Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Key Facts About Chronic Bronchitis
Key Facts About Chronic Bronchitis
Uploaded by
kvishwanath0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesBronchitis is the inflammation of the bronchi in the lungs which causes severe coughing spells that bring up mucus, wheezing, chest pain and shortness of breath. There are two main types, acute and chronic. Unlike acute bronchitis which usually develops from a respiratory infection and goes away within a few weeks, chronic bronchitis is a more serious condition that develops over time and causes symptoms that never completely go away due to extended periods of inflammation and mucus buildup in the airways. Chronic bronchitis is included under the umbrella term COPD and is caused primarily by cigarette smoking but can also be caused by air pollution, dust or toxic gases. It is diagnosed based on a productive cough for at least three
Original Description:
lung condition
Original Title
Chronic Bronchitis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBronchitis is the inflammation of the bronchi in the lungs which causes severe coughing spells that bring up mucus, wheezing, chest pain and shortness of breath. There are two main types, acute and chronic. Unlike acute bronchitis which usually develops from a respiratory infection and goes away within a few weeks, chronic bronchitis is a more serious condition that develops over time and causes symptoms that never completely go away due to extended periods of inflammation and mucus buildup in the airways. Chronic bronchitis is included under the umbrella term COPD and is caused primarily by cigarette smoking but can also be caused by air pollution, dust or toxic gases. It is diagnosed based on a productive cough for at least three
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesKey Facts About Chronic Bronchitis
Key Facts About Chronic Bronchitis
Uploaded by
kvishwanathBronchitis is the inflammation of the bronchi in the lungs which causes severe coughing spells that bring up mucus, wheezing, chest pain and shortness of breath. There are two main types, acute and chronic. Unlike acute bronchitis which usually develops from a respiratory infection and goes away within a few weeks, chronic bronchitis is a more serious condition that develops over time and causes symptoms that never completely go away due to extended periods of inflammation and mucus buildup in the airways. Chronic bronchitis is included under the umbrella term COPD and is caused primarily by cigarette smoking but can also be caused by air pollution, dust or toxic gases. It is diagnosed based on a productive cough for at least three
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
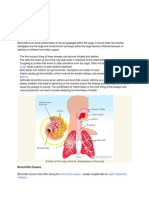
Bronchitis is when the airways in your lungs,
your bronchi, become inflamed. This irritation
can cause severe coughing spells that bring up
mucus, wheezing, chest pain and shortness of
breath. There are two main types, acute and
chronic.
Unlike acute bronchitis, which usually
develops from a respiratory infection such as a
cold and goes away in a week or two, chronic
bronchitis is a more serious condition that
develops over time. Symptoms may get better
or worse, but they will never completely go
away. These extended periods of inflammation
cause sticky mucus to build up in the airways,
leading to long-term breathing difficulties.
Along with emphysema, chronic bronchitis is
one of the lung diseases that comprise COPD
(chronic obstructive pulmonary disease).
There are a number of treatments available to
help control symptoms and ease breathing
problems.
Key Facts about Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is included in the
umbrella term COPD (chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease). Your doctor may refer
to your disease as either chronic bronchitis
or COPD.
Cigarette smoking is a major cause of
chronic bronchitis. Other factors that
increase your risk of developing this
disease include exposure to air pollution as
well as dust or toxic gases in the
workplace or environment. It may also
occur more frequently in individuals who
have a family history of bronchitis.
To diagnose chronic bronchitis, your
doctor will look for a productive cough
(producing mucus) that lasts at least three
months and happens multiple times over
the course of at least two years. Tests used
to diagnose chronic bronchitis include
pulmonary function tests, chest X-rays or
CT scans.
Chronic bronchitis is not curable but there
are a number of treatments that can help
you manage your symptoms. These
include bronchodilators that open your
airways, steroids to reduce inflammation,
oxygen therapy and pulmonary
rehabilitation.
You might also like
- LESSON PLAN BronchitisDocument3 pagesLESSON PLAN BronchitisDiana Laura Lei100% (1)
- Chronic BronchitisDocument3 pagesChronic BronchitisMuniza KhaliqNo ratings yet
- What Is BronchitisDocument1 pageWhat Is BronchitisMelvin Lopez SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Chronic Bronchitis: Written By: Sanabila Yasmin M 030.07.231Document17 pagesChronic Bronchitis: Written By: Sanabila Yasmin M 030.07.231gegeoygegeNo ratings yet
- BHS Ingg BronkitisDocument12 pagesBHS Ingg BronkitisdeyrikaNo ratings yet
- Chronic B. 234Document4 pagesChronic B. 234Sheene Ainasthazia Diego AngNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis (Biochem Presentation)Document42 pagesBronchitis (Biochem Presentation)SiewLiZhenNo ratings yet
- Copd (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)Document11 pagesCopd (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)Catherine MetraNo ratings yet
- Chronic BronchitisDocument3 pagesChronic Bronchitisdenoh100% (1)
- Acute Bronchitis Lance Angelo Bernandino BSN IIDocument2 pagesAcute Bronchitis Lance Angelo Bernandino BSN IILance Angelo BernandinoNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument3 pagesBronchitisjosanne938No ratings yet
- Chronic Bronchitis PosterDocument1 pageChronic Bronchitis Posterinesmaria.silvaortiz76No ratings yet
- Chronic BronchitisDocument2 pagesChronic BronchitisKhalid Mahmud ArifinNo ratings yet
- By DPS StudentsDocument10 pagesBy DPS StudentszarakonhaiNo ratings yet
- Chronic BronchitisDocument5 pagesChronic BronchitisJemalyn M. Saludar100% (2)
- BronchitisDocument15 pagesBronchitisAakanksha vaishnav100% (1)
- COPD, or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument18 pagesCOPD, or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseemilliansNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH Mom OliveDocument9 pagesMAKALAH Mom Olivemaragantigaming04officialNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disorders: Grace Monserata 9 GradeDocument14 pagesRespiratory Disorders: Grace Monserata 9 GradeRg MonserataNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument3 pagesBronchitiscorsaruNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis: Week 5 1Document5 pagesBronchitis: Week 5 1jessNo ratings yet
- Chronic BronchitisDocument9 pagesChronic BronchitisSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument5 pagesCase StudyJhosua RoldanNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument9 pagesBronchitisMS AntikaNo ratings yet
- COPD Information Sheet For BHPs Version 3Document3 pagesCOPD Information Sheet For BHPs Version 3Aleem ShahidNo ratings yet
- COPDDocument8 pagesCOPDNader Smadi100% (1)
- TB and Copd!Document9 pagesTB and Copd!RachnaNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Chronic BronchitisDocument6 pagesCase Study For Chronic BronchitisGabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- "Bronchitis": Respiratory DisorderDocument40 pages"Bronchitis": Respiratory Disorderaswin379No ratings yet
- What Is Acute BronchitisDocument11 pagesWhat Is Acute BronchitisKerri-DojhnHallNo ratings yet
- Copd ScriptDocument17 pagesCopd ScriptHydie Mae AlcabedosNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Symptoms, Treatments, and Medication for Asthma and BronchitisFrom EverandAsthma: Symptoms, Treatments, and Medication for Asthma and BronchitisNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument6 pagesBronchitisNader Smadi100% (1)
- Signs & SymptomsDocument2 pagesSigns & SymptomsWahyuni ErwinNo ratings yet
- Chronic Bronchitis, Emphysema and COPD ('Smoker's Lung')Document3 pagesChronic Bronchitis, Emphysema and COPD ('Smoker's Lung')Alina AdrianaNo ratings yet
- Op Op Op OpDocument4 pagesOp Op Op OpVannie MaramotNo ratings yet
- Chronic-Bronchitis MedBackDocument37 pagesChronic-Bronchitis MedBackclaire.deveraNo ratings yet
- BRONCHITIS Know Your Symptoms and When to Seek Professional Help As It Can Be DeadlyFrom EverandBRONCHITIS Know Your Symptoms and When to Seek Professional Help As It Can Be DeadlyNo ratings yet
- Asthma Vs BronchitisDocument4 pagesAsthma Vs BronchitisEmma CebanNo ratings yet
- Bronchopneumonia Treatment - Symptoms, Causes of Broncho PneumoniaDocument5 pagesBronchopneumonia Treatment - Symptoms, Causes of Broncho Pneumoniajaizel_mhine14No ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument4 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseAudrey Nicole GabianaNo ratings yet
- BrochiectasisDocument6 pagesBrochiectasisEdward AwiNo ratings yet
- How to Deal with Bronchitis: Coping with Bronchitis and Its Health EffectsFrom EverandHow to Deal with Bronchitis: Coping with Bronchitis and Its Health EffectsNo ratings yet
- COPD Patient Information Version 3Document7 pagesCOPD Patient Information Version 3contehamosaNo ratings yet
- COPD Case Pres2Document29 pagesCOPD Case Pres2Kelly Queenie Andres100% (2)
- Acute BronchitisDocument2 pagesAcute BronchitisChristabella Natalia WijayaNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Applied MedicineDocument17 pagesAssignment: Applied MedicineKhadija BakhtawarNo ratings yet
- BrochitisDocument1 pageBrochitisdlyafana365No ratings yet
- Defenition of BronchitisDocument3 pagesDefenition of BronchitisulfhasNo ratings yet
- Lungs InfectionsDocument7 pagesLungs InfectionsMac PhersonNo ratings yet
- Chronic BronchitisDocument3 pagesChronic BronchitisDawn Steffanny Solen CorderoNo ratings yet
- COPD Treatment, DiagnoseDocument8 pagesCOPD Treatment, Diagnoseaghamohsin1No ratings yet
- Problem in OxygenationDocument11 pagesProblem in OxygenationNikky Rossel FloresNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Pneumonia ArticleDocument2 pagesBacterial Pneumonia ArticleGabriela AlejandraNo ratings yet
- Symptoms of Bronchopneumonia in Adults and Children: PneumoniaDocument10 pagesSymptoms of Bronchopneumonia in Adults and Children: PneumoniajessyNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis and EphysemaDocument5 pagesBronchitis and EphysemaWamani Linus KirungiNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis: Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The Bronchial Tubes, TheDocument6 pagesBronchitis: Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The Bronchial Tubes, TheRoy VergaraNo ratings yet
- Broncho PneumoniaDocument9 pagesBroncho Pneumoniamunie munieNo ratings yet
- Non-Communicable Disease - COPDDocument4 pagesNon-Communicable Disease - COPDCamilogsNo ratings yet