Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Accountants Accountants: MBA, Y 5
Accountants Accountants: MBA, Y 5
Uploaded by
thapitcherOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Accountants Accountants: MBA, Y 5
Accountants Accountants: MBA, Y 5
Uploaded by
thapitcherCopyright:
Available Formats
Accountants
Accountants
Let YY be
Let be the
theyears
years of
of professional
professional experience.
experience. Then
Then we
we are
aregiven:
given: P(MBA)
P(MBA) == 0.35,
0.35, P(Y<5)
P(Y<5) ==0.45,
0.45, and
and P(MBA
P(MBAand
an
andY<5).
and Y<5).
Therefore, P(Y>=5)
Therefore, P(Y>=5) == 11-- P(Y<5)
P(Y<5) == 11-- 0.45
0.45 ==0.55
0.55and
andP(no
P(no MBA)
MBA) ==11 -- P(MBA)
P(MBA) == 11 --0.35
0.35 == 0.65.
0.65. So,
So, the
thedesired
desiredp
P(MBA and Y<5) + P(no MBA and
P(MBA and Y<5) + P(no MBA and Y>=5). Y>=5).
Let'sconcentrate
Let's concentrate on onfinding
finding the
theP(no
P(no MBA
MBA and
and Y>=5).
Y>=5).First,
First, P(MBA
P(MBA and
and Y>=5)
Y>=5) ++ P(no
P(no MBA
MBA and
and Y>=5)
Y>=5) == P(Y>=5)
P(Y>=5
andY>=5)
and Y>=5) == 0.55
0.55 --P(no
P(no MBA
MBA andandY>=5).
Y>=5).
Furthermore, P(no
Furthermore, P(no MBA
MBA and
and Y<5)
Y<5) ++P(no
P(no MBA
MBA and
and Y>=5)
Y>=5) ==P(no
P(no MBA)
MBA) ==0.65.
0.65. But
Butfrom
fromthe
the given
giveninformation
information tt
4/3*P(MBA and
4/3*P(MBA andY>=5).
Y>=5).This
This implies
implies 4/3*P(MBA
4/3*P(MBA and
and Y>=
Y>=5)
5) ++ P(no
P(no MBA
MBA and
and Y>=
Y>= 5)
5) ==0.65.
0.65. Alternatively,
Alternatively, P(MBA
P(MBA
MBA and
MBA and Y>=5)]
Y>=5)]== 3/4(0.65)
3/4(0.65) -- 3/4P(no
3/4P(no MBA
MBA and
andY>=5).
Y>=5).
These relationships
These relationships can
canbebe used
usedto
to find
find that
that 0.55
0.55-- P(no
P(no MBA
MBA andand Y>=5)
Y>=5) == 3/4(0.65)
3/4(0.65) -- 3/4P(no
3/4P(no MBA
MBA andand Y>=5).
Y>=5).
0.75(0.65) ==0.25P(no
0.75(0.65) 0.25P(no MBA
MBA and
andY>=5).
Y>=5).Equivalently,
Equivalently, 0.25
0.25 == P(no
P(no MBA
MBA and
and Y>=5)
Y>=5) which
which implies
implies that
that P(MBA
P(MBA and
and
But P(MBA
But P(MBA andand Y<5)
Y<5) == P(MBA)
P(MBA) --P(MBA
P(MBA and and Y>=5)
Y>=5) == 0.35
0.35-- 0.30
0.30 ==0.05.
0.05.
Finally, the
Finally, thedesired
desiredprobability
probabilityis0.05
is0.05++ 0.25
0.25 ==0.30.
0.30.
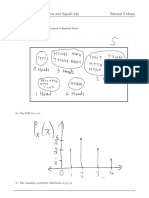
Analternative
An alternative more
morevisual
visual approach
approach isis toto draw
draw aarectangle
rectangle as
as shown
shown below
below and
andtry
try to
to fill
fill in
in the
the pieces,
pieces, using
using th t
problem. But basically the same calculations are still necessary. (The diagram below isn't drawn to scale, i.e., iti
problem. But basically the same calculations are still necessary. (The diagram below isn't drawn to scale, i.e.,
probabilitiescorrectly,
probabilities correctly, but
butitit gets
gets you
you started.)
started.)
MBA, Y<5 MBA, Y>=5
no MBA, Y<5 no MBA, Y>=5
= 0.35,
0.35, P(Y<5)
P(Y<5) ==0.45,
0.45, and
and P(MBA
P(MBAand
andY>=5)
Y>=5) == 0.75
0.75 **P(no
P(no MBA
MBA
A) == 11 --0.35
A) 0.35 == 0.65.
0.65. So,
So, the
thedesired
desiredprobability
probabilityisisthe
the sum
sumof
of
=5) ++ P(no
=5) P(no MBA
MBA and
and Y>=5)
Y>=5) == P(Y>=5)
P(Y>=5) ==0.55.
0.55. Alternatively,
Alternatively, P(MBA
P(MBA
65. But
65. Butfrom
fromthe
the given
giveninformation
information that
that P(no
P(no MBA
MBA and
andY<5)
Y<5) ==
dd Y>=
Y>= 5)
5) ==0.65.
0.65. Alternatively,
Alternatively, P(MBA
P(MBA and
and Y>=5)
Y>=5) ==3/4[0.65
3/4[0.65 -- P(no
P(no
3/4(0.65)
/4(0.65) -- 3/4P(no
3/4P(no MBA
MBA andand Y>=5).
Y>=5). This
Thisreduces
reduces toto0.55
0.55 --
Y>=5) which
Y>=5) which implies
implies that
that P(MBA
P(MBA and
andY>=5)
Y>=5) == 0.55
0.55 -- 0.25
0.25 == 0.30.
0.30.
w and
w andtry
try to
to fill
fill in
in the
the pieces,
pieces, using
using thethe information
informationgiven
givenin
inthe
the
am below isn't drawn to scale, i.e., it doesn't represent
am below isn't drawn to scale, i.e., it doesn't represent the the
You might also like
- Assignment 6Document3 pagesAssignment 6Nuo XuNo ratings yet
- Sept 22Document2 pagesSept 22Sia SJNo ratings yet
- SS344 Tut3 MemoDocument6 pagesSS344 Tut3 Memolovejoy mhishiNo ratings yet
- Math Wajib 2Document3 pagesMath Wajib 2danishaNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Q4 WK4 Las3Document1 pageMath 10 Q4 WK4 Las3HarleysheinNo ratings yet
- 03 RA - (Probability) GRP 1.0 SolutionDocument4 pages03 RA - (Probability) GRP 1.0 SolutionrudrabeproductiveNo ratings yet
- DOKA Paper R (For Year Level 5-6) Sample Questions: (Part A - Basic Reasoning)Document4 pagesDOKA Paper R (For Year Level 5-6) Sample Questions: (Part A - Basic Reasoning)Mehdi MoradiNo ratings yet
- Chap 005Document18 pagesChap 005Bruno MarinsNo ratings yet
- Ial Maths s1 CR4Document10 pagesIal Maths s1 CR4Martha MessinaNo ratings yet
- Case: Blake Electronics: Prior Probabilities Conditional Probabilities From I&KDocument3 pagesCase: Blake Electronics: Prior Probabilities Conditional Probabilities From I&KgerralanuzaNo ratings yet
- TimeTable July 2019 FinalDocument14 pagesTimeTable July 2019 FinalUtkarsh GoelNo ratings yet
- Patterns, Sequences and Series: AnswersDocument10 pagesPatterns, Sequences and Series: AnswersDaniel M ZapataNo ratings yet
- Final Exam (Econ 301, Spring 2015) : NameDocument3 pagesFinal Exam (Econ 301, Spring 2015) : Name범상준No ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Making Hard Decisions With DecisionTools 3rd Edition Clemen Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument44 pages(Download PDF) Making Hard Decisions With DecisionTools 3rd Edition Clemen Solutions Manual Full Chapterdrehnvrus100% (9)
- More-Frank Sinatra - FULL Big BandDocument1 pageMore-Frank Sinatra - FULL Big BandlcastillodamianNo ratings yet
- Probability - SolutionsDocument9 pagesProbability - SolutionsFrank MartinezNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For College Algebra Concepts Through Functions 3Rd Edition by Sullivan Isbn 0321925742 9780321925749 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesTest Bank For College Algebra Concepts Through Functions 3Rd Edition by Sullivan Isbn 0321925742 9780321925749 Full Chapter PDFbryan.sanchez186100% (11)
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 ProbabilityDocument65 pagesNCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 Probabilitysoniyavrma0967No ratings yet
- Chap005 ASBE 6e IMDocument16 pagesChap005 ASBE 6e IMAmarjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Circle Approach To Trigonometry 3rd Edition Sullivan 0321931041 9780321931047Document36 pagesCircle Approach To Trigonometry 3rd Edition Sullivan 0321931041 9780321931047robert.huff822100% (11)
- Stat 4710 HW 3Document8 pagesStat 4710 HW 310802117No ratings yet
- Sachs Presentation V8 Jan 5Document24 pagesSachs Presentation V8 Jan 5brentNo ratings yet
- Stat 330 Solution To Homework 3 1 Independence, Baron P. 40Document4 pagesStat 330 Solution To Homework 3 1 Independence, Baron P. 40Pei JingNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Cap 17Document8 pagesSolucionario Cap 17Avril Bolondi MedinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02-Describing Distributions With Numbers-2023!09!13Document22 pagesChapter 02-Describing Distributions With Numbers-2023!09!13amandaluvsanimalsNo ratings yet
- Math10 Q4 Week2Document6 pagesMath10 Q4 Week2Shakira MunarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Review: Sin 40°cos10° - Cos 40°sin10° As Cos (X - Y) Sin yDocument8 pagesChapter Review: Sin 40°cos10° - Cos 40°sin10° As Cos (X - Y) Sin yMer CyNo ratings yet
- Complex Analysis PracticalsDocument15 pagesComplex Analysis PracticalsChitparaNo ratings yet
- Set Algebra: Universal Set Set ElementDocument10 pagesSet Algebra: Universal Set Set ElementvalladiNo ratings yet
- Precalculus Concepts Through Functions A Unit Circle Approach To Trigonometry 3rd Edition Sullivan Test BankDocument31 pagesPrecalculus Concepts Through Functions A Unit Circle Approach To Trigonometry 3rd Edition Sullivan Test Banksparpoil.pian.dpxd100% (33)
- B6644642 Siritidaporn Tubson HW7Document5 pagesB6644642 Siritidaporn Tubson HW7siri250448No ratings yet
- Apuntes CVDocument7 pagesApuntes CVMichael HinojosaNo ratings yet
- HW2 - TH ChenDocument4 pagesHW2 - TH ChensandyNo ratings yet
- RUBd XAVBVJaaoh SMBL VFX BFW 0 KHBSewnz GPip FC 2Document4 pagesRUBd XAVBVJaaoh SMBL VFX BFW 0 KHBSewnz GPip FC 2omardohim1No ratings yet
- Term 3 Sek Tinggi KLG (A)Document4 pagesTerm 3 Sek Tinggi KLG (A)Masytah YazidNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods and ProgrammingDocument197 pagesNumerical Methods and Programmingsatyajeetsince2001No ratings yet
- Cbjemacq07 PDFDocument24 pagesCbjemacq07 PDFHilsa Das Hilsa DasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Methods in New SyllabusDocument17 pagesAssessment Methods in New SyllabusAdityaNo ratings yet
- Coordinate and Trigonometry BashingDocument9 pagesCoordinate and Trigonometry BashingAayush BorkarNo ratings yet
- Fall 2023 - MTH302 - 1 - BC230430565Document2 pagesFall 2023 - MTH302 - 1 - BC230430565afaqnawab40No ratings yet
- Dermatophagoides Pteronyssinus ImmunotherapyDocument1 pageDermatophagoides Pteronyssinus ImmunotherapyTahia Fernández DuarteNo ratings yet
- QREf Vu W0 U 4 L 8 B1 A L1 SHFROo 79 Uaai IBr GM 9 Ja RYKDocument4 pagesQREf Vu W0 U 4 L 8 B1 A L1 SHFROo 79 Uaai IBr GM 9 Ja RYKmkalhrby69No ratings yet
- Rzuty Fizyka NotatkaDocument2 pagesRzuty Fizyka Notatkalenka.wasiakNo ratings yet
- Solution Mid 2021Document9 pagesSolution Mid 2021minh hoangNo ratings yet
- Curves IIDocument28 pagesCurves IIPablo Villa JaramilloNo ratings yet
- CSEC Add Maths 2022 June Past Paper SolutionsDocument27 pagesCSEC Add Maths 2022 June Past Paper SolutionsAnu RNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - TOPIC 13.4 Economics - 15 August 2022Document26 pagesMathematics - TOPIC 13.4 Economics - 15 August 2022mike reyes100% (1)
- Prob Theory 1Document4 pagesProb Theory 1Lourd John JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 SDocument16 pagesTutorial 4 SKUSUMITA PALNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Latihan 4BDocument4 pagesJawapan Latihan 4BSITI NURSYAKIRAH BINTI ZAINUDDINNo ratings yet
- Or 415 Tut 3prep - 2024 MemoDocument8 pagesOr 415 Tut 3prep - 2024 Memoaidanansley2468No ratings yet
- D2 Fill Up To 5600m-4060Document1 pageD2 Fill Up To 5600m-4060FeteneNo ratings yet
- Copia de CW 1-8 Hypothesis Testing For P and Mu PINTO - ABRILDocument6 pagesCopia de CW 1-8 Hypothesis Testing For P and Mu PINTO - ABRILNatalie Abril MuñozNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 201/1/2017: Quantitative Modelling 1 DSC1520Document7 pagesTutorial Letter 201/1/2017: Quantitative Modelling 1 DSC1520Khathutshelo KharivheNo ratings yet
- COPO TrailDocument63 pagesCOPO TrailnaacabrsubmitNo ratings yet
- Mercullo HW Non ParametricDocument5 pagesMercullo HW Non ParametricEndrei Clyne MerculloNo ratings yet
- Qommcan: P (Amb: (Document2 pagesQommcan: P (Amb: (4g7sk4fbm5No ratings yet
- The Probability Distribution of X Is As Follows: X P (X X) 2.0 0.1111 2.5 0.2222 3.0 0.4444 3.5 0.2222 Check: 1.000Document1 pageThe Probability Distribution of X Is As Follows: X P (X X) 2.0 0.1111 2.5 0.2222 3.0 0.4444 3.5 0.2222 Check: 1.000thapitcherNo ratings yet
- The Probability Distribution of X Is As Follows: X P (X X) 0 0.1 1 0.2 2 0.3 3 0.3 4 0.1 1.000Document1 pageThe Probability Distribution of X Is As Follows: X P (X X) 0 0.1 1 0.2 2 0.3 3 0.3 4 0.1 1.000thapitcherNo ratings yet
- Gaining New Subscriptions Gaining New SubscriptionsDocument2 pagesGaining New Subscriptions Gaining New SubscriptionsthapitcherNo ratings yet
- Construction Management Chapter 4Document33 pagesConstruction Management Chapter 4thapitcherNo ratings yet
- Household Security Systems Household Security SystemsDocument2 pagesHousehold Security Systems Household Security SystemsthapitcherNo ratings yet
- Construction Management Chapter 5Document37 pagesConstruction Management Chapter 5thapitcherNo ratings yet
- Construction Management Chapter 2Document92 pagesConstruction Management Chapter 2thapitcherNo ratings yet
- Construction Management Chapter 3Document113 pagesConstruction Management Chapter 3thapitcherNo ratings yet
- I4eti UPSDocument4 pagesI4eti UPSRavi prasad GurugubelliNo ratings yet
- Revision Guide Chemistry 7J: Current Electricity Exploring Science PAGE 151 TO 165Document7 pagesRevision Guide Chemistry 7J: Current Electricity Exploring Science PAGE 151 TO 165TALAL ALNAIMYNo ratings yet
- Distillation Column Tray Selection & SizingDocument20 pagesDistillation Column Tray Selection & SizingMOHANRAJ.GNo ratings yet
- Dimension Analysis and SimultideDocument11 pagesDimension Analysis and SimultideShavin ChandNo ratings yet
- AIATS Schedule For RM (XII Passed) 2020-21 - Version 3.0-2Document2 pagesAIATS Schedule For RM (XII Passed) 2020-21 - Version 3.0-2Saksham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 2Q Exam Study GuideDocument7 pagesPhysical Science 2Q Exam Study GuideSir HakuNo ratings yet
- CHE 101 Out Line-Lecture Schedule 2020-21Document2 pagesCHE 101 Out Line-Lecture Schedule 2020-21AG STXLEZNo ratings yet
- Elegantia College (Sponsored by Education Convergence) Second Term Examination (2018 - 2019) Form 5 Combined Science - Physics (Section A)Document10 pagesElegantia College (Sponsored by Education Convergence) Second Term Examination (2018 - 2019) Form 5 Combined Science - Physics (Section A)edmond 黃No ratings yet
- Aashto T324-14Document10 pagesAashto T324-14kevin zamudio portocarreroNo ratings yet
- Présentation de La Norme CEMA ConvoyeursDocument36 pagesPrésentation de La Norme CEMA ConvoyeursahmedNo ratings yet
- PD Cen TR 13930-2009 (2010)Document32 pagesPD Cen TR 13930-2009 (2010)Sadek SadNo ratings yet
- 01 Synchronous Generators 2Document63 pages01 Synchronous Generators 2JeremiahNo ratings yet
- 3GBA282270 ADF M2bax 280smg 4Document2 pages3GBA282270 ADF M2bax 280smg 4chmatias3No ratings yet
- 2 1 Causes of Friction 2Document8 pages2 1 Causes of Friction 2Tiisetso MokwaneNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides CHM457Document59 pagesAlkyl Halides CHM457AIMAN IMAN SHAIFUDDINNo ratings yet
- Laser QuizDocument1 pageLaser QuizAhmed AboelataNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Geotechnical Engineering TermsDocument18 pagesGlossary of Geotechnical Engineering TermsAmanda CervantesNo ratings yet
- 01 - Lecture 2 - 1D 2D MotionDocument80 pages01 - Lecture 2 - 1D 2D MotionONCE ThaqiefNo ratings yet
- Acsanm.9b02407 IMPDocument14 pagesAcsanm.9b02407 IMPDharmesh VaradeNo ratings yet
- Manual Metasys MST1 SeparatorDocument16 pagesManual Metasys MST1 SeparatorCezar Sebastian AntoniuNo ratings yet
- EVC600C User Manual (English)Document6 pagesEVC600C User Manual (English)dhany reza100% (1)
- CartoDocument5 pagesCartoLaarni HilarioNo ratings yet
- Apparatus:: AIM: Acquire The Knowledge of Output Devices Like CRO and DSO For Observing OutputDocument5 pagesApparatus:: AIM: Acquire The Knowledge of Output Devices Like CRO and DSO For Observing OutputAdwait BorikarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-01: The Solid StateDocument15 pagesCBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-01: The Solid StateRitik Kumar NayakNo ratings yet
- CentspotDocument2 pagesCentspotvicky khanNo ratings yet
- Class 10th 2m, 4m and 7m NP QuestionDocument9 pagesClass 10th 2m, 4m and 7m NP Questiondharunace7No ratings yet
- Pump FMEADocument177 pagesPump FMEASyed ASIM motplNo ratings yet
- PID&Ctrl 4dummiesDocument17 pagesPID&Ctrl 4dummiesRamius HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Aerodynamics ThesisDocument6 pagesVehicle Aerodynamics Thesiskimberlythomasarlington100% (2)
- Chapter 6XDocument70 pagesChapter 6XvinidesoNo ratings yet