Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet 1.1 (Lesson 1.1 Representation of Function)
Worksheet 1.1 (Lesson 1.1 Representation of Function)
Uploaded by
Wendelyn SumpoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet 1.1 (Lesson 1.1 Representation of Function)
Worksheet 1.1 (Lesson 1.1 Representation of Function)
Uploaded by
Wendelyn SumpoCopyright:
Available Formats
WORKSHEET 1.1 (LESSON 1.
1 REPRESENTATION OF FUNCTION)
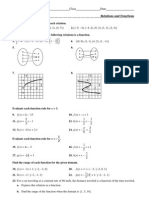
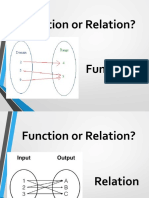
I. Determine whether or not each relation is a function. Give the domain and range of
each relation.
1. {(2, 3), (4, 5), (6, 6)} Function
Domain (x) — {2, 4, 6} ; Range (y) — {3, 5, 6}
2. {(4, 5), (4, 6), (5, 5), (5, 6)} Relation
Domain (x) — {4, 5} ; Range (y) — {5, 6}
3. {(-2, -2), (-1, -1), (0, 0), (1, 1)} Function
Domain (x) — {-2, -1, 0, 1}; Range (y) — {-2, -1, 0, 1}
4. {(−6, −6), (−4, −4), (−2, −2), (0, 0)} Function
Domain (x) — {-6, -4, -2, 0}; Range (y) — {-6, -4, -2, 0}
5. {(5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3)} Relation
Domain (x) — {5} ; Range (y) — {1, 2, 3}
II. Fill in each blank to make a true statement.
1. Suppose that a set of ordered pairs has no elements having the same first coordinates,
such as set is called a (n) function.
2. A method of determining whether or not a graph represents a function is called the
vertical line test.
3. The symbol f(x) is read as f of x/function of x.
4. for the function {(3,4), (6,0),(-3,-1)}, the set {3,6,-3} is called the domain, and the set
{4,0,- 1} is called the range.
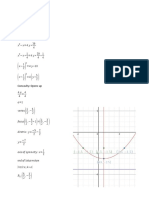
5. The domain of f(x) = √x − 2 is x ∈ (2, ∞) or {x|x≥2}.
You might also like
- Relation, Functions and GraphsDocument54 pagesRelation, Functions and GraphsCamille Francisco AgustinNo ratings yet
- Functions PDFDocument7 pagesFunctions PDFPaolo NaguitNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Functions, Function Notation, Domain & RangeDocument27 pagesLesson 1 - Functions, Function Notation, Domain & RangeJerome FresadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 2 - Intro To FunctionsDocument32 pagesChapter 3 2 - Intro To Functionsapi-263209117No ratings yet
- Worksheet 5 FunctionsDocument7 pagesWorksheet 5 FunctionsSong LyricsNo ratings yet
- The Rudest Book EverDocument14 pagesThe Rudest Book EverIrene B. LuisNo ratings yet
- Objectives: The Student Will Be Able ToDocument13 pagesObjectives: The Student Will Be Able ToBogz GarciaNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument13 pagesFunctionsRosemarie Agpaua BajetNo ratings yet
- A.7d PowerpointDocument48 pagesA.7d Powerpointm8thmilitantNo ratings yet
- Relations and FunctionsDocument7 pagesRelations and FunctionsshaluNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument25 pagesFunctionsROLLY BALONo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument25 pagesFunctionsJohn Philip EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Functions and LimitsDocument78 pagesLecture 1 Functions and Limitsjoemer cabayaoNo ratings yet
- Objectives: The Student Will Be Able ToDocument13 pagesObjectives: The Student Will Be Able ToMohammad Faizal Azwar AnnasNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Relations and FunctionsDocument15 pages2.1 Relations and FunctionsJesimie OriasNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument25 pagesFunctionsJANELLA ALVAREZNo ratings yet
- Ana Lea Joy: Ben Carl JunDocument5 pagesAna Lea Joy: Ben Carl JunJay P. CajesNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument12 pagesFunctionsElmabeth Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 15: Finding The Domain and Range of Inverse FunctionsDocument14 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 15: Finding The Domain and Range of Inverse FunctionsAthena Kirsten MarceloNo ratings yet
- Functions PDFDocument73 pagesFunctions PDFRabi Shankar DashNo ratings yet
- Section 1.2 Basics of FunctionsDocument44 pagesSection 1.2 Basics of FunctionsdavogezuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Lessons 1-4)Document95 pagesChapter 3 (Lessons 1-4)Retchelle Palmero SangcoNo ratings yet
- Introduction_Relation & Function (1)Document15 pagesIntroduction_Relation & Function (1)e.aniciete0816No ratings yet
- Relations and FunctionsDocument12 pagesRelations and FunctionsAngela OrenseNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts On FUNCTIONSDocument41 pagesKey Concepts On FUNCTIONSCarl Jose CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Functions: One Element y in The RangeDocument7 pagesFunctions: One Element y in The RangePaolo NaguitNo ratings yet
- Objectives: The Student Will Be Able ToDocument14 pagesObjectives: The Student Will Be Able Tomangu bhukyaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 - Introduction of FunctionsDocument17 pagesWEEK 1 - Introduction of FunctionsHerynadel AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Welcome General Mathematics For Grade 11: Mr. Adonis C. Honasan Teacher IIIDocument21 pagesWelcome General Mathematics For Grade 11: Mr. Adonis C. Honasan Teacher IIIRyan Joseph HernoNo ratings yet
- Week 3 GenMAth AutosavedDocument31 pagesWeek 3 GenMAth AutosavedYuri BallierbareNo ratings yet
- 1.2 The Algebra of FunctionsDocument16 pages1.2 The Algebra of FunctionsYukiC123No ratings yet
- NAMEDocument1 pageNAMEAngelo SarinasNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument25 pagesFunctionsMooni BrokeNo ratings yet
- FunctionDocument107 pagesFunctionAh Naweed Najeeb SakhaNo ratings yet
- Representation of Functions: Aaron Paul A. CasabarDocument78 pagesRepresentation of Functions: Aaron Paul A. CasabarM MNo ratings yet
- Bal Bharati Public School Ganga Ram Hospital Marg, New Delhi-60Document2 pagesBal Bharati Public School Ganga Ram Hospital Marg, New Delhi-60Himanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Relations and FunctionsDocument2 pagesRelations and FunctionsayeshaNo ratings yet
- CBSE XII HOTS Relation and Functions Chapter 1Document4 pagesCBSE XII HOTS Relation and Functions Chapter 1Sandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Day 10 - Relations and Functions Homework WorksheetDocument2 pagesDay 10 - Relations and Functions Homework WorksheetSeth AikensNo ratings yet
- GenMath - LESSON 1Document1 pageGenMath - LESSON 1Russell AngelesNo ratings yet
- 2.relations and FunctionsDocument2 pages2.relations and FunctionsDisha Tripathi - 10-ENo ratings yet
- Math 111: Functions and RelationsDocument27 pagesMath 111: Functions and Relationsalvin bautistaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesNcert Important Questionsrath01108No ratings yet
- MATH 101 M-Relations FunctionsDocument35 pagesMATH 101 M-Relations FunctionsDaisy Marie A. RoselNo ratings yet
- Genmath Module 1Document19 pagesGenmath Module 1Eunice SiervoNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 FunctionsDocument27 pagesRD Sharma Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 FunctionsShivam Mutkule100% (1)
- GENMATH Exam Q1Document5 pagesGENMATH Exam Q1miniriftyNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 AE Name - Some CH 3 Review: G F F G X F G X G FDocument3 pagesAlgebra 2 AE Name - Some CH 3 Review: G F F G X F G X G FxpgongNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Concept of A FunctionDocument10 pages1.1 Concept of A FunctionJoe VicenteNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Part 1Document6 pagesLesson 1 Part 1Adelaide CNo ratings yet
- Function or Relation?Document14 pagesFunction or Relation?Daniel ClementeNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 2 - Finding Function's DomainDocument19 pagesLECTURE 2 - Finding Function's Domainrmm eateryNo ratings yet
- Function and Evaluation of FunctionDocument9 pagesFunction and Evaluation of Functionbrice burgosNo ratings yet
- Algebra MATH 1201-01 - AY2022-T5 Written Assignement Unit 4Document5 pagesAlgebra MATH 1201-01 - AY2022-T5 Written Assignement Unit 4buihuonguyenNo ratings yet
- LMS1 FunctionsDocument15 pagesLMS1 FunctionsMay LelisNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Q2M2Document3 pagesMath 8 Q2M2glorivy perigoNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 4 FunctionsDocument2 pagesTUTORIAL 4 FunctionsHijau TrujilloNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument28 pagesFunctionsbruhwhatdoievenwritenaymore123No ratings yet
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- ASSESSMENTDocument2 pagesASSESSMENTWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- Application 1Document2 pagesApplication 1Wendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- PE Midterms PDFDocument61 pagesPE Midterms PDFWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- Application AssessmentDocument1 pageApplication AssessmentWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- APPLICATIONDocument2 pagesAPPLICATIONWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- PLDTDocument1 pagePLDTWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- History and Scope of MicrobiologyDocument3 pagesHistory and Scope of MicrobiologyWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- Assessment CuesDocument3 pagesAssessment CuesWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- FencingDocument10 pagesFencingWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENTDocument1 pageASSESSMENTWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENTDocument2 pagesASSESSMENTWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- Elements of Fiction: by Jerick E. Fegarido, LPTDocument20 pagesElements of Fiction: by Jerick E. Fegarido, LPTWendelyn Sumpo100% (2)
- Elements of PoetryDocument26 pagesElements of PoetryWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument25 pagesFigures of SpeechWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- SOP 1. What Particular Factors Made The Filipino Youth Involve Themselves in Politics Code Name LineDocument33 pagesSOP 1. What Particular Factors Made The Filipino Youth Involve Themselves in Politics Code Name LineWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- Alfred Wegener, A German Meteorologist Who Proposed An Explanation For The OriginDocument4 pagesAlfred Wegener, A German Meteorologist Who Proposed An Explanation For The OriginWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics TheoryDocument8 pagesPlate Tectonics TheoryWendelyn Sumpo100% (1)
- Worksheet 1.3 (Lesson 1.3 Operations On Functions)Document6 pagesWorksheet 1.3 (Lesson 1.3 Operations On Functions)Wendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- Essay Function of CommunicationDocument1 pageEssay Function of CommunicationWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1.2 (Lesson 1.2 Evaluation of Functions) : 1) H (T) - T + 2 - + 3 Find HDocument4 pagesWorksheet 1.2 (Lesson 1.2 Evaluation of Functions) : 1) H (T) - T + 2 - + 3 Find HWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- A. Identify The Center and Radius of Each. Then Sketch The Graph. 1. 2.Document9 pagesA. Identify The Center and Radius of Each. Then Sketch The Graph. 1. 2.Wendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet
- Pre CalculusDocument2 pagesPre CalculusWendelyn SumpoNo ratings yet