Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Halfwave Rectifier Operation
Halfwave Rectifier Operation
Uploaded by
Rina Abay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThe document discusses the operation and characteristics of a half-wave rectifier. It operates by using a diode connected to an AC source and load resistor, allowing only the positive half-cycles of the input voltage to appear at the load. The average value of the output voltage is determined by calculating the area under the voltage curve over a full cycle. A diode must be rated to withstand the peak inverse voltage of the input signal plus a safety margin.
Original Description:
Original Title
Halfwave Rectifier Operation.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the operation and characteristics of a half-wave rectifier. It operates by using a diode connected to an AC source and load resistor, allowing only the positive half-cycles of the input voltage to appear at the load. The average value of the output voltage is determined by calculating the area under the voltage curve over a full cycle. A diode must be rated to withstand the peak inverse voltage of the input signal plus a safety margin.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageHalfwave Rectifier Operation
Halfwave Rectifier Operation
Uploaded by
Rina AbayThe document discusses the operation and characteristics of a half-wave rectifier. It operates by using a diode connected to an AC source and load resistor, allowing only the positive half-cycles of the input voltage to appear at the load. The average value of the output voltage is determined by calculating the area under the voltage curve over a full cycle. A diode must be rated to withstand the peak inverse voltage of the input signal plus a safety margin.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
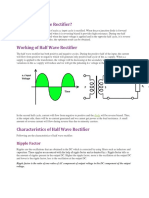
The Half-Wave Rectifier Operation
A diode is connected to an ac source and to a load resistor, RL, forming a half-wave
rectifier.
The current produces an output voltage across the load RL, which has the same shape as
the positive half-cycle of the input voltage.
The net result is that only the positive half-cycles of the AC input voltage appear across
the load.
The Average Value of the Half-Wave Output Voltage
The average value of the half-wave rectified output voltage is the value you would
measure on a dc voltmeter.
It is determined by finding the area under the curve over a full cycle, and then dividing by
the number of radians in a full cycle.
Effect of the Barrier Potential on the Half-Wave Rectifier Output
When the practical diode model is used with the barrier potential of 0.7 V taken into
account.
Peak Inverse Voltage (PIV)
The peak inverse voltage (PIV) equals the peak value of the input voltage, and the diode
must be capable of withstanding this amount of repetitive reverse voltage
A diode should be rated at least 20% higher than the PIV.
You might also like
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifierDocument8 pagesHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifierArun Jyothi82% (11)
- Half Wave RectifierDocument3 pagesHalf Wave RectifierdvgfvgfNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document7 pagesLecture 4Altaher Bushra AdamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Part-dIIDocument60 pagesChapter 2 Part-dIIAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- EE 152 Chapter 3Document53 pagesEE 152 Chapter 3Gideon AdomNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument2 pagesHalf Wave RectifierBerny Manalang100% (1)
- Chapter Five Diode Circuit ApplicationsDocument31 pagesChapter Five Diode Circuit Applicationsfouad abdNo ratings yet
- Unit II RectifiersDocument37 pagesUnit II Rectifiersdawa penjorNo ratings yet
- Diode Applications: Rectifier CircuitsDocument7 pagesDiode Applications: Rectifier Circuitseric labordoNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument27 pagesRectifiersDariele AlabanNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument27 pagesRectifiersDenver ExcondeNo ratings yet
- R13 EDC Unit-3Document22 pagesR13 EDC Unit-3praveen3.rkNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Analogue Electronics I)Document7 pagesLecture 3 (Analogue Electronics I)amash.emillyNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument16 pagesRectifiersJaiom JoshiNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier - PDFDocument4 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier - PDFSagnik RoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5b Diode - EEDocument90 pagesChapter 5b Diode - EEHarithZakariaNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier: Physics ProjectDocument14 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier: Physics ProjectRohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifierDocument6 pagesHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifierBilal KhanNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics EEE-339: Basic Concepts and RectifiersDocument60 pagesPower Electronics EEE-339: Basic Concepts and RectifiersZAHIDUL SALMANNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument26 pagesRectifierShuvo Kumar Modak100% (2)
- Class 12 Physics Project - Measuring Current Using Halfwave RectifierDocument19 pagesClass 12 Physics Project - Measuring Current Using Halfwave RectifierSarthak GoelNo ratings yet
- AC To DC Converter (Rectifiers) : Dirangkum Oleh: I Nyoman Wahyu Satiawan, ST, M.SC, PH.DDocument37 pagesAC To DC Converter (Rectifiers) : Dirangkum Oleh: I Nyoman Wahyu Satiawan, ST, M.SC, PH.DsatryaNo ratings yet
- يجوملا موقملا RectifierDocument18 pagesيجوملا موقملا RectifierYacine KhalidNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RactifierDocument3 pagesHalf Wave RactifierGAMMA GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Uncontrolled CircuitDocument64 pagesChapter 2 Uncontrolled CircuitSyiham HatmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document19 pagesChapter 3Ayesha TahirNo ratings yet
- Name Quantity: Diodes1N4007 (Si) 1 Resistor 1K 1 Capacitor 100 F 1Document5 pagesName Quantity: Diodes1N4007 (Si) 1 Resistor 1K 1 Capacitor 100 F 1avinash_yuvarajNo ratings yet
- 7 - FW RectificationDocument28 pages7 - FW Rectificationahsankhoso0007No ratings yet
- 2 Power Supply (Voltage Regulator) - 2Document78 pages2 Power Supply (Voltage Regulator) - 2Winter NaiNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument14 pagesHalf Wave RectifierAjay AgrawalNo ratings yet
- يجوملا موقملا RectifierDocument18 pagesيجوملا موقملا RectifierYacine KhalidNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:-Submitted To:-: Arush Swaroop (CS-C) Noor - E-ZaraDocument13 pagesSubmitted By:-Submitted To:-: Arush Swaroop (CS-C) Noor - E-ZaraArush Swaroop100% (1)
- 03 Chapter 4 Diode Application DELGDocument31 pages03 Chapter 4 Diode Application DELGaniq.halmyNo ratings yet
- دايود ريكتفايرDocument7 pagesدايود ريكتفايرalamryzhra62No ratings yet
- Exp. 4 DECADocument8 pagesExp. 4 DECAaparnasaluja22No ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifiersDocument7 pagesHalf Wave RectifiersSurajNo ratings yet
- Electronic Device and CircuitsDocument121 pagesElectronic Device and Circuitssanthosh216eeeNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument15 pagesHalf Wave RectifierYash Mangal40% (5)
- ELECS M3M4 FAsDocument30 pagesELECS M3M4 FAsartNo ratings yet
- 5 (A) - Half Wave Rectifier - Docx - 20231127 - 143415 - 0000Document4 pages5 (A) - Half Wave Rectifier - Docx - 20231127 - 143415 - 0000smrtyfaizan786No ratings yet
- Experiment No.02 To Observe The Characteristics of A Half Wave RectifierDocument4 pagesExperiment No.02 To Observe The Characteristics of A Half Wave RectifierWaqas MughalNo ratings yet
- 2 (1) .DIODE APPLICATIONS - FinalDocument37 pages2 (1) .DIODE APPLICATIONS - FinalSanjana HaqueNo ratings yet
- 2b RectifierDocument21 pages2b RectifierLove Strike100% (1)
- Precision Rectifier CircuitsDocument13 pagesPrecision Rectifier CircuitsWaqas PervaizNo ratings yet
- Power Diodes and RectifiersDocument5 pagesPower Diodes and Rectifiersmansoor.ahmed100No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument14 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSURAJ GAUTAMNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Lecture # 2: Diode As A RectifierDocument35 pagesBasic Electronics Lecture # 2: Diode As A Rectifierawais898989100% (2)
- Full Wave RectifierDocument5 pagesFull Wave RectifierAmulya TengNo ratings yet
- Rectifier: Half Wave Rectifier Full Wave RectifierDocument21 pagesRectifier: Half Wave Rectifier Full Wave RectifierKuAdenan KuSyakranNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Week 2halffullbridgerectifiernew2Document30 pages2.0 Week 2halffullbridgerectifiernew2Aideel zakwanNo ratings yet
- Electronics Page 18-21Document4 pagesElectronics Page 18-21Safia Younus ShaggyNo ratings yet
- Diode Circuits Perspective: Dr. Rajan Pandey Associate Professor, SENSEDocument23 pagesDiode Circuits Perspective: Dr. Rajan Pandey Associate Professor, SENSEDEEPIKA PAVUNDOSS 20BEC0285No ratings yet
- Q. What Do You Mean by Half Wave Rectification and Full Wave Rectification?Document5 pagesQ. What Do You Mean by Half Wave Rectification and Full Wave Rectification?Huidrom SharatNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument6 pagesPhysics ProjectRaj58% (19)
- Electronics and Communication Circuits Lab. Experiment #4 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Bridge RectifierDocument8 pagesElectronics and Communication Circuits Lab. Experiment #4 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Bridge RectifierEng. Ahmad ELsamakNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Transformer Coupling: Sec PriDocument1 pageTransformer Coupling: Sec PriRina AbayNo ratings yet
- Total Parallel ResistanceDocument1 pageTotal Parallel ResistanceRina AbayNo ratings yet
- Rectifier: The Basic DC Power SupplyDocument1 pageRectifier: The Basic DC Power SupplyRina AbayNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff'S Voltage Law: V V + V + V + VDocument1 pageKirchhoff'S Voltage Law: V V + V + V + VRina AbayNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument1 pageBipolar Junction TransistorRina AbayNo ratings yet
- Basic BJT OperationDocument1 pageBasic BJT OperationRina AbayNo ratings yet
- Another Classification of Disasters Will Be As FollowsDocument1 pageAnother Classification of Disasters Will Be As FollowsRina AbayNo ratings yet
- Disaster, Hazard, Vulnerability and RiskDocument1 pageDisaster, Hazard, Vulnerability and RiskRina AbayNo ratings yet
- Phase of DisasterDocument1 pagePhase of DisasterRina AbayNo ratings yet