Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ces511 - 3 Hinged Lab - Discussion
Ces511 - 3 Hinged Lab - Discussion
Uploaded by
marina zamriOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ces511 - 3 Hinged Lab - Discussion
Ces511 - 3 Hinged Lab - Discussion
Uploaded by
marina zamriCopyright:
Available Formats
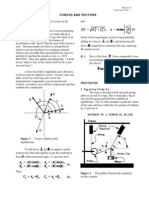
Graph 1: graph shows the different between Experimental Horizontal Thrust (N) and Actual
Horizontal Thrust (N) for Set 1.
Set 1
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
0
5 10 15 20 25
Actual Thrust Experimental Hprizontal Thrust
Graph 2: graph shows the different between Experimental Horizontal Thrust (N) and Actual
Horizontal Thrust (N) for Set 6.
Set 6
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
0
Test 1 Test 2 Test 3 Test 4 Test 5
Actual Horizontal Thrust (N) Experimental Horizontal Thrust (N)
DISCUSSION
support and the applied load are
directly proportional, the higher
the
load the higher the horizontal
thrust at the support
We can conclude that the
relationship between horizontal
thrust at the
support and the applied load are
directly proportional, the higher
the
load the higher the horizontal
thrust at the support
From the experiment, we can conclude that the relationship between horizontal thrust at the
support and the applied load is directly proportional, the higher the load the higher the horizontal
thrust at the support.
At hinge at the crown, the rotation of the connected structure is not prevented Therefore, the
moment is zero as it does not resist rotation. Whereas in fixed supports, the bending moment is
nonzero as it resists rotation of the connected structure.
Based on the result for test 1 (Graph 1), the Experimental Horizontal Thrust value is lower than
Theoretical Horizontal Thrust value. The bigger the loads applied, the bigger the gaps between
Experimental Horizontal Thrust’s line and the Theoretical Horizontal Thrust’s line.
The result for test 6 (Graph 2), the Experimental Horizontal Thrust is higher than Theoretical
Horizontal Thrust value. The gap between each Horizontal Thrust value is almost same indicates
that the value of experimental and theoretical for this experiment is almost the same.
The percentage error for Set 1 were in between of 49% to 51% which are more than 15%, while
the percentage errors for Set 6 are in between 5 % to 10%. The accuracy is how close the
experimental value with theoretical value, this shows that Set 1 have the higher accuracy than Set
6. That often relates to the calibration of the device. Percent error is just the determination of
how the possible values may varies from the actual value.
There are many causes of that, such as the digital indicator cannot detect the remaining load that
acted on the arch after changing the load multiple times. The type of arch material may also
affect the distribution load on its body.
You might also like
- Lab ReportDocument14 pagesLab ReportByron DizonNo ratings yet
- Total Evaporable Moisture Content of Aggregate by Drying: Standard Test Method ForDocument3 pagesTotal Evaporable Moisture Content of Aggregate by Drying: Standard Test Method ForYarisel Shosha MuñozNo ratings yet
- Lab Report (Spring) - Behaviour of Simple BeamsDocument16 pagesLab Report (Spring) - Behaviour of Simple BeamslemonteemanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 8Document4 pagesLab Report 8Stefan JenkinsNo ratings yet
- Experiment - Three Hinge ArchDocument4 pagesExperiment - Three Hinge ArchAmeera AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Critical Depth 171Document7 pagesCritical Depth 171Vintila DragosNo ratings yet
- Phys101l E02Document3 pagesPhys101l E02Ej psNo ratings yet
- Cast Steel: True Stress - True Strain Curve: AbstractDocument5 pagesCast Steel: True Stress - True Strain Curve: AbstractAli ErdoganNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Martin Kgoleyamotho 202201867Document14 pagesLab 2 Martin Kgoleyamotho 202201867aaschlysebakisoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: - 03 Name of Experiment: - The Torsion System. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesExperiment No: - 03 Name of Experiment: - The Torsion System. ObjectivesNewton ShikderNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 LRDocument13 pagesLab 6 LRAlimin AnniNo ratings yet
- Shear Force (1) : ObjectiveDocument6 pagesShear Force (1) : ObjectiveAltamashuddin KhanNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 (Topic 9)Document4 pagesLab 2 (Topic 9)diva nathanNo ratings yet
- H21SEM: Group A13Document28 pagesH21SEM: Group A13TsukomaruNo ratings yet
- Experiment 102 Friction: PhysicsDocument4 pagesExperiment 102 Friction: PhysicsJag MasterNo ratings yet
- Objective Lab1Document27 pagesObjective Lab1Karthik MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Measurements of Force, Torque and Pressure: ObjectivesDocument34 pagesMeasurements of Force, Torque and Pressure: ObjectivesDr. Nandini R MechanicalNo ratings yet
- Force Table LabDocument5 pagesForce Table LabqwesghwqedfgNo ratings yet
- 6.0 Result: Mass (G) Load (N) Force (N) Experimental Shear Force (N) Theoretical Shear Force (N)Document11 pages6.0 Result: Mass (G) Load (N) Force (N) Experimental Shear Force (N) Theoretical Shear Force (N)Nazreen RahimNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Blog DraftDocument4 pagesExperiment 2 - Blog DraftNikko San QuimioNo ratings yet
- 4 Forces, Density & PressureDocument26 pages4 Forces, Density & PressureAmad AliNo ratings yet
- Topic 3: Shear Force of A BeamDocument19 pagesTopic 3: Shear Force of A BeamhafizNo ratings yet
- ch04 07ggggDocument5 pagesch04 07ggggwill bellNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Balancing of RotorsDocument60 pagesDynamic Balancing of RotorsAmir Mahmoud Mahdavi Abhari100% (3)
- E105 FrictionDocument14 pagesE105 FrictionJoshNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5: Hooke's LawDocument8 pagesExperiment 5: Hooke's LawDave Vendivil SambranoNo ratings yet
- 09 CH-1 1.8 and 1.9 Testing of MaterialsDocument16 pages09 CH-1 1.8 and 1.9 Testing of MaterialsTooling ganeshNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of ForcesDocument10 pagesEquilibrium of ForcesArakans RedxNo ratings yet
- Corrected True Stress - True Strain CurvDocument3 pagesCorrected True Stress - True Strain CurvPunith MlNo ratings yet
- KissDocument4 pagesKissapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Three Hinged ArchDocument11 pagesThree Hinged ArchPak Ru JingNo ratings yet
- Lab 03Document3 pagesLab 03Ranu GamesNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Report 5Document3 pagesPhysics Lab Report 5raphaelNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Report Solid MechanicsDocument8 pagesExperiment 1 Report Solid MechanicsRizqy AgungNo ratings yet
- Strain MeasurementDocument40 pagesStrain MeasurementNavinRajSakaranNo ratings yet
- Bending MomentDocument12 pagesBending Momenthazheer1100% (2)
- Sulam ProjectDocument21 pagesSulam ProjectAhmed RaeesNo ratings yet
- True Stress Strain Curve PDFDocument4 pagesTrue Stress Strain Curve PDFSelva BabuNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 02Document5 pagesExperiment No 02Farhan AliNo ratings yet
- Test ImpactDocument14 pagesTest ImpactDomnica StanciuNo ratings yet
- Shear Force Bending MomentDocument3 pagesShear Force Bending Momenttan hongNo ratings yet
- Engineering Structural Integrity Assessment: Where Are We Today?Document1 pageEngineering Structural Integrity Assessment: Where Are We Today?Rana Muhammad Abdullah WakeelNo ratings yet
- E105Document10 pagesE105Kenneth PeraNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyDocument6 pagesEquilibrium of A Rigid BodyAnchezska Tan0% (1)
- Lab #10Document3 pagesLab #105377773No ratings yet
- Equilibrium and StaticsDocument5 pagesEquilibrium and StaticsRyuuji021No ratings yet
- BFM2821 Mechanics Laboratory ReportDocument6 pagesBFM2821 Mechanics Laboratory ReportIqbal Jafar75% (4)
- Report 4Document6 pagesReport 4Paul Adrian JavénNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials II: UET, TaxilaDocument61 pagesMechanics of Materials II: UET, TaxilaSyh TfkNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Loadings: Prismatic BarDocument7 pagesFundamental Loadings: Prismatic BarAGEGTAMNo ratings yet
- Curved BeamsDocument19 pagesCurved BeamsRobel MetikuNo ratings yet
- Forces Vectors and EquilibriumDocument12 pagesForces Vectors and Equilibriumgaragegreat26No ratings yet
- Portal FrameDocument7 pagesPortal FrameAzzren Azzrain100% (2)
- Experiment No: - 04 Name of Experiment: - Tension System. ObjectivesDocument8 pagesExperiment No: - 04 Name of Experiment: - Tension System. ObjectivesNewton ShikderNo ratings yet
- Portal FrameDocument7 pagesPortal FrameMuhammad Hasrul HasnanNo ratings yet
- ET202A B-1 (Unit 3)Document21 pagesET202A B-1 (Unit 3)Darrell Carl Rizo JoseNo ratings yet
- Gorom Angelica Lirio R. Phys101l b8 E102 2q1819Document3 pagesGorom Angelica Lirio R. Phys101l b8 E102 2q1819Janno RafaelNo ratings yet
- HES1125 Equilbrium of CantileverDocument6 pagesHES1125 Equilbrium of CantileverFarrukhNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid: "COOH" Redirects Here. For The Bulgarian Musician, SeeDocument9 pagesCarboxylic Acid: "COOH" Redirects Here. For The Bulgarian Musician, SeeFighter_ace_97No ratings yet
- Introductory Thermal Physics Worksheets and SolutionsDocument30 pagesIntroductory Thermal Physics Worksheets and SolutionsLetmiDwiridalNo ratings yet
- Makalah Astronomi (Bulan Fixx)Document28 pagesMakalah Astronomi (Bulan Fixx)PoniahNo ratings yet
- Objective (MCQ) Chemical Engineering SampleDocument25 pagesObjective (MCQ) Chemical Engineering SampleKapilSahu50% (2)
- Certificate of Analysis - Certified Reference Material Certipur Sulfur ICP Standard 1000 MG/L SDocument2 pagesCertificate of Analysis - Certified Reference Material Certipur Sulfur ICP Standard 1000 MG/L SAndresOchoaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction of Steel StructureDocument57 pages1.1 Introduction of Steel StructureNazihahNo ratings yet
- Cold Pilger Rolling - Part One - KEY To METALS ArticleDocument3 pagesCold Pilger Rolling - Part One - KEY To METALS Articlekumarpankaj030No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 10: Junior High School DepartmentDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Science 10: Junior High School DepartmentJoanne GodezanoNo ratings yet
- Alan - Macdonald 2012 A.survey - Of.geometric - Algebra.and - Geometric.calculusDocument33 pagesAlan - Macdonald 2012 A.survey - Of.geometric - Algebra.and - Geometric.calculusgiantgeorgeNo ratings yet
- General Pre Stress and ElasticDocument28 pagesGeneral Pre Stress and ElasticJorge Nickolai NavalesNo ratings yet
- SKYMARK C-Series Water-Cooled Self-Contained Units Catalog (1112)Document24 pagesSKYMARK C-Series Water-Cooled Self-Contained Units Catalog (1112)Carlos MelgarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 HydraulicsDocument9 pagesExperiment 1 Hydraulicsmon patrick pradoNo ratings yet
- LagrangeDocument32 pagesLagrangepuiteraNo ratings yet
- Dan Flavin Through The Eyes of Death of The AuthorDocument4 pagesDan Flavin Through The Eyes of Death of The AuthorMarshall BergNo ratings yet
- DC Lab ReportDocument22 pagesDC Lab ReportNaveen KarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- Basics in Mineral Processing-Introduction1Document9 pagesBasics in Mineral Processing-Introduction1makedo33100% (1)
- SCH2100 43 62494596-HeaterDocument2 pagesSCH2100 43 62494596-HeaterstretchthesleepyNo ratings yet
- ZZ - Introduction To Lorentz Geometry Curves and Surfaces by Alexandre Lymberopoulos and Ivo Terek CoutoDocument351 pagesZZ - Introduction To Lorentz Geometry Curves and Surfaces by Alexandre Lymberopoulos and Ivo Terek Coutorajesh kumarNo ratings yet
- As 2378-1996 Density BottlesDocument7 pagesAs 2378-1996 Density BottlesSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- SCIT - SampleTest Pattern For 2015Document8 pagesSCIT - SampleTest Pattern For 2015heeNo ratings yet
- Lifting Lug - Skid - 2018.07.16Document4 pagesLifting Lug - Skid - 2018.07.16RaghNo ratings yet
- Vario by VELUX - Sales BrochureDocument17 pagesVario by VELUX - Sales BrochuredanNo ratings yet
- Protection Relay Tester: Model No. JBC-702Document3 pagesProtection Relay Tester: Model No. JBC-702pemanr1914No ratings yet
- Final Presentation On Super CapacitorDocument40 pagesFinal Presentation On Super Capacitorapi-3798420100% (1)
- S.T.E.M: Unit Plan For SemesterDocument23 pagesS.T.E.M: Unit Plan For SemesterDavid DowningNo ratings yet
- AVK Dam Reservoir Applications Glenfield PDFDocument16 pagesAVK Dam Reservoir Applications Glenfield PDFsexmanijakNo ratings yet
- The DelFly 9401792070.the1bstDocument221 pagesThe DelFly 9401792070.the1bstAnonymous QlJjisdlLI0% (1)
- 10th Science Question Bank Experiment-3Document5 pages10th Science Question Bank Experiment-3mukul kumarNo ratings yet
- X Maths PaperDocument5 pagesX Maths Paperankurpapneja4100% (1)