Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views3-69 Shigley
3-69 Shigley
Uploaded by
inivlaviThe document analyzes the forces, torques, shear forces, and bending moments acting on a shaft assembly with two motors attached at different distances. It is determined that:
1) The torque produced by the first motor is 2880 N and the second motor is 432 N.
2) The reaction force at point C is 1794 N.
3) The maximum bending moment of 698.28 N-m occurs at a distance of 230 mm from end A.
4) The maximum normal and shear stresses are 275.51 MPa and 143.8 MPa respectively.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- B18 Statics - Moment - Problems PDFDocument30 pagesB18 Statics - Moment - Problems PDFifa noskiNo ratings yet
- WMS (Method Statement For Pouring Concrete On Slab On Grade)Document4 pagesWMS (Method Statement For Pouring Concrete On Slab On Grade)PUI CHEE KHIAN100% (1)
- 3-69 ShigleyDocument3 pages3-69 ShigleyinivlaviNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Test 07Document29 pagesSolutions To Test 07Princess Gupo TañasNo ratings yet
- 2020 03 10Document12 pages2020 03 10AndikaNo ratings yet
- U1 v1 U2 v2 U1 v1 U2 v2Document12 pagesU1 v1 U2 v2 U1 v1 U2 v2AndikaNo ratings yet
- 2020 03 10Document12 pages2020 03 10Tito WirasatyaNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2Manupriya KapleshNo ratings yet
- HX 103Document13 pagesHX 103Weng Keat ChongNo ratings yet
- Lifting Lug Cal PDFDocument1 pageLifting Lug Cal PDFveeru2906No ratings yet
- Shrink FitDocument6 pagesShrink FitParag NaikNo ratings yet
- Resulting Force On Pipe BendDocument5 pagesResulting Force On Pipe BendJiaching LiewNo ratings yet
- 2WAY Slab Design TOMAS 2Document4 pages2WAY Slab Design TOMAS 2kingazure31No ratings yet
- Design of Replaceent Scheme of Inadequate GussetDocument9 pagesDesign of Replaceent Scheme of Inadequate GussetPartha GangopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and ConstructionDocument32 pagesReinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and ConstructiongauravNo ratings yet
- B17 Statics - Moment - ProblemsDocument30 pagesB17 Statics - Moment - ProblemsJCLLNo ratings yet
- MD Singh Power Electronics Solution Manual To Chapter 15Document15 pagesMD Singh Power Electronics Solution Manual To Chapter 15Anoop MathewNo ratings yet
- B16 Statics - Moment - Problems PDFDocument31 pagesB16 Statics - Moment - Problems PDFMuhammad Fazeel KhanNo ratings yet
- ME511 AssignmentDocument10 pagesME511 AssignmentridwanmuhammadtajudeenNo ratings yet
- 02-04 Chap GereDocument12 pages02-04 Chap GereSri DNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Davit CalculationDocument8 pagesDokumen - Tips Davit CalculationJagdish KotadiyaNo ratings yet
- Section 3A - Dynamic StabilityDocument8 pagesSection 3A - Dynamic StabilityAhmad YasserNo ratings yet
- Torsion Report PDFDocument31 pagesTorsion Report PDFSheikh BajunaidNo ratings yet
- Resolver Smart SynDocument12 pagesResolver Smart SynLeon de RuijterNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument41 pagesInduction MotorRiyadh Al Nur0% (1)
- Numerical ExamplesDocument20 pagesNumerical ExampleslitrakhanNo ratings yet
- Solution: Given Data:: 165 Kpa 69 CDocument30 pagesSolution: Given Data:: 165 Kpa 69 Cyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- Solution: Given Data:: 165 Kpa 69 CDocument83 pagesSolution: Given Data:: 165 Kpa 69 Cyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- SFB Longi ExtDocument11 pagesSFB Longi ExtJhonmar DelapenaNo ratings yet
- FisicaDocument2 pagesFisicajonathantorresloboNo ratings yet
- PR - PR - (5380)Document17 pagesPR - PR - (5380)Notrex 24No ratings yet
- Module 4 Activity No. 3Document7 pagesModule 4 Activity No. 3John Mark AlvesNo ratings yet
- CNG FoundationDocument19 pagesCNG FoundationsamiNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Cap. 4 Mecánica de Materiales ChapraDocument12 pagesSolucionario Cap. 4 Mecánica de Materiales ChapraXavier Pacheco PaulinoNo ratings yet
- C6. Bolted Moment Connection SupplementDocument11 pagesC6. Bolted Moment Connection SupplementKURONo ratings yet
- Power Transmitting ElementsDocument10 pagesPower Transmitting ElementsLAMPASA JOSE ROGER JR.No ratings yet
- One-Way Slab (CONTINOUS) - ACI - Code - Good OKDocument18 pagesOne-Way Slab (CONTINOUS) - ACI - Code - Good OKjdpdeleonNo ratings yet
- Destructive Effects of Nuclear Weapons: Blast Damage Thermal Damage Radiation Damage EM-pulseDocument34 pagesDestructive Effects of Nuclear Weapons: Blast Damage Thermal Damage Radiation Damage EM-pulsesmartmathNo ratings yet
- Ch. 6... (Part.3)Document6 pagesCh. 6... (Part.3)darwishailesiNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Equation of Motion - Curvilinear Motion ProblemsDocument21 pagesDynamics Equation of Motion - Curvilinear Motion ProblemsDiana VegaNo ratings yet
- R R R W: 0.4 Rad/s 0.8 Rad/sDocument3 pagesR R R W: 0.4 Rad/s 0.8 Rad/sGupta GurunadhGuptaNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 2 - Mohr Circle, Strain Tran, Thin Thick Cylinder - SolutionDocument5 pagesTUTORIAL 2 - Mohr Circle, Strain Tran, Thin Thick Cylinder - SolutionNurul Nadia100% (3)
- CDocument3 pagesCachrafkchaw96888939No ratings yet
- Calculation Table of Vertical Bracing Connection: WhereDocument1 pageCalculation Table of Vertical Bracing Connection: WhereZULFIKAR AZANNo ratings yet
- Floor Slab DesignDocument3 pagesFloor Slab DesignAnonymous jLLjBdrNo ratings yet
- PEF 2309 Fundamentos de Mecânica Das Estruturas Timoshenko, S.P.,PWS Publishing Company, 1997, Boston, USA, p.408-410, 580-583. Example 8-4Document6 pagesPEF 2309 Fundamentos de Mecânica Das Estruturas Timoshenko, S.P.,PWS Publishing Company, 1997, Boston, USA, p.408-410, 580-583. Example 8-4Jc FortNo ratings yet
- Panel Board SchedDocument3 pagesPanel Board Schedchuck laygoNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - TorsionDocument44 pagesWeek 11 - TorsionRichie BobbyNo ratings yet
- Mech Tut7 AnsDocument11 pagesMech Tut7 AnsPunit SinghNo ratings yet
- Combined ExampleDocument19 pagesCombined ExampleTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Initial Velocity 0 Distance Traveled, S 10m Time T 4s 40 KG Using The Equation of MotionDocument15 pagesInitial Velocity 0 Distance Traveled, S 10m Time T 4s 40 KG Using The Equation of MotionAnonymous ncBe0B9bNo ratings yet
- Forced Damped VibrationsDocument7 pagesForced Damped VibrationskalpanaadhiNo ratings yet
- VRATILO Petar FinishDocument28 pagesVRATILO Petar FinishPetar JuricNo ratings yet
- 2 - STATICALLY INDETERMINTE MEMBERS - UploadDocument11 pages2 - STATICALLY INDETERMINTE MEMBERS - UploadNiaz KilamNo ratings yet
- ShipTheory Project 2Document11 pagesShipTheory Project 2Barış YükselNo ratings yet
- 3 Forced VibrationsDocument62 pages3 Forced VibrationsAshishAgarwalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 14Document1 pageMathematics 14kapindoNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio 2 Examen - MayraDocument4 pagesEjercicio 2 Examen - MayraBelen ErcillaNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 5: Objective:: Fig: 5.1 (Impulse Turbine)Document7 pagesExperiment # 5: Objective:: Fig: 5.1 (Impulse Turbine)AkramNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- For Quotation Only: Vanson Engineering. Pvt. LTDDocument1 pageFor Quotation Only: Vanson Engineering. Pvt. LTDRadha KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Constant Mesh Manual Transmission Gear BoxDocument33 pagesConstant Mesh Manual Transmission Gear BoxBirhanu AsfawNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Design of Components With Casting ConsiderationDocument48 pagesModule 4 Design of Components With Casting ConsiderationMaheshNo ratings yet
- Pandanus Leaves S Litter PresserDocument6 pagesPandanus Leaves S Litter PresserEdson BachaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Manual: INTEGREX E-1060v/6 IIDocument156 pagesMaintenance Manual: INTEGREX E-1060v/6 IIzotya54100% (2)
- PF Pump Specification: Stanadyne"Document2 pagesPF Pump Specification: Stanadyne"Miguel RojasNo ratings yet
- Gate Valve CatalogueDocument8 pagesGate Valve CatalogueSheng SygilNo ratings yet
- ICC 117.1.2009 - Sections 608-610Document7 pagesICC 117.1.2009 - Sections 608-610strv zkngNo ratings yet
- List of Testing Measuring and Monitoring Equipments 31st July 2022Document2 pagesList of Testing Measuring and Monitoring Equipments 31st July 2022Jamal Mohamed RahamathullahNo ratings yet
- NBM RWMA Booklet PDFDocument48 pagesNBM RWMA Booklet PDFSebastian MolinaNo ratings yet
- Tilt Steering Column ReassemblyDocument2 pagesTilt Steering Column ReassemblyjuanNo ratings yet
- Technical-notice-ASAP-CE-2 PDFDocument25 pagesTechnical-notice-ASAP-CE-2 PDFANDREA PAOLANo ratings yet
- 1.11、HBT801590E拖式混凝土泵零件图册 - (中英)Document106 pages1.11、HBT801590E拖式混凝土泵零件图册 - (中英)Sherman KillerNo ratings yet
- Tool Maintenance - CU-Profi - Station - C - EN - 02-2022Document12 pagesTool Maintenance - CU-Profi - Station - C - EN - 02-2022RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Interface Engineering Company: List of Construction MachinesDocument2 pagesInterface Engineering Company: List of Construction MachinesMian M KhurramNo ratings yet
- Dymax+BHL+brochure+4 20 18Document2 pagesDymax+BHL+brochure+4 20 18forever2uNo ratings yet
- Prince Hydraulics - LVS Loader Valve Offered by PRC Industrial SupplyDocument6 pagesPrince Hydraulics - LVS Loader Valve Offered by PRC Industrial SupplyPRC Industrial Supply100% (1)
- Bubble DeckDocument12 pagesBubble DeckConstantin OvidiuNo ratings yet
- Steel Design Shear Block Sample ProblemDocument9 pagesSteel Design Shear Block Sample ProblemJimNo ratings yet
- Pascua M2 Seu-1Document31 pagesPascua M2 Seu-1Jemuel Flores100% (1)
- HKR Master File: No Marks of Pkg's Description of Goods SpecificationDocument8 pagesHKR Master File: No Marks of Pkg's Description of Goods SpecificationPHAM PHI HUNGNo ratings yet
- Cat Pump RexrothDocument19 pagesCat Pump RexrothMohammedElkatan100% (1)
- UNJF - Unified Fine Threads With Controlled Root Radius and Increased Minor DiameterDocument1 pageUNJF - Unified Fine Threads With Controlled Root Radius and Increased Minor Diametertruc taNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Bolted, Riveted and Welded JointDocument4 pagesAssignment On Bolted, Riveted and Welded JointRitesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Safe Deployment of Cables: Vor Cumberland (Cable Handling)Document2 pagesSafe Deployment of Cables: Vor Cumberland (Cable Handling)Henrique NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Wire Loops - PrecastDocument2 pagesWire Loops - PrecastkamakshiNo ratings yet
- EN - DRAA1621 - Spindle Replacement of The Milling Unit M1 - WebDocument11 pagesEN - DRAA1621 - Spindle Replacement of The Milling Unit M1 - WebJPNo ratings yet
- Asme B36-10M-2004 (Schedule STD)Document1 pageAsme B36-10M-2004 (Schedule STD)Jesús Alberto Díaz CostaNo ratings yet
3-69 Shigley
3-69 Shigley
Uploaded by
inivlavi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views3 pagesThe document analyzes the forces, torques, shear forces, and bending moments acting on a shaft assembly with two motors attached at different distances. It is determined that:
1) The torque produced by the first motor is 2880 N and the second motor is 432 N.
2) The reaction force at point C is 1794 N.
3) The maximum bending moment of 698.28 N-m occurs at a distance of 230 mm from end A.
4) The maximum normal and shear stresses are 275.51 MPa and 143.8 MPa respectively.
Original Description:
Original Title
3-69 shigley.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document analyzes the forces, torques, shear forces, and bending moments acting on a shaft assembly with two motors attached at different distances. It is determined that:
1) The torque produced by the first motor is 2880 N and the second motor is 432 N.
2) The reaction force at point C is 1794 N.
3) The maximum bending moment of 698.28 N-m occurs at a distance of 230 mm from end A.
4) The maximum normal and shear stresses are 275.51 MPa and 143.8 MPa respectively.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views3 pages3-69 Shigley
3-69 Shigley
Uploaded by
inivlaviThe document analyzes the forces, torques, shear forces, and bending moments acting on a shaft assembly with two motors attached at different distances. It is determined that:
1) The torque produced by the first motor is 2880 N and the second motor is 432 N.
2) The reaction force at point C is 1794 N.
3) The maximum bending moment of 698.28 N-m occurs at a distance of 230 mm from end A.
4) The maximum normal and shear stresses are 275.51 MPa and 143.8 MPa respectively.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
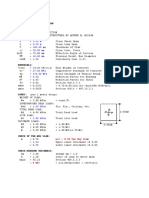
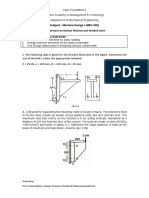
Given Data:
T2 0.15T1
Resolving solving forces Due to torques
for equilibrium T 0
1800-270 200 T2 T1 125 0
306000 T2 T1 125 0
306000
0.15T1 T1
125
0.85T1 2448
2448
T1
0.85
T1 2880 N
T2 0.15 T1
T2 0.15 2880
T2 432 N
Taking Moment about O
for equilibrium M O 0
RC (230 280) (2880 432) 230 (1800 270) (230 280 300) 0
RC (510) (3312) 230 (2070) (810) 0
RC (510) 761760 1676700 0
RC (510) 914940 0
914940
RC
510
RC 1794 N
resolving vertical force for equilibrium Fy 0
RO (2880 432) 1794 (1800 270) 0
RO 3312 1794 2070 0
RO 3036 0
RO 3036 N
R O =3036 N Direction opp to assumption
Shear force calculation
At O
LHS shear force is zero
RHS Shear force is RO 3036 N
Now At B
LHS of B shear forceis RO 3036 N
RHS of B Shear forceis RO 3312 3036 3312 276 N
Now At C
LHS of C shear force is RO 3312 3036 3312 276 N
RHS of C Shear force is RO 3312 1794 3036 3312 1794 2070 N
Now At A
LHS of A shear forceis RO 3312 1794 3036 3312 1794 2070 N
RHS of A Shear forceis RO 3312 1794 3036 3312 1794 2070 0
Bending Moment Calculations
At M O 3312 230 1794 510 2070 810 0
At M B 1794 280 2070 580 698.28 N m
At M C 2070 300 621.00 N m
At M A 3312 230 1794 510 2070 810 0
The maximum bending moment is at x = 230
M max 698.28 N m
Because here the shaft experiance the tension and compression
So, the Torque transmitted between AB is
TAB =(1800-270) 200
TAB =306000 N mm
TAB 306 N m
Therefore
The Bending and Torsionsl stresses are
My
=
I
32 M
d3
32 698.28
0.033
263.43MPa
Tr
=
J
16T
3
d
16 306
0.033
57.7 MPa
The principle Stresses are
2
max/min x x xy 2
2 2
2
263.43 263.43
max/min 57.7
2
2 2
max/min 131.715 20678.131
max/min 131.715 143.799
max 131.715 143.799
max 275.514 MPa
min 131.715 143.799
max 12.1MPa
2
263.43
max 57.7
2
2
max 143.799 MPa
You might also like
- B18 Statics - Moment - Problems PDFDocument30 pagesB18 Statics - Moment - Problems PDFifa noskiNo ratings yet
- WMS (Method Statement For Pouring Concrete On Slab On Grade)Document4 pagesWMS (Method Statement For Pouring Concrete On Slab On Grade)PUI CHEE KHIAN100% (1)
- 3-69 ShigleyDocument3 pages3-69 ShigleyinivlaviNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Test 07Document29 pagesSolutions To Test 07Princess Gupo TañasNo ratings yet
- 2020 03 10Document12 pages2020 03 10AndikaNo ratings yet
- U1 v1 U2 v2 U1 v1 U2 v2Document12 pagesU1 v1 U2 v2 U1 v1 U2 v2AndikaNo ratings yet
- 2020 03 10Document12 pages2020 03 10Tito WirasatyaNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2Manupriya KapleshNo ratings yet
- HX 103Document13 pagesHX 103Weng Keat ChongNo ratings yet
- Lifting Lug Cal PDFDocument1 pageLifting Lug Cal PDFveeru2906No ratings yet
- Shrink FitDocument6 pagesShrink FitParag NaikNo ratings yet
- Resulting Force On Pipe BendDocument5 pagesResulting Force On Pipe BendJiaching LiewNo ratings yet
- 2WAY Slab Design TOMAS 2Document4 pages2WAY Slab Design TOMAS 2kingazure31No ratings yet
- Design of Replaceent Scheme of Inadequate GussetDocument9 pagesDesign of Replaceent Scheme of Inadequate GussetPartha GangopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and ConstructionDocument32 pagesReinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and ConstructiongauravNo ratings yet
- B17 Statics - Moment - ProblemsDocument30 pagesB17 Statics - Moment - ProblemsJCLLNo ratings yet
- MD Singh Power Electronics Solution Manual To Chapter 15Document15 pagesMD Singh Power Electronics Solution Manual To Chapter 15Anoop MathewNo ratings yet
- B16 Statics - Moment - Problems PDFDocument31 pagesB16 Statics - Moment - Problems PDFMuhammad Fazeel KhanNo ratings yet
- ME511 AssignmentDocument10 pagesME511 AssignmentridwanmuhammadtajudeenNo ratings yet
- 02-04 Chap GereDocument12 pages02-04 Chap GereSri DNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Davit CalculationDocument8 pagesDokumen - Tips Davit CalculationJagdish KotadiyaNo ratings yet
- Section 3A - Dynamic StabilityDocument8 pagesSection 3A - Dynamic StabilityAhmad YasserNo ratings yet
- Torsion Report PDFDocument31 pagesTorsion Report PDFSheikh BajunaidNo ratings yet
- Resolver Smart SynDocument12 pagesResolver Smart SynLeon de RuijterNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument41 pagesInduction MotorRiyadh Al Nur0% (1)
- Numerical ExamplesDocument20 pagesNumerical ExampleslitrakhanNo ratings yet
- Solution: Given Data:: 165 Kpa 69 CDocument30 pagesSolution: Given Data:: 165 Kpa 69 Cyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- Solution: Given Data:: 165 Kpa 69 CDocument83 pagesSolution: Given Data:: 165 Kpa 69 Cyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- SFB Longi ExtDocument11 pagesSFB Longi ExtJhonmar DelapenaNo ratings yet
- FisicaDocument2 pagesFisicajonathantorresloboNo ratings yet
- PR - PR - (5380)Document17 pagesPR - PR - (5380)Notrex 24No ratings yet
- Module 4 Activity No. 3Document7 pagesModule 4 Activity No. 3John Mark AlvesNo ratings yet
- CNG FoundationDocument19 pagesCNG FoundationsamiNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Cap. 4 Mecánica de Materiales ChapraDocument12 pagesSolucionario Cap. 4 Mecánica de Materiales ChapraXavier Pacheco PaulinoNo ratings yet
- C6. Bolted Moment Connection SupplementDocument11 pagesC6. Bolted Moment Connection SupplementKURONo ratings yet
- Power Transmitting ElementsDocument10 pagesPower Transmitting ElementsLAMPASA JOSE ROGER JR.No ratings yet
- One-Way Slab (CONTINOUS) - ACI - Code - Good OKDocument18 pagesOne-Way Slab (CONTINOUS) - ACI - Code - Good OKjdpdeleonNo ratings yet
- Destructive Effects of Nuclear Weapons: Blast Damage Thermal Damage Radiation Damage EM-pulseDocument34 pagesDestructive Effects of Nuclear Weapons: Blast Damage Thermal Damage Radiation Damage EM-pulsesmartmathNo ratings yet
- Ch. 6... (Part.3)Document6 pagesCh. 6... (Part.3)darwishailesiNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Equation of Motion - Curvilinear Motion ProblemsDocument21 pagesDynamics Equation of Motion - Curvilinear Motion ProblemsDiana VegaNo ratings yet
- R R R W: 0.4 Rad/s 0.8 Rad/sDocument3 pagesR R R W: 0.4 Rad/s 0.8 Rad/sGupta GurunadhGuptaNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 2 - Mohr Circle, Strain Tran, Thin Thick Cylinder - SolutionDocument5 pagesTUTORIAL 2 - Mohr Circle, Strain Tran, Thin Thick Cylinder - SolutionNurul Nadia100% (3)
- CDocument3 pagesCachrafkchaw96888939No ratings yet
- Calculation Table of Vertical Bracing Connection: WhereDocument1 pageCalculation Table of Vertical Bracing Connection: WhereZULFIKAR AZANNo ratings yet
- Floor Slab DesignDocument3 pagesFloor Slab DesignAnonymous jLLjBdrNo ratings yet
- PEF 2309 Fundamentos de Mecânica Das Estruturas Timoshenko, S.P.,PWS Publishing Company, 1997, Boston, USA, p.408-410, 580-583. Example 8-4Document6 pagesPEF 2309 Fundamentos de Mecânica Das Estruturas Timoshenko, S.P.,PWS Publishing Company, 1997, Boston, USA, p.408-410, 580-583. Example 8-4Jc FortNo ratings yet
- Panel Board SchedDocument3 pagesPanel Board Schedchuck laygoNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - TorsionDocument44 pagesWeek 11 - TorsionRichie BobbyNo ratings yet
- Mech Tut7 AnsDocument11 pagesMech Tut7 AnsPunit SinghNo ratings yet
- Combined ExampleDocument19 pagesCombined ExampleTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Initial Velocity 0 Distance Traveled, S 10m Time T 4s 40 KG Using The Equation of MotionDocument15 pagesInitial Velocity 0 Distance Traveled, S 10m Time T 4s 40 KG Using The Equation of MotionAnonymous ncBe0B9bNo ratings yet
- Forced Damped VibrationsDocument7 pagesForced Damped VibrationskalpanaadhiNo ratings yet
- VRATILO Petar FinishDocument28 pagesVRATILO Petar FinishPetar JuricNo ratings yet
- 2 - STATICALLY INDETERMINTE MEMBERS - UploadDocument11 pages2 - STATICALLY INDETERMINTE MEMBERS - UploadNiaz KilamNo ratings yet
- ShipTheory Project 2Document11 pagesShipTheory Project 2Barış YükselNo ratings yet
- 3 Forced VibrationsDocument62 pages3 Forced VibrationsAshishAgarwalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 14Document1 pageMathematics 14kapindoNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio 2 Examen - MayraDocument4 pagesEjercicio 2 Examen - MayraBelen ErcillaNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 5: Objective:: Fig: 5.1 (Impulse Turbine)Document7 pagesExperiment # 5: Objective:: Fig: 5.1 (Impulse Turbine)AkramNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- For Quotation Only: Vanson Engineering. Pvt. LTDDocument1 pageFor Quotation Only: Vanson Engineering. Pvt. LTDRadha KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Constant Mesh Manual Transmission Gear BoxDocument33 pagesConstant Mesh Manual Transmission Gear BoxBirhanu AsfawNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Design of Components With Casting ConsiderationDocument48 pagesModule 4 Design of Components With Casting ConsiderationMaheshNo ratings yet
- Pandanus Leaves S Litter PresserDocument6 pagesPandanus Leaves S Litter PresserEdson BachaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Manual: INTEGREX E-1060v/6 IIDocument156 pagesMaintenance Manual: INTEGREX E-1060v/6 IIzotya54100% (2)
- PF Pump Specification: Stanadyne"Document2 pagesPF Pump Specification: Stanadyne"Miguel RojasNo ratings yet
- Gate Valve CatalogueDocument8 pagesGate Valve CatalogueSheng SygilNo ratings yet
- ICC 117.1.2009 - Sections 608-610Document7 pagesICC 117.1.2009 - Sections 608-610strv zkngNo ratings yet
- List of Testing Measuring and Monitoring Equipments 31st July 2022Document2 pagesList of Testing Measuring and Monitoring Equipments 31st July 2022Jamal Mohamed RahamathullahNo ratings yet
- NBM RWMA Booklet PDFDocument48 pagesNBM RWMA Booklet PDFSebastian MolinaNo ratings yet
- Tilt Steering Column ReassemblyDocument2 pagesTilt Steering Column ReassemblyjuanNo ratings yet
- Technical-notice-ASAP-CE-2 PDFDocument25 pagesTechnical-notice-ASAP-CE-2 PDFANDREA PAOLANo ratings yet
- 1.11、HBT801590E拖式混凝土泵零件图册 - (中英)Document106 pages1.11、HBT801590E拖式混凝土泵零件图册 - (中英)Sherman KillerNo ratings yet
- Tool Maintenance - CU-Profi - Station - C - EN - 02-2022Document12 pagesTool Maintenance - CU-Profi - Station - C - EN - 02-2022RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Interface Engineering Company: List of Construction MachinesDocument2 pagesInterface Engineering Company: List of Construction MachinesMian M KhurramNo ratings yet
- Dymax+BHL+brochure+4 20 18Document2 pagesDymax+BHL+brochure+4 20 18forever2uNo ratings yet
- Prince Hydraulics - LVS Loader Valve Offered by PRC Industrial SupplyDocument6 pagesPrince Hydraulics - LVS Loader Valve Offered by PRC Industrial SupplyPRC Industrial Supply100% (1)
- Bubble DeckDocument12 pagesBubble DeckConstantin OvidiuNo ratings yet
- Steel Design Shear Block Sample ProblemDocument9 pagesSteel Design Shear Block Sample ProblemJimNo ratings yet
- Pascua M2 Seu-1Document31 pagesPascua M2 Seu-1Jemuel Flores100% (1)
- HKR Master File: No Marks of Pkg's Description of Goods SpecificationDocument8 pagesHKR Master File: No Marks of Pkg's Description of Goods SpecificationPHAM PHI HUNGNo ratings yet
- Cat Pump RexrothDocument19 pagesCat Pump RexrothMohammedElkatan100% (1)
- UNJF - Unified Fine Threads With Controlled Root Radius and Increased Minor DiameterDocument1 pageUNJF - Unified Fine Threads With Controlled Root Radius and Increased Minor Diametertruc taNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Bolted, Riveted and Welded JointDocument4 pagesAssignment On Bolted, Riveted and Welded JointRitesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Safe Deployment of Cables: Vor Cumberland (Cable Handling)Document2 pagesSafe Deployment of Cables: Vor Cumberland (Cable Handling)Henrique NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Wire Loops - PrecastDocument2 pagesWire Loops - PrecastkamakshiNo ratings yet
- EN - DRAA1621 - Spindle Replacement of The Milling Unit M1 - WebDocument11 pagesEN - DRAA1621 - Spindle Replacement of The Milling Unit M1 - WebJPNo ratings yet
- Asme B36-10M-2004 (Schedule STD)Document1 pageAsme B36-10M-2004 (Schedule STD)Jesús Alberto Díaz CostaNo ratings yet