Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 viewsChem
Chem
Uploaded by
Uɱɘʀ JʌŋɩThis document discusses the functions of two types of glycerophospholipids - phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. Phosphatidylethanolamine is the second most abundant phospholipid in mammalian cell membranes, plays important roles in membrane fusion and cell division, and has various functions in the liver, heart, blood clotting, and bacterial cell membranes. Phosphatidylcholine may help protect the large intestine in people with ulcerative colitis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Enzymes Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesEnzymes Review WorksheetJamil Samira E. Buizon100% (3)
- Phospholipids Across Scales: Lipid Patterns and Plant DevelopmentDocument20 pagesPhospholipids Across Scales: Lipid Patterns and Plant DevelopmentAswad ZEllzNo ratings yet
- Carcinogenesis - Arno HelmbergDocument4 pagesCarcinogenesis - Arno HelmbergHafsah ShoaibNo ratings yet
- NO.11 1. Golgi ApparatusDocument25 pagesNO.11 1. Golgi ApparatusEkaterina SurguladzeNo ratings yet
- Lysosomal Biology in CancerDocument16 pagesLysosomal Biology in CancerZi JianNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi HaidDocument66 pagesFisiologi HaidRizna AriyaniNo ratings yet
- Plasma MembraneDocument6 pagesPlasma Membraneparashakthi PRNo ratings yet
- Science PosterDocument1 pageScience PosterWeljun GallardoNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument2 pagesCell TransportAshleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Protein Folding and MisfoldingDocument17 pagesChapter Protein Folding and MisfoldingMazhar FarNo ratings yet
- Chaperones in Protein Biological Important of Molecular FoldingDocument2 pagesChaperones in Protein Biological Important of Molecular FoldingSanele100% (1)
- The Cell MembraneDocument36 pagesThe Cell Membraneanulorance98No ratings yet
- CSIR Life Science Sample Cell BiologyDocument17 pagesCSIR Life Science Sample Cell Biologygamer zoneNo ratings yet
- Study On PhosphatidylcholineDocument121 pagesStudy On Phosphatidylcholinearun_kedia648100% (1)
- Funcion Endocrina de La Placenta HumanaDocument30 pagesFuncion Endocrina de La Placenta HumanaSofia RossoNo ratings yet
- Activity in General BiologyDocument2 pagesActivity in General BiologyMore, Mary RuthNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 3. Plasma MembraneDocument14 pagesKuliah 3. Plasma MembraneYusuf SumarNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Siklus HaidDocument70 pagesFisiologi Siklus HaidsilviNo ratings yet
- Signal TransductionDocument11 pagesSignal TransductionAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Structural Components of Cell Membrane: Group 4Document12 pagesStructural Components of Cell Membrane: Group 4Jeongyeonnie OppaNo ratings yet
- Phospholipid: From: Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry, 2019Document8 pagesPhospholipid: From: Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry, 2019Eiann Jasper LongcayanaNo ratings yet
- Functional Microdomains in Bacterial Membranes: Material SupplementalDocument11 pagesFunctional Microdomains in Bacterial Membranes: Material SupplementaltommystarfireNo ratings yet
- Kim Et Al 2024 Non Vesicular Phosphatidylinositol Transfer Plays Critical Roles in Defining Organelle Lipid CompositionDocument27 pagesKim Et Al 2024 Non Vesicular Phosphatidylinositol Transfer Plays Critical Roles in Defining Organelle Lipid CompositionDaniel DavidNo ratings yet
- Signaling. This Requires A Signal From The Cardiogenic Mesoderm Composed of FGF. (Point at Mesoderm)Document5 pagesSignaling. This Requires A Signal From The Cardiogenic Mesoderm Composed of FGF. (Point at Mesoderm)Cara JaenNo ratings yet
- Fot 247Document26 pagesFot 247Malini KolekarNo ratings yet
- CropDocument11 pagesCropHall OwnNo ratings yet
- Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta: Michel Record, Kevin Carayon, Marc Poirot, Sandrine Silvente-PoirotDocument13 pagesBiochimica Et Biophysica Acta: Michel Record, Kevin Carayon, Marc Poirot, Sandrine Silvente-PoirotGlauce L TrevisanNo ratings yet
- Physio Oral Report NotesDocument3 pagesPhysio Oral Report NotesMariel AsisNo ratings yet
- Primary HemostasisDocument10 pagesPrimary HemostasisMariella DingleNo ratings yet
- Signaling Pathways That Depend On Regulated Proteolysis WNT, Notch & HedgehogDocument36 pagesSignaling Pathways That Depend On Regulated Proteolysis WNT, Notch & HedgehogHarry HartNo ratings yet
- Hippo Signaling in Embryogenesis and DevelopmentDocument13 pagesHippo Signaling in Embryogenesis and DevelopmentRan LinNo ratings yet
- Placentation: Lorem Ipsum DolorDocument15 pagesPlacentation: Lorem Ipsum DolorAnyaNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument2 pagesTransport MechanismStephanie Cyrelle Jane BacaniNo ratings yet
- Lysosomes 160910093840Document32 pagesLysosomes 160910093840sekharurlaNo ratings yet
- BIO3153 Module5 PDFDocument35 pagesBIO3153 Module5 PDFMoatter SyedNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane in Transport MechanismsDocument29 pagesCell Membrane in Transport MechanismsAnnie LouNo ratings yet
- JCB 202102001Document15 pagesJCB 202102001Apollo ApolloNo ratings yet
- SF - MD.0145.T.22 Ally Omary MwambelaDocument10 pagesSF - MD.0145.T.22 Ally Omary MwambelaAlly OmaryNo ratings yet
- GDF-9 and BMP-15 Direct The Follicle Symphony: The Oocyte - A Key Player in Ovarian FunctionDocument10 pagesGDF-9 and BMP-15 Direct The Follicle Symphony: The Oocyte - A Key Player in Ovarian FunctionashaNo ratings yet
- Posttranslational Modifications and Protein Transport.Document7 pagesPosttranslational Modifications and Protein Transport.carlottabovi28No ratings yet
- Phospholipid SDocument17 pagesPhospholipid Sgowrie sangkarNo ratings yet
- English 202C Technical DescriptionDocument4 pagesEnglish 202C Technical Descriptiondns5130No ratings yet
- Dr. M. Azhar Chishti Dept. Medical BiochemistryDocument46 pagesDr. M. Azhar Chishti Dept. Medical Biochemistryvarsha CRNo ratings yet
- Prolactin - A Pleiotropic Factor in Health and DiseaseDocument10 pagesProlactin - A Pleiotropic Factor in Health and Diseasepopa.irinaNo ratings yet
- ApoptosisDocument5 pagesApoptosisHenry LauNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue Culture: Topic Landmark Inventions in The Field of Animal Biotechnology and Their ImportanceDocument12 pagesAnimal Tissue Culture: Topic Landmark Inventions in The Field of Animal Biotechnology and Their ImportanceAkshay MankotiaNo ratings yet
- CellMembrane Structure and Functional PropertiesDocument5 pagesCellMembrane Structure and Functional PropertiesAnastasiafynnNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Siklus Haid (DR - Kanadi SumaprajaDocument70 pagesFisiologi Siklus Haid (DR - Kanadi SumaprajaIntan DhyaksariNo ratings yet
- Related Lipids BiochemistryDocument11 pagesRelated Lipids Biochemistrymontrelriley08No ratings yet
- Lipid Traffic Floppy Drives and A SuperhighwayDocument12 pagesLipid Traffic Floppy Drives and A SuperhighwayJohan AlarcónNo ratings yet
- Tissue Factor and Breast CancerDocument9 pagesTissue Factor and Breast CancerBioscience and Bioengineering CommunicationsNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane ReportDocument30 pagesCell Membrane ReportRetchel Cadayong NavalesNo ratings yet
- AngelaDocument27 pagesAngelaMehedi HossainNo ratings yet
- Genbio Plasma Membrane ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenbio Plasma Membrane ReviewerEleah MelchorNo ratings yet
- LO Week 7Document22 pagesLO Week 7Matthew ChristopherNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptDocument13 pagesNIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptAqila RefianiNo ratings yet
- Caputto 2014Document6 pagesCaputto 2014manuelNo ratings yet
- The Awesome Lysosome: Louis-Jeantet Prize Winner: PerspectiveDocument4 pagesThe Awesome Lysosome: Louis-Jeantet Prize Winner: Perspectivexoco xocoNo ratings yet
- PtdSer Death KnellPhosphatidylserine, A Death Knell.Document13 pagesPtdSer Death KnellPhosphatidylserine, A Death Knell.Miss_BayesNo ratings yet
- Summary of Clinical Research For LaminineDocument10 pagesSummary of Clinical Research For LaminineDocAxi Maximo Jr AxibalNo ratings yet
- Influence of FOX genes on aging and aging-associated diseasesFrom EverandInfluence of FOX genes on aging and aging-associated diseasesNo ratings yet
- 8 - Genetic MaterialDocument22 pages8 - Genetic MaterialCrisha LimNo ratings yet
- მიტოქონდრიის ფუნქცია და კიბოDocument1 pageმიტოქონდრიის ფუნქცია და კიბოEMD GROUPNo ratings yet
- Lewins Genes XiDocument968 pagesLewins Genes Xicranek1234No ratings yet
- Honors Biology AssignmentDocument8 pagesHonors Biology AssignmentMatt WedekindNo ratings yet
- MCQ AduaDocument4 pagesMCQ AduaAG KhanNo ratings yet
- Paternity Test by Multiplex PCR On STR Polymorphic Markers: (Practical Activity in The Cybertory Virtual Laboratory)Document3 pagesPaternity Test by Multiplex PCR On STR Polymorphic Markers: (Practical Activity in The Cybertory Virtual Laboratory)Albita LameiroNo ratings yet
- Lipid Movement BiochemDocument9 pagesLipid Movement BiochemCrowNo ratings yet
- Full Download Essentials of Physical Anthropology 10th Edition Jurmain Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Essentials of Physical Anthropology 10th Edition Jurmain Solutions Manualudalbornhockeyspl2100% (31)
- 05-02-Genetika MikroorganismeDocument48 pages05-02-Genetika MikroorganismeKinad DanikNo ratings yet
- BCDB Qualifying Exam Student X May 22 & 23, 2018Document19 pagesBCDB Qualifying Exam Student X May 22 & 23, 2018Kemi' RedlipsNo ratings yet
- AP1 AP2 PCR Method For AHPND Detection - Flegel 2013Document6 pagesAP1 AP2 PCR Method For AHPND Detection - Flegel 2013Alden ReynaNo ratings yet
- Using Entrez: An Integrated Database Search and Retrieval SystemDocument53 pagesUsing Entrez: An Integrated Database Search and Retrieval SystemshooberNo ratings yet
- Dna Structure Function and Replication ActivityDocument6 pagesDna Structure Function and Replication Activityapi-299996815100% (1)
- Lecture 7 Notes - MITx - 7.28.1x Molecular Biology - DNA Replication and RepairDocument10 pagesLecture 7 Notes - MITx - 7.28.1x Molecular Biology - DNA Replication and RepairNaresh Prasad SapkotaNo ratings yet
- Masters and Perlman 2013 in Fields Virology 1Document34 pagesMasters and Perlman 2013 in Fields Virology 1s_navroopNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction - WikipediaDocument36 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction - Wikipedia93428ZEFHDNo ratings yet
- Recombinant Dna Technology: M 13 BacteriophageDocument5 pagesRecombinant Dna Technology: M 13 BacteriophagePrashant BajpaiNo ratings yet
- 07 Nucleic Acids Test PDFDocument8 pages07 Nucleic Acids Test PDFUkjun JungNo ratings yet
- BMB 515 Electronic Course Pack Sessions 21 - CADocument148 pagesBMB 515 Electronic Course Pack Sessions 21 - CANabeel ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Biology Tutorial (Set 1)Document18 pagesBiology Tutorial (Set 1)Jin MingNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosporylation in Cancer CellsDocument9 pagesOxidative Phosporylation in Cancer CellsM Naufal IlmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Macromlecules HWDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Macromlecules HWapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Gel Electrophoresis: The Purification of MacromoleculesDocument24 pagesGel Electrophoresis: The Purification of MacromoleculesCatherine KovalNo ratings yet
- Classification and Function of Small Open Reading FramesDocument17 pagesClassification and Function of Small Open Reading FramesMandanirina RakotoarimananaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Practice AnswersDocument3 pagesBiomolecules Practice AnswersNoura RoseNo ratings yet
- Alteration of Host Cell Behavior by PathogensDocument7 pagesAlteration of Host Cell Behavior by PathogensAbhijit SatpatiNo ratings yet
- PYQ Polymer ScienceDocument1 pagePYQ Polymer ScienceAnubhav MauryaNo ratings yet
- Post Transcriptional ModificationDocument4 pagesPost Transcriptional Modificationrustyryan770% (1)
- Synthetic Biology PracticalDocument33 pagesSynthetic Biology PracticalChandra PradhitaNo ratings yet
Chem
Chem
Uploaded by
Uɱɘʀ Jʌŋɩ0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThis document discusses the functions of two types of glycerophospholipids - phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. Phosphatidylethanolamine is the second most abundant phospholipid in mammalian cell membranes, plays important roles in membrane fusion and cell division, and has various functions in the liver, heart, blood clotting, and bacterial cell membranes. Phosphatidylcholine may help protect the large intestine in people with ulcerative colitis.
Original Description:
chemistery important notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the functions of two types of glycerophospholipids - phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. Phosphatidylethanolamine is the second most abundant phospholipid in mammalian cell membranes, plays important roles in membrane fusion and cell division, and has various functions in the liver, heart, blood clotting, and bacterial cell membranes. Phosphatidylcholine may help protect the large intestine in people with ulcerative colitis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesChem
Chem
Uploaded by
Uɱɘʀ JʌŋɩThis document discusses the functions of two types of glycerophospholipids - phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. Phosphatidylethanolamine is the second most abundant phospholipid in mammalian cell membranes, plays important roles in membrane fusion and cell division, and has various functions in the liver, heart, blood clotting, and bacterial cell membranes. Phosphatidylcholine may help protect the large intestine in people with ulcerative colitis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
NAME: ESHA
REG NO: 1277-FBAS/BSBT/F19
ASSIGNMENT: FUNCTIONS OF COMPLEX
LIPIDS
SUBMITTED TO: DR. NAUREEN
DATE: 30TH OCT, 2020
INTERNATIONAL ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
ISLAMABAD
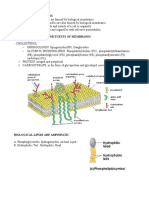
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
1) GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS:
Phosphatidylethanolamine:
The second most abundant phospholipid in mammalian membranes
is phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), which is enriched in mitochondrial inner
membranes (~ 40% of total phospholipids) compared to other organelles (15–25% of
total phospholipids).
Phosphatidylethanolamines are found in all living cells, composing 25% of all
phospholipids.
They are found particularly in nervous tissue such as the white matter of brain, nerves,
neural tissue, and in spinal cord, where they make up 45% of all phospholipids.
Play a role in membrane fusion and in disassembly of the contractile
ring during cytokinesis in cell division.
Regulates membrane curvature.
An important precursor, substrate, or donor in several biological pathways metabolism
of phosphatidylethanolamine is thought to be important in the heart. When blood flow
to the heart is restricted, the asymmetrical distribution of phosphatidylethanolamine
between membrane leaflets is disrupted, and as a result the membrane is disrupted.
Plays a role in the secretion of lipoproteins in the liver.
Able to propagate infectious prions without the assistance of any proteins or nucleic
acids, this is a unique characteristic of it.
Play a role in blood clotting, as it works with phosphatidylserine to increase the rate
of thrombin formation by promoting binding to Factor V and Factor X, two proteins
which catalyze the formation of thrombin from prothrombin.
Principle phospholipid in bacteria. One of the primary roles for
phosphatidylethanolamine in bacterial membranes is to spread out the negative charge
caused by anionic membrane phospholipids.
In the bacterium E. coli, it plays a role in supporting lactose permeases active transport
of lactose into the cell, and may play a role in other transport systems as well.
Enables bacterial multidrug transporters to function properly and allows the formation
of intermediates that are needed for the transporters to properly open and close.
Phosphatidylcholine:
Phosphatidylcholine might help to protect the wall of the large
intestine in people with a type of inflammatory bowel disease
(ulcerative colitis).
You might also like
- Enzymes Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesEnzymes Review WorksheetJamil Samira E. Buizon100% (3)
- Phospholipids Across Scales: Lipid Patterns and Plant DevelopmentDocument20 pagesPhospholipids Across Scales: Lipid Patterns and Plant DevelopmentAswad ZEllzNo ratings yet
- Carcinogenesis - Arno HelmbergDocument4 pagesCarcinogenesis - Arno HelmbergHafsah ShoaibNo ratings yet
- NO.11 1. Golgi ApparatusDocument25 pagesNO.11 1. Golgi ApparatusEkaterina SurguladzeNo ratings yet
- Lysosomal Biology in CancerDocument16 pagesLysosomal Biology in CancerZi JianNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi HaidDocument66 pagesFisiologi HaidRizna AriyaniNo ratings yet
- Plasma MembraneDocument6 pagesPlasma Membraneparashakthi PRNo ratings yet
- Science PosterDocument1 pageScience PosterWeljun GallardoNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument2 pagesCell TransportAshleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Protein Folding and MisfoldingDocument17 pagesChapter Protein Folding and MisfoldingMazhar FarNo ratings yet
- Chaperones in Protein Biological Important of Molecular FoldingDocument2 pagesChaperones in Protein Biological Important of Molecular FoldingSanele100% (1)
- The Cell MembraneDocument36 pagesThe Cell Membraneanulorance98No ratings yet
- CSIR Life Science Sample Cell BiologyDocument17 pagesCSIR Life Science Sample Cell Biologygamer zoneNo ratings yet
- Study On PhosphatidylcholineDocument121 pagesStudy On Phosphatidylcholinearun_kedia648100% (1)
- Funcion Endocrina de La Placenta HumanaDocument30 pagesFuncion Endocrina de La Placenta HumanaSofia RossoNo ratings yet
- Activity in General BiologyDocument2 pagesActivity in General BiologyMore, Mary RuthNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 3. Plasma MembraneDocument14 pagesKuliah 3. Plasma MembraneYusuf SumarNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Siklus HaidDocument70 pagesFisiologi Siklus HaidsilviNo ratings yet
- Signal TransductionDocument11 pagesSignal TransductionAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Structural Components of Cell Membrane: Group 4Document12 pagesStructural Components of Cell Membrane: Group 4Jeongyeonnie OppaNo ratings yet
- Phospholipid: From: Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry, 2019Document8 pagesPhospholipid: From: Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry, 2019Eiann Jasper LongcayanaNo ratings yet
- Functional Microdomains in Bacterial Membranes: Material SupplementalDocument11 pagesFunctional Microdomains in Bacterial Membranes: Material SupplementaltommystarfireNo ratings yet
- Kim Et Al 2024 Non Vesicular Phosphatidylinositol Transfer Plays Critical Roles in Defining Organelle Lipid CompositionDocument27 pagesKim Et Al 2024 Non Vesicular Phosphatidylinositol Transfer Plays Critical Roles in Defining Organelle Lipid CompositionDaniel DavidNo ratings yet
- Signaling. This Requires A Signal From The Cardiogenic Mesoderm Composed of FGF. (Point at Mesoderm)Document5 pagesSignaling. This Requires A Signal From The Cardiogenic Mesoderm Composed of FGF. (Point at Mesoderm)Cara JaenNo ratings yet
- Fot 247Document26 pagesFot 247Malini KolekarNo ratings yet
- CropDocument11 pagesCropHall OwnNo ratings yet
- Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta: Michel Record, Kevin Carayon, Marc Poirot, Sandrine Silvente-PoirotDocument13 pagesBiochimica Et Biophysica Acta: Michel Record, Kevin Carayon, Marc Poirot, Sandrine Silvente-PoirotGlauce L TrevisanNo ratings yet
- Physio Oral Report NotesDocument3 pagesPhysio Oral Report NotesMariel AsisNo ratings yet
- Primary HemostasisDocument10 pagesPrimary HemostasisMariella DingleNo ratings yet
- Signaling Pathways That Depend On Regulated Proteolysis WNT, Notch & HedgehogDocument36 pagesSignaling Pathways That Depend On Regulated Proteolysis WNT, Notch & HedgehogHarry HartNo ratings yet
- Hippo Signaling in Embryogenesis and DevelopmentDocument13 pagesHippo Signaling in Embryogenesis and DevelopmentRan LinNo ratings yet
- Placentation: Lorem Ipsum DolorDocument15 pagesPlacentation: Lorem Ipsum DolorAnyaNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument2 pagesTransport MechanismStephanie Cyrelle Jane BacaniNo ratings yet
- Lysosomes 160910093840Document32 pagesLysosomes 160910093840sekharurlaNo ratings yet
- BIO3153 Module5 PDFDocument35 pagesBIO3153 Module5 PDFMoatter SyedNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane in Transport MechanismsDocument29 pagesCell Membrane in Transport MechanismsAnnie LouNo ratings yet
- JCB 202102001Document15 pagesJCB 202102001Apollo ApolloNo ratings yet
- SF - MD.0145.T.22 Ally Omary MwambelaDocument10 pagesSF - MD.0145.T.22 Ally Omary MwambelaAlly OmaryNo ratings yet
- GDF-9 and BMP-15 Direct The Follicle Symphony: The Oocyte - A Key Player in Ovarian FunctionDocument10 pagesGDF-9 and BMP-15 Direct The Follicle Symphony: The Oocyte - A Key Player in Ovarian FunctionashaNo ratings yet
- Posttranslational Modifications and Protein Transport.Document7 pagesPosttranslational Modifications and Protein Transport.carlottabovi28No ratings yet
- Phospholipid SDocument17 pagesPhospholipid Sgowrie sangkarNo ratings yet
- English 202C Technical DescriptionDocument4 pagesEnglish 202C Technical Descriptiondns5130No ratings yet
- Dr. M. Azhar Chishti Dept. Medical BiochemistryDocument46 pagesDr. M. Azhar Chishti Dept. Medical Biochemistryvarsha CRNo ratings yet
- Prolactin - A Pleiotropic Factor in Health and DiseaseDocument10 pagesProlactin - A Pleiotropic Factor in Health and Diseasepopa.irinaNo ratings yet
- ApoptosisDocument5 pagesApoptosisHenry LauNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue Culture: Topic Landmark Inventions in The Field of Animal Biotechnology and Their ImportanceDocument12 pagesAnimal Tissue Culture: Topic Landmark Inventions in The Field of Animal Biotechnology and Their ImportanceAkshay MankotiaNo ratings yet
- CellMembrane Structure and Functional PropertiesDocument5 pagesCellMembrane Structure and Functional PropertiesAnastasiafynnNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Siklus Haid (DR - Kanadi SumaprajaDocument70 pagesFisiologi Siklus Haid (DR - Kanadi SumaprajaIntan DhyaksariNo ratings yet
- Related Lipids BiochemistryDocument11 pagesRelated Lipids Biochemistrymontrelriley08No ratings yet
- Lipid Traffic Floppy Drives and A SuperhighwayDocument12 pagesLipid Traffic Floppy Drives and A SuperhighwayJohan AlarcónNo ratings yet
- Tissue Factor and Breast CancerDocument9 pagesTissue Factor and Breast CancerBioscience and Bioengineering CommunicationsNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane ReportDocument30 pagesCell Membrane ReportRetchel Cadayong NavalesNo ratings yet
- AngelaDocument27 pagesAngelaMehedi HossainNo ratings yet
- Genbio Plasma Membrane ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenbio Plasma Membrane ReviewerEleah MelchorNo ratings yet
- LO Week 7Document22 pagesLO Week 7Matthew ChristopherNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptDocument13 pagesNIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptAqila RefianiNo ratings yet
- Caputto 2014Document6 pagesCaputto 2014manuelNo ratings yet
- The Awesome Lysosome: Louis-Jeantet Prize Winner: PerspectiveDocument4 pagesThe Awesome Lysosome: Louis-Jeantet Prize Winner: Perspectivexoco xocoNo ratings yet
- PtdSer Death KnellPhosphatidylserine, A Death Knell.Document13 pagesPtdSer Death KnellPhosphatidylserine, A Death Knell.Miss_BayesNo ratings yet
- Summary of Clinical Research For LaminineDocument10 pagesSummary of Clinical Research For LaminineDocAxi Maximo Jr AxibalNo ratings yet
- Influence of FOX genes on aging and aging-associated diseasesFrom EverandInfluence of FOX genes on aging and aging-associated diseasesNo ratings yet
- 8 - Genetic MaterialDocument22 pages8 - Genetic MaterialCrisha LimNo ratings yet
- მიტოქონდრიის ფუნქცია და კიბოDocument1 pageმიტოქონდრიის ფუნქცია და კიბოEMD GROUPNo ratings yet
- Lewins Genes XiDocument968 pagesLewins Genes Xicranek1234No ratings yet
- Honors Biology AssignmentDocument8 pagesHonors Biology AssignmentMatt WedekindNo ratings yet
- MCQ AduaDocument4 pagesMCQ AduaAG KhanNo ratings yet
- Paternity Test by Multiplex PCR On STR Polymorphic Markers: (Practical Activity in The Cybertory Virtual Laboratory)Document3 pagesPaternity Test by Multiplex PCR On STR Polymorphic Markers: (Practical Activity in The Cybertory Virtual Laboratory)Albita LameiroNo ratings yet
- Lipid Movement BiochemDocument9 pagesLipid Movement BiochemCrowNo ratings yet
- Full Download Essentials of Physical Anthropology 10th Edition Jurmain Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Essentials of Physical Anthropology 10th Edition Jurmain Solutions Manualudalbornhockeyspl2100% (31)
- 05-02-Genetika MikroorganismeDocument48 pages05-02-Genetika MikroorganismeKinad DanikNo ratings yet
- BCDB Qualifying Exam Student X May 22 & 23, 2018Document19 pagesBCDB Qualifying Exam Student X May 22 & 23, 2018Kemi' RedlipsNo ratings yet
- AP1 AP2 PCR Method For AHPND Detection - Flegel 2013Document6 pagesAP1 AP2 PCR Method For AHPND Detection - Flegel 2013Alden ReynaNo ratings yet
- Using Entrez: An Integrated Database Search and Retrieval SystemDocument53 pagesUsing Entrez: An Integrated Database Search and Retrieval SystemshooberNo ratings yet
- Dna Structure Function and Replication ActivityDocument6 pagesDna Structure Function and Replication Activityapi-299996815100% (1)
- Lecture 7 Notes - MITx - 7.28.1x Molecular Biology - DNA Replication and RepairDocument10 pagesLecture 7 Notes - MITx - 7.28.1x Molecular Biology - DNA Replication and RepairNaresh Prasad SapkotaNo ratings yet
- Masters and Perlman 2013 in Fields Virology 1Document34 pagesMasters and Perlman 2013 in Fields Virology 1s_navroopNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction - WikipediaDocument36 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction - Wikipedia93428ZEFHDNo ratings yet
- Recombinant Dna Technology: M 13 BacteriophageDocument5 pagesRecombinant Dna Technology: M 13 BacteriophagePrashant BajpaiNo ratings yet
- 07 Nucleic Acids Test PDFDocument8 pages07 Nucleic Acids Test PDFUkjun JungNo ratings yet
- BMB 515 Electronic Course Pack Sessions 21 - CADocument148 pagesBMB 515 Electronic Course Pack Sessions 21 - CANabeel ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Biology Tutorial (Set 1)Document18 pagesBiology Tutorial (Set 1)Jin MingNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosporylation in Cancer CellsDocument9 pagesOxidative Phosporylation in Cancer CellsM Naufal IlmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Macromlecules HWDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Macromlecules HWapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Gel Electrophoresis: The Purification of MacromoleculesDocument24 pagesGel Electrophoresis: The Purification of MacromoleculesCatherine KovalNo ratings yet
- Classification and Function of Small Open Reading FramesDocument17 pagesClassification and Function of Small Open Reading FramesMandanirina RakotoarimananaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Practice AnswersDocument3 pagesBiomolecules Practice AnswersNoura RoseNo ratings yet
- Alteration of Host Cell Behavior by PathogensDocument7 pagesAlteration of Host Cell Behavior by PathogensAbhijit SatpatiNo ratings yet
- PYQ Polymer ScienceDocument1 pagePYQ Polymer ScienceAnubhav MauryaNo ratings yet
- Post Transcriptional ModificationDocument4 pagesPost Transcriptional Modificationrustyryan770% (1)
- Synthetic Biology PracticalDocument33 pagesSynthetic Biology PracticalChandra PradhitaNo ratings yet