Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsWenckebach) and Type II AV Block.: Click Here To View
Wenckebach) and Type II AV Block.: Click Here To View
Uploaded by
Lwin Maung Maung ThikeThis document discusses different types of heart block abnormalities seen on electrocardiograms (ECGs). It describes Type I or Wenckebach heart block where the PR interval gets progressively longer until a beat is dropped, with the post-pause RR interval being shorter than the preceding two. Type II or Mobitz heart block shows constant PR intervals until a beat is suddenly dropped, with equal pre-and post-pause RR intervals. The document provides examples of ECG tracings demonstrating these two types of heart block.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- ECG InterpretationDocument1 pageECG InterpretationCecil-An DalanonNo ratings yet
- Atrioventricular Conduction AbnormalitiesDocument11 pagesAtrioventricular Conduction AbnormalitiesRaul OrtegaNo ratings yet
- BAV 1-S2.0-S1443950623043585-MainDocument4 pagesBAV 1-S2.0-S1443950623043585-MainconstanzacaceresgalvezNo ratings yet
- Ecg 7Document9 pagesEcg 7api-3757039No ratings yet
- Atrioventricular Conductiondiseaseand Block: Leila Laroussi,, Nitish BadhwarDocument14 pagesAtrioventricular Conductiondiseaseand Block: Leila Laroussi,, Nitish BadhwarTor JaNo ratings yet
- Wolff-Parkinson-White and Atrioventricular (AV) Heart BlocksDocument33 pagesWolff-Parkinson-White and Atrioventricular (AV) Heart BlocksMonika Putong PaatNo ratings yet
- AV Nodal Blocks: 1st Degree AV Block 2nd Degree AV Block, Type I 2nd Degree AV Block, Type II 3rd Degree AV BlockDocument14 pagesAV Nodal Blocks: 1st Degree AV Block 2nd Degree AV Block, Type I 2nd Degree AV Block, Type II 3rd Degree AV BlockEdRobertArnad100% (1)
- Degree), Intermittent Degree), or Complete Conduction Failure (3 Degree) - inDocument1 pageDegree), Intermittent Degree), or Complete Conduction Failure (3 Degree) - inLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis: Sinus Arrhythmia Without SA Block. TheDocument1 pageDifferential Diagnosis: Sinus Arrhythmia Without SA Block. TheLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Conduction DisturbancesDocument64 pagesCardiac Conduction DisturbancesGroup M1869No ratings yet
- Type I Wenckebach Second-Degree AV Block: A Matter of DefinitionDocument4 pagesType I Wenckebach Second-Degree AV Block: A Matter of DefinitionMSNo ratings yet
- AV BlockDocument2 pagesAV BlocksaikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Ecg Strips (Blocks) S-02Document33 pagesEcg Strips (Blocks) S-02Bhagwani BaiNo ratings yet
- How To Read EcgDocument3 pagesHow To Read EcgAlloy Trixia BaguioNo ratings yet
- Ecgs Made Easy 6th Edition Aehlert Test BankDocument16 pagesEcgs Made Easy 6th Edition Aehlert Test Bankexoynambuj7100% (35)
- ECG Rhythm Interpretation: Module IV CDocument18 pagesECG Rhythm Interpretation: Module IV CsrimatsimhasaneshwarNo ratings yet
- AV BlocksDocument12 pagesAV BlocksIhdina Khoirin NisaNo ratings yet
- Duration of QRS Complex in Frontal PlaneDocument1 pageDuration of QRS Complex in Frontal PlaneLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrioventricular (AV) Heart BlockDocument12 pagesAtrioventricular (AV) Heart BlockSharon SchauerteNo ratings yet
- Module 4cDocument21 pagesModule 4cSuharto SanduyoganNo ratings yet
- 09 ECG Atrioventricular ConductionDocument12 pages09 ECG Atrioventricular ConductionJevisco LauNo ratings yet
- AV BlockDocument16 pagesAV BlockRiimt Ruum AdjaNo ratings yet
- BradyarrhythimasDocument61 pagesBradyarrhythimasMhmd A LubadNo ratings yet
- Bradyarrhythmias LUIFER1Document62 pagesBradyarrhythmias LUIFER1Luis Fernando Morales JuradoNo ratings yet
- LAB 1 - Station 5Document6 pagesLAB 1 - Station 5william atmadjiNo ratings yet
- Conduction DisturbancesDocument51 pagesConduction Disturbancesapi-298936498No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 5th Edition AehlertDocument19 pagesTest Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 5th Edition AehlertGraceLopezyfmox100% (40)
- Prof. Ia Avaliani: Bradycardias-The Slow Rhythms. Abnormalities With Conduction. Conduction BlockDocument65 pagesProf. Ia Avaliani: Bradycardias-The Slow Rhythms. Abnormalities With Conduction. Conduction BlockSASIDHARNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument24 pagesHow To Read An ECGredroseeeeeeNo ratings yet
- ECG Made Easy - A Slow Turtle VsDocument37 pagesECG Made Easy - A Slow Turtle VsabdallahNo ratings yet
- DR Dhanveer Singh MD (Medicine) Assisstant Professor Dept. of Medicine Subharti Medical CollegeDocument40 pagesDR Dhanveer Singh MD (Medicine) Assisstant Professor Dept. of Medicine Subharti Medical CollegeSahil KakkarNo ratings yet
- Click Here To View: Degree) AV BlockDocument1 pageClick Here To View: Degree) AV BlockLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECGCFTCNo ratings yet
- 35 7-PDF EcDocument1 page35 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- ECG Rhythm InterpretationDocument21 pagesECG Rhythm Interpretationvanstar7100% (1)
- AV Nodal BlocksDocument19 pagesAV Nodal BlocksHarsha VijaykumarNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECG: Confirm DetailsDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECG: Confirm DetailsRinothja RajaratnamNo ratings yet
- Click Here To View: What They Are, and That's The Next Topic For Discussion!Document1 pageClick Here To View: What They Are, and That's The Next Topic For Discussion!Lwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- C./issociation, Current Topics Second-Degree Atrioventricular BlockDocument8 pagesC./issociation, Current Topics Second-Degree Atrioventricular BlockKevin Ariel Tiopan SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Ecg Part Ii: V1-V2 Anteroseptal Wall Ii, Iii, Avf Inferior WallDocument7 pagesEcg Part Ii: V1-V2 Anteroseptal Wall Ii, Iii, Avf Inferior WallsyuaibsazaliNo ratings yet
- AV Conduction Blocks, BBBDocument33 pagesAV Conduction Blocks, BBBroseneels9No ratings yet
- Idar Mappangara-BradiaritmiaDocument28 pagesIdar Mappangara-BradiaritmiaIwan IrwanNo ratings yet
- Tri Fascicular BlockDocument28 pagesTri Fascicular BlockSubhashini KNo ratings yet
- Heart BlockDocument17 pagesHeart Blocklitan dasNo ratings yet
- Interpretasi ElektrokardiogramDocument36 pagesInterpretasi ElektrokardiogramendahNo ratings yet
- Relationship of P Waves To QrssDocument1 pageRelationship of P Waves To QrssJessica PuentesNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECGcharlyn206No ratings yet
- 2017 - Pocket Guide ECG InterpretationDocument21 pages2017 - Pocket Guide ECG Interpretationmaria0% (1)
- ECG - How To Read An ECGDocument20 pagesECG - How To Read An ECGokenyinancyNo ratings yet
- Second Degree AV Block: Type 1 (Mobitz I/Wenckebach)Document2 pagesSecond Degree AV Block: Type 1 (Mobitz I/Wenckebach)aldwinngNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument21 pagesHow To Read An ECGSlychenkoNo ratings yet
- Module 4cDocument19 pagesModule 4capi-3738700No ratings yet
- Geekymedics.com-How to Read an ECGDocument15 pagesGeekymedics.com-How to Read an ECGSravya ValisettiNo ratings yet
- Av BlockDocument38 pagesAv BlockLanna Harumiya100% (1)
- How To Read An ECGDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECGSarah RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Module 4c.haert ArryhtmiasDocument19 pagesModule 4c.haert ArryhtmiasFerry SofyanriNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmias I: Atrioventricular Conduction Disturbances and BradyarrhythmiasDocument73 pagesCardiac Arrhythmias I: Atrioventricular Conduction Disturbances and BradyarrhythmiasVijay GadagiNo ratings yet
- Ekg by DR RezaDocument105 pagesEkg by DR RezaYoga KarsendaNo ratings yet
- Left Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageLeft Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- ST Segment Depression-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageST Segment Depression-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- A Very Subtle 1st Degree AV BlockDocument1 pageA Very Subtle 1st Degree AV BlockLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
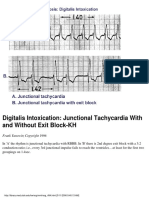
- Digitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without Exit Block-KHDocument1 pageDigitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without Exit Block-KHLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 142 7-PDF EcDocument1 page142 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 137 7-PDF Ec PDFDocument1 page137 7-PDF Ec PDFLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 129 7-PDF Ec PDFDocument1 page129 7-PDF Ec PDFLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
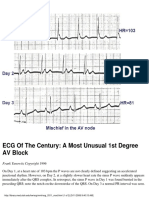
- ECG of The Century: A Most Unusual 1st Degree AV BlockDocument1 pageECG of The Century: A Most Unusual 1st Degree AV BlockLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 129 7-PDF EcDocument1 page129 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 135 7-PDF EcDocument1 page135 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 130 7-PDF EcDocument1 page130 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Digitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without AV Block-KHDocument1 pageDigitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without AV Block-KHLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 126 7-PDF Ec PDFDocument1 page126 7-PDF Ec PDFLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction: Lead V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction: Lead V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 128 7-PDF EcDocument1 page128 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With Variable AV Block - Marquette-KHDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With Variable AV Block - Marquette-KHLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With 2:1 Conduction: Leads II, III, V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With 2:1 Conduction: Leads II, III, V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
Wenckebach) and Type II AV Block.: Click Here To View
Wenckebach) and Type II AV Block.: Click Here To View
Uploaded by
Lwin Maung Maung Thike0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThis document discusses different types of heart block abnormalities seen on electrocardiograms (ECGs). It describes Type I or Wenckebach heart block where the PR interval gets progressively longer until a beat is dropped, with the post-pause RR interval being shorter than the preceding two. Type II or Mobitz heart block shows constant PR intervals until a beat is suddenly dropped, with equal pre-and post-pause RR intervals. The document provides examples of ECG tracings demonstrating these two types of heart block.
Original Description:
44ec
Original Title
44_7-PDF_EC
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses different types of heart block abnormalities seen on electrocardiograms (ECGs). It describes Type I or Wenckebach heart block where the PR interval gets progressively longer until a beat is dropped, with the post-pause RR interval being shorter than the preceding two. Type II or Mobitz heart block shows constant PR intervals until a beat is suddenly dropped, with equal pre-and post-pause RR intervals. The document provides examples of ECG tracings demonstrating these two types of heart block.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageWenckebach) and Type II AV Block.: Click Here To View
Wenckebach) and Type II AV Block.: Click Here To View
Uploaded by
Lwin Maung Maung ThikeThis document discusses different types of heart block abnormalities seen on electrocardiograms (ECGs). It describes Type I or Wenckebach heart block where the PR interval gets progressively longer until a beat is dropped, with the post-pause RR interval being shorter than the preceding two. Type II or Mobitz heart block shows constant PR intervals until a beat is suddenly dropped, with equal pre-and post-pause RR intervals. The document provides examples of ECG tracings demonstrating these two types of heart block.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
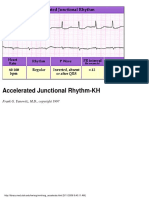
Lesson VI - ECG Conduction Abnormalities
click here to view
Wenckebach) and Type II AV block.
click here to view
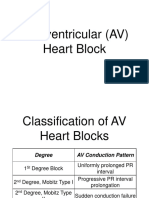
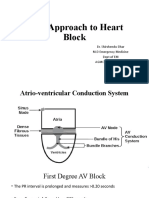
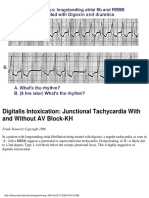
In "classic" Type I (Wenckebach) AV block the PR interval gets longer (by
shorter increments) until a nonconducted P wave occurs. The RR interval of
the pause is less than the two preceding RR intervals, and the RR interval after
the pause is greater than the RR interval before the pause. These are the
classic rules of Wenckebach (atypical forms can occur). In Type II (Mobitz)
AV block the PR intervals are constant until a nonconducted P wave occurs.
There must be two consecutive constant PR intervals to diagnose Type II AV
block (i.e., if there is 2:1 AV block we can't be sure if its type I or II). The RR
interval of the pause is equal to the two preceding RR intervals.
Type I (Wenckebach) AV block (note the RR intervals in ms duration):
click here to view
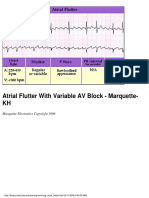
Type I AV block is almost always located in the AV node,
which means that the QRS duration is usually narrow, unless
there is preexisting bundle branch disease.
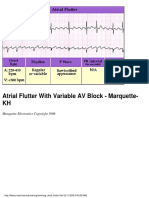
Type II (Mobitz) AV block(note there are two consecutive constant PR
intervals before the blocked P wave):
click here to view
http://library.med.utah.edu/kw/ecg/ecg_outline/Lesson6/index.html (4 of 11) [5/11/2006 9:39:39 AM]
You might also like
- ECG InterpretationDocument1 pageECG InterpretationCecil-An DalanonNo ratings yet
- Atrioventricular Conduction AbnormalitiesDocument11 pagesAtrioventricular Conduction AbnormalitiesRaul OrtegaNo ratings yet
- BAV 1-S2.0-S1443950623043585-MainDocument4 pagesBAV 1-S2.0-S1443950623043585-MainconstanzacaceresgalvezNo ratings yet
- Ecg 7Document9 pagesEcg 7api-3757039No ratings yet
- Atrioventricular Conductiondiseaseand Block: Leila Laroussi,, Nitish BadhwarDocument14 pagesAtrioventricular Conductiondiseaseand Block: Leila Laroussi,, Nitish BadhwarTor JaNo ratings yet
- Wolff-Parkinson-White and Atrioventricular (AV) Heart BlocksDocument33 pagesWolff-Parkinson-White and Atrioventricular (AV) Heart BlocksMonika Putong PaatNo ratings yet
- AV Nodal Blocks: 1st Degree AV Block 2nd Degree AV Block, Type I 2nd Degree AV Block, Type II 3rd Degree AV BlockDocument14 pagesAV Nodal Blocks: 1st Degree AV Block 2nd Degree AV Block, Type I 2nd Degree AV Block, Type II 3rd Degree AV BlockEdRobertArnad100% (1)
- Degree), Intermittent Degree), or Complete Conduction Failure (3 Degree) - inDocument1 pageDegree), Intermittent Degree), or Complete Conduction Failure (3 Degree) - inLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis: Sinus Arrhythmia Without SA Block. TheDocument1 pageDifferential Diagnosis: Sinus Arrhythmia Without SA Block. TheLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Conduction DisturbancesDocument64 pagesCardiac Conduction DisturbancesGroup M1869No ratings yet
- Type I Wenckebach Second-Degree AV Block: A Matter of DefinitionDocument4 pagesType I Wenckebach Second-Degree AV Block: A Matter of DefinitionMSNo ratings yet
- AV BlockDocument2 pagesAV BlocksaikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Ecg Strips (Blocks) S-02Document33 pagesEcg Strips (Blocks) S-02Bhagwani BaiNo ratings yet
- How To Read EcgDocument3 pagesHow To Read EcgAlloy Trixia BaguioNo ratings yet
- Ecgs Made Easy 6th Edition Aehlert Test BankDocument16 pagesEcgs Made Easy 6th Edition Aehlert Test Bankexoynambuj7100% (35)
- ECG Rhythm Interpretation: Module IV CDocument18 pagesECG Rhythm Interpretation: Module IV CsrimatsimhasaneshwarNo ratings yet
- AV BlocksDocument12 pagesAV BlocksIhdina Khoirin NisaNo ratings yet
- Duration of QRS Complex in Frontal PlaneDocument1 pageDuration of QRS Complex in Frontal PlaneLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrioventricular (AV) Heart BlockDocument12 pagesAtrioventricular (AV) Heart BlockSharon SchauerteNo ratings yet
- Module 4cDocument21 pagesModule 4cSuharto SanduyoganNo ratings yet
- 09 ECG Atrioventricular ConductionDocument12 pages09 ECG Atrioventricular ConductionJevisco LauNo ratings yet
- AV BlockDocument16 pagesAV BlockRiimt Ruum AdjaNo ratings yet
- BradyarrhythimasDocument61 pagesBradyarrhythimasMhmd A LubadNo ratings yet
- Bradyarrhythmias LUIFER1Document62 pagesBradyarrhythmias LUIFER1Luis Fernando Morales JuradoNo ratings yet
- LAB 1 - Station 5Document6 pagesLAB 1 - Station 5william atmadjiNo ratings yet
- Conduction DisturbancesDocument51 pagesConduction Disturbancesapi-298936498No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 5th Edition AehlertDocument19 pagesTest Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 5th Edition AehlertGraceLopezyfmox100% (40)
- Prof. Ia Avaliani: Bradycardias-The Slow Rhythms. Abnormalities With Conduction. Conduction BlockDocument65 pagesProf. Ia Avaliani: Bradycardias-The Slow Rhythms. Abnormalities With Conduction. Conduction BlockSASIDHARNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument24 pagesHow To Read An ECGredroseeeeeeNo ratings yet
- ECG Made Easy - A Slow Turtle VsDocument37 pagesECG Made Easy - A Slow Turtle VsabdallahNo ratings yet
- DR Dhanveer Singh MD (Medicine) Assisstant Professor Dept. of Medicine Subharti Medical CollegeDocument40 pagesDR Dhanveer Singh MD (Medicine) Assisstant Professor Dept. of Medicine Subharti Medical CollegeSahil KakkarNo ratings yet
- Click Here To View: Degree) AV BlockDocument1 pageClick Here To View: Degree) AV BlockLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECGCFTCNo ratings yet
- 35 7-PDF EcDocument1 page35 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- ECG Rhythm InterpretationDocument21 pagesECG Rhythm Interpretationvanstar7100% (1)
- AV Nodal BlocksDocument19 pagesAV Nodal BlocksHarsha VijaykumarNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECG: Confirm DetailsDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECG: Confirm DetailsRinothja RajaratnamNo ratings yet
- Click Here To View: What They Are, and That's The Next Topic For Discussion!Document1 pageClick Here To View: What They Are, and That's The Next Topic For Discussion!Lwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- C./issociation, Current Topics Second-Degree Atrioventricular BlockDocument8 pagesC./issociation, Current Topics Second-Degree Atrioventricular BlockKevin Ariel Tiopan SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Ecg Part Ii: V1-V2 Anteroseptal Wall Ii, Iii, Avf Inferior WallDocument7 pagesEcg Part Ii: V1-V2 Anteroseptal Wall Ii, Iii, Avf Inferior WallsyuaibsazaliNo ratings yet
- AV Conduction Blocks, BBBDocument33 pagesAV Conduction Blocks, BBBroseneels9No ratings yet
- Idar Mappangara-BradiaritmiaDocument28 pagesIdar Mappangara-BradiaritmiaIwan IrwanNo ratings yet
- Tri Fascicular BlockDocument28 pagesTri Fascicular BlockSubhashini KNo ratings yet
- Heart BlockDocument17 pagesHeart Blocklitan dasNo ratings yet
- Interpretasi ElektrokardiogramDocument36 pagesInterpretasi ElektrokardiogramendahNo ratings yet
- Relationship of P Waves To QrssDocument1 pageRelationship of P Waves To QrssJessica PuentesNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECGcharlyn206No ratings yet
- 2017 - Pocket Guide ECG InterpretationDocument21 pages2017 - Pocket Guide ECG Interpretationmaria0% (1)
- ECG - How To Read An ECGDocument20 pagesECG - How To Read An ECGokenyinancyNo ratings yet
- Second Degree AV Block: Type 1 (Mobitz I/Wenckebach)Document2 pagesSecond Degree AV Block: Type 1 (Mobitz I/Wenckebach)aldwinngNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument21 pagesHow To Read An ECGSlychenkoNo ratings yet
- Module 4cDocument19 pagesModule 4capi-3738700No ratings yet
- Geekymedics.com-How to Read an ECGDocument15 pagesGeekymedics.com-How to Read an ECGSravya ValisettiNo ratings yet
- Av BlockDocument38 pagesAv BlockLanna Harumiya100% (1)
- How To Read An ECGDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECGSarah RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Module 4c.haert ArryhtmiasDocument19 pagesModule 4c.haert ArryhtmiasFerry SofyanriNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmias I: Atrioventricular Conduction Disturbances and BradyarrhythmiasDocument73 pagesCardiac Arrhythmias I: Atrioventricular Conduction Disturbances and BradyarrhythmiasVijay GadagiNo ratings yet
- Ekg by DR RezaDocument105 pagesEkg by DR RezaYoga KarsendaNo ratings yet
- Left Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageLeft Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- ST Segment Depression-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageST Segment Depression-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- A Very Subtle 1st Degree AV BlockDocument1 pageA Very Subtle 1st Degree AV BlockLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Digitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without Exit Block-KHDocument1 pageDigitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without Exit Block-KHLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 142 7-PDF EcDocument1 page142 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 137 7-PDF Ec PDFDocument1 page137 7-PDF Ec PDFLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 129 7-PDF Ec PDFDocument1 page129 7-PDF Ec PDFLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- ECG of The Century: A Most Unusual 1st Degree AV BlockDocument1 pageECG of The Century: A Most Unusual 1st Degree AV BlockLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 129 7-PDF EcDocument1 page129 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 135 7-PDF EcDocument1 page135 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 130 7-PDF EcDocument1 page130 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Digitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without AV Block-KHDocument1 pageDigitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without AV Block-KHLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 126 7-PDF Ec PDFDocument1 page126 7-PDF Ec PDFLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction: Lead V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction: Lead V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 128 7-PDF EcDocument1 page128 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With Variable AV Block - Marquette-KHDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With Variable AV Block - Marquette-KHLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With 2:1 Conduction: Leads II, III, V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With 2:1 Conduction: Leads II, III, V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet