Professional Documents
Culture Documents
93 - Assignment - Geometrical Optics
93 - Assignment - Geometrical Optics
Uploaded by
jAy jAyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
93 - Assignment - Geometrical Optics
93 - Assignment - Geometrical Optics
Uploaded by
jAy jAyCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIVERSITY of GUYANA
Turkeyen Campus, Turkeyen, Greater Georgetown, P.O. Box 101110, Guyana, South America
Website: uog.edu.gy
---------------------------------
FACULTY OF NATURAL SCIENCES
Department of Mathematics, Physics & Statistics
Tel: + (592) 222-4926
PHY 1104 – Fundamentals of Physics (Recess 2020)
Lecturer: Mr Samuel Lee
Assignment # 3: Geometrical Optics
(Electronic Copy is Due Monday September 28, 2020)
Instructions to Students:
Attempt two (2) questions. This assignment is to be type-written or scanned then submitted as a
portable document (pdf). For type-written documents formatting is as follows: font theme – Times
New Roman; font size – 12; spacing – 1.0.
Physical Constant(s): Absolute refractive index of glass = 1.50; Absolute refractive index of
water = 1.33; Speed of light in a vacuum = 3.0 × 108 ms-1.
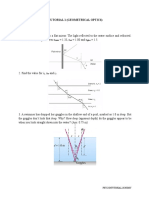
1. Two plane mirrors of length 0.5 m and 20.0 cm apart are placed with their reflecting
surfaces facing each other. If a ray of light were incident at the tip of one of the mirrors at
an angle of incidence 450, how many reflections would this ray suffer before leaving the
mirror system? (3)
2. A man 2.0 m tall, whose eye level is 1.84 m above the ground, looks at his image in a
vertical mirror. With the aid of a diagram, determine the minimum vertical length of the
mirror and the distance its lower edge must be above the floor if the man is to be able to
see his entire body provided he stands erect. (1.0 m; .92 cm)
3. A ray of light strikes a plane mirror at an angle of incidence 450. The mirror undergoes a
rotation of 150 into a new position, while the incident ray is kept fixed. What are the angle
of reflection and the angle through which the reflected ray is rotated? If the angle of
incidence is made 600 instead of 450, what is the angle of rotation of the reflected ray?
(600; 300)
14
4. A light wave has a frequency of 5.09 × 10 Hz in water and diamond of refractive index
2.42. What is the wavelength of this light in each medium? (4.4 × 10-7 m; (2.4 × 10-7 m)
5. A layer of oil (no = 1.45) floats on an unknown liquid. A ray of light shines from the oil
into the unknown liquid. The angles of incidence and refraction are respectively, 65 0 and
530. What is the refractive index of the unknown liquid and the speed of light in both
liquids? (1.7; 2.0 × 108 ms-1; 1.8 × 108 ms-1)
6. A ray of monochromatic light is incident at an angle of 300 on a prism of which the
refractive index is 1.52. What is the maximum refracting angle of the prism if the light is
just to emerge from the opposite face? (600)
7. A small logo is embedded in a thick block of crown glass (n = 1.52), 3.2 cm beneath the
top of the glass. The block is put under water, so there is 1.5 cm of water above the top of
the surface of the block. An observer in air views the logo directly above. How far beneath
the top surface of the water does the logo appear to be? (3.2 cm)
8. An optical fibre consists of a glass core of refractive index 1.60 and a glass cladding of
refractive index 1.40. What is the minimum angle of incidence that a ray of light in the
glass core must make at the core-cladding boundary to suffer total internal reflection?
(620)
9. If a concave mirror has a focal length of 10.0 cm, find the two positions where an object
can be placed to give, in each case, an image twice the size of the object. (5 cm; 15 cm)
10. When an object is placed 15 cm from a concave mirror, a real image four times the size of
the object is formed. Determine the focal length of the mirror and where the object must
be placed to produce a virtual image four times the height of the object. (12 cm; 9 cm)
11. An object is placed (i) 12 cm, (ii) 4 cm from a converging lens of focal length 6 cm.
Calculate the image position and magnification in each case.
(12 cm on opposite side; 1; 6 cm on same side; 1.5)
12. An object is placed 50.0 cm in front of a concave lens producing an image half its size.
Determine the focal length of the lens. (-25 cm)
You might also like
- SS2 Physics 3rd Term Lesson Note PDFDocument22 pagesSS2 Physics 3rd Term Lesson Note PDFAloysius Emmanuel100% (1)
- ZADATAK1 - Greda Sa Prepustom - BEAMGURU - Beam Calculator OnlineDocument3 pagesZADATAK1 - Greda Sa Prepustom - BEAMGURU - Beam Calculator OnlineDamir MatešićNo ratings yet
- Assignment #1 - Geometrical Optics and Interference: PHS - 1201: E, M & ODocument3 pagesAssignment #1 - Geometrical Optics and Interference: PHS - 1201: E, M & OShouvik MitraNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01: Science & Technology (Class-10) Chapter 10: Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument1 pageCbse Test Paper-01: Science & Technology (Class-10) Chapter 10: Light - Reflection and RefractionPawan SinghNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics AssgnDocument3 pagesRay Optics AssgnHimanshi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Practice Worksheet - Reflection, Refraction, LensDocument2 pagesPractice Worksheet - Reflection, Refraction, LensNaim RahmanNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Physics Holiday HomeworkDocument2 pagesClass 10 Physics Holiday Homeworkemailblaster1122No ratings yet
- CLASS_X_SCIENCE_5_29_2024_1_23_09_PMDocument15 pagesCLASS_X_SCIENCE_5_29_2024_1_23_09_PMmanjotdhiman459No ratings yet
- All Questions Are Compulsory: Topic - Reflection & RefractionDocument3 pagesAll Questions Are Compulsory: Topic - Reflection & Refractionshivanshu kushwahaNo ratings yet
- TEST ON LIGHT- LENS AND POWER - 2025Document3 pagesTEST ON LIGHT- LENS AND POWER - 2025dhruvdesh3No ratings yet
- OpticsDocument29 pagesOpticsVr MageshNo ratings yet
- Optics F 1 Ass 1Document11 pagesOptics F 1 Ass 1NikhilPrakashNo ratings yet
- Light-NCERT Notes Class 10Document2 pagesLight-NCERT Notes Class 10akashraj7713No ratings yet
- Light 1Document2 pagesLight 1SUSMIT SAHANo ratings yet
- PPP0101 Principles of Physics Tutorial 6Document3 pagesPPP0101 Principles of Physics Tutorial 6TAN XIN YINo ratings yet
- XII PHYSICS Sample Paper For CBSEDocument2 pagesXII PHYSICS Sample Paper For CBSEHari Om SinghNo ratings yet
- Exercise Solution of Reflection and RefractionDocument17 pagesExercise Solution of Reflection and RefractioniTutor Classes BapiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Frequency and Wavelength (Similar To One in The Book)Document29 pages1.1 Frequency and Wavelength (Similar To One in The Book)HarishNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Ray OpticsDocument2 pagesAssignment-Ray OpticstejvanshsandhuNo ratings yet
- Class 10 pt1 2023Document2 pagesClass 10 pt1 2023Laxman SdNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Phy250Document9 pagesTutorial 1 Phy250Muhammad AziziNo ratings yet
- Light - Intext & ExerciseDocument8 pagesLight - Intext & ExerciseTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Phys 162 Chapter 161-4Document4 pagesPhys 162 Chapter 161-4Aisha NurymgaliNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument33 pagesPadhle 10th - Light - Reflection & Refractionshreyasbandi0904No ratings yet
- 2013 Optics Assignment 1Document9 pages2013 Optics Assignment 1Marcos Aaron TherthensNo ratings yet
- 10 - Light Reflection and RefractionDocument6 pages10 - Light Reflection and RefractionsamNo ratings yet
- Reflection & Refraction of Light (Revision Questions) : Very Short Answer Type (1 Mark)Document10 pagesReflection & Refraction of Light (Revision Questions) : Very Short Answer Type (1 Mark)Muthu KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6: Optics - Ray Optics: Question BankDocument4 pagesUNIT 6: Optics - Ray Optics: Question BankNathanianNo ratings yet
- FHSC1034 Tutorial 6Document2 pagesFHSC1034 Tutorial 6Krishnaah SmuglerzzNo ratings yet
- Optics Class 10 PhysicsDocument16 pagesOptics Class 10 PhysicsKumkum KumariNo ratings yet
- Brilliant: Study Centre Repeaters Neet ExaminationDocument36 pagesBrilliant: Study Centre Repeaters Neet ExaminationRoronoa ZoroNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Ncert Ch10Document11 pages10 Science Ncert Ch10Kamal MaharaNo ratings yet
- 12 ISC, Physics, Prelim 2, Optics, 24-Dec-17, PodarDocument3 pages12 ISC, Physics, Prelim 2, Optics, 24-Dec-17, PodarNeelNo ratings yet
- OPTICS 1. Light From Sodium Lamp PassesDocument21 pagesOPTICS 1. Light From Sodium Lamp PassesNavneet100% (1)
- Me CB Problems 4Document1 pageMe CB Problems 4ddcvNo ratings yet
- Exam - OpticsDocument6 pagesExam - OpticsMahbubur Bhuiyan100% (2)
- Physical Optics - Problem Set 2Document2 pagesPhysical Optics - Problem Set 2Abhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and Refraction Part 2Document7 pagesLight - Reflection and Refraction Part 2Saji JayarajNo ratings yet
- Light - Class WorkDocument6 pagesLight - Class Workarunkumar0909iqNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics - 23 Jan - NADocument3 pagesRay Optics - 23 Jan - NAAnnieNo ratings yet
- CH. LIGHT-MLP - 2 (2023-24) (To Take Printout For Class Discussion)Document2 pagesCH. LIGHT-MLP - 2 (2023-24) (To Take Printout For Class Discussion)DhdubNo ratings yet
- Optics 1Document3 pagesOptics 1Pubg AppleNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet 1EDENINo ratings yet
- ISC Board Questions On Ray Optics Grade 12Document6 pagesISC Board Questions On Ray Optics Grade 12iraNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Assignment3Document3 pagesRay Optics Assignment3hsofficial910No ratings yet
- Refraction Q &a 10th ClassDocument2 pagesRefraction Q &a 10th ClassprakashNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument1 pageRay OpticsPornachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- X PhyDocument6 pagesX PhyTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics 2Document2 pagesRay Optics 2AryaNo ratings yet
- Extra Problem Phys 4 CH 2Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 4 CH 2Mario SamuelNo ratings yet
- CbseDocument15 pagesCbseYaaroNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper - 2011 Class - X Subject - Physics Light: Reflection and RefractionDocument2 pagesSample Paper - 2011 Class - X Subject - Physics Light: Reflection and RefractionArslaan MD BelalNo ratings yet
- LIGHT-PAST PAPER QnsDocument6 pagesLIGHT-PAST PAPER QnsARSHAD JAMIL100% (1)
- Ray Optics Questions STD Xii Holiday HWDocument5 pagesRay Optics Questions STD Xii Holiday HWamritmohanty1000No ratings yet
- Worksheet Ray OpticsDocument4 pagesWorksheet Ray OpticsYug GandhiNo ratings yet
- 1 Mark Questions: Subject:-Physics Topic: - Ray Optics Class-10 /12 Total Marks: 46 Marks Time: - 2 HrsDocument3 pages1 Mark Questions: Subject:-Physics Topic: - Ray Optics Class-10 /12 Total Marks: 46 Marks Time: - 2 HrsPriyanka Chandan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics: Previous Years' Board QuestionsDocument5 pagesRay Optics: Previous Years' Board QuestionsRudra SathwaraNo ratings yet
- 10_refraction19Document4 pages10_refraction19Gaurav SarohaNo ratings yet
- 1 LightDocument6 pages1 LightManmohan AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Science ACE - Atomic Model PamphletDocument2 pagesScience ACE - Atomic Model PamphletBenedict Lee100% (1)
- Advanced Drug Delivery System-Practical NoteDocument87 pagesAdvanced Drug Delivery System-Practical NoteOLA LUHANNo ratings yet
- Aromaticity PDFDocument9 pagesAromaticity PDFKishore KishoreNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cells: Galvanic Cell Oxidizing Agent Reducing Agent ProductDocument4 pagesFuel Cells: Galvanic Cell Oxidizing Agent Reducing Agent Productbashar68No ratings yet
- Advancements in Impulse Response Measurements by Sine SweepsDocument52 pagesAdvancements in Impulse Response Measurements by Sine SweepsFredy AlzateNo ratings yet
- Turbine HandbookDocument15 pagesTurbine HandbookViki Hari Fitrianto100% (6)
- Rinhs Science 9 4th Activity 2 Projectile Motion Word PuzzleDocument2 pagesRinhs Science 9 4th Activity 2 Projectile Motion Word PuzzleRyan BersaminNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument34 pagesPhysicsKoustav Pal70% (10)
- Recently Developed Heat Pump Assisted Distillation Configurations - A Comparative StudyDocument21 pagesRecently Developed Heat Pump Assisted Distillation Configurations - A Comparative StudyanirudhNo ratings yet
- Understanding Lyophilization Formulation Development: Frank Kofi Bedu-AddoDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Lyophilization Formulation Development: Frank Kofi Bedu-AddoRajeeb Chandra ShahaNo ratings yet
- Sample: Exhibit 1 Exhibit 1Document1 pageSample: Exhibit 1 Exhibit 1jessy eghNo ratings yet
- Review of Naphthenic Acid Corrosion in Oil RefiningDocument7 pagesReview of Naphthenic Acid Corrosion in Oil RefiningNoorain AhmadNo ratings yet
- China Standards and Foreign Standards Comparison Table 1.0Document14 pagesChina Standards and Foreign Standards Comparison Table 1.0papathsheilaNo ratings yet
- Ground Wires and Conductors 9.1 Mechanical ModelDocument1 pageGround Wires and Conductors 9.1 Mechanical Modelsulav shresthaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Design Project ReportDocument5 pagesHeat Transfer Design Project Reportapi-251662461No ratings yet
- PHD Thesis Zhiyin Duan PDFDocument189 pagesPHD Thesis Zhiyin Duan PDFYunus Emre GüzelelNo ratings yet
- Combined QP - M3 OCRDocument71 pagesCombined QP - M3 OCRhenry liuNo ratings yet
- Chap006 1 PDFDocument61 pagesChap006 1 PDFMR no oneNo ratings yet
- ASNTDocument5 pagesASNTshifaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Biology: College PhysicsDocument29 pagesConcepts of Biology: College PhysicsSamiNo ratings yet
- ICSE-Physics Sample Paper-1-Class 10 Question PaperDocument5 pagesICSE-Physics Sample Paper-1-Class 10 Question PaperFirdosh Khan100% (2)
- A Project Report On Wavelength of Sodium Light Using Newton's RingsDocument27 pagesA Project Report On Wavelength of Sodium Light Using Newton's RingsAnirudh Mittal100% (1)
- FLOCALC Calculation DetailsDocument21 pagesFLOCALC Calculation DetailsAhmed Hussein100% (1)
- Ate Shells 14218 PDFDocument38 pagesAte Shells 14218 PDFflorinelvv100% (1)
- Chaptest BDocument6 pagesChaptest BJun MitsuhashiNo ratings yet
- Vapor-Liquid Miscibility: Equilibria EthylDocument4 pagesVapor-Liquid Miscibility: Equilibria EthylRafael HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Veefill 222 H TDSDocument3 pagesVeefill 222 H TDSsaravanaplusNo ratings yet
- Tunnelling in Rock Masses - Guidelines: Part 2 Mechanized Tunnelling Methods by Tunnel Boring MachinesDocument38 pagesTunnelling in Rock Masses - Guidelines: Part 2 Mechanized Tunnelling Methods by Tunnel Boring MachinesDevesh Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions in Optical FiberDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Questions in Optical Fibersuresh100% (1)