heat produced (ii) hydrogen chloride is a strong acid [1]
[1] hydrogen fluoride is a weak acid [1]
if not given in (d)(i) any comments such as weaker or stronger correctly applied for [2]
“reaction has stopped” can gain mark
(iii) 1.33 / 1.3 / 1.3333 (mol/dm3) scores both (iii) hydrogen chloride (aqueous) would have
marks [2] lower pH [1]
not 1.34 OR hydrogen fluoride (aqueous) would have
higher pH
for a correct method – M1 V1 / moles of NaOH If values suggested, not over 7
= 0.02 [Total: 8]
with an incorrect answer only [1]
PAGE 86
PAGE 82
5 (a) (i) Ca2+ + 2F– → CaF2 [2]
(c) base [1] Not balanced ONLY [1]
not alkali Both species must be correct for first mark.
accepts a proton [2] Second mark is for correct balancing.
accepts hydrogen ion / H+ only [1] (ii) Mole ratio Ca2+: F– is 1:2 [1]
proton and H+ [2] Answer must mention moles
accept argument based on charges or number
PAGE 83 of ions
accept 2 moles of NaF react with 1 mole of
(d) (i) thalium sulfate + ammonia + water [1] CaCl2
(ii) 2TlOH + H2SO4 _ Tl2SO4 + 2H2O [2] NOT just “2” in equation
not balanced = [1] If fluorine must specify atoms or ions
incorrect formula = [0] (iii) to remove traces of solutions or to remove
(iii) green precipitate or solid (ignore shades of soluble
green but not bluey green etc.) [1] impurities or to remove a named salt sodium
Fe2+ + 2OH– _ Fe(OH)2 accept multiples [1] chloride
or sodium fluoride or calcium chloride [1]
PAGE 84 To remove impurities is not enough
(iv) to dry (precipitate) or to remove water or to
6 (a) (i) Tl 2S [1] evaporate water [1]
(ii) TlCl 3 [1] NOT to evaporate some of water NOT to
(b) filter / centrifuge / decant crystallise salt
wash the precipitate
dry the solid / heat the solid (in oven) / press (b) T3(PO4)2 allow correct example [1]
between filter paper [3] explain why 8 cm3 react fully [1]
all three stated but not in correct order = [2] comment about mole ratio [1]
two out of three stated in any order = [1] [Total: 8]
(c) (i) silver chloride / silver bromide [1]
photography / cameras / films / photo chromic PAGE 88
lenses / sunglasses [1]
(ii) increase distance between lamp and paper 7 (a) repeat experiment without indicator or
or put lamp far away / use carbon to remove indicator [1]
put a screen or translucent or semi-opaque (partially) evaporate or boil or heat [1]
material between them / allow to cool or crystallise or crystals [1]
use a less powerful or low voltage or dim lamp dry crystals [1]
/ MUST be in correct order
lower the temperature
NB evaporate to dryness, marks one and two hydrochloric acid 1
ONLY sodium hydroxide 13
ethanoic acid 4
PAGE 89 All correct [2]
Two correct [1]
(c) hydrogen chloride or hydrochloric acid [1] (b) With strong acid bulb brighter [1]
carbon dioxide or carbonic acid or hydrogen faster rate of bubbles [1]
carbonate [1] OR corresponding comments for weak acid
(d) 8e around both chlorine atoms [1] (c) proton NOT hydrogen ion [1]
4e between carbon and oxygen atoms [1] H+ not conditional on proton [1]
8e around carbon atom [1] Only way for [2] is proton and H+
8e around oxygen [1] (d) (i) CaO and MgO [1]
if a bond contains a line with no electrons, no (ii) CO2 and SO2 [1]
marks for atoms joined by that line (iii) Al2O3 [1]
ignore keying (iv) CO [1]
[TOTAL = 10]
PAGE 90
(c) reaction no reaction [1]
4 (a) (i) magnesium + sulphuric acid = reaction reaction [1]
magnesium sulphate + hydrogen [1]
ACCEPT hydrogen sulphate PAGE 94
(ii) Li2O + H2SO4 _ Li2SO4 + H2O [2]
formulae correct but not balanced [1] 4 (a) (i) correct word equation (carbon dioxide
(iii) CuO + H2SO4 _ CuSO4 + H2O [2] and water) [1]
OR CuO + 2HCl _ CuCl2 + H2O Accept correct symbol equation
OR CuO + 2HNO3 _ Cu(NO3)2 +H2O (ii) Must have a correct reagent otherwise wc =
formulae correct but not balanced [1] 0
(iv) sodium carbonate + sulphuric acid _ add (acidified) barium chloride(aq) or nitrate or
sodium sulphate + carbon dioxide + water [1] add barium ions [1]
(b) it accepts a proton [2] COND white precipitate [1]
it accepts a hydrogen ion [1] ONLY NOT lead(II) compounds
(c) sulphuric acid is completely ionised [1] (iii) low pH or universal indicator turns red(aq)
or few molecules and many ions [1]
ethanoic acid is partially ionised [1] pH 3 or less
or many molecules and few ions
[Total: 10] (b) (i) to remove fibres or remove solid
NOT precipitate, NOT impurities, NOT to
PAGE 91 obtain a filtrate [1]
(ii) because silver atoms have lost electrons [1]
3 (i) method C [1] OR oxidation number increased
sulphuric acid (allow if given in equation) [1] (iii) silver chloride [1]
zinc oxide + sulphuric acid = zinc sulphate +
water [1] PAGE 95
(ii) method A [1]
hydrochloric acid [1] 2 (a) Zn + I2 = Zn2+ + 2I - [2]
KOH + HCl = KCl + H2O [1] For having either reactants or products correct
(iii) method B [1] ONLY [1]
potassium iodide or any soluble iodide [1] (b) for zinc and sodium hydroxide white
Pb2+ + 2I- = PbI2 accept a correct equation even precipitate [1]
if soluble iodide is wrong [2] dissolves in excess (only if precipitate
Not balanced - Pb2+ + I- = PbI2 ONLY [1] mentioned) [1]
[Total: 10] for zinc and ammonia same results [1]
Mark either first (sodium hydroxide or aqueous
PAGE 92 ammonia), if completely correct, then an
additional [1] can be awarded for stating that
3 (a) ammonia 10 the other has the same results.
PAGE 96 [1]
4 (a) (i) Named soluble zinc salt [1]
PAGE 99
corresponding sodium salt [1]
5 (a) (i) equilibrium to left or many molecules
If hydroxide or oxide then 0/2
and few ions or
(ii) Correct equation [2]
partially ionised or reverse reaction favoured
not balanced [1] only
[1]
(iii) Correct equation [2]
(ii) Water donates proton [1]
(b) (i) Fe3+ + 3OH = Fe(OH)3 [1]
methylamine accepts a proton [1]
(ii) Max at 8cm3
NOTE If hydrogen ion then ONLY [1] provided
[1]
both are correct
Same shape of graph
(b) less than 12 more than 7 [1]
smaller concentration of hydroxide ions or
partially dissociated or
poor proton acceptor or poor H+ acceptor [1]
NOT it is a weak base
(c) (i) CH3NH2 + HCl = CH3NH3Cl [1]
methylammonium chloride [1]
Just the above shape, the height of the
NOTE the equation must be as written, the
precipitate and the volume
equation with sulphuric acid has been
of sodium hydroxide are irrelevant [1]
given as guidance.
(ii) brown precipitate [1]
(iii) Maximum then height of precipitate
ACCEPT orange or red/brown or brick red or
decreases [1]
brown/red
or graph slopes down to x axis or comes to zero (iii) sodium hydroxide or any named strong
hydroxide dissolves in excess or it is base [1]
amphoteric [1] [Total: 9]
PAGE 97 PAGE 100
(c) (i) Any reasonable explanation
(b) (i) potassium [1] Plants prefer soil pH about 7
(ii) ammonium sulphate [1] Plants do not grow (well) in acidic soils/plants grow
(iii) Ca3(PO4)2 [1] better
Ca(H2PO4)2 [1] To increase crop yields
(iv) only acceptable responses are: Any ONE [1]
accepts a proton [2] Do NOT accept in acidic soils plants die
(ii) With calcium carbonate, pH cannot go above 7
accepts H+
[1]
[1] only It is not washed away by the rain/remains longer in
the soil
PAGE 98 It is not absorbed by the plant [1]
(d) Add excess lead oxide to nitric acid OR
can imply excess With calcium oxide, pH can go above 7 [1]
It is washed away by the rain [1]
filter NOT if residue is lead nitrate (iii) Any correct use - making steel/iron, making
evaporate or heat solution cement, making glass, [1]
disposing of acid wastes, removing sulphur dioxide
(b) (i) white precipitate from flue
gases, (stone in) building, indigestion tablets,
COND upon a precipitate toothpaste, cosmetics etc
dissolves in excess or forms solution (b)(i) sulphuric acid
[1] COND description of titration
[1] repeat without indicator or with carbon
(ii) blue precipitate evaporation
COND upon a precipitate any TWO [3]
does not dissolve in excess (ii) suitable reactants calcium chloride and
[1] sodium fluoride [1]
COND upon correct reagents
filter [1] 8 (a) same general formula
wash and dry precipitate [1] same chemical properties
OR Accept synthesis same functional group
calcium [1] physical properties vary in predictable way
fluorine [1] common methods of preparation
burn or heat [1] [3] consecutive members differ by CH2
any two [2]
PAGE 101 mark first two
(b)(i) calcium ethanoate + hydrogen [1] ignore others unless it contradicts a point
(ii) zinc oxide or hydroxide [1] which has been awarded a mark
(b) (i) 2HCOOH + CaCO3 _ Ca(HCOO)2 + CO2
(c) CH3COOH + NaOH º CH3COONa + H2O
+ H2O [2]
[2] not balanced = [1]
reactants [1] products [1] (ii) zinc + methanoic acid _ zinc methanoate +
2 dilute hydrogen [2]
filter [1] for each product
saturated (iii) protected by oxide layer [1]
cool (c) butanoic acid [1]
blue CH3-CH2-CH2-COOH / C4H8O2 / C3H7COOH /
sulphate [6] C4H7OOH [1]
C2H4O [1]
PAGE 102 mark ecf to molecular formula
PAGE 105
7 (a) repeat without indicator / repeat
using same volumes of acid and alkali or
use
carbon / charcoal to remove indicator (1)
evaporate / heat / warm / boil / leave in
sun (1)
until most of the water has gone / some
water is left / saturation (point) /
crystallisation point (1)
leave / allow to cool / allow to
crystallise (1)
filter (off crystals) / wash(with
distilled water) / dry crystals with
filter paper / dry
PAGE 103
crystals in warm place / oven /
windowsill (1) [5]
(c) name or formula of strong acid and
alkali (1)
reacts with or neutralises both acid and
base or alkali (then amphoteric) (1)
it dissolves / soluble in both(acid and
alkali) or form solutions in both (1) [3]
PAGE 106
(c) (i) zinc + propanoic acid → zinc
PAGE 104 propanoate (+ hydrogen) (1) [1]
(ii) calcium oxide + propanoic acid → warm [1]
calcium propanoate + water (1) [1] (only) ammonium phosphate gives off
(iii) LiOH + CH3CH2 COOH → CH3CH2COOLi + H2O ammonia / gas (which will turn red litmus
(1) [1] paper
blue) [1]
(ii) potassium / K (1) or:
phosphorus / P (1) [2] sodium hydroxide solution [1]
(b) (i) burn fossil fuels / burn fuels dissolve fertiliser in water [1]
containing sulfur / burn compounds Ca2+ gives (white) ppt [1]
containing or:
sulfur / burn ores containing sulfur / flame test [1]
roast metal sulfides / burn metal Ca2+ brick red / orange / orange-red [1]
sulfides NH4
+ no colour [1]
(1)
sulfur dioxide / SO2 (formed) (1) (b) iron catalyst [1]
(form) sulfuric / H2SO4 / sulfurous acid / pressure 150–300 atmospheres [1]
H2SO3 (1) temperature 370–470 °C [1]
OR N2 + 3H2 ⇌ 2NH3 [1]
nitrogen and oxygen (in air) react at note: units required for temperature and
high temperatures / in jet engines / car pressure
engines / lightning. (1) (c) potassium / K [1]
(form) oxides of nitrogen (1) (d) (i) needs to be soluble / in solution
(form) nitric acid / HNO3 / nitrous acid / (to be absorbed by plants) [1]
HNO2 (1) [3] (ii) base [1]
proton acceptor [1]
PAGE 107 (e) plant growth depends on soil acidity
(b) (i) malonic is a weaker acid/less or pH / plants have optimum pH (for
dissociated growth) [1]
OR sulfuric acid is a stronger acid/more add Ca(OH)2 / CaO / CaCO3 / lime / slaked
dissociated [1] lime / quicklime / limestone [1]
NOT sulfuric acid is a strong acid
(ii) add piece of suitable metal, e.g. Mg PAGE 109
ALLOW Al, Ca NOT K, Na, Cu [1]
6 (a) (i) to neutralise all the acid / so all acid
sulfuric acid reacts faster OR malonic reacts
reacts [1]
slower [1]
not: reaction goes to completion
OR
(ii) remove excess carbonate / removes
as above add a piece of CaCO3, if soluble
unreacted carbonate [1]
carbonate then [1] only
not: remove solid
OR measure electrical conductivity [1]
(iii) need water of crystallisation / hydrated
sulfuric acid is the better conductor
crystals / to get crystals [1]
OR malonic acid poorer conductor [1]
(iv) filter / decant / wash crystals [1]
NOT sulfuric acid is a good conductor
dry with filter paper or tissues etc. [1]
accept: in warm oven / warm place / in sun
(c) (i) sodium malonate and water [1]
not: just heat
(ii) CuSO4
(b) (i) potassium carbonate is soluble / both
H2O [2]
salts soluble [1]
(iii) CH2(COO)2 Mg
(ii) use potassium carbonate solution [1]
H2 [2]
accept: implication of solution – in pipette /
(iv) K2SO4
burette / 25 cm3
CO2 and H2O NOT H2CO3 [2]
titrate / titration term required [1]
use an indicator accept: any named acid/base
PAGE 108 indicator [1]
3 (a) sodium hydroxide solution [1]
repeat without indicator / use carbon to remove measure electrical conductivity [1]
indicator [1] sulfuric acid is the better conductor [1]
OR
PAGE 110 add magnesium / named fairly reactive
(b) test it with both hydrochloric acid and metal [1]
sodium hydroxide(aq) [1] ethanedioic acid gives the slower
accept: any named strong acid and any strong
alkali reaction [1]
if only acid and alkali given then max = 3 NOTE result must refer to rate not
basic oxide reacts with acid [1] amount
acidic oxide reacts with alkali/base [1] OR
amphoteric reacts with both [1] add a carbonate [1]
accept: for react – form salt and water ethanedioic acid gives the slower
reaction [1]
PAGE 111 NOTE result must refer to rate not
1 (a) (i) lithium oxide / strontium oxide amount
[1]
(ii) sulfur dioxide / nitrogen dioxide [1] (ii) add sodium hydroxide(aq) / alkali [1]
(iii) aluminium oxide [1] carbon dioxide dissolves, leaving methane
(iv) carbon monoxide [1] [1]
accept: correct formulae
(b) sulfur dioxide [1] (c) (i) V2O3 [1]
burn (fossil) fuel containing sulfur / VO2 [1]
volcanoes [1] (ii) add sodium hydroxide(aq) or other named
nitrogen dioxide [1] alkali [1]
reaction of nitrogen and oxygen [1] not ammonia
high temperatures / in car engine [1] cond vanadium(IV) oxide dissolves / reacts [1]
not: exhaust filter (to remove vanadium(III) oxide) [1]
PAGE 112 PAGE 114
8 (a) filter / centrifuge / decant [1] 2 (a) pH < 7 [1]
(partially) evaporate / heat / boil [1]
example [1]
allow to crystallise / cool / let crystals form [1]
dry crystals / dry between filter paper / leave inpH > 7 [1]
a warm place to dry [1] example [1]
“dry” on its own must be a verb NOT amphoteric oxides Be, Al, Zn, Pb, Sn
evaporate to dryness only marks 1 and 2 etc
note if discuss residue only mark 1 pH = 7 [1]
example H2O, CO, NO [1]
(b) (i) zinc / aluminium / lead / tin / chromium the two marks are not linked, mark each
[1] independently
(ii) white precipitate [1]
NOT amphoteric oxides Be, Al, Zn, Pb, Sn
precipitate dissolves / colourless solution forms
/ forms a clear solution etc.
/ soluble in excess [1] (b) (i) shows both basic and acidic
properties [1]
PAGE 113 (ii) a named strong acid [1]
(c) (i) proton donor [1] a named alkali [1]
(ii) measure pH / use pH paper [1]
sulfuric acid has the lower pH [1] PAGE 115
accept colours / appropriate numerical 4 (a) (i) C6H5COOH or C6H5CO2H [1]
values NOT C7H6O2 /C6H6COO
OR (ii) sodium hydroxide + benzoic acid = sodium
benzoate + water [1]
correct spelling needed NOT benzenoate
ACCEPT correct symbol equation
(iii) sodium carbonate or oxide or
hydrogencarbonate
any TWO [2]
NOT Na
You might also like
- Mole Conversions Mazefor Reviewor AssessmentDocument9 pagesMole Conversions Mazefor Reviewor AssessmentAsiaNo ratings yet
- Naming Ionic Compounds Practice WorksheetDocument5 pagesNaming Ionic Compounds Practice Worksheetsofiavmoreira100% (1)
- CHM2 Group2 and Group7 ADocument14 pagesCHM2 Group2 and Group7 Aareyouthere92100% (1)
- AS - Group 1,2& 7 MSDocument14 pagesAS - Group 1,2& 7 MSvintu pvNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Acids Bases and SaltsDocument12 pagesChapter - 2 Acids Bases and SaltsAditya yadav G1606No ratings yet
- 5070 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesDocument7 pages5070 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesMushtaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry Paper 2 Worked SolutionsDocument6 pagesCSEC Chemistry Paper 2 Worked Solutionskay5christie9081No ratings yet
- Acids, Bases & Salts 3 MS PDFDocument3 pagesAcids, Bases & Salts 3 MS PDFMohammad AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry AnswerDocument41 pagesAnalytical Chemistry AnswerNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- CHM2 Group2 and Group7 ADocument15 pagesCHM2 Group2 and Group7 AGM Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Trial Paper 2 MS PerlisDocument8 pagesTrial Paper 2 MS PerlisZaiton RoslanNo ratings yet
- 0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 SeriesDocument6 pages0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 SeriesMr HeckerNo ratings yet
- Identification of Ions & Gases MS PDFDocument5 pagesIdentification of Ions & Gases MS PDFClinton ChikengezhaNo ratings yet
- Sec 4E Chem (SPA) MY Marking Scheme 2012Document5 pagesSec 4E Chem (SPA) MY Marking Scheme 2012Hui XiuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Igcse: Answer Key Acid, Base & Salt Identification of Ion & MetalDocument2 pagesChemistry Igcse: Answer Key Acid, Base & Salt Identification of Ion & MetalArda RahmainiNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Paper 2 November 2009Document10 pagesPhysical Science Paper 2 November 2009BRANDON TINASHENo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry 4335 2H Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2008Document10 pagesIGCSE Chemistry 4335 2H Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2008gkawsar22No ratings yet
- PLKVKTCSFC - F6 - 2019-2020 - Chem Ans - Kuok KellyDocument8 pagesPLKVKTCSFC - F6 - 2019-2020 - Chem Ans - Kuok KellyOof GucciNo ratings yet
- 0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument4 pages0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersVarun PanickerNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases & Salts 4 MS PDFDocument5 pagesAcids, Bases & Salts 4 MS PDFMohammad AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics 2 MSDocument4 pagesChemical Energetics 2 MSAli SiddiqNo ratings yet
- 2018 Sec 4 CT 1 Paper Answers (Final)Document2 pages2018 Sec 4 CT 1 Paper Answers (Final)Timothy CNo ratings yet
- Exam 1A For First 6 Chapters MS OnlineDocument5 pagesExam 1A For First 6 Chapters MS Onlinehalahossam8899No ratings yet
- 0620 s06 Ms 3Document5 pages0620 s06 Ms 3Varun PanickerNo ratings yet
- 0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2012 SeriesDocument6 pages0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2012 SeriesPiyal ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Paper ChemistryDocument20 pagesMarking Scheme Paper ChemistryArvin DiNozzoNo ratings yet
- Acids Salts Test Year 10 2018 - 9Document3 pagesAcids Salts Test Year 10 2018 - 9Kamiye OdebadeNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Group 2 - MSDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table Group 2 - MSBadNo ratings yet
- 0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument6 pages0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersfarahgraceNo ratings yet
- NT Chemistry Answers Chapter 11Document4 pagesNT Chemistry Answers Chapter 11Charlotte CoxNo ratings yet
- Sec 4EXP Pure Chemistry Paper Marking SchemeDocument7 pagesSec 4EXP Pure Chemistry Paper Marking SchemeHui XiuNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Answers ElectrolysisDocument2 pagesWorksheet Answers ElectrolysisedenNo ratings yet
- Module A Chemistry: Contents: (A) Common Mistakes (B) Commands Task Answering Effectively (C) Sample QuestionsDocument13 pagesModule A Chemistry: Contents: (A) Common Mistakes (B) Commands Task Answering Effectively (C) Sample QuestionsJOANNA MAGDALIN A/P JOSEPH MoeNo ratings yet
- QC - 2019-20 - Mock - S6 - Chem 1 - AnsDocument7 pagesQC - 2019-20 - Mock - S6 - Chem 1 - AnsOof GucciNo ratings yet
- 0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2012 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument7 pages0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2012 Question Paper For The Guidance of Teachersmartinhenok60No ratings yet
- 0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument6 pages0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersVarun PanickerNo ratings yet
- 0620 s14 Ms 63Document4 pages0620 s14 Ms 63BrianChanNo ratings yet
- Answerpelangi 2Document10 pagesAnswerpelangi 2Yu YanNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry 5 MSDocument5 pagesElectricity & Chemistry 5 MSAli SiddiqNo ratings yet
- AS 11 AnsDocument15 pagesAS 11 AnsthegreatwardiniNo ratings yet
- 5070 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2009 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument8 pages5070 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2009 Question Paper For The Guidance of Teachersatul purnaNo ratings yet
- Answers To 2.5 ExercisesDocument2 pagesAnswers To 2.5 ExercisesMohammed Al RaeesiNo ratings yet
- Chem Unit 5 Transition Metals AnswersDocument13 pagesChem Unit 5 Transition Metals Answersareyouthere9250% (2)
- Skema BK2 KimiaDocument12 pagesSkema BK2 KimiaazmiNo ratings yet
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument1 pageAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and SaltsJust Harish100% (1)
- (/Rtf1/Ansi/Ansicpg1252/Uc0/Deff0 (/fonttbl (/f0/Fswiss/Fcharset0/Fprq2 Arial ) (/f1/Froman/Fcharset0/Fprq2 Times New Roman )Document6 pages(/Rtf1/Ansi/Ansicpg1252/Uc0/Deff0 (/fonttbl (/f0/Fswiss/Fcharset0/Fprq2 Arial ) (/f1/Froman/Fcharset0/Fprq2 Times New Roman )api-25909541No ratings yet
- Alcohols & Carboxylic Acids 4 MSDocument5 pagesAlcohols & Carboxylic Acids 4 MSkrishav shuklaNo ratings yet
- Salts: Quick Check (Page 214)Document3 pagesSalts: Quick Check (Page 214)何小霞No ratings yet
- Redox Review HL MarkschemeDocument2 pagesRedox Review HL MarkschemenishutamilNo ratings yet
- 0620 s07 Ms 3Document6 pages0620 s07 Ms 3Varun PanickerNo ratings yet
- Polymers 7 MSDocument6 pagesPolymers 7 MSkhalil rehmanNo ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers 7 Asal Chem CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 7 Asal Chem CBraphaelademetriadesNo ratings yet
- 10 FEB HydrogenDocument27 pages10 FEB Hydrogensachin anuseNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Making and Identifying Salts: Summary QuestionsDocument3 pagesUnit 11 Making and Identifying Salts: Summary QuestionsLei YinNo ratings yet
- Kiangsu-Chekiang College (Shatin) MID-YEAR EXAMINATION (2013-2014) Form 5 Chemistry Marking Scheme: Section A: (30%)Document5 pagesKiangsu-Chekiang College (Shatin) MID-YEAR EXAMINATION (2013-2014) Form 5 Chemistry Marking Scheme: Section A: (30%)wslNo ratings yet
- 4541 123 Skema Kim Trial SPM 2013Document22 pages4541 123 Skema Kim Trial SPM 2013Robert HicksNo ratings yet
- Hyrdogen Storage TechnologiesFrom EverandHyrdogen Storage TechnologiesMehmet SankirNo ratings yet
- Al Aufaaq Volume 10Document50 pagesAl Aufaaq Volume 10Ali Ashraf100% (1)
- Chemistry Topical PapersDocument406 pagesChemistry Topical PapersAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- Al Aufaaq Volume 09Document61 pagesAl Aufaaq Volume 09Ali Ashraf100% (1)
- Sahih Hisnul Muslam SpecialDocument115 pagesSahih Hisnul Muslam SpecialAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- Al Aufaaq Volume 05Document38 pagesAl Aufaaq Volume 05Ali AshrafNo ratings yet
- Al Aufaaq Volume 07Document58 pagesAl Aufaaq Volume 07Ali AshrafNo ratings yet
- Al Aufaaq Volume 06Document78 pagesAl Aufaaq Volume 06Ali Ashraf50% (2)
- Hisn Ul Muslim 01Document216 pagesHisn Ul Muslim 01Ali AshrafNo ratings yet
- Al Aufaaq Volume 03Document98 pagesAl Aufaaq Volume 03Ali AshrafNo ratings yet
- M.sc. BiochemistryDocument102 pagesM.sc. BiochemistryAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- Duniya or Akhirat Ki DuaDocument177 pagesDuniya or Akhirat Ki DuaAli Ashraf100% (1)
- Al Aufaaq Volume 02Document62 pagesAl Aufaaq Volume 02Ali AshrafNo ratings yet
- Biology 7b Worksheet No.2Document12 pagesBiology 7b Worksheet No.2Ali AshrafNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Gce and Igcse Only Complete 2014 PDFDocument51 pagesAtomic Structure Gce and Igcse Only Complete 2014 PDFAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts Igcse Only Complete 2014 With Marking Scheme Protected PDFDocument126 pagesAcids Bases and Salts Igcse Only Complete 2014 With Marking Scheme Protected PDFAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- Join Now:https://t.me/igcse - FilesDocument6 pagesJoin Now:https://t.me/igcse - FilesAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- Biology 8B Worksheet No.6 PDFDocument10 pagesBiology 8B Worksheet No.6 PDFAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Igcse Only Complete 2014 PDFDocument38 pagesAtomic Structure Igcse Only Complete 2014 PDFAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Mass and Weight: Key IdeasDocument7 pages1.3 Mass and Weight: Key IdeasAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts Igcse Only Basic Questions Only PDFDocument25 pagesAcids Bases and Salts Igcse Only Basic Questions Only PDFAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding (Igcse 0620 - MCQS)Document86 pagesChemical Bonding (Igcse 0620 - MCQS)Ali AshrafNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Igcse Only Complete 2014 ML PDFDocument88 pagesChemical Bonding Igcse Only Complete 2014 ML PDFAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- CO2 Capture by Aqueous Na2CO3 Integrated With High-Quality CaCO3 Formation and Pure CO2 Release at Room ConditionsDocument9 pagesCO2 Capture by Aqueous Na2CO3 Integrated With High-Quality CaCO3 Formation and Pure CO2 Release at Room ConditionsJafar KhademNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Acid Base and SaltDocument37 pagesCHAPTER 2 Acid Base and SaltRaghav ParasharNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1c ChemistryDocument11 pagesExercise 1c Chemistryapi-533545229No ratings yet
- PH Dan Larutan PenyanggaDocument38 pagesPH Dan Larutan PenyanggaSri Novita YandaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals: One Mark QuestionsDocument13 pagesMetals and Non-Metals: One Mark QuestionsSwain SubhankarNo ratings yet
- 6e. Aquatic GeochemistryDocument46 pages6e. Aquatic GeochemistrysudhakarNo ratings yet
- Potential Application of Bacteria To Improve The Strength of Cement ConcreteDocument4 pagesPotential Application of Bacteria To Improve The Strength of Cement ConcreteTaryNo ratings yet
- Classification by Numeric Range E NumbersDocument24 pagesClassification by Numeric Range E NumbersrohitindiaNo ratings yet
- Controlling HCL at The Geysers WeresKendrick GRC PaperDocument23 pagesControlling HCL at The Geysers WeresKendrick GRC PapergauravNo ratings yet
- Cleaning & Cleaning VerificationDocument53 pagesCleaning & Cleaning Verificationjack theNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept WorksheetDocument3 pagesMole Concept WorksheetRoland SocoNo ratings yet
- Stable Prenucleation Mineral Clusters Are Liquid-Like Ionic PolymersDocument8 pagesStable Prenucleation Mineral Clusters Are Liquid-Like Ionic PolymersSaeed AbdNo ratings yet
- MERC120045 Emd Fluxes Spectromelt Low PDFDocument8 pagesMERC120045 Emd Fluxes Spectromelt Low PDFsaeedhoseiniNo ratings yet
- 2001 - March - Boiler (Part 1)Document6 pages2001 - March - Boiler (Part 1)arunkumar23101No ratings yet
- JR VSA Q and A Wtih Star Marks (2023) PDFDocument42 pagesJR VSA Q and A Wtih Star Marks (2023) PDFShaik irfan basha Shaik irfan bashaNo ratings yet
- Haram and Halal E CodesDocument17 pagesHaram and Halal E CodesMohd NajidNo ratings yet
- Copper ChlorideDocument3 pagesCopper ChloridePushpa KaladeviNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Form 3 Final ExaminationDocument23 pagesChemistry: Form 3 Final Examinationjonas hoNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Internal CorrosionDocument15 pagesPipeline Internal CorrosionJabari KaneNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Groundwater Quality For Irrigation of Green Spaces in The Rourkela City of Odisha, IndiaDocument11 pagesAssessment of Groundwater Quality For Irrigation of Green Spaces in The Rourkela City of Odisha, Indiaghalit mohammadNo ratings yet
- c1 Higher Revision Questions - Set 1 OnlyDocument94 pagesc1 Higher Revision Questions - Set 1 Onlyapi-320022467No ratings yet
- WP1A3.01 EnAlgae SOP Report-V10 FINALDocument395 pagesWP1A3.01 EnAlgae SOP Report-V10 FINALAli MohsinNo ratings yet
- V2 Materials Technology 2Document526 pagesV2 Materials Technology 2Liya Nur SholihahNo ratings yet
- Cape Chem U2 P2 2006Document13 pagesCape Chem U2 P2 2006Daniella SalandyNo ratings yet
- Lime Popping PhenomenonDocument4 pagesLime Popping PhenomenonFayyaz Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- June 2012 Edexcel Chemistry Unit 2Document20 pagesJune 2012 Edexcel Chemistry Unit 2EzioAudi77No ratings yet
- K2Co3 by DEADocument5 pagesK2Co3 by DEAamirNo ratings yet
- Notes November 2020 CH 11: Preparing Common Salts Grade: 8 Subjects: ChemistryDocument5 pagesNotes November 2020 CH 11: Preparing Common Salts Grade: 8 Subjects: Chemistryanish kanthethiNo ratings yet