Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Guide To Submersible Well Pump Selection: 1. Well Capacity 6. 2-WIRE VS. 3-WIRE
Guide To Submersible Well Pump Selection: 1. Well Capacity 6. 2-WIRE VS. 3-WIRE
Uploaded by
Bassel El Sayed AliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Guide To Submersible Well Pump Selection: 1. Well Capacity 6. 2-WIRE VS. 3-WIRE
Guide To Submersible Well Pump Selection: 1. Well Capacity 6. 2-WIRE VS. 3-WIRE
Uploaded by
Bassel El Sayed AliCopyright:
Available Formats
Guide to Submersible Well Pump Selection
A deep well submersible water system is used to supply domestic water Before planning or installation can begin, two questions must be
automatically to the plumbing system of a home or building from a answered: How much water will be required for daily use; and, can the
private well. The complete pumping unit is submerged in the well below well produce enough water to meet daily requirements?
water level. The basic components of the system are the pump, pressure The following discussion will assist you in answering the questions
switch, and tank. above and help you choose the right size pump.
1. WELL CAPACITY 6. 2-WIRE VS. 3-WIRE
How much water will the well produce in GPM (gallons per minute)? 3-wire pumps have the advantage of being equipped with high-starting
Determine this by: a) well driller's log, or b) use of an older cleanout torque motors. A high-starting torque is sometimes needed to break free
pump to determine flow rate. (NOTE: Never use a new pump for this mineral deposits that may adhere to the pump's moving parts. 2-wire
service.) After cleanout pump operates for 30 minutes at free flow, fill pumps should not be used where abrasives or heavy water scale are
a 5-gallon bucket and make a note of the time it takes to reach capac- present.
ity. Use this data in the following formula: 7. CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS
gal. of water (5)
x 60 = GPM (gallons per minute)
a. Cast-iron basic construction represents good value and is useful in
seconds many applications.
GPH (gallons per hour) = GPM x 60
b. Thermoplastic construction provides excellent value and corrosion
Note: If at any time during the 30 minutes of free flow water fails to flow, pump should resistance.
be turned off immediately. Wait 3 to 4 hours, lower pump deeper into well, and throttle c. Stainless steel construction has superior corrosion resistance.
(use a gate valve) pump back by closing valve 1/4 turn. The above procedure should be
repeated until water flows continuously for 30 minutes. Not doing so could result in
dry running and destruction of the pump. The pump should never be closer than 10
feet to the bottom of the well.
5 GPM Series
For low-capacity wells where a higher series would "overpump" the
well, causing pump failure.
10 GPM Series
For average-capacity wells. The most popular choice in farm and home
applications.
20 to 27 GPM Series
For high-capacity wells where more than normal water supply is
required: ranches, dairy farms, light irrigation, and light industrial
water systems.
35 to 85 GPM Series
For very high capacity wells and/or very deep wells. For irrigation and
industrial water systems where higher water volume is needed.
2. DEPTH OF WELL
This can be determined by 1 of the following: a) well driller's log, or b)
tie a heavy weight to a string, lower into well until it reaches bottom,
and measure this distance.
3. DEPTH TO WATER (WATER PUMPING LEVEL)
To determine this, 2 vertical distances must be added together: a) total
vertical feet from the highest service outlet to ground level, and b) total
vertical feet from ground level to the pumping level of the water. The
Water Pumping Level is defined as the standing water level in the well
when the pump is operating, and the water being pumped out equals
the water entering the well. This level is generally several feet lower
than the water level in the well when pump is not operating.
It should be understood that pump setting depth does not determine
pump performance. The main criterion is the Water Pumping Level.
The depth of the pump below this water level is of no significance in
relation to gallons and pressure delivered by the pump.
4. VOLUME
Each outlet that may be left on for continuous use will require about
3 gallons per minute (GPM). A 1-bathroom house is usually sized for
2 continuous-use outlets, and a 2-bathroom house is usually sized
for 3 continuous-use outlets. Livestock requirements are in addition
to home requirements and, of course, must be added in order to
determine the final volume requirement.
5. PRESSURE With the pump running, adjust gate valve until pressure gauge located
Many homes use a 30 to 50 pressure (psi) setting. Higher cut-in on pump side of the valve reads 10 psi higher than the highest tank
and cut-out (40 to 60 psi) settings may be needed where automatic pressure gauge reading; e.g., if the system is set for 20 to 40 psi, the
appliances require higher pressure for proper operation. pressure gauge on the pump side of gate valve will show 50 psi.
You might also like
- Oil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesFrom EverandOil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Fire Pump Sizing and SelectionDocument7 pagesFire Pump Sizing and Selectionaalokeroy100% (2)
- Sewer Bypass Fundamentals PDFDocument4 pagesSewer Bypass Fundamentals PDFHung Leung Sang Eddy0% (1)
- Method Statement: Water Leakage Detection SurveyDocument16 pagesMethod Statement: Water Leakage Detection SurveyPhara LuckyNo ratings yet
- PD 198 (Revised 2010) Provincial Water Utilities ActDocument97 pagesPD 198 (Revised 2010) Provincial Water Utilities ActRoel Briones67% (3)
- Tank SizingDocument2 pagesTank SizingsamehNo ratings yet
- Water System Sizing LectureDocument11 pagesWater System Sizing LectureBliven GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Sizing Boiler Feed Pumps CalculationDocument3 pagesThe Sizing Boiler Feed Pumps CalculationArun Kumar DeyNo ratings yet
- Size PumpsDocument0 pagesSize Pumpsaravoof84No ratings yet
- Size PumpsDocument2 pagesSize PumpsLoretta KimNo ratings yet
- Fluid Machinery - Eng - Pump - Part2 (Compatibility Mode)Document65 pagesFluid Machinery - Eng - Pump - Part2 (Compatibility Mode)ณัฐวัศ มั่นบุญสมNo ratings yet
- Earth Safe: Your Questions Answered (47) Fuel Transfer SystemsDocument12 pagesEarth Safe: Your Questions Answered (47) Fuel Transfer Systemsdeepak2628No ratings yet
- Sump Submersible Pumps DesignDocument4 pagesSump Submersible Pumps DesignAnonymous wIPMQ5rhNo ratings yet
- Water System Sizing Worksheet: Joe Agricola ExampleDocument5 pagesWater System Sizing Worksheet: Joe Agricola ExampleMaruf ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Sizing A Well Pump: Wellcare®Document3 pagesSizing A Well Pump: Wellcare®toots guiaoNo ratings yet
- Allen, Laura - Greywater, Green Landscape - How To Install Simple Water-Saving Irrigation Systems in Your Yard-Storey Publishing (2017) - 9Document20 pagesAllen, Laura - Greywater, Green Landscape - How To Install Simple Water-Saving Irrigation Systems in Your Yard-Storey Publishing (2017) - 9Hector Alfredo Gutierrez RomeroNo ratings yet
- Fire Pump Sizing and CalculationsDocument5 pagesFire Pump Sizing and CalculationsNikhil NambiarNo ratings yet
- Applications For Water PumpingDocument18 pagesApplications For Water PumpingjeniNo ratings yet
- Pumps AG 7 - 1 PDFDocument4 pagesPumps AG 7 - 1 PDFquiron2010No ratings yet
- Give Me A Boost!: Plumbing Design by The NumbersDocument2 pagesGive Me A Boost!: Plumbing Design by The NumbersSuhas NatuNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Excavator Truck DesignDocument8 pagesVacuum Excavator Truck DesignajcapetillogNo ratings yet
- Why Bladder Tanks - 8!16!17Document10 pagesWhy Bladder Tanks - 8!16!17bla blaNo ratings yet
- All Code Jurisdictions Have Maximum Allowable Turnover Times For FiltrationDocument13 pagesAll Code Jurisdictions Have Maximum Allowable Turnover Times For FiltrationCamilo RochaNo ratings yet
- Operation & Maintanance Manual For HVWS SystemDocument18 pagesOperation & Maintanance Manual For HVWS SystemVijay Patel100% (1)
- Hydraulics in High Rise Satnam SinghDocument10 pagesHydraulics in High Rise Satnam SinghsauroNo ratings yet
- Fire Pump Sizing and Selectio1Document14 pagesFire Pump Sizing and Selectio1Rahul Deva100% (2)
- Ram Pump PDFDocument9 pagesRam Pump PDFoliververonamanuelNo ratings yet
- Hosereel SystemDocument5 pagesHosereel Systemrmaffireschool100% (3)
- Bpump PDFDocument20 pagesBpump PDFgpskumar22No ratings yet
- Choosing A Pump SicDocument6 pagesChoosing A Pump Sicchipora3No ratings yet
- Residential Pump FundamentalsDocument25 pagesResidential Pump FundamentalsperoooNo ratings yet
- 5.13. ProblemsDocument3 pages5.13. Problemsاسماعیل ادریس عبدالعزیزNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Simulator Training Institute: Bakreswar Thermal Power Project: WBPDCLDocument22 pagesPower Plant Simulator Training Institute: Bakreswar Thermal Power Project: WBPDCLRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- How To Size Hydropneumatic TankDocument3 pagesHow To Size Hydropneumatic TankfelipeNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Sizing: FeaturesDocument8 pagesGuidelines For Sizing: FeaturesApih Ibrahim100% (1)
- How To Size A Hydropneumatic Tank in A Pressure Booster SystemDocument3 pagesHow To Size A Hydropneumatic Tank in A Pressure Booster SystemAnonymous mNQq7ojNo ratings yet
- How To Read A PumpDocument14 pagesHow To Read A PumpAmeer AbbasNo ratings yet
- Variable Speed Pumps AmDocument9 pagesVariable Speed Pumps Amraveekas6148No ratings yet
- Pumps StudentsDocument62 pagesPumps StudentsAKHIL JOSEPH100% (1)
- Pumped Outlets For Subsurface Drainage: Technical, Planning and DesignDocument3 pagesPumped Outlets For Subsurface Drainage: Technical, Planning and DesignAli HydarNo ratings yet
- 6 Boiler Feedwater PumpsDocument20 pages6 Boiler Feedwater PumpsCristhian Garcia VillarroelNo ratings yet
- Pump Filter SizingDocument3 pagesPump Filter SizingkavjoNo ratings yet
- Fire Pump Sizing and SelectionDocument5 pagesFire Pump Sizing and SelectionEshref AlemdarNo ratings yet
- Pump ED 101: How Curve Shape Can Influence Pump SelectionDocument5 pagesPump ED 101: How Curve Shape Can Influence Pump Selectionmercedes_rico_5No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics-II AssignmentDocument7 pagesFluid Mechanics-II AssignmentMuntaha AnjumNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Submersible Pump Set For Bore Well, Tube Well & Dug Well (Open Well)Document16 pagesGuidelines For Submersible Pump Set For Bore Well, Tube Well & Dug Well (Open Well)Santosh Kumar88% (8)
- 006 - 2008 Jockey Pumps - RH May 18Document5 pages006 - 2008 Jockey Pumps - RH May 18Amin UdinNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Ram PumpsDocument4 pagesHydraulic Ram PumpsSersio BordiosNo ratings yet
- AODDs and Viscosity FluidsDocument3 pagesAODDs and Viscosity FluidsDarshan PatelNo ratings yet
- A W11-2011 GS-SV en XylemDocument128 pagesA W11-2011 GS-SV en XylemCristóbal ScheelNo ratings yet
- CCI Power ApplicationsDocument57 pagesCCI Power Applicationssukanya_ravichandran100% (1)
- Sump PumpDocument5 pagesSump PumpTanvir ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document35 pagesModule 1Bryan GarlejoNo ratings yet
- High Speed Pump IntroductionDocument28 pagesHigh Speed Pump IntroductionAnddy PérezNo ratings yet
- How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesFrom EverandHow to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pneumatic and Hydrautic Conveying of Both Fly Ash and Bottom AshFrom EverandPneumatic and Hydrautic Conveying of Both Fly Ash and Bottom AshNo ratings yet
- Practical Rules for the Management of a Locomotive Engine in the Station, on the Road, and in cases of AccidentFrom EverandPractical Rules for the Management of a Locomotive Engine in the Station, on the Road, and in cases of AccidentNo ratings yet
- PP3-Advance HVAC Course OEA2Document55 pagesPP3-Advance HVAC Course OEA2Bassel El Sayed AliNo ratings yet
- PP4 - Advance HVAC Course OEADocument16 pagesPP4 - Advance HVAC Course OEABassel El Sayed AliNo ratings yet
- PP2 - Advance HVAC Course OEA - 1Document49 pagesPP2 - Advance HVAC Course OEA - 1Bassel El Sayed AliNo ratings yet
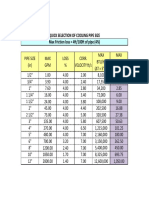
- Quick Selection of Cooling Pipe Size Max Friction Loss 4ft/100ft of Pipe (4%)Document2 pagesQuick Selection of Cooling Pipe Size Max Friction Loss 4ft/100ft of Pipe (4%)Bassel El Sayed AliNo ratings yet
- PP1 Water Cooled - Air CooledDocument28 pagesPP1 Water Cooled - Air CooledBassel El Sayed AliNo ratings yet
- Chap 10 Technique 1 Air DistributionDocument19 pagesChap 10 Technique 1 Air DistributionBassel El Sayed AliNo ratings yet
- Ground Water Conservation in Kerala Policies and Practice With Special Emphasis On Ground Water Conservation in IndiaDocument38 pagesGround Water Conservation in Kerala Policies and Practice With Special Emphasis On Ground Water Conservation in IndiaS.Alec Knowle100% (1)
- B. Tech Major Project Design Constraints: Engineering Design Is A Process of Devising ADocument2 pagesB. Tech Major Project Design Constraints: Engineering Design Is A Process of Devising AgfgfghNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabusVinothNo ratings yet
- Water and Wastewater Engineering: Design of Water Supply System of Bahria Town Phase 1Document39 pagesWater and Wastewater Engineering: Design of Water Supply System of Bahria Town Phase 1Omaya Tariq100% (1)
- WSD Manual - of - Mainlaying - Practice - 2012 PDFDocument127 pagesWSD Manual - of - Mainlaying - Practice - 2012 PDFtongdannyNo ratings yet
- Final Inception Report With Appendices PDFDocument233 pagesFinal Inception Report With Appendices PDFAnAs Nassar100% (1)
- Future of Urban Water Manila Final CompDocument64 pagesFuture of Urban Water Manila Final CompFrida Faye LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- (Astm Special Technical Publication - STP) John C. Monday, Timothy B. Shugart, Joseph A. Tamayo-Manual On Coating and Lining Methods For Cooling Water Systems in Power Plants-Astm Intl (1995) PDFDocument58 pages(Astm Special Technical Publication - STP) John C. Monday, Timothy B. Shugart, Joseph A. Tamayo-Manual On Coating and Lining Methods For Cooling Water Systems in Power Plants-Astm Intl (1995) PDFidigitiNo ratings yet
- Residential Building ConstructionDocument40 pagesResidential Building ConstructionRaj Verma67% (9)
- FGFFGDocument25 pagesFGFFGCharan Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- How Potable Water Rises To The Top of Skyscrapers - Octo-Dec05Document3 pagesHow Potable Water Rises To The Top of Skyscrapers - Octo-Dec05jkedar_78No ratings yet
- Water Supply Inspection ReportDocument11 pagesWater Supply Inspection ReportAlyannaKatePalasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Water Supply EngineeringDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Water Supply EngineeringAshly Anshad100% (1)
- Water Supply Systems Lecture 1 PDFDocument38 pagesWater Supply Systems Lecture 1 PDFNur Khaliza100% (1)
- Pumping Stations Design Lecture 6Document45 pagesPumping Stations Design Lecture 6njvargascNo ratings yet
- Subject Disinfection of Water Tank and Distribution System Comments: A、 ReferencesDocument2 pagesSubject Disinfection of Water Tank and Distribution System Comments: A、 ReferencesSuman BajracharyaNo ratings yet
- Project Progress ReportDocument9 pagesProject Progress ReportMorvin BudhanNo ratings yet
- Cold Water Plumbing Design NotesDocument18 pagesCold Water Plumbing Design NotesShahril Shahibullah100% (1)
- 13 Candelaria 429-443Document15 pages13 Candelaria 429-443Arnold Magdalita FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Kruthumal Case Study Report - Final-Feb2014-1Document26 pagesKruthumal Case Study Report - Final-Feb2014-1Alamandha Madhan Kumar100% (1)
- UET PostGrad Thesis-2Document33 pagesUET PostGrad Thesis-2Abdur RafaiNo ratings yet
- New Guidelines SANS 10090 - 45_04_17_3660Document9 pagesNew Guidelines SANS 10090 - 45_04_17_3660deanolemmetjies05No ratings yet
- Assessment Report On The Electrical Pump BreakdownsDocument22 pagesAssessment Report On The Electrical Pump BreakdownsEdwin Cob GuriNo ratings yet
- RuralDrinkingWater 2ndapril PDFDocument116 pagesRuralDrinkingWater 2ndapril PDFsai praneethNo ratings yet
- En Comuna Biharia FinalDocument72 pagesEn Comuna Biharia Finaltomi_penzesNo ratings yet
- Gram Panchayat ReportDocument68 pagesGram Panchayat ReportGautam KumarNo ratings yet
- SC6.4.3.23 Water and Sewer Network Modelling GuidelinesDocument11 pagesSC6.4.3.23 Water and Sewer Network Modelling GuidelinesAmri YusrulNo ratings yet
- Seattle Plumbing CodeDocument243 pagesSeattle Plumbing CodeAouina Chokri100% (2)