Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsCasual Comparative Research (Ex-Post Facto) PDF
Casual Comparative Research (Ex-Post Facto) PDF
Uploaded by
melbe5jane5quiamcoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Minutes Negotiation Conference 01182019 Ro11Document4 pagesMinutes Negotiation Conference 01182019 Ro11melbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Lifestyle Diseases: Consequences, Characteristics, Causes and ControlDocument4 pagesLifestyle Diseases: Consequences, Characteristics, Causes and Controlmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
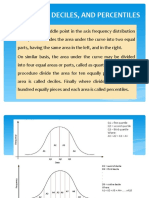
- Measures of Relative PositionDocument17 pagesMeasures of Relative Positionmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Malakas Na Ulan, Hanging Dala NG Bagyong Ulysses Ramdam Na Sa Catanduanes - ABS-CBN NewsDocument5 pagesMalakas Na Ulan, Hanging Dala NG Bagyong Ulysses Ramdam Na Sa Catanduanes - ABS-CBN Newsmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgDFbM KvcShNjszJLS7jTnRt3iy1LD1kx6pIcd HJvr8kFv0dRRPXTFtiGK25P SrKI82D620Gqvhgw 3fICaZ8ZkwgG4LurEtsDDpxt5OYRf2NLk3wW7o NvPfJM5be6GA QA6LUEDlkagDocument3 pagesACFrOgDFbM KvcShNjszJLS7jTnRt3iy1LD1kx6pIcd HJvr8kFv0dRRPXTFtiGK25P SrKI82D620Gqvhgw 3fICaZ8ZkwgG4LurEtsDDpxt5OYRf2NLk3wW7o NvPfJM5be6GA QA6LUEDlkagmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Creative Nonfiction Activity Sheet Literary Elements and Literary TechniquesDocument4 pagesCreative Nonfiction Activity Sheet Literary Elements and Literary Techniquesmelbe5jane5quiamco100% (2)
- 5-Minute Exercises To Make Your Belly Fat Melt Like SnowDocument6 pages5-Minute Exercises To Make Your Belly Fat Melt Like Snowmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Creative Nonfiction Activity Sheet Literary Elements and Literary TechniquesDocument4 pagesCreative Nonfiction Activity Sheet Literary Elements and Literary Techniquesmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- How To Use Photoshop CC - Beginners - 11 Steps - InstructablesDocument6 pagesHow To Use Photoshop CC - Beginners - 11 Steps - Instructablesmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Acfrogbc-Hwv7mbxqhr1c89nimlgohn1ozfd4wq6ny5a5ibm-6j J U5mo7rigcr98e79qpv Bc56z0ezgicp8gzgejopymofnuy9vr-J0qqigqile Goxyrke7sm8efwpsjbtosw3zbl5gc7khhDocument5 pagesAcfrogbc-Hwv7mbxqhr1c89nimlgohn1ozfd4wq6ny5a5ibm-6j J U5mo7rigcr98e79qpv Bc56z0ezgicp8gzgejopymofnuy9vr-J0qqigqile Goxyrke7sm8efwpsjbtosw3zbl5gc7khhmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- TLEDocument6 pagesTLEmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- TractorDocument4 pagesTractormelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- BakuDocument11 pagesBakumelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Hand Tool Project Requirements: The Case of Banana Cultivation and Its Physical Demands (OWAS)Document13 pagesHand Tool Project Requirements: The Case of Banana Cultivation and Its Physical Demands (OWAS)melbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Blog:: 2. MangaDocument3 pagesBlog:: 2. Mangamelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Juan PDFDocument5 pagesJuan PDFmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- 30 Flash Fiction of QuiamcoDocument1 page30 Flash Fiction of Quiamcomelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
Casual Comparative Research (Ex-Post Facto) PDF
Casual Comparative Research (Ex-Post Facto) PDF
Uploaded by
melbe5jane5quiamco0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views28 pagesOriginal Title
Casual Comparative Research[ Ex-Post Facto].pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views28 pagesCasual Comparative Research (Ex-Post Facto) PDF
Casual Comparative Research (Ex-Post Facto) PDF
Uploaded by
melbe5jane5quiamcoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 28
Scribd will begin operating the SlideShare business on December 1, 2020 As of this date, Scribd will
‘manage your SlideShare account and any content you may have on SlideShare, and Scribd's General Terms of
Use and Privacy Policy will apply. If you wish to opt out, please close your SlideShare account. Learn mor
SlideShare Explore Search You
we slideshare
© Search ‘Submit Search
* Home
© Explore
‘Search
Successfully reported this slideshow.
We use your Linkedin profile and activity data to personalize ads and to show you more relevant ads. You can
Q
2 of 25
Causal Comparative Research / Ex- Post Facto
julliana marie torres
allow
uae eeAOO)
EAF 410
Full Name
Comment goes here.
12 hours ago
Are you sure you want to
Your message goes here
2
‘Share your thoughts...
Post
Finally found a service provider which actually supplies an essay with an engaging introduction leading to
the main body of the exposition Here is the site =>=>WRITE-MY-PAPER net Gee
2 days ago
‘Are you sure you want to Yes No
Your message goes here
*
> www.HelpWriting.net © is a good website if you're looking to get your essay written for you. You can
also request things like research papers or dissertations. It’s really convenient and helpful.
1 month ago
Are you sure you want to Yes No
Your message goes here
Hello! I can recommend a site that has helped me. It’s called => www. WritePaper.info = So make sure to
check it out!
3 months ago
‘Are you sure you want to Yes No
Your message goes here
—Differences already exist
* Ex post facto
= Much research in medi
sociology
sustrtes= ee
No Downloads
Views
Total views
10,558
On SlideShare
0
From Embeds
0
Number of Embeds
38
Actions
Shares
0
Downloads
260
‘Comments
5
Likes
8
Embeds 0
No embeds
No notes for slide
Causal Comparative Research / Ex- Post Facto
1: 1; Causal-ComiparativeCausal-Comparative ResearchResearch July 23, 2001Suly 23, 2001 BAF 410F.AF
410
2. 2 What is it?What is it? + AssociationalAssociational « Differences between/among groupsDitictences
i i GistDifferences already
Much research in medicine &
° How ied
2 yee
administratiy:
‘Gecisions att
Dften lead to
experimental researchOfen lead to experimental research * Don't allow variable manipulationDon't allow
variable manipulation + Attempt to explore causationAttempt to explore causation
Causal-ComparativeCausal-Comparative -compare groups-compare groups -categorical variable(s)-
categorical variable(s) -crossbreak tables-crossbreak tables CorrelationalCorrelational -individual scores-
individual scores -quantitative variables-quantitative variables -scatterplots &-scatterplots & rr Similarities
withSimilarities with Correlational ResearchCorrelational Research
Steps InvolvedSteps Involved ¢ Identify & clarify research problemIdentify & clarify research problem
= Several alternative hypothesesSeveral alternative hypotheses * Select subjects (groups)Select subjects
(groups) — Homogenous on some variablesHomogenous on some variables +
InstrumentationInstrumentation — No limitsNo limits
Steps InvolvedSteps Involved (continued)(continued) * DesignDesign — Groups differ on specific
variableGroups differ on specific variable — Groups compared on other variable(s)Groups compared on
other variable(s)
Evaluating ThreatsEvaluating Threats * What other factors affect theWhat other factors affect the
comparison variable?comparison variable? * What is the likelihood of the What is the likelihood of the
groups differing on these factors?groups differing on these factors? « Evaluate threats on likelihood
ofEvaluate threats on likelihood of their effect and plan to control.their effect and plan to control.
Survey ResearchSurvey Research July 23, 2001 July 23, 2001 EAF 410EAF 410
‘Three CharacteristicsThree Characteristics * Information collected to describeInformation collected to
describe + Information collected by askingInformation collected by asking questionsquestions +
Information collected from alnformation collected from a samplesample
Major PurposeMajor Purpose + To describe the characteristics of aTo describe the characteristics of a
populationpopulation * Not so concerned aboutNot so concerned about whywhy * Concerned
aboutConcerned about what iswhat is
Types of SurveysTypes of Surveys + Cross-sectional StudyCross-sectional Study ~ information
collected at just oneinformation collected at just one point in timepoint in time * Longitudinal
‘StudyLongitudinal Study — information collected at differentinformation collected at different points in
timepoints in time
‘Types of LongitudinalTypes of Longitudinal StudiesStudies * TrendTrend — Different samplesDifferent
samples — Population may changePopulation may change + CohortCohort — Different samplesDifferent
samples — Population doesn’t changePopulation doesn’t change
“Types of LongitudinalTypes of Longitudinal StudiesStudies (continued)(continued) * PanelPanel —
Same sampleSame sample ~ Population doesn’t changePopulation doesn’t change
Steps in Survey ResearchSteps in Survey Research + Clearly define objectivesClearly define objectives
+ Construct clear questionsConstruct clear questions + Sample (unit of analysis)Sample (unit of analysis) +
Collect dataCollect data — “live” to a grouplive” to a group — mailmail — phonephone — face-to-face
interviewsface-to-face interviews
Preparing the InstrumentPreparing the Instrument + Not too longNot too long * Questions easy to
answerQuestions easy to answer Carefully wordedCarefully worded — can be asked as writtencan be
asked as written — will mean same to allwill mean same to all — can be answeredcan be answered — will be
answeredwill be answered
22, 22. Types of Questions Types of Questions * Closed-endedClosed-ended — answers providedanswers
provided * Open-endedOpen-ended — respondent provides answersrespondent provides answers
2,
‘Suggestions for Closed-Suiggestions Tor Closed- Ended QuestionsEnded Questions
‘UnambiguousUnambiguous « Simple focusSimple focus « ShortShort » Common languageCo:nmon
“Unbiased” termsUnbiased” terms * Not leading questionsNot leading questions > Nw double
nbership in a group
ut differences in student beh:
saused by gender?
as
Sn
Seas
* Studies causes of group
membership
—Why do ISU students enroll in EAF
410 during the summer session?
O
‘No public clipboards found for this slide
Select another clipboard
O
Looks like you've clipped this slide to already.
‘Search for a clipboard
Create a clipboard
You just clipped your first slide!
Clipping is a handy way to collect important slides you want to go back to later. Now customize the name of a
Clipboard to store your clips.
‘Name* Best of Slides
Description Add a brief description so otf
Visibility
Others can see my Clipboard
Cancel Save
Save this presentation
* Studies the consequences of an
intervention.
—How do students who have taken
EAF 410 evaluate research articles?
° Does gender cause differences?
—Girls read better
—Boys ar
* Other probable links in the causal
chain
° Noted difference between two
groups
* Look for causes/consequer
Similarities withSimilarities with Correlational ResearchCorrelational Research + AssociationalAssociational *
Attempt to .
sal-Comparative -compare groups-compare groups -categorical variable(s)=
categorical variable(s) -cros...
Steps InvolvedSteps Involved + Identify & clarify research problemldentify & clarify research problem —
Several alternativ...
Steps InvolvedSteps Involved (continued)(continued) + DesignDesign — Groups differ on specific
variableGroups differ on sp..
Evaluating ThreatsEvaluating Threats + What other factors affect theWhat other factors affect the comparison
variable?eomp..
Survey ResearchSurvey Research July 23,
, 2001 July 23, 2001 EAF 410EAF 410
jaracteristics + Information collected to describeInformation collected to
describe + Informat.,
Major PurposeMajor Purpose + To describe the characteristics of ao describe the characteristics of a
populationpopulation...
‘Types of Surveys Types of Surveys + Cross-sectional Study ctional Study — information collected at
just oneinformati...
‘Types of LongitudinalTypes of Longitudinal StudiesStudies + Trend Trend — Different samplesDifferent
samples ~ Population m...
‘Types of Longitudinal Types of Longitudinal StudiesStudies (continued)(continued) + PanelPanel — Same
sampleSame sample - P,
Steps in Survey ResearchSteps in Survey Research + Clearly define objectivesClearly define objectives +
Construct clear qu.
Preparing the InstrumentPreparing the Instrument + Not too longNot too long + Questions easy to
answerQuestions easy to an...
‘Types of Questions Types of Questions * Closed-endedClosed-ended — answers providedanswers provided +
Open-endedOpen-ended ...
Suggestions for Closed-Suggestions for Closed Ended QuestionsEnded Questions *
UnambiguousUnambiguous + Simple focusSimpl.
Suggestions for QuestionsSuggestions for Questions * Try them out on a similar sampleTry them out on
similar sample * Ma...
NonresponseNonresponse * Some will not return surveySome will not return survey + Some items will not be
answeredSome item.
Upcoming SlideShare
Loading in ...5
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Minutes Negotiation Conference 01182019 Ro11Document4 pagesMinutes Negotiation Conference 01182019 Ro11melbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Lifestyle Diseases: Consequences, Characteristics, Causes and ControlDocument4 pagesLifestyle Diseases: Consequences, Characteristics, Causes and Controlmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Measures of Relative PositionDocument17 pagesMeasures of Relative Positionmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Malakas Na Ulan, Hanging Dala NG Bagyong Ulysses Ramdam Na Sa Catanduanes - ABS-CBN NewsDocument5 pagesMalakas Na Ulan, Hanging Dala NG Bagyong Ulysses Ramdam Na Sa Catanduanes - ABS-CBN Newsmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgDFbM KvcShNjszJLS7jTnRt3iy1LD1kx6pIcd HJvr8kFv0dRRPXTFtiGK25P SrKI82D620Gqvhgw 3fICaZ8ZkwgG4LurEtsDDpxt5OYRf2NLk3wW7o NvPfJM5be6GA QA6LUEDlkagDocument3 pagesACFrOgDFbM KvcShNjszJLS7jTnRt3iy1LD1kx6pIcd HJvr8kFv0dRRPXTFtiGK25P SrKI82D620Gqvhgw 3fICaZ8ZkwgG4LurEtsDDpxt5OYRf2NLk3wW7o NvPfJM5be6GA QA6LUEDlkagmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Creative Nonfiction Activity Sheet Literary Elements and Literary TechniquesDocument4 pagesCreative Nonfiction Activity Sheet Literary Elements and Literary Techniquesmelbe5jane5quiamco100% (2)
- 5-Minute Exercises To Make Your Belly Fat Melt Like SnowDocument6 pages5-Minute Exercises To Make Your Belly Fat Melt Like Snowmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Creative Nonfiction Activity Sheet Literary Elements and Literary TechniquesDocument4 pagesCreative Nonfiction Activity Sheet Literary Elements and Literary Techniquesmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- How To Use Photoshop CC - Beginners - 11 Steps - InstructablesDocument6 pagesHow To Use Photoshop CC - Beginners - 11 Steps - Instructablesmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Acfrogbc-Hwv7mbxqhr1c89nimlgohn1ozfd4wq6ny5a5ibm-6j J U5mo7rigcr98e79qpv Bc56z0ezgicp8gzgejopymofnuy9vr-J0qqigqile Goxyrke7sm8efwpsjbtosw3zbl5gc7khhDocument5 pagesAcfrogbc-Hwv7mbxqhr1c89nimlgohn1ozfd4wq6ny5a5ibm-6j J U5mo7rigcr98e79qpv Bc56z0ezgicp8gzgejopymofnuy9vr-J0qqigqile Goxyrke7sm8efwpsjbtosw3zbl5gc7khhmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- TLEDocument6 pagesTLEmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- TractorDocument4 pagesTractormelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- BakuDocument11 pagesBakumelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Hand Tool Project Requirements: The Case of Banana Cultivation and Its Physical Demands (OWAS)Document13 pagesHand Tool Project Requirements: The Case of Banana Cultivation and Its Physical Demands (OWAS)melbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Blog:: 2. MangaDocument3 pagesBlog:: 2. Mangamelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- Juan PDFDocument5 pagesJuan PDFmelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet
- 30 Flash Fiction of QuiamcoDocument1 page30 Flash Fiction of Quiamcomelbe5jane5quiamcoNo ratings yet