Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Examples: Exciting Story
Examples: Exciting Story
Uploaded by
Lorenzo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views3 pagesThis document outlines an English lesson plan focusing on verbals. It provides definitions and examples of infinitives, participles, and other verb forms used as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs. A series of learning activities are included to help students clarify their understanding of verbals, process questions about their uses, frame correct sentences, and write a short essay applying verbals to a current issue.
Original Description:
ENGLISH 9 MODULES
Original Title
ENGLISH 9
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines an English lesson plan focusing on verbals. It provides definitions and examples of infinitives, participles, and other verb forms used as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs. A series of learning activities are included to help students clarify their understanding of verbals, process questions about their uses, frame correct sentences, and write a short essay applying verbals to a current issue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views3 pagesExamples: Exciting Story
Examples: Exciting Story
Uploaded by
LorenzoThis document outlines an English lesson plan focusing on verbals. It provides definitions and examples of infinitives, participles, and other verb forms used as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs. A series of learning activities are included to help students clarify their understanding of verbals, process questions about their uses, frame correct sentences, and write a short essay applying verbals to a current issue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
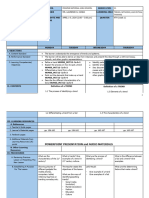
Name Year&Sec:
Subject ENGLISH 9 1st week
Expert Teacher Ms. Marichele D. Sebial Contact #: 09388532732
Activity No. 2.1 October 26-30, 2020
Topic USING VERBALS
Content Standard The learner demonstrates understanding of how world literatures and other text
types serve as vehicles of expressing and resolving conflicts among individuals or
group; also how to use strategies in critical reading, listening, and viewing, and
affirmation and negation markers to deliver impromptu and extemporaneous
speeches.
Performance Standard The learner proficiently delivers an argumentative speech emphasizing how to
solve conflicts among individuals or group.
Learning Competency Relate text content to particular social issues, concerns, or dispositions in real life
Learning Target Relate text content to particular social issues, concerns, or dispositions in real life
Reference RO-X Self Learning Modules
Values Attitudes Excellence
LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET
S.Y. 2020-2021
I. ESSENTIAL IDEAS
A noun or an adjective derived from a verb is a verbal. The infinitive is the “dictionary form” of the verb, i.e.,
the form used as an entry in the dictionary. It is usually, but not always, preceded by to.
The infinitive has several functions:
1. The infinitive may act as a noun. As a noun, it may be used as:
Subject: To act like that is childish.
Direct object: I want to know the answer.
Complement: My plan is to travel before I settle down.
2. The infinitive may act as an adjective.
That is not the way to speak to your elders. (modifies way)
The clothes to iron are on my bed. (modifies clothes)
3. The infinitive may act as an adverb, generally of purpose.
You came here to study.
Mother went to the shore to buy fruit.
As a verbal, the participle is a verb form used as an adjective.
1. The present participle ends in -ing.
Examples: exciting story
disappointing news
falling leaves
2. The past participle ends with -d or -ed for regular verbs and -en and -n for most irregular verbs.
Examples: tired farmers
broken heart
torn letters
3. A participle usually precedes the noun it modifies, but when used as part of a phrase, the
participle follows the word it modifies.
Examples: broken sword
sword broken in the battle
4. The participial phrase is an equivalent of an adjective clause.
Example: man driving the car (man who is/was driving the car)
5. A dangling participle results when the noun modified is not the doer of the action expressed by
the verbal.
Example: Standing on the tower, the whole village could be seen.
(Did the village the stand on the tower? The sentence should read: Standing on the tower,I
saw the whole below me.)
6. A number of common participial expressions are used as independent constructions.
Example: Generally speaking, cartoons are funny.
7. The nominative absolute is an independent phrase composed of a noun followed by a participle.
Examples: Tuesday being a holiday, the stores are all closed.
II. LEARNING EXPERIENCES
A. Clarifying Understanding: Day 1
Direction: Underline the infinitive and tell how it is used in each sentence below. If it is used as a noun,
write its function on the line before the number. If as an adjective or adverb, write what word is being
modifies.
________________1. To complete the book in a month was a great achievement.
________________2. All creatures, even humans, eat to live.
________________3. The Philippines fought to gain independence.
________________4. The boys learned to work when they were young.
________________5. The book to read is Noli Me Tangere.
________________6. We need a computer to do the work faster.
________________7. Roger’s resolution is to practice at the piano more.
________________8. Lina is working late to make up for her absence yesterday.
________________9. Her only ambition is to give her mother a happy old age.
________________10.Please give this child something to eat.
B. Processing Questions: Day 2
Direction: Read the questions carefully and answer it with two to three sentences.
1. What is verbal?
2. Explain the use of verbal.
3. How can this lesson be a help in your daily life?
C. Framing Concept: Day 3
Direction: Revise the following sentences by retaining the participial phrases and eliminating the dangling
participle. An example has been done for you.
Example: Sliding in the mud, Sliding in the mud, I made
everyone laughed at me. everyone laugh.
1.Starting at the school, our
route goes along the highway
2. Stepping carelessly off the
sidewalk, the bus hit the boy.
4. Going downstairs, the railing
helped steady him.
5. Shot at the Luneta, I knew
Rizal died a hero.
D. Lifelong Learning
Direction: Choose one current issue in the Philippines. Make a two-paragraph essay about it. Apply the use
of verbal and underline it.
You might also like
- The Giver Unit PlanDocument11 pagesThe Giver Unit PlanStephanie Vasse94% (16)
- Introduction To The Guest of Honor and SpeakerDocument3 pagesIntroduction To The Guest of Honor and SpeakerLorenzo83% (12)
- DLP-8-Q1mODULE-5-Remefe SolamilloDocument5 pagesDLP-8-Q1mODULE-5-Remefe SolamilloKristell C. Lagarde100% (1)
- Grade 7 Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesGrade 7 Lesson PlanJuliet Orabiles Martinez100% (3)
- Caps Hats Socks and Mittens A Book About The Four SeasonsDocument36 pagesCaps Hats Socks and Mittens A Book About The Four Seasons12uf765mmmNo ratings yet
- English: Learner's Activity Sheet Assessment ChecklistDocument10 pagesEnglish: Learner's Activity Sheet Assessment ChecklistNoraima MangorandaNo ratings yet
- MELC5 - First ObservationDocument4 pagesMELC5 - First ObservationMayca Solomon GatdulaNo ratings yet
- English 7Document4 pagesEnglish 7MA.RESA M.GALIDONo ratings yet
- 1QTR Eng7 Mod6-Revised PDFDocument8 pages1QTR Eng7 Mod6-Revised PDFBenedick Conrad R. GlifuniaNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 1 - Module 4Document12 pagesEnglish: Quarter 1 - Module 4Imee Lintag100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in English 8 03 21 23Document4 pagesLesson Plan in English 8 03 21 23Dan Manuel BautistaNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed RapunzelDocument8 pagesSemi Detailed RapunzelAlyssa ErminoNo ratings yet
- English Le-Q1 Week-3-4Document8 pagesEnglish Le-Q1 Week-3-4Leo Enriquez Jr.No ratings yet
- Shs - Readwrite - q3 - Mod1 - Patterns of Written TextsDocument19 pagesShs - Readwrite - q3 - Mod1 - Patterns of Written TextsJeryn Ritz Mara HeramizNo ratings yet
- English8 - Q3 - Mod6 - Explain Figurative Language UsedDocument16 pagesEnglish8 - Q3 - Mod6 - Explain Figurative Language UsedLanamhae CuevasNo ratings yet
- B.inggris Doddy PrabowoDocument7 pagesB.inggris Doddy PrabowoDevi UtariNo ratings yet
- Week 6 1st QuarterDocument3 pagesWeek 6 1st QuarterMyvic ImperialNo ratings yet
- Phrases, Clauses, & Sentence Structure: Unit TwoDocument29 pagesPhrases, Clauses, & Sentence Structure: Unit TwoAzhar HussainNo ratings yet
- Learning Area English Learning Delivery Modality Modular-Distance Modality (Learners-Led Modality)Document9 pagesLearning Area English Learning Delivery Modality Modular-Distance Modality (Learners-Led Modality)Liberty LugatocNo ratings yet
- Infinitives Lesson-PlanDocument4 pagesInfinitives Lesson-PlanGwyneth BabaoNo ratings yet
- DLP-January 4-5, 2023-Eng.10Document6 pagesDLP-January 4-5, 2023-Eng.10Chrisneliane BarilNo ratings yet
- Objectives: San Pedro Integrated SchoolDocument8 pagesObjectives: San Pedro Integrated SchoolEljean LaclacNo ratings yet
- Traveling Might Satisfy Your Desire For New Experiences.: Shaken, He Walked Away From The Wrecked CarDocument5 pagesTraveling Might Satisfy Your Desire For New Experiences.: Shaken, He Walked Away From The Wrecked CarRholdan Simon AurelioNo ratings yet
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in English 5Document7 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in English 5Cat MallariNo ratings yet
- GRADE 7 LAS 6 Week 7Document9 pagesGRADE 7 LAS 6 Week 7Rutchel100% (1)
- Alexis Jean Feolino Dilao Q4 Week 5 Worksheet TASKSDocument5 pagesAlexis Jean Feolino Dilao Q4 Week 5 Worksheet TASKShat hatNo ratings yet
- Basic Writing Skills: Main Clause Subordinate ClausesDocument22 pagesBasic Writing Skills: Main Clause Subordinate ClausesKiruNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: English 7Document4 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: English 7VINCENT CAILING100% (1)
- Q1 Week 6 Grade 7 LAS Phrases Clauses SentencesDocument5 pagesQ1 Week 6 Grade 7 LAS Phrases Clauses SentencesVeronica Almera ManuelNo ratings yet
- Teacher'S Guide: Quarter 2 Week 4 I. ObjectivesDocument13 pagesTeacher'S Guide: Quarter 2 Week 4 I. ObjectivesKorrine Angelica Benzon LimetaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English 10aDocument20 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in English 10aMelbayne AglugubNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument23 pagesActive and Passive VoiceTrixiaNo ratings yet
- LEARNING PLAN - ZelDocument15 pagesLEARNING PLAN - ZelAizelle Salibay OinalNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 General English - Unit 1-Unit 3Document23 pagesModul 1 General English - Unit 1-Unit 3Fitri RisnawatiNo ratings yet
- English Grade 7 Q1 LP 6Document7 pagesEnglish Grade 7 Q1 LP 6Karen Creo BelchezNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson PlanEjay AbanteNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH-7-Q1-Week-7.las 7Document6 pagesENGLISH-7-Q1-Week-7.las 7Lacey Marie LimNo ratings yet
- Module English 8 Week 1 Sdo Calooan 1Document10 pagesModule English 8 Week 1 Sdo Calooan 1Rashly Virlle SullanoNo ratings yet
- English Grade 11 Note 1Document8 pagesEnglish Grade 11 Note 1Kaleab AlebachewNo ratings yet
- 10 TH Grade Vocabulary Worksheets SampleDocument12 pages10 TH Grade Vocabulary Worksheets SampleKenny FongNo ratings yet
- Module 4 English Summaries (Ipte)Document33 pagesModule 4 English Summaries (Ipte)Malack ChagwaNo ratings yet
- COT Lesson Plan in English 3 - AdjectivesDocument4 pagesCOT Lesson Plan in English 3 - AdjectivesIzis Dionio S - Mandal100% (1)
- Department of EducationDocument3 pagesDepartment of EducationElvira JuanNo ratings yet
- Want More Practice? Vocabulary Building: The College Skills ZoneDocument2 pagesWant More Practice? Vocabulary Building: The College Skills ZoneLily S-ovaNo ratings yet
- 2405 Unit 2-Phrases, Clauses, Sentence StructureDocument29 pages2405 Unit 2-Phrases, Clauses, Sentence Structuretrang11291.ftuNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 1 - Module 13Document17 pagesEnglish: Quarter 1 - Module 13Dane Canlas100% (1)
- English 10 Q2 Week 2 ValidatedDocument10 pagesEnglish 10 Q2 Week 2 ValidatedMarriane Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document21 pagesModule 1Awrey CutieNo ratings yet
- 3RD Term JS1 EnglishDocument31 pages3RD Term JS1 EnglishsubdayvibesNo ratings yet
- LP-8 Oct.24,2022Document4 pagesLP-8 Oct.24,2022Mharnelisa Abaring DeonNo ratings yet
- English 9-Quarter-2-MELC-1-Making Connections Between Texts To Particular Issues, Concerns or Dispositions in Real LifeDocument25 pagesEnglish 9-Quarter-2-MELC-1-Making Connections Between Texts To Particular Issues, Concerns or Dispositions in Real LifeAldrin PaguiriganNo ratings yet
- English 9-Quarter-2-MELC-1-Making Connections Between Texts To Particular Issues, Concerns or Dispositions in Real LifeDocument24 pagesEnglish 9-Quarter-2-MELC-1-Making Connections Between Texts To Particular Issues, Concerns or Dispositions in Real LifeAldrin PaguiriganNo ratings yet
- Tulong-Dunong: Context/ Tutor'S Reflection Lesson No. and TopicDocument6 pagesTulong-Dunong: Context/ Tutor'S Reflection Lesson No. and TopicDamien100% (1)
- Q1 LC1 Module - Week-1Document12 pagesQ1 LC1 Module - Week-1Anarhiza MalenabNo ratings yet
- 1st QUARTER - Final English 10Document31 pages1st QUARTER - Final English 10Amy TabaconNo ratings yet
- Phrases, Clauses, Sentence StructureDocument29 pagesPhrases, Clauses, Sentence StructureMdMehediHasanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ENGLISH 10 Q4 W5 Day 3Document8 pagesLesson Plan ENGLISH 10 Q4 W5 Day 3Tel Tel HitaladaNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document8 pagesModule 9Cathleen Joy LopezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Exemplar Nov. 9-13-G7 - JJLRDocument5 pagesLesson Exemplar Nov. 9-13-G7 - JJLRJoscelle Joyce RiveraNo ratings yet
- Modules G7 Q1-W6Document10 pagesModules G7 Q1-W6jammelacosta23No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in EnglishDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in EnglishDan Manuel BautistaNo ratings yet
- P.E. 11 Module (Badminton)Document6 pagesP.E. 11 Module (Badminton)LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Draft TQ HOPE2 MIDTERMDocument8 pagesDraft TQ HOPE2 MIDTERMLorenzoNo ratings yet
- RDT Blueprint in G-12 HOPE (Health Optimizing Physical Education)Document1 pageRDT Blueprint in G-12 HOPE (Health Optimizing Physical Education)LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Music HistoryDocument3 pagesMidterm Exam Music HistoryLorenzoNo ratings yet
- Anne New ResumeDocument6 pagesAnne New ResumeLorenzoNo ratings yet
- New Template Travel AuthorityDocument1 pageNew Template Travel AuthorityLorenzoNo ratings yet
- Hope 12 Aquatics Critical Thinking TestDocument1 pageHope 12 Aquatics Critical Thinking TestLorenzoNo ratings yet
- Tnacts Week 1Document6 pagesTnacts Week 1LorenzoNo ratings yet
- 1st SummativeDocument2 pages1st SummativeLorenzoNo ratings yet
- Apznzaabeeb9fh0logrzchykbcfocmpjon1g6f8kbcszb761cd Fblpgjii35jonpya1papdmxbzxccudr78py2wkkh 77-Lt Tnpo224haf88wl6r85ckijd6v6qv8lxw7manflaqrzjoi6cgemygz2nqizjjxmro8zbwimwe 545ppxs80gdqct5qrty-Dr1drz Ie5pit9Document5 pagesApznzaabeeb9fh0logrzchykbcfocmpjon1g6f8kbcszb761cd Fblpgjii35jonpya1papdmxbzxccudr78py2wkkh 77-Lt Tnpo224haf88wl6r85ckijd6v6qv8lxw7manflaqrzjoi6cgemygz2nqizjjxmro8zbwimwe 545ppxs80gdqct5qrty-Dr1drz Ie5pit9LorenzoNo ratings yet
- TNCT LAS 1 Perception of A TrendDocument1 pageTNCT LAS 1 Perception of A TrendLorenzoNo ratings yet
- Template For Year End Accomplishment MAPEHDocument2 pagesTemplate For Year End Accomplishment MAPEHLorenzoNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 10 Week 8Document4 pagesMapeh 10 Week 8LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Adlaw GabiiDocument1 pageAdlaw GabiiLorenzoNo ratings yet
- Poster Topics ScheduleDocument3 pagesPoster Topics ScheduleLorenzoNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 9 Week 4Document11 pagesMapeh 9 Week 4LorenzoNo ratings yet
- DISS11ahsjddj - W3 - Explaining The Major Events and Its Contribution - (Judelyn A. Abedong)Document11 pagesDISS11ahsjddj - W3 - Explaining The Major Events and Its Contribution - (Judelyn A. Abedong)LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Alma Mater Song (Lourdes College)Document10 pagesAlma Mater Song (Lourdes College)LorenzoNo ratings yet
- TA Orientation On Induction ProgramDocument1 pageTA Orientation On Induction ProgramLorenzoNo ratings yet
- History of AssessmentDocument15 pagesHistory of AssessmentLorenzoNo ratings yet
- SNSU Hymn (With Chords)Document3 pagesSNSU Hymn (With Chords)LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Teacher'S Payroll: Saint Augustine Institute Ipil, Gigaquit, Surigao Del NorteDocument1 pageTeacher'S Payroll: Saint Augustine Institute Ipil, Gigaquit, Surigao Del NorteLorenzoNo ratings yet
- Snsu Hymn Lyrics NewDocument1 pageSnsu Hymn Lyrics NewLorenzo100% (1)
- CamScanner 08-20-2022 15.20-1Document6 pagesCamScanner 08-20-2022 15.20-1LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Surigao Del Norte State University (SNSU) Hymn 2Document3 pagesSurigao Del Norte State University (SNSU) Hymn 2LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Halina Espiritu Santo Pentecost Bill Kevin Del RosarioDocument1 pageHalina Espiritu Santo Pentecost Bill Kevin Del RosarioLorenzoNo ratings yet
- SF5 - 2019 - Grade 10 (Year IV) - SAINT MARYDocument2 pagesSF5 - 2019 - Grade 10 (Year IV) - SAINT MARYLorenzoNo ratings yet
- SF1 - 2019 - Grade 10 (Year IV) - SAINT MARYDocument3 pagesSF1 - 2019 - Grade 10 (Year IV) - SAINT MARYLorenzoNo ratings yet
- SF2 - 2019 - Grade 10 (Year IV) - SAINT MARY 2Document2 pagesSF2 - 2019 - Grade 10 (Year IV) - SAINT MARY 2LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Like Pale Gold - The Great Gatsby (Part 1) #4Document6 pagesLike Pale Gold - The Great Gatsby (Part 1) #4krmce pNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Literary AppreciationDocument18 pagesUNIT 3 Literary AppreciationEM ON THE BEATNo ratings yet
- Interview BBCDocument11 pagesInterview BBCjapgunkaur1No ratings yet
- Firdavs Harry Potter FullDocument10 pagesFirdavs Harry Potter Fullsherali hasanzoaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Literature During Martial LawDocument2 pagesPhilippine Literature During Martial LawJulie Fe VergaraNo ratings yet
- John DonneDocument9 pagesJohn DonneHammad Ur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Can Progress Be MadeDocument10 pagesCan Progress Be MadeB SalahNo ratings yet
- Timpanogos Half - Age GroupsDocument16 pagesTimpanogos Half - Age GroupsjshimaneNo ratings yet
- Murder of Roger Ackroyd NarratorDocument4 pagesMurder of Roger Ackroyd Narratoraroychowdhury30No ratings yet
- William Dean HowellsDocument2 pagesWilliam Dean Howellsdiana_gheorghe930% (1)
- (Sugoi) Basic Japanese With ComicsDocument6 pages(Sugoi) Basic Japanese With ComicsdustinbrNo ratings yet
- Sree Vishnu Sahasra Nama Stotram - Kannada Lyrics (Text)Document20 pagesSree Vishnu Sahasra Nama Stotram - Kannada Lyrics (Text)HarshithaShrinathNo ratings yet
- What Is A Book Review?: College of EducationDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Book Review?: College of EducationVincent Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Ge6 Final Examination PointersDocument4 pagesGe6 Final Examination PointersGelo BalladaresNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document5 pagesLesson 5pearlyNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Statistics For Business Decision Making and Analysis 2nd Edition Stine Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Statistics For Business Decision Making and Analysis 2nd Edition Stine Solutions Manual PDFwellbornfinikin407k2o100% (14)
- Class XI - XII Seating ArrangementDocument7 pagesClass XI - XII Seating ArrangementSΞIKH SΛMIMNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Test A: GrammarDocument4 pagesUnit 9 Test A: GrammarDato JavakhishviliNo ratings yet
- Story Elements Worksheet PDF - Imagine ForestDocument5 pagesStory Elements Worksheet PDF - Imagine ForestJunrey RamadaNo ratings yet
- Literary Analysis Rough Draft - OdtDocument3 pagesLiterary Analysis Rough Draft - OdtChristine NelsonNo ratings yet
- FIL Answer Key 5Document4 pagesFIL Answer Key 5Aira GaluraNo ratings yet
- English HSC Advanced NotesDocument14 pagesEnglish HSC Advanced NotesVidhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Angles and PolygonsDocument38 pagesAngles and PolygonsSyeda Inaaya TalhaNo ratings yet
- Use of Literature in Language Teaching and Learning: A Critical AssessmentDocument7 pagesUse of Literature in Language Teaching and Learning: A Critical AssessmentAleixo Domingos CaetanoNo ratings yet
- Adventures of PerseusDocument2 pagesAdventures of PerseusÑìkhíl GãürâvNo ratings yet
- Manga: A Report in EL 3127 Contemporary, Popular and Emergent LiteratureDocument9 pagesManga: A Report in EL 3127 Contemporary, Popular and Emergent LiteratureJulien Lumines EwayNo ratings yet
- Hostia: History, Authorship, and The O9ADocument5 pagesHostia: History, Authorship, and The O9AThormyndNo ratings yet
- One Way Trigger: The StrokesDocument4 pagesOne Way Trigger: The Strokesgabriel vasquez rendonNo ratings yet
- NAPPS SCHEME for PRI 4-6 - 1st Term 2020-2021Document52 pagesNAPPS SCHEME for PRI 4-6 - 1st Term 2020-2021ibemusipreciousNo ratings yet