Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tarea #1 PDF
Tarea #1 PDF
Uploaded by
Manuel Hernández MontecilloOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tarea #1 PDF
Tarea #1 PDF
Uploaded by
Manuel Hernández MontecilloCopyright:
Available Formats
Aire acondicionado y refrigeración
Agosto-Diciembre 2020
Instructor: Dr. Julio César Moreno Blanco (jc.morenoblanco@ugto.mx)
Universidad de Guanajuato
Departamento de Ingeniería Mecánica
Tarea #1
Fecha de entrega: 08 de Octubre de 2020
Enviar en formato pdf titulado con su NUA.
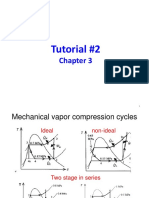
1.- Consider an ideal refrigeration cycle that has a 6.- A split evaporator is used to cool the refrigerator
condenser temperature of 45 °C and an evaporator section and separate cooling of the freezer section, as
temperature of −15 °C. Determine the COP of this shown in Figure. Assume constant pressure in the two
refrigerator for the working fluids R-134a and R-410a. evaporators. How does the COP = (QL1 + QL2)/W
compare to that of a refrigerator with a single evaporator
2.- A window-mounted air conditioner supplies 19 at the lowest temperature?
m3/min of air at 15 °C, 1 bar to a room. Air returns from
the room to the evaporator of the unit at 22 °C. The air
conditioner operates at steady state on a vapor-
compression refrigeration cycle with Refrigerant-22
entering the compressor at 4 bar, 10 °C. Saturated liquid
refrigerant at 9 bar leaves the condenser. The compressor
has an isentropic efficiency of 70%, and refrigerant exits
the compressor at 9 bar. Determine the compressor power,
in kW, the refrigeration capacity, in tons, and the
coefficient of performance.
3.- An air conditioner in the airport of Timbuktu runs a
cooling system using R-410a with a high pressure of 1500
kPa and a low pressure of 200 kPa. It should cool the
desert air at 45 °C down to 15 °C. Find the cycle COP.
Will the system work?
7.- A refrigerator using R-410a is powered by a small
4.- A refrigerator using R-134a is located in a 20 °C room. natural gas–fired heat engine with a thermal efficiency of
Consider the cycle to be ideal, except that the compressor 25%, as shown in Figure. The R-410a condenses at 40 °C,
is neither adiabatic nor reversible. Saturated vapor at −20 it evaporates at −20 °C, and the cycle is standard. Find the
°C enters the compressor, and the R-134a exits the two specific heat transfers in the refrigeration cycle. What
compressor at 50 °C. The condenser temperature is 40 °C. is the overall COP as QL/Q1?
The mass flowrate of refrigerant around the cycle is 0.2
kg/s, and the COP is measured and found to be 2.3. Find
the power input to the compressor and the rate of entropy
generation in the compressor process.
5.- In an actual refrigeration cycle using R-134a as the
working fluid, the refrigerant flow rate is 0.05 kg/s. Vapor
enters the compressor at 150 kPa and −10 °C and leaves
at 1.2MPa and 75 °C. The power input to the non-
adiabatic compressor is measured and found to be 2.4 kW.
The refrigerant enters the expansion valve at 1.15 MPa
and 40 °C and leaves the evaporator at 175 kPa and −15 8.- Consider a two-stage cascade refrigeration system
°C. Determine the entropy generation in the compression operating between the pressure limits of 1.2 MPa and 200
process, the refrigeration capacity, and the COP for this kPa with refrigerant-134a as the working fluid. The
cycle. refrigerant leaves the condenser as a saturated liquid and
is throttled to a flash chamber operating at 0.45 MPa. Part
of the refrigerant evaporates during this flashing process,
and this vapor is mixed with the refrigerant leaving the refrigerant at the compressor exit, (b) the rate of heat
low-pressure compressor. The mixture is then generation by the people in the room, (c) the COP of the
compressed to the condenser pressure by the high- air conditioner, and (d) the minimum volume flow rate of
pressure compressor. The liquid in the flash chamber is the refrigerant at the compressor inlet for the same
throttled to the evaporator pressure and cools the compressor inlet and exit conditions.
refrigerated space as it vaporizes in the evaporator. The
mass flow rate of the refrigerant through the low-pressure
compressor is 0.15 kg/s. Assuming the refrigerant leaves
the evaporator as a saturated vapor and the isentropic
efficiency is 80 percent for both compressors, determine
(a) the mass flow rate of the refrigerant through the high-
pressure compressor, (b) the rate of heat removal from the
refrigerated space, and (c) the COP of this refrigerator.
Also, determine (d) the rate of heat removal and the COP
if this refrigerator operated on a single-stage cycle
between the same pressure limits with the same
compressor efficiency and the same flow rate as in part
(a).
9.- An air conditioner with refrigerant-134a as the
working fluid is used to keep a room at 26°C by rejecting
the waste heat to the outside air at 34°C. The room is
gaining heat through the walls and the windows at a rate
of 250 kJ/min while the heat generated by the computer,
TV, and lights amounts to 900 W. An unknown amount
of heat is also generated by the people in the room. The
condenser and evaporator pressures are 1200 and 500 kPa,
respectively. The refrigerant is saturated liquid at the
condenser exit and saturated vapor at the compressor
inlet. If the refrigerant enters the compressor at a rate of
100 L/min and the isentropic efficiency of the compressor
is 75 percent, determine (a) the temperature of the
You might also like
- Sauer Compressor: Typ: WP 400Document206 pagesSauer Compressor: Typ: WP 400john smithNo ratings yet
- Calculating Settle Out PressureDocument5 pagesCalculating Settle Out PressureBehnam HosseinzadehNo ratings yet
- EME2146 Tutorial 6Document2 pagesEME2146 Tutorial 6iwqb0% (1)
- HW-3, Ch-11Document6 pagesHW-3, Ch-11Tshepho Ketshepha KeisangNo ratings yet
- Assignment 12Document7 pagesAssignment 12Anonymous mqIqN5zNo ratings yet
- Tugas PendinginDocument8 pagesTugas PendinginFilianti Gianita0% (1)
- Manual lb75b PDFDocument178 pagesManual lb75b PDFnery ardila100% (1)
- Multi V IV - Engineer ManualDocument152 pagesMulti V IV - Engineer ManualHung Tran83% (6)
- Ceccato CompressorDocument29 pagesCeccato Compressorpeterpunk7586% (7)
- PC 843 T 5046 Compressor Spare Parts PDF - Google SearchDocument2 pagesPC 843 T 5046 Compressor Spare Parts PDF - Google Searchamogmhetre0% (1)
- Overview of Rotating Equipment PDFDocument96 pagesOverview of Rotating Equipment PDFAiyappa Devraj100% (7)
- Tutorial 4 Refrigeration System BDA 3043 - Thermodynamics II Winardi SaniDocument4 pagesTutorial 4 Refrigeration System BDA 3043 - Thermodynamics II Winardi Saniwanpudin0% (1)
- ME16104 - 1st AssignmentDocument3 pagesME16104 - 1st AssignmentManish kumarNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document3 pagesSheet 1Esmail AnasNo ratings yet
- ME183 Lectures 1LE Problem Solving Pages 21-30Document10 pagesME183 Lectures 1LE Problem Solving Pages 21-30Paul RodgersNo ratings yet
- Ques 1Document6 pagesQues 1ANKIT KUMAR0% (1)
- Ref Review ProblemsDocument3 pagesRef Review ProblemsGiancarlo SantosNo ratings yet
- Tutorials Refrigiration and Heat Pumps 2024 ThermoDocument2 pagesTutorials Refrigiration and Heat Pumps 2024 Thermosphesihlemchunu40No ratings yet
- Problems On VC CycleDocument8 pagesProblems On VC Cyclesushil.vgiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document2 pagesAssignment 5hossamkandil7No ratings yet
- RAC Tutorial Sheet 1-5Document6 pagesRAC Tutorial Sheet 1-5abhip2041No ratings yet
- Aircond Ref1Document33 pagesAircond Ref1Ghaith AlhadiNo ratings yet
- Sheet No.Document2 pagesSheet No.mohamed eldrwanyNo ratings yet
- ME183 Lectures 1LE Problem Solving Pages 31-38Document8 pagesME183 Lectures 1LE Problem Solving Pages 31-38Paul RodgersNo ratings yet
- Problems On VCRSDocument7 pagesProblems On VCRSFraol100% (1)
- Sheet 5Document3 pagesSheet 5Mechanical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Tutorials For Canot RefrigirationDocument3 pagesTutorials For Canot Refrigirationsphesihlemchunu40No ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument8 pagesRefrigerationHectorCabz0% (1)
- Question Bank - Module 2Document3 pagesQuestion Bank - Module 2Mohammed ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- Sheets 1 TO 6Document13 pagesSheets 1 TO 6Tito HeshamNo ratings yet
- Explain A Simple Vapour Compression Cycle Giving Clearly Its Flow Diagram?Document5 pagesExplain A Simple Vapour Compression Cycle Giving Clearly Its Flow Diagram?Ashok DaraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1, RAC - KME 601Document3 pagesAssignment 1, RAC - KME 601ANSH VERMANo ratings yet
- ME44001 17 18 S2 Tutorial 2Document48 pagesME44001 17 18 S2 Tutorial 2Tsz Chun YuNo ratings yet
- Termo2 PR3 2013Document3 pagesTermo2 PR3 2013Faiz FebriantoNo ratings yet
- ME 417 ProblemsDocument5 pagesME 417 ProblemsReina Grace PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Assignment On 'Refrigeration Cycle'Document3 pagesAssignment On 'Refrigeration Cycle'Anonymous GGtvR65MRNo ratings yet
- Exercise ASTU-1Document2 pagesExercise ASTU-1mikialeNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 2Document2 pagesAssignment No 2ISHPAL singhNo ratings yet
- RAC 6 SemDocument6 pagesRAC 6 SemAmrinder Singh SangheraNo ratings yet
- Quiz PendinginDocument3 pagesQuiz PendinginRamadhan ChavaleraNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document5 pagesSheet 2Ezz eldeen AymanNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Heat PumpDocument21 pagesRefrigeration and Heat PumpAnantaNo ratings yet
- RefgrigDocument1 pageRefgrigJj LewandyNo ratings yet
- ME405 RAC Question BankDocument8 pagesME405 RAC Question BankDeepakNo ratings yet
- Advanced Refrigeration Technology: o o P oDocument6 pagesAdvanced Refrigeration Technology: o o P oDhruvakumar Mallappa0% (2)
- Cap 04Document3 pagesCap 04Jorge PozoNo ratings yet
- Assinmnet 2 SampleDocument21 pagesAssinmnet 2 SampleHamair AliNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics - Refrigeration Cycle - Quiz 3Document88 pagesApplied Thermodynamics - Refrigeration Cycle - Quiz 3yashbhutada156No ratings yet
- Old Question Papers 2006-11-2Document27 pagesOld Question Papers 2006-11-2Sandip GurnuleNo ratings yet
- Rac Gtu SumsDocument8 pagesRac Gtu SumsNainesh SorathiyaNo ratings yet
- Section-1: Basic and Modified Vapor Compression CyclesDocument2 pagesSection-1: Basic and Modified Vapor Compression CyclesCesar ValenciaNo ratings yet
- RAC Assign 1Document2 pagesRAC Assign 1Arun BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering, IIT Madras ME3103: Energy Conversion Systems Tutorial - 2Document3 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering, IIT Madras ME3103: Energy Conversion Systems Tutorial - 2Harsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cascade SystemsDocument5 pagesCascade SystemsMark De LeonNo ratings yet
- Tugas 29 April 2016Document3 pagesTugas 29 April 2016api-316036600No ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument6 pagesRefrigerationriniz92No ratings yet
- Refrigeration HomeworkDocument1 pageRefrigeration HomeworkSimphiweNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3. Refrigeration Cycles 2Document37 pagesLecture 3. Refrigeration Cycles 2addisudagneNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration & Air Conditioning (1) - Sheets SolutionDocument25 pagesRefrigeration & Air Conditioning (1) - Sheets SolutionMohamed Maher100% (3)
- RAC Assignment No. 1Document3 pagesRAC Assignment No. 1Ankur SachdevaNo ratings yet
- BDA 37201 Engineering Lab V: Thermodynamics Air Conditioning SystemDocument18 pagesBDA 37201 Engineering Lab V: Thermodynamics Air Conditioning SystemMuhd I-dilNo ratings yet
- A.C Lecture 2Document5 pagesA.C Lecture 2mamnd tahaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 (ECE3153)Document1 pageAssignment 5 (ECE3153)Shahul14No ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 Heat Transfer Processes and Equipment Refrigeration ProcessesDocument2 pagesTutorial 9 Heat Transfer Processes and Equipment Refrigeration ProcessesHoài ThươngNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Pallav AgrawalNo ratings yet
- LIT - RFA Series Dryers - SAPRFADRY - enDocument4 pagesLIT - RFA Series Dryers - SAPRFADRY - encarlos chavezNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Analysis of A Ground-Source Heat Pump System For District HeatingDocument17 pagesThermodynamic Analysis of A Ground-Source Heat Pump System For District HeatingGile SimunovicNo ratings yet
- Zuari Cement, YerraguntlaDocument26 pagesZuari Cement, YerraguntlaKvnaveen KvnNo ratings yet
- TD42T DiagramDocument15 pagesTD42T DiagramleighNo ratings yet
- Leroi Gas Compressors: Installation - Operations Maintenance and Service GuideDocument36 pagesLeroi Gas Compressors: Installation - Operations Maintenance and Service Guidedavid lesmesNo ratings yet
- Fridge Dryer - UDA UDW GB - Rev2 PDFDocument4 pagesFridge Dryer - UDA UDW GB - Rev2 PDFGodel KHolikNo ratings yet
- Hisense VRF 60HzDocument71 pagesHisense VRF 60HzEdisson ValdiviezoNo ratings yet
- Dailey War Emergency Thrust Augmentation For The J47 Engine in TheDocument74 pagesDailey War Emergency Thrust Augmentation For The J47 Engine in TheAlice DeeNo ratings yet
- Industrial Refrigeration: Güntner CompetenceDocument19 pagesIndustrial Refrigeration: Güntner CompetenceWINNo ratings yet
- NL7.3FT Tropical Compressor R134a 220-240V 50Hz: GeneralDocument2 pagesNL7.3FT Tropical Compressor R134a 220-240V 50Hz: Generalbram samyNo ratings yet
- PTX (R-410A) SeriesDocument112 pagesPTX (R-410A) Seriesmorad omr0% (1)
- Mfsiimini - Fuel - Station Modular Extendable - SystemDocument4 pagesMfsiimini - Fuel - Station Modular Extendable - SystemKaiser IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lay Up Repairs - Engine 2017Document4 pagesLay Up Repairs - Engine 2017Mariyath Muraleedharan KiranNo ratings yet
- NRL2 50 186yDocument3 pagesNRL2 50 186yOnofreNo ratings yet
- Brosura ESM 2 - 5Document2 pagesBrosura ESM 2 - 5Valentin MalihinNo ratings yet
- Rotordynamics Problems in TurboMachinery PDFDocument443 pagesRotordynamics Problems in TurboMachinery PDFvickyflyer1No ratings yet
- EMYE70CLP Compressor p/r600Document4 pagesEMYE70CLP Compressor p/r600Alexandrojp OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Codigos de Falla Qsb6.7Document8 pagesCodigos de Falla Qsb6.7nortonNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Polymer & Polymerization: 3.1.1 Types of PolymersDocument41 pages3.1 Polymer & Polymerization: 3.1.1 Types of PolymersSumaira SaifNo ratings yet
- York Chiller YcivDocument80 pagesYork Chiller Ycivatiq100% (1)
- Maracaibo Oct 2010Document50 pagesMaracaibo Oct 2010garciahoNo ratings yet
- Is A Variable Speed Drive (VSD) Compressor The Right Choice For Your Facility?Document3 pagesIs A Variable Speed Drive (VSD) Compressor The Right Choice For Your Facility?Ahmad DeyabNo ratings yet
- Handbook For Cogeneration and Combined Cycle Power Plants: Second EditionDocument18 pagesHandbook For Cogeneration and Combined Cycle Power Plants: Second Editionsetyo nugrohoNo ratings yet