Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy of An Animal Cell
Anatomy of An Animal Cell
Uploaded by
Yuki0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 views4 pagesThe document describes the components of animal and plant cells. Both cell types contain a cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes and vacuoles. Plant cells also have a cell wall and chloroplasts, which are the sites of photosynthesis. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, which converts sunlight to chemical energy through photosynthesis.
Original Description:
Original Title
cellss.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the components of animal and plant cells. Both cell types contain a cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes and vacuoles. Plant cells also have a cell wall and chloroplasts, which are the sites of photosynthesis. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, which converts sunlight to chemical energy through photosynthesis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 views4 pagesAnatomy of An Animal Cell
Anatomy of An Animal Cell
Uploaded by
YukiThe document describes the components of animal and plant cells. Both cell types contain a cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes and vacuoles. Plant cells also have a cell wall and chloroplasts, which are the sites of photosynthesis. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, which converts sunlight to chemical energy through photosynthesis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
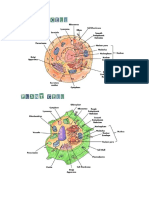
Anatomy of an Animal Cell
The components of animal cell:
Cell membrane - the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell. The cell
membrane is semipermeable, allowing some substances to pass into the cell and
blocking others.
Cytoplasm - the jellylike material outside the cell nucleus in which the organelles are
located.
Golgi body - (also called the Golgi apparatus or golgi complex) a flattened, layered,
sac-like organelle that looks like a stack of pancakes and is located near the nucleus. It
produces the membranes that surround the lysosomes. The Golgi body packages
proteins and carbohydrates into membrane-bound vesicles for "export" from the cell.
Lysosome - (also called cell vesicles) round organelles surrounded by a membrane
and containing digestive enzymes. This is where the digestion of cell nutrients takes
place.
Mitochondria - spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane. The inner
membrane is infolded many times, forming a series of projections (called cristae). The
mitochondrion converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
for the cell.
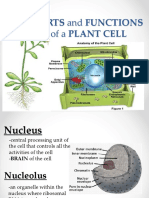
Nucleolus - an organelle within the nucleus - it is where ribosomal RNA is produced.
Some cells have more than one nucleolus.
Nucleus - spherical body containing many organelles, including the nucleolus. The
nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis) and
contains DNA (in chromosomes). The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane.
Ribosome - small organelles composed of RNA-rich cytoplasmic granules that are sites
of protein synthesis.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum - (rough ER) a vast system of interconnected,
membranous, infolded and convoluted sacks that are located in the cell's cytoplasm (the
ER is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane). Rough ER is covered with
ribosomes that give it a rough appearance. Rough ER transports materials through the
cell and produces proteins in sacks called cisternae (which are sent to the Golgi body,
or inserted into the cell membrane).
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum - (smooth ER) a vast system of interconnected,
membranous, infolded and convoluted tubes that are located in the cell's cytoplasm (the
ER is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane). The space within the ER is called
the ER lumen. Smooth ER transports materials through the cell. It contains enzymes
and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane proteins; smooth ER buds off
from rough ER, moving the newly-made proteins and lipids to the Golgi body,
lysosomes, and membranes.
Vacuole - fluid-filled, membrane-surrounded cavities inside a cell. The vacuole fills with
food being digested and waste material that is on its way out of the cell.
Anatomy of a Plant Cell
The components of plant cell:
Amyloplast - an organelle in some plant cells that stores starch. Amyloplasts are found
in starchy plants like tubers and fruits.
Cell membrane - the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell, but is inside
the cell wall. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing some substances to pass
into the cell and blocking others.
Cell wall - a thick, rigid membrane that surrounds a plant cell. This layer of cellulose
fiber gives the cell most of its support and structure. The cell wall also bonds with other
cell walls to form the structure of the plant.
Centrosome - (also called the "microtubule organizing center") a small body located
near the nucleus - it has a dense center and radiating tubules. The centrosomes is
where microtubules are made. During cell division (mitosis), the centrosome divides and
the two parts move to opposite sides of the dividing cell. Unlike the centrosomes in
animal cells, plant cell centrosomes do not have centrioles.
Chlorophyll - chlorophyll is a molecule that can use light energy from sunlight to turn
water and carbon dioxide gas into sugar and oxygen (this process is called
photosynthesis). Chlorophyll is magnesium based and is usually green.
Chloroplast - an elongated or disc-shaped organelle containing chlorophyll.
Photosynthesis (in which energy from sunlight is converted into chemical energy - food)
takes place in the chloroplasts.
Christae - (singular crista) the multiply-folded inner membrane of a cell's mitochondrion
that are finger-like projections. The walls of the cristae are the site of the cell's energy
production (it is where ATP is generated).
Cytoplasm - the jellylike material outside the cell nucleus in which the organelles are
located.
Golgi body - (also called the golgi apparatus or golgi complex) a flattened, layered,
sac-like organelle that looks like a stack of pancakes and is located near the nucleus.
The golgi body packages proteins and carbohydrates into membrane-bound vesicles for
"export" from the cell.
Mitochondrion - spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane. The
inner membrane is infolded many times, forming a series of projections (called cristae).
The mitochondrion converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP (adenosine
triphosphate) for the cell.
Nuclear membrane - the membrane that surrounds the nucleus.
Nucleolus - an organelle within the nucleus - it is where ribosomal RNA is produced.
Nucleus - spherical body containing many organelles, including the nucleolus. The
nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis) and
contains DNA (in chromosomes). The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane
Photosynthesis - a process in which plants convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide
into food energy (sugars and starches), oxygen and water. Chlorophyll or closely-
related pigments (substances that color the plant) are essential to the photosynthetic
process.
Ribosome - small organelles composed of RNA-rich cytoplasmic granules that are sites
of protein synthesis.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum - (rough ER) a vast system of interconnected,
membranous, infolded and convoluted sacks that are located in the cell's cytoplasm (the
ER is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane). Rough ER is covered with
ribosomes that give it a rough appearance. Rough ER transport materials through the
cell and produces proteins in sacks called cisternae (which are sent to the Golgi body,
or inserted into the cell membrane).
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum - (smooth ER) a vast system of interconnected,
membranous, infolded and convoluted tubes that are located in the cell's cytoplasm (the
ER is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane). The space within the ER is called
the ER lumen. Smooth ER transport materials through the cell. It contains enzymes and
produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane proteins; smooth ER buds off from
rough ER, moving the newly-made proteins and lipids to the Golgi body and
membranes
Vacuole - a large, membrane-bound space within a plant cell that is filled with fluid.
Most plant cells have a single vacuole that takes up much of the cell. It helps maintain
the shape of the cell.
You might also like
- Is Constant Use of Electronic Media Changing Our MindsDocument4 pagesIs Constant Use of Electronic Media Changing Our MindsVi Le50% (4)
- What Is Decarbonization ?: Main Engine Decarb Preparation, Procedure & Commissioning Sumit NarayanDocument3 pagesWhat Is Decarbonization ?: Main Engine Decarb Preparation, Procedure & Commissioning Sumit NarayanManisha100% (1)
- Animal CellDocument3 pagesAnimal CellKu Ya ÇhrisNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesComparison of Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsmalathyNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesDocument5 pagesAnimal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument2 pagesAnimal CellRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- The Following Is A Glossary of Animal Cell TermsDocument5 pagesThe Following Is A Glossary of Animal Cell Termsnelah roswatiNo ratings yet
- CellDocument3 pagesCellLeordan SanimNo ratings yet
- Bio11-Plant AnimalcomparisonDocument5 pagesBio11-Plant Animalcomparisonapi-246377724No ratings yet
- CellDocument5 pagesCellapi-267979304No ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument3 pagesAnimal CellKent Orriele FadriquelNo ratings yet
- Lecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellDocument4 pagesLecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellTRISTAN KENT SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsDocument15 pagesPlant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsanyoyoyNo ratings yet
- Cells Vocabulary PDFDocument2 pagesCells Vocabulary PDFMoody SaiiNo ratings yet
- The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy Terms.: Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria ChloroplastsDocument6 pagesThe Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy Terms.: Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria ChloroplastsHitesh MoreNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Anatomy: Plant Cell Printout Bacterium Cell PrintoutDocument3 pagesAnimal Cell Anatomy: Plant Cell Printout Bacterium Cell Printoutjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions: of A Plant CellDocument15 pagesParts and Functions: of A Plant CellAlleen Joy SolivioNo ratings yet
- Membran Sel Sitoplasma NukleusDocument32 pagesMembran Sel Sitoplasma NukleusAsmaul HusniNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellPrincess MillanNo ratings yet
- CYTOLOGYDocument3 pagesCYTOLOGYJessa Mae DarulloNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organelles Coloring PagesDocument5 pagesCells and Organelles Coloring Pagescarsontk421No ratings yet
- Cell Organelles FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Organelles FunctionsSeiji MingNo ratings yet
- Cell Intro InfoDocument12 pagesCell Intro Infoapi-237058097No ratings yet
- Hannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationDocument5 pagesHannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationAngelo AbulenciaNo ratings yet
- Cells Structure and FunctionDocument56 pagesCells Structure and FunctionAnnisa DiyanabilaNo ratings yet
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocument5 pagesNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell and Animal CellDocument8 pagesPlant Cell and Animal CelltipsyleopardNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- Biology 1st DiscussionDocument52 pagesBiology 1st DiscussionBea BulasaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15No ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument6 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYAngel ManlaviNo ratings yet
- Functions of A CellDocument4 pagesFunctions of A CellyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsJonathan MayoNo ratings yet
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- Week 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021Document4 pagesWeek 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021yui kirigayayuukiNo ratings yet
- Ans 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument33 pagesAns 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsAdewaleNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatDocument7 pagesCell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatSpongie BobNo ratings yet
- Notes Science CellsDocument12 pagesNotes Science CellsHina SharmaNo ratings yet
- STM123 OutlineDocument19 pagesSTM123 OutlineNur-Aiza AlamhaliNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument6 pagesCELLSFenny May SebonNo ratings yet
- Cell. Prikaryotic and Euk.Document30 pagesCell. Prikaryotic and Euk.avneeshraj100% (1)
- Cells and Organelles - 1Document6 pagesCells and Organelles - 1Izabayo philippeNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function: Endoplasmic Reticulum ERDocument2 pagesCell Structure & Function: Endoplasmic Reticulum ERLiling CassiopeiaNo ratings yet
- Activity No.1 - The CellDocument3 pagesActivity No.1 - The CellCelestine MambulaoNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDocument45 pagesTopic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDe Guia, Yuan Loriene Nina100% (1)
- Animal Cell and Plant CellDocument7 pagesAnimal Cell and Plant CellNancy judith Vallejo ToroNo ratings yet
- BIO ReviewerDocument14 pagesBIO ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument18 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellssalahuddin_md5935100% (1)
- Unit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument10 pagesUnit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesEds BernardoNo ratings yet
- The Role of Cytoplasm in A CellDocument5 pagesThe Role of Cytoplasm in A CellRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Notes Cell - The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument6 pages9th Class Notes Cell - The Fundamental Unit of LifepralexprajapatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceDocument34 pagesChapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceMadhav DayareNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument38 pagesCell Organellesjeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- CellDocument7 pagesCellnik29569No ratings yet
- Cytosol and Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Cytoplasm Refers To The Jelly-Like Material With Organelles in ItDocument6 pagesCytosol and Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Cytoplasm Refers To The Jelly-Like Material With Organelles in ItBridget SequeaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Cells Structure and FunctionDocument42 pagesLecture 5 Cells Structure and FunctionnindaleNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMark MagatNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell and Its FunctionsDocument2 pagesAnimal Cell and Its FunctionsaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Hoyle sg02Document17 pagesHoyle sg02YukiNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory: (Test Bank) Gerardo S. RoqueDocument82 pagesAuditing Theory: (Test Bank) Gerardo S. RoqueYukiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Auditing Theory L. R. Cabarles AT.1807-Preliminary Engagement Activities OCTOBER 2013Document7 pagesLecture Notes: Auditing Theory L. R. Cabarles AT.1807-Preliminary Engagement Activities OCTOBER 2013YukiNo ratings yet
- Inventories: Chapter 8: Theory of Accounts ReviewerDocument25 pagesInventories: Chapter 8: Theory of Accounts ReviewerYuki100% (1)
- This Study Resource Was: Advanced Accounting Ifrs 15Document6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Advanced Accounting Ifrs 15YukiNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument11 pagesDocxYukiNo ratings yet
- Student Answer:: - 703637150 Multiplechoice 15 True 0 - 703637150 Multiplechoice 15Document15 pagesStudent Answer:: - 703637150 Multiplechoice 15 True 0 - 703637150 Multiplechoice 15YukiNo ratings yet
- Revn01n Module 4Document11 pagesRevn01n Module 4YukiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: B Is CorrectDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: B Is CorrectYukiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document88 pagesChapter 15YukiNo ratings yet
- Pamela Galang Bsa 2 IA3 Quiz - Cash Flows True or FalseDocument10 pagesPamela Galang Bsa 2 IA3 Quiz - Cash Flows True or FalseYukiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Advanced Accounting Ifrs 15Document6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Advanced Accounting Ifrs 15YukiNo ratings yet
- Ipaubaya Computers Manufactures and Sells Pagers and Radio Paging Systems Which Include A 180 Day WaDocument12 pagesIpaubaya Computers Manufactures and Sells Pagers and Radio Paging Systems Which Include A 180 Day WaYukiNo ratings yet
- Name: - Score: - Year/Course/Section: - ScheduleDocument10 pagesName: - Score: - Year/Course/Section: - ScheduleYukiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Econometrics Ii (Econ-3062) : Mohammed Adem (PHD)Document83 pagesIntroduction To Econometrics Ii (Econ-3062) : Mohammed Adem (PHD)ፍቅር እስከ መቃብር100% (2)
- Managemen Disritmia: Dr. Rofika Hanifa, SPPDDocument20 pagesManagemen Disritmia: Dr. Rofika Hanifa, SPPDavivlabirdNo ratings yet
- IA BrochureDocument12 pagesIA BrochureChris WallaceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Eco LiteracyDocument15 pagesChapter 10 - Eco LiteracyMichelle Bandoquillo100% (1)
- Tassilipdf PDFDocument33 pagesTassilipdf PDFJustin LoucksNo ratings yet
- Website ErrorDocument5 pagesWebsite ErrorJosé DavidNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Dorb001 Bsce3aDocument16 pagesGroup 1 Dorb001 Bsce3aJan TheGamerNo ratings yet
- Problem Statement SubhanDocument5 pagesProblem Statement SubhanTech UniverseNo ratings yet
- Talent Acquisition 2008 - Survey and Analysis of The Changing Recruiting Landscape PDFDocument20 pagesTalent Acquisition 2008 - Survey and Analysis of The Changing Recruiting Landscape PDFVaishnavi SivaNo ratings yet
- Take Home Quizes Al-JaberDocument21 pagesTake Home Quizes Al-JaberalfredomedardoNo ratings yet
- The Pre-Production Process EvaluationDocument8 pagesThe Pre-Production Process EvaluationMC_Onnell100% (1)
- 8 Parts of A Business LetterDocument41 pages8 Parts of A Business LetterkennysawegNo ratings yet
- Ubuntu FeistyDocument242 pagesUbuntu FeistySlamet Budi SantosoNo ratings yet
- Handel e RuspoliDocument57 pagesHandel e RuspoliAndrea100% (1)
- The Wild BunchDocument2 pagesThe Wild BuncharnoldNo ratings yet
- TFG Miguel SanchezDocument77 pagesTFG Miguel SanchezMazin MursiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans WK 26Document7 pagesLesson Plans WK 26api-280840865No ratings yet
- PCR AslamkhanDocument1 pagePCR AslamkhanKoteswar MandavaNo ratings yet
- Aaroure: Salah EddineDocument2 pagesAaroure: Salah EddineAy OùbNo ratings yet
- Wawa Evolution of Business Process Design PDFDocument35 pagesWawa Evolution of Business Process Design PDFotchmarzNo ratings yet
- Asterisk For Dumb MeDocument164 pagesAsterisk For Dumb MeAndy CockroftNo ratings yet
- 3GPP TS 22.278Document51 pages3GPP TS 22.278bhushan7408No ratings yet
- 1sem-Tata Motors-Emerging MarketsDocument25 pages1sem-Tata Motors-Emerging MarketsAayush SisodiaNo ratings yet
- Sentences, Fragments, & Run-OnsDocument6 pagesSentences, Fragments, & Run-Onslu liu100% (1)
- Design For MaintainabilityDocument2 pagesDesign For MaintainabilityJulianna BakerNo ratings yet
- Apps SynonymsDocument42 pagesApps SynonymsMuhammad Sumair100% (1)
- Human Behavior Management (Introduction)Document17 pagesHuman Behavior Management (Introduction)Paola QuintosNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electricity PDFDocument371 pagesPrinciples of Electricity PDFJohn C. Stephens100% (5)