Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cost of Quality 26072011 PDF
Cost of Quality 26072011 PDF
Uploaded by
MACOY0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views26 pagesOriginal Title
Cost-of-Quality-26072011.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views26 pagesCost of Quality 26072011 PDF
Cost of Quality 26072011 PDF
Uploaded by
MACOYCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 26
Cost of quality
Dr. Essam Hamed Amin
MQM, DBAQM
Business Development Consultant
The lecturer
Dr. Essam Hamed Amin
MQM, DBAQM
Senior Quality Consultant
Member of The Egyptian Society for Quality in Health
Care (ESQua)
Member of The International Society for Quality In Health
Care (ISQua)
Team Leader In Sheikh Khalifa Excellence Award (SKEA)
Team Leader in Abu Dhabi Award for Excellence in
Government Performance (ADAEP)
Lead Auditor (IRCA register) for ISO 9001:2000
“Cost of quality is …
the expense of nonconformance –
the cost of doing things wrong.”
Opportunity to Reduce Real Costs
• Understand quality costs enables you to
– Understand hidden costs
– Reduce and eliminate unnecessary cost
• Prevent problems from happening
• Management responsibility to enable this
Understand Quality Costs
• Quality costs are real and estimated at:
– 25% of costs in manufacturing
– 35% of costs in service industry
• Quality costs can be categorised to enable
better understanding
Categories of Quality Costs
• Failure Costs
• Repair Costs
• Appraisal Costs
• Prevention Costs
Failure Costs
• Those costs incurred because poor quality
products do exist
• Can be further divided into sub-categories of:
– Internal failure costs
– External failure costs
Repair Costs
• Those costs incurred if poor quality products
receive further processing
• If this occurs then the previous processing is
wasted cost
• Why would you do this?
Appraisal Costs
• Those costs incurred because poor quality
products might exist
• If these costs are necessary then the process
is flawed and management is guilty
• Why would you permit this?
Prevention Costs
• Those costs incurred because poor quality
products can exist and
• Those costs incurred because management is
committed to prevent poor quality products
from happening
• Why would you not do this?
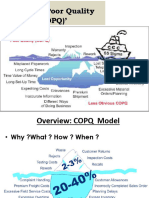
Preventing Poor Quality Pays
Prevention Costs
Benefit
Appraisal Costs
$ Repair Costs Prevention Costs
Failure Costs Appraisal Costs
• Internal Repair Costs
• External Failure Costs
Before Quality After Quality
Cost Alignment Cost Alignment
Preventing Poor Quality Pays
• Would it not make sense to prevent poor
quality products from happening?
• How can this be done?
• Whose responsibility is this?
How to Prevent Poor Quality
• Prepare to measure costs of quality
– Determine categories of quality costs
– Create measurement system that captures
categories of quality costs
• Assign responsibility to collect data
• Analyse collected data
Determine Quality Cost Categories
• Understand your product
• Understand your process
• Understand where problems occur
• Determine precisely what goes wrong
• Determine what costs represents each
problem
Creating Data Collection System
• Create measurement system
– Attempt to harness existing financial
accounting system
– Manipulate existing financial data
– Collect costs as they occur
• Whatever you do ensure costs are accurate
Assign Responsibility
• Make individuals at all levels responsible for
collecting quality cost data:
– If quality cost data is required then make it
the responsibility of the person who
creates the cost to collect the data
• If no one is responsible no one will bother
Analyse Collected Data
• Data on its own is useless
• You must have it analysed to be able to extract
meaning
• Determine what knowledge you require
• Develop an analysis system that provides the
knowledge you require
Useful Quality Cost Knowledge
• What you need to know is useful
• What you do not need to know is useless
• Only ask for knowledge you need to know
• Demand that knowledge is presented so that it
can be understood easily
Management is Responsible
• Management decides what to produce in terms
of Products (goods and / or services)
• Management assigns responsibilities to
produce products
• Management is accountable for effectively
using resources to produce products
Examples
“Cost of quality is …
the expense of nonconformance
–
the cost of doing things wrong.”
Thank
You
You might also like
- Quality Management SystemDocument59 pagesQuality Management SystemKentDemeterio100% (9)
- Gmail - Turkish Airlines - Online Ticket - Information MessageDocument5 pagesGmail - Turkish Airlines - Online Ticket - Information MessageOmar AlassouraNo ratings yet
- RA 11203 Reflection PaperDocument3 pagesRA 11203 Reflection PaperDiana Pasuit86% (7)
- Fuyao North America BrochureDocument11 pagesFuyao North America BrochureJadeNo ratings yet
- Cost of Quality: "Cost of Quality Is The Expense of Noncomformance - The Cost of Doing Things Wrong."Document18 pagesCost of Quality: "Cost of Quality Is The Expense of Noncomformance - The Cost of Doing Things Wrong."sandeep_rana65No ratings yet
- Assignment No 2 Inspection & Quality ControlDocument13 pagesAssignment No 2 Inspection & Quality ControlKashif RasheedNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document26 pagesUnit 2GAURAV GUPTANo ratings yet
- Cost of QualityDocument17 pagesCost of QualityJeffery GulNo ratings yet
- CMA1.D2.5.Operational Effeciency 2LPDocument70 pagesCMA1.D2.5.Operational Effeciency 2LPjosejonitaNo ratings yet
- Cost of QualityDocument3 pagesCost of QualityManish DharNo ratings yet
- Deming Crosby JuranDocument93 pagesDeming Crosby Juranmannarmannan2No ratings yet
- What Is Cost of Poor Quality (Copq) ?Document7 pagesWhat Is Cost of Poor Quality (Copq) ?Christine LoNo ratings yet
- COPQDocument83 pagesCOPQakash.vd.1603No ratings yet
- Cost of QualityDocument14 pagesCost of QualitySahil ShirkeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quality ControlDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Quality ControlSakeena Naureen Ashraf100% (1)
- Unit 1quality ConceptsDocument27 pagesUnit 1quality ConceptsManish PakhideNo ratings yet
- 17 Quality ManagementDocument45 pages17 Quality ManagementAbhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- Quality Is FreeDocument30 pagesQuality Is FreeAndraNo ratings yet
- A Power Point Presentation On TQMDocument46 pagesA Power Point Presentation On TQMtafere99No ratings yet
- Operation ManagementDocument129 pagesOperation ManagementVishwanath SN100% (1)
- Total Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsDocument35 pagesTotal Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key Elementsronski17No ratings yet
- Organiztional Innovations TQMDocument26 pagesOrganiztional Innovations TQMAlexa Daphne M. EquisabalNo ratings yet
- Operations Manager: - Deliver A Quality Product/service ToDocument23 pagesOperations Manager: - Deliver A Quality Product/service ToakshaynnaikNo ratings yet
- Ge8077 TQM Unit IV NotesDocument30 pagesGe8077 TQM Unit IV NotesTT GAMER VBKNo ratings yet
- Total Quality ManagementDocument42 pagesTotal Quality ManagementSindhuja KumarNo ratings yet
- 3-Costs of QualityDocument19 pages3-Costs of QualityKAMPARA MANOHAR 122010318056No ratings yet
- Operations Management Rabindra Silwal: Quality Management Norman AugustineDocument38 pagesOperations Management Rabindra Silwal: Quality Management Norman AugustineSudip DhakalNo ratings yet
- MutuDocument93 pagesMutuEko HardjoNo ratings yet
- QualityDocument74 pagesQualityPratik V Pandhare0% (1)
- QualityDocument25 pagesQualitygsidhu156276No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document33 pagesChapter 9Denise BaterinaNo ratings yet
- Why TQMDocument58 pagesWhy TQMpazilarsp100% (1)
- Quality+Statistical ProcessDocument173 pagesQuality+Statistical ProcessAyush KishoreNo ratings yet
- Cost of QualityDocument14 pagesCost of QualitySreenath HtaneersNo ratings yet
- OM Chapter FiveDocument67 pagesOM Chapter FiveLakachew GetasewNo ratings yet
- 3 QualityDocument45 pages3 QualityAyush KishoreNo ratings yet
- Quality CostingDocument8 pagesQuality CostingDhruv SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Cost of Quality: A Cost Accounting PresentationDocument32 pagesCost of Quality: A Cost Accounting PresentationkarankbhallaNo ratings yet
- POM Module2 Unit3Document12 pagesPOM Module2 Unit3Izzabel Sarmiento BaniquedNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management: Mechanical Engineering Technology MET - 523TQMDocument24 pagesTotal Quality Management: Mechanical Engineering Technology MET - 523TQMsubhan sibghatNo ratings yet
- Total Quality ManagementDocument97 pagesTotal Quality ManagementRodiemerNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - TQMDocument37 pagesUnit 8 - TQMAshutosh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- OM-Chapter 6Document73 pagesOM-Chapter 6Almaz GetachewNo ratings yet
- Total Quality ManagementDocument12 pagesTotal Quality ManagementAnaya MalikNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Overview of TQMDocument30 pagesLesson 1 Overview of TQMGlycel GayatinNo ratings yet
- TQM MidtermDocument51 pagesTQM MidtermcutierineeeNo ratings yet
- QM Lesson 7Document23 pagesQM Lesson 7Daus VillaNo ratings yet
- CostDocument2 pagesCosthsWSNo ratings yet
- TQM and Cost IssuesDocument22 pagesTQM and Cost IssuesDebasmita NathNo ratings yet
- Iis-Sii Industri 03 Slide Indra AlmahdyDocument21 pagesIis-Sii Industri 03 Slide Indra AlmahdyFarhan YuzevanNo ratings yet
- 01 Quality Management Concept - Lecture 01 - 05Document71 pages01 Quality Management Concept - Lecture 01 - 05OcktaNo ratings yet
- ACC804 Advanced Management Accounting: Lecture: Week 8Document16 pagesACC804 Advanced Management Accounting: Lecture: Week 8Ravinesh PrasadNo ratings yet
- Two Examples of TQM: - Texas TelecomDocument11 pagesTwo Examples of TQM: - Texas Telecomshru_87No ratings yet
- How To Measure QualityDocument8 pagesHow To Measure QualityRobu MihaelaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Quality ManagementDocument101 pagesCH 2 Quality Managementmoyo josephNo ratings yet
- Different Type of Quality CostDocument2 pagesDifferent Type of Quality CostKamardeen NazurudeenNo ratings yet
- Quality CostsDocument14 pagesQuality Costsvisruth.humanstoriesNo ratings yet
- Quality Cost: by Dr. Lawrence WongDocument23 pagesQuality Cost: by Dr. Lawrence WongAtif Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Quality Cost 20 Okt 2021Document17 pagesQuality Cost 20 Okt 2021asmaul husna usemahNo ratings yet
- Basic of Quality, SPC, Process CapabilityDocument110 pagesBasic of Quality, SPC, Process CapabilityminionNo ratings yet
- Quality CostDocument7 pagesQuality CostSourabh Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- 011.previous Approved Material Submittal LogDocument101 pages011.previous Approved Material Submittal LogMACOYNo ratings yet
- Draft Warranty: Al Sultan Industrial CementDocument1 pageDraft Warranty: Al Sultan Industrial CementMACOYNo ratings yet
- ABG Measuring Water Flow Through A Geotextile TECH NOTEDocument1 pageABG Measuring Water Flow Through A Geotextile TECH NOTEMACOYNo ratings yet
- 10 Reasons For Employers To Invest in Staff MH DigitalDocument1 page10 Reasons For Employers To Invest in Staff MH DigitalMACOYNo ratings yet
- New Corporate ProfileDocument17 pagesNew Corporate ProfileMACOYNo ratings yet
- ITB-KEOC-2013-009 - Section VIII C - Mechanical SpecificationsDocument151 pagesITB-KEOC-2013-009 - Section VIII C - Mechanical SpecificationsMACOYNo ratings yet
- QMS Internal Auditor Training 3FOLD V1Document4 pagesQMS Internal Auditor Training 3FOLD V1MACOYNo ratings yet
- 10 Keys To Happier Living Wall PosterDocument1 page10 Keys To Happier Living Wall PosterMACOYNo ratings yet
- C) MSDS Curing Agent (02nd Coat)Document10 pagesC) MSDS Curing Agent (02nd Coat)MACOYNo ratings yet
- C) MSDS Curing Agent (03rd Coat)Document9 pagesC) MSDS Curing Agent (03rd Coat)MACOYNo ratings yet
- Excavation Shoring and Foundation General Requirements PDFDocument1 pageExcavation Shoring and Foundation General Requirements PDFMACOYNo ratings yet
- Questions and AnswersDocument19 pagesQuestions and AnswersMACOYNo ratings yet
- Construction Accidents Lessons Learnt PDFDocument52 pagesConstruction Accidents Lessons Learnt PDFMACOYNo ratings yet
- Cea Presidential Environment Award 2024Document2 pagesCea Presidential Environment Award 2024anupamabNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Marketing GS 3 AdilDocument21 pagesAgricultural Marketing GS 3 AdilArav-வும் Sri-யும்No ratings yet
- Research Analysis of Food Hub TrendsDocument62 pagesResearch Analysis of Food Hub TrendsPatrickNo ratings yet
- Final 1Document49 pagesFinal 1Aphrodite ArgennisNo ratings yet
- The Contributions of Jimmy Ocean Osorio Guevara To FidupetrolDocument2 pagesThe Contributions of Jimmy Ocean Osorio Guevara To FidupetrolJimmy Ocean OsorioNo ratings yet
- BRM AssignmentDocument18 pagesBRM AssignmentSanskriti SinghNo ratings yet
- Vadodara Institute of Engineering: Agriculture Crop Cutting EquipmentDocument8 pagesVadodara Institute of Engineering: Agriculture Crop Cutting EquipmentKrupal GandhiNo ratings yet
- Master Dock Cleaning Check ListDocument4 pagesMaster Dock Cleaning Check ListJordanNo ratings yet
- Costing and Pricing - 02 - Activity - 1Document1 pageCosting and Pricing - 02 - Activity - 1JERMAINE APRIL LAGURASNo ratings yet
- StatementOfAccount 50456096257 16082023 141039Document186 pagesStatementOfAccount 50456096257 16082023 141039Praveen SainiNo ratings yet
- SBFP Iar Milk Component 2021Document6 pagesSBFP Iar Milk Component 2021Damdamin RahimaNo ratings yet
- Awb 1818215604Document2 pagesAwb 1818215604Desy RiskianahNo ratings yet
- ICEA BrochureDocument4 pagesICEA BrochureSRINIVAS RAONo ratings yet
- شركة سالم محي الدين ضد عمان للبناء PDFDocument6 pagesشركة سالم محي الدين ضد عمان للبناء PDFSaso SasoNo ratings yet
- PSFU Annual Report 2018 - FINALDocument52 pagesPSFU Annual Report 2018 - FINALTwino KartelNo ratings yet
- New Project-MbaDocument87 pagesNew Project-MbamuralimadhavaregurigupthaNo ratings yet
- Soft BindDocument35 pagesSoft BindMark RamirezNo ratings yet
- Address of Shortlisted PMC Firms For Smart Cities ProposalDocument8 pagesAddress of Shortlisted PMC Firms For Smart Cities Proposalyash.ajmeraNo ratings yet
- Value Chain of The Wooden Furniture IndustryDocument3 pagesValue Chain of The Wooden Furniture Industryjacalyn_19900% (1)
- Jai-Blr Airasia TicketDocument4 pagesJai-Blr Airasia TicketArihant AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On Garments Merchandising Process Loophole and Challenges in A CompanyDocument55 pagesInternship Report On Garments Merchandising Process Loophole and Challenges in A CompanyEbrahim Hossain SumonNo ratings yet
- FTTCI All PANel Database All Cities in OneDocument1,022 pagesFTTCI All PANel Database All Cities in OneNazim KhanNo ratings yet
- OligopolyDocument15 pagesOligopolyMussadique HussainNo ratings yet
- PWC Internship Placement Program: Powered by CrimsonDocument19 pagesPWC Internship Placement Program: Powered by CrimsonShaurya BhallaNo ratings yet
- Disclosable Version of The ISR Sri Lanka Agriculture Sector Modernization Project P156019 Sequence No 09Document7 pagesDisclosable Version of The ISR Sri Lanka Agriculture Sector Modernization Project P156019 Sequence No 09agonzal1974No ratings yet
- g1 - Hss3013 Presentation in English (British Presence To India)Document26 pagesg1 - Hss3013 Presentation in English (British Presence To India)veniNo ratings yet
- Anna February 14-19 2022Document49 pagesAnna February 14-19 2022Jona Marie FormelozaNo ratings yet