Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 13 Study Guide - Bio 1: Sofia Iadipaolo
Chapter 13 Study Guide - Bio 1: Sofia Iadipaolo
Uploaded by
Sofia IadipaoloOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 13 Study Guide - Bio 1: Sofia Iadipaolo
Chapter 13 Study Guide - Bio 1: Sofia Iadipaolo
Uploaded by
Sofia IadipaoloCopyright:
Available Formats
Sofia Iadipaolo
NAME ____________________
CHAPTER 13 STUDY GUIDE – BIO 1
DEFINITIONS
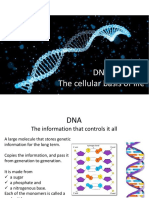
1. Transcription
changes the message from DNA to RNA
2. Translation
genetic code from mRNA to amino acids
3. Codon
it codes for amino acid, it is also matched
by tRNA bring amino acid to ribosome
4. Anticodon
a sequence of three nucleotides forming
a unit of genetic code
IMPORTANT IDEAS
5. What are the 3 types of RNA? What do they do and what do they look like?
mRNA- (messenger) looks like half a DNA
rRNA- (ribosomal) looks like a blob with mRNA in it
tRNA-(transfer) looks like a key with the code attached to it
6. How is it possible for an amino acid to be called for by more than one codon?
because certain codones have the same outputs
7. What is a mutation?
a mutation is a change in the DNA sequence.
shifting everything over a causing it to change
8. What is the difference between a point mutation and a chromosomal mutation?
chromosomal mutation can cause down
syndrome and point mutation is less serious
and only causes small changes
9. Explain gene regulation in eukaryotes. How are genes regulated/expressed?
by repressors and transcriptional activators. they
bind to specific DNA and transcription
10. Why do cells have different functions? HOW do they have different functions?
NAME ____________________
CHAPTER 13 STUDY GUIDE – BIO 1
11. How is pre-mRNA converted to final mRNA?
spliceosomes cut introns out of pre-RNA. exons
put back together and cap and tail them.
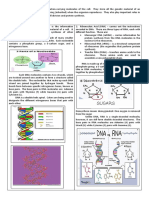
12. Explain the similarities and differences between RNA & DNA.
DNA RNA BOTH
~ double stranded ~single stranded ~store genetic info
~ storing and transferring ~ directly codes for amino acids ~large biological polymers
genetic info ~acts like a messenger ~consist of sugar, nitrogen bases, etc
13. Be able to transcribe and translate a molecule of DNA.
Replication Transcription Translation
DNA or RNA product? DNA RNA RNA
Single or double double stranded double stranded single stranded
stranded product?
Where does this take in the cytoplasm of in the nucleus different cellular
place? prokaryotes and in the compartments
nucleus of eukaryotes
You might also like
- Guyton Hall Physiology Review Guyton Physiology 4Th Edition John E Hall PHD Full ChapterDocument67 pagesGuyton Hall Physiology Review Guyton Physiology 4Th Edition John E Hall PHD Full Chapterangelita.linton34971% (7)
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetEderlyn Zate100% (1)
- Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 11Th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument29 pagesHuman Genetics Concepts and Applications 11Th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFmagdalavicemanocgp100% (11)
- (Deja Review) Naheedy, John H. - Orringer, Daniel A - Deja Review. USMLE Step 1-McGraw-Hill Medical (2010)Document413 pages(Deja Review) Naheedy, John H. - Orringer, Daniel A - Deja Review. USMLE Step 1-McGraw-Hill Medical (2010)Vansley, V.100% (5)
- Transcription and Translation - Worksheet - StudentDocument9 pagesTranscription and Translation - Worksheet - StudentGiselle Muhammad50% (2)
- Study Guide For 3rd Test-BSC 2010LDocument7 pagesStudy Guide For 3rd Test-BSC 2010LPepitinNo ratings yet
- C Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 3 (Week 4)Document14 pagesC Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 3 (Week 4)Daisy Soriano Prestoza100% (1)
- Biotech STE 8 Q2 Lesson 5 Role of DNA RNA and Protein in The Transmission of Hereditary Traits 3Document14 pagesBiotech STE 8 Q2 Lesson 5 Role of DNA RNA and Protein in The Transmission of Hereditary Traits 3Aileen Ocampo100% (1)
- Biology Today and Tomorrow Without Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manual 1Document10 pagesBiology Today and Tomorrow Without Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manual 1sook100% (38)
- Biology Today and Tomorrow Without Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manual 1Document14 pagesBiology Today and Tomorrow Without Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manual 1janesilvapwoikcfjgb100% (30)
- Dna Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument9 pagesDna Replication and Protein Synthesisbravebrave2005No ratings yet
- Lecture - 30oct13Document41 pagesLecture - 30oct13Dagon BrownNo ratings yet
- Rna & Protein SynthesisDocument41 pagesRna & Protein SynthesisJoeric CarinanNo ratings yet
- Study Dna DnaDocument45 pagesStudy Dna DnaKrystel BeltranNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Week 10Document4 pagesEarth and Life Science Week 10Ma. Jhysavil ArcenaNo ratings yet
- How Cells Work CompilationDocument18 pagesHow Cells Work CompilationJocelyn Diaz AbangNo ratings yet
- How Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityDocument5 pagesHow Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityAdonis Besa100% (1)
- Transcription Translation - Types of RNA 2022Document20 pagesTranscription Translation - Types of RNA 2022Merey ZiyabekNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lesson 10 OnwardsDocument18 pagesGenetics Lesson 10 OnwardsMa. Joy JocosolNo ratings yet
- I. DNA, Chromosomes, Chromatin, and GenesDocument12 pagesI. DNA, Chromosomes, Chromatin, and GeneshanzNo ratings yet
- The Role of RNA DNA and PROTEIN in The Transmission of TraitsDocument21 pagesThe Role of RNA DNA and PROTEIN in The Transmission of TraitsrebugiocosmeNo ratings yet
- Transcription, Translation and Replication PDFDocument12 pagesTranscription, Translation and Replication PDFrorNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Biology Chapter 6 - Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument8 pagesClass Xii Biology Chapter 6 - Molecular Basis of InheritanceAkshit Sharma VIII Diasy Roll no 6No ratings yet
- De La Proteina La GenaDocument67 pagesDe La Proteina La GenaiuventasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document14 pagesLecture 10tasfia2829No ratings yet
- CMB MODULE IV SEC 3 Gene Expression RegulationDocument22 pagesCMB MODULE IV SEC 3 Gene Expression RegulationTanalgo JPNo ratings yet
- Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions ManualDocument12 pagesHuman Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions Manualantheagian4p4y4100% (33)
- Chapter IV Introduction To Bacterial Genetics-1Document67 pagesChapter IV Introduction To Bacterial Genetics-1temesgensemahegn55No ratings yet
- Types of Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pagesTypes of Nucleic AcidsJomari Alipante100% (1)
- Dna Transparency TeacherDocument12 pagesDna Transparency Teacherapi-445198464100% (1)
- Transcription WorkingDocument51 pagesTranscription Workingapi-3858544No ratings yet
- InstructionsDocument5 pagesInstructionsLord NiquidNo ratings yet
- RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) : RNA Is A Polymer of Ribonucleotides Linked Together by 3'-5' Phosphodiester LinkageDocument37 pagesRNA (Ribonucleic Acid) : RNA Is A Polymer of Ribonucleotides Linked Together by 3'-5' Phosphodiester Linkagefaheem sarwarNo ratings yet
- RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) : RNA Is A Polymer of Ribonucleotides Linked Together by 3'-5' Phosphodiester LinkageDocument37 pagesRNA (Ribonucleic Acid) : RNA Is A Polymer of Ribonucleotides Linked Together by 3'-5' Phosphodiester Linkagefaheem sarwarNo ratings yet
- Microbial GeneticsDocument11 pagesMicrobial GeneticskimeehhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument33 pagesLesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologySherwin YenogacioNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of DNA and RNADocument3 pagesStructure and Functions of DNA and RNAokonabasimfreke09No ratings yet
- DNAto ProteinDocument41 pagesDNAto ProteinJimmy gogoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10-DLP10-DNARep-Protein-Synthesis-Trsc-TrnsDocument3 pagesSCIENCE 10-DLP10-DNARep-Protein-Synthesis-Trsc-TrnsSharlene Cecil PagoboNo ratings yet
- Essentials of The Living World 5th Edition George Johnson Solutions ManualDocument5 pagesEssentials of The Living World 5th Edition George Johnson Solutions Manualjuliemcintyretzydiengcr100% (30)
- IB Biology Notes - 35 Transcription TranslationDocument2 pagesIB Biology Notes - 35 Transcription TranslationJohn Philip D. NapalNo ratings yet
- L18 Polypeptide SynthesisDocument18 pagesL18 Polypeptide Synthesisareejhussaini26No ratings yet
- Structure of RNADocument36 pagesStructure of RNAsohamdasofficial02No ratings yet
- BIO-5dll 3rdDocument15 pagesBIO-5dll 3rdarlene dioknoNo ratings yet
- 05-02-Genetika MikroorganismeDocument48 pages05-02-Genetika MikroorganismeKinad DanikNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Complete PowerpointDocument48 pagesProtein Synthesis Complete PowerpointJohn Osborne100% (1)
- Protein ReviewerDocument2 pagesProtein ReviewerangelamaevillonNo ratings yet
- From Genes To ProteinsDocument32 pagesFrom Genes To ProteinsVanessa QuinolNo ratings yet
- 60855f4d-BIF 14 Gene Expression From Gene To ProteinDocument61 pages60855f4d-BIF 14 Gene Expression From Gene To ProteinMarcus RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument35 pagesProtein SynthesisDaryl GumacalNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Genetic CodeDocument30 pages1.4 Genetic CodeMehar SaeedNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology: InstructorDocument20 pagesCell Biology: Instructorahmed mediaNo ratings yet
- AsomaDocument45 pagesAsomaTetra HedronNo ratings yet
- CH 13 RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument12 pagesCH 13 RNA and Protein SynthesisHannah50% (2)
- Science Q3 WK5.Document14 pagesScience Q3 WK5.Hellow FriendzNo ratings yet
- Genes and How They WorkDocument114 pagesGenes and How They WorkClaire ChavezNo ratings yet
- Module 4-From Gene To Protein Basic Molecular Genetic MechanismsDocument43 pagesModule 4-From Gene To Protein Basic Molecular Genetic MechanismsBelinda GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Genetic Mutations Science Presentation in Blue Orange Flat Graphic StyleDocument30 pagesGenetic Mutations Science Presentation in Blue Orange Flat Graphic StylechrishhhaaNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Life: Transcription and TranslationDocument13 pagesCentral Dogma of Life: Transcription and TranslationLamia AkterNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - GeneticsDocument23 pagesWeek 5 - GeneticsJuan Pablo Valencia LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Part I - BIOL2520-2Document22 pagesChapter 7 Part I - BIOL2520-2shrilpatel2001No ratings yet
- Topic 15-18 Content ADocument28 pagesTopic 15-18 Content ALeanne Krystel CastroNo ratings yet
- Module 4 KKKDocument32 pagesModule 4 KKKbhrayancachero100% (1)
- MYCO VIRO 1-MergedDocument29 pagesMYCO VIRO 1-MergedGennelyn Ross Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatics I: Lecture NotesDocument180 pagesBioinformatics I: Lecture NotesDaniela GuardiaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & Physiology I - Dr. Sullivan Unit IV - Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (Meiosis Only)Document5 pagesHuman Anatomy & Physiology I - Dr. Sullivan Unit IV - Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (Meiosis Only)Steve SullivanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To mRNA Production and TFF.Document20 pagesIntroduction To mRNA Production and TFF.Ahmed RaslanNo ratings yet
- Transcription and ModificationDocument23 pagesTranscription and ModificationWarlin FernandezNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme For June 2010: BiologyDocument22 pagesMark Scheme For June 2010: Biologyamar_12345No ratings yet
- A Physiological Approach To DNA MusicDocument7 pagesA Physiological Approach To DNA Musicstarwarp2000No ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument35 pagesTranscription and TranslationMing mingNo ratings yet
- Eoc Biology Rview Packet 2012-2013Document48 pagesEoc Biology Rview Packet 2012-2013api-282682755No ratings yet
- MRNA StudyDocument30 pagesMRNA StudyTom DemasNo ratings yet
- Aidan Budd (Auth.), Maria Anisimova (Eds.) Evolutionary Genomics - Statistical and Computational Methods, Volume 1 2012Document467 pagesAidan Budd (Auth.), Maria Anisimova (Eds.) Evolutionary Genomics - Statistical and Computational Methods, Volume 1 2012Conchita PinzonNo ratings yet
- 18MSMB2H01 MolecularBiology 2019Document19 pages18MSMB2H01 MolecularBiology 2019Pranav KbNo ratings yet
- Archives of Oral Biology: Ying Jin, Chenglin Wang, Si Cheng, Zhihe Zhao, Prof., Juan LiDocument9 pagesArchives of Oral Biology: Ying Jin, Chenglin Wang, Si Cheng, Zhihe Zhao, Prof., Juan LiJuan Carlos MeloNo ratings yet
- Exercise and Problems Types of Nucleic Acids (Section 22.1)Document7 pagesExercise and Problems Types of Nucleic Acids (Section 22.1)Azyrah Lyren Seguban UlpindoNo ratings yet
- AP Bio CH 15Document17 pagesAP Bio CH 15Jhun Banual ZaspaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Code 12Document16 pagesGenetic Code 12Jahnavi Joshi0% (1)
- Cell PhysiologyDocument7 pagesCell PhysiologyReslie Joy Serrano100% (1)
- SuspensorDocument8 pagesSuspensorWaqas GhazlaniNo ratings yet
- From Gene To Protein: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionDocument75 pagesFrom Gene To Protein: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionFENo ratings yet
- Icmr JRF PaperDocument13 pagesIcmr JRF PaperSushmita ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Review Polyamine-Dependent Gene Expression: Cellular and Molecular Life SciencesDocument13 pagesReview Polyamine-Dependent Gene Expression: Cellular and Molecular Life SciencesxprakashNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetJuan Esteban Escandon AgudeloNo ratings yet
- A2 Level Biology Unit 4 EdexcelDocument27 pagesA2 Level Biology Unit 4 EdexcelLulwa KhaskiehNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular Biology PDFDocument474 pagesCell and Molecular Biology PDFluishernandorenaNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesCell (Biology) - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaapi-3714451100% (2)
- 18 Lecture PresentationDocument49 pages18 Lecture PresentationMuhammad Rifki RamadhanNo ratings yet