Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 viewsOct30revprint PDF
Oct30revprint PDF
Uploaded by
supratik30Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5824)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Physics Ch2ForcesAndMotionp2p4p6worksheetwithanswersDocument14 pagesPhysics Ch2ForcesAndMotionp2p4p6worksheetwithanswerssupratik30No ratings yet
- Physics Ch2ForcesAndMotionp2p4p6worksheetwithanswersDocument14 pagesPhysics Ch2ForcesAndMotionp2p4p6worksheetwithanswerssupratik30No ratings yet
- International Olymic FOundation SAMPLE-CertificateDocument1 pageInternational Olymic FOundation SAMPLE-Certificatesupratik30No ratings yet
- Work, Power, & Efficiency Worksheet: Equations To Use: W F D P W/T For Ideal MachinesDocument1 pageWork, Power, & Efficiency Worksheet: Equations To Use: W F D P W/T For Ideal Machinessupratik30No ratings yet
- Ig1physics PDFDocument8 pagesIg1physics PDFsupratik30No ratings yet
- International Olympiad Foundation UserGuideDocument4 pagesInternational Olympiad Foundation UserGuidesupratik30No ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Revision Ch1 To 3Document16 pagesIGCSE Physics Revision Ch1 To 3supratik30No ratings yet
- 0625 - w15 - QP - 63with Ms PDFDocument9 pages0625 - w15 - QP - 63with Ms PDFsupratik30No ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency WorksheetDocument3 pagesEnergy Efficiency Worksheetsupratik30No ratings yet
- Genetically Modified Corn PDFDocument3 pagesGenetically Modified Corn PDFsupratik30No ratings yet
- Mixed Economy Advantages - : DisadvantagesDocument1 pageMixed Economy Advantages - : Disadvantagessupratik30No ratings yet
- Spanish Subject Pronouns PDFDocument2 pagesSpanish Subject Pronouns PDFsupratik30No ratings yet
- Guwahati University Application Form For Registration Certificate PDFDocument2 pagesGuwahati University Application Form For Registration Certificate PDFsupratik30No ratings yet
Oct30revprint PDF
Oct30revprint PDF
Uploaded by
supratik300 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views14 pagesOriginal Title
Oct30revprint.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views14 pagesOct30revprint PDF
Oct30revprint PDF
Uploaded by
supratik30Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 14
wL9SroLoLsie
Cambridge International Examinations
Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
PHYSICS 0625/21
Paper 2 Multiple Choice (Extended) May/June 2018
45 minutes
Additional Materials: Multiple Choice Answer Sheet
Soft clean eraser
Soft pencil (type B or HB recommended)
READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST
Write in soft pencil
Do not use staples, paper clips, glue or correction fluid.
Write your name, Centre number and candidate number on the Answer Sheet in the spaces provided
unless this has been done for you.
DO NOT WRITE IN ANY BARCODES.
There are forty questions on this paper. Answer all questions. For each question there are four possible
answers A, B, C and D.
Choose the one you consider correct and record your choice in soft pencil on the separate Answer Sheet
Read the instructions on the Answer Sheet very carefully.
Each correct answer will score one mark. A mark will not be deducted for a wrong answer.
‘Any rough working should be done in this booklet.
Electronic calculators may be used.
Take the weight of 1.0kg to be 10N (acceleration of free fall = 10m/s’).
‘Tho eylabus le approved or use a England, Woe an Noreen Koln 2¢ a Cambriége Intrnatena! Level eval 2 Comat
This document consists of 15 printed pages and 1 blank page.
118 06_0625_213RP CAMBRIDGE
OUCLES 2078 [ternational Esaminations [Tum over
2
4 Alength of cotton is measured between two points on a ruler.
| eaten,
om 12 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 M 12 13 14 15
When the length of cotton is wound closely around a pen, it goes round si
six tums of cotton
pen
What is the distance once round the pen?
A 220m B 26cm © 13.2em D 15.6cm
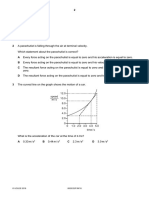
2 When does an object falling vertically through the air reach terminal velocity?
‘A when the acceleration of the object becomes negative
B__ when the acceleration of the object is equal to g
C when the air resistance equals the weight of the object
D
when the air resistance is greater than the weight of the object
@uctes 2018 ooasi2t mre
3
3° Acaris moving along a straight, level road, with a constant acceleration
Which graph shows the motion of the car?
distance
A
speed
@uctes 2018
0 time
0 time
B
distance
time
D
speed
0
0 time
osasi2tmura
[Turn over
4
4 Diagram 1 shows a beam balance. A beaker with a wire loop balances the standard masses.
The beaker is then removed and hung from a spring. The spring extends by 5.0cm, as in
diagram 2
diagram 1 diagram 2
\ A
\
beam beaker with _—-spring
gly balance wire loop
enol | attached
beaker with
_— wire loop
attached
The experiment is repeated with the same apparatus on the Moon, where the acceleration of free
fall is less than on Earth,
Which statement describes what happens on the Moon?
A The beam balance is balanced and the spring extends by 5.0m.
‘The beam balance is balanced and the spring extends by less than 5.0cm.
B
C The right-hand balance pan is higher and the spring extends by 5.0.cm,
D
The right-hand balance pan is higher and the spring extends by less than 5.0cm.
5 An object always has mass but dees not always have weight,
What must be present and acting on the mass for it to have weight?
A. a gravitational field
B asotof scales
C displaced water
D
friction due to air resistance
6 A force acting on a moving balll causes its motion to change. This force stays constant.
‘What makes the force produce a greater change in the motion of the ball?
‘A decreasing the total mass of the ball
B increasing the temperature of the ball
C using a ball with a hollow centre but the same mass
D
using a different material for the ball so that it has a lower density but the same mass
euctes 2018 ooasi2t mre
5
7 Aballoon and a mass are attached to a rod that is pivoted at P.
_balloon
45_40_ 35
cm
25 20 15 10
The balloon is filled with helium, a gas less dense than air, so that it applies an upward force on
the rod.
The rod is horizontal and stationary,
Which action causes the rod to rotate clockwise?
‘A Move both the balloon and mass 10cm to the left.
Move both the balloon and mass 10cm to the right.
B
Move both the balloon and mass to the 25cm mark.
D
Move the balloon to the 20cm mark and the mass to the 30cm mark.
8 Acar is moving in a straight line on a level road. Its engine provides a forward force on the car. A
second force of equal size acts on the car due to resistive forces.
Which statement describes what happens?
‘A The car changes direction.
B_ The car moves at a constant speed
The car slows down.
D
The car speeds up.
9 Which expression gives the momentum of an object?
A mass x acceleration
B__ mass = gravitational field strength
C mass x velocity
D
} x mass x (velocity)?
@uctes 2018 osasi2tmura [Turn over
40
1
12
13
14
6
‘As energy is transferred into different forms, it eventually becomes dissipated.
What does this mean?
A. Allthe energy disappears.
B_ The energy finally changes into every possible form of energy.
© The energy spreads out among the objects and their surroundings.
D
The total amount of energy becomes less.
A ball of mass 1.2kg is dropped from a height of 30m. As it falls, 25% of its initial gravi
potential energy is transferred to thermal energy.
What is the kinetic energy of the ball just before it hits the ground?
A 275 B 90J © 270d D 360J
‘A girl hangs by her hands from a bar in the gymnasium. She pulls herself up until her chin is level
with the bar.
The mass of the girl is 48kg.
She pulls herself up through a distance of 0.25m.
She does this in 2.0s.
What is the useful power she uses to pull herself up?
A 6.0W B 24W c sow D 240w
Four identical beakers are filled with equal volumes of liquids P or Q, as shown. Liquid P is more
dense than liquid Q
At which point is the pressure the least?
} if \ f \
liquid P~ “B
Ae c
‘An oil tank has a base of area 2.5m? and is filled with oil to a depth of 1.2m.
The density of the oil is 800 kg/m’.
What is the force exerted on the base of the tank due to the oil?
A 960N B 2400N c 9600N D 24000N
ucts 2018 ooasi2t mre
45
16
47
18
7
When molecules of a gas rebound from a wall of a container, the wall experiences a pressure.
‘What is the cause of this pressure?
‘A the change in energy of the molecules
B the change in momentum of the molecules
C the change in power of the molecules
D
the change in speed of the molecules
A student wishes to calibrate a mercury-in-glass thermometer with a °C scale.
Which values should she use for the lower fixed point and for the upper fixed point?
lower fixed point upper fixed point
A melting point of ice boiling point of mercury
B melting point of ice boiling point of water
© | melting point of mercury boiling point of mercury
D | meting point of mercury boiling point of water
Which statements about boiling and about evaporation are both correct?
boiling evaporation
takes place only at the surface takes place only at the surface
takes place throughout the liquid __takes place only at the surface
A
B___ takes place only at the surface takes place throughout the liquid
c
D___ takes place throughout the liquid takes place throughout the liquid
On a cold day, a metal front-door knob X and a similar plastic knob Y are at the same
temperature.
Why does X feel cooler to the touch than Y?
A Xconvects thermal energy better than Y.
B Xisa better thermal conductor than Y.
C Xisa better insulator than Y.
D
Xs a better radiator of thermal energy than Y.
@UCLES 2018 osasiatnnuia [Turn over
0625/21 Cambridge IGCSE - Mark Scheme May/June 2018
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
1
2
3
10
"
12
13
14
15,
16
7
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
a
elolalolol>lol>|/mlolmlalalalololola olola|als/> alalol>
28
@uctes 2018 Page 20f
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS
International General
Certificate of Secondary Education
CANDIDATE
NAME
CENTRE CANDIDATE
NUMBER NUMBER
PHYSICS 0625/61
Paper 6 Alternative to Practical October/November 2012
1 hour
Candidates answer on the Question Paper
No Additional Materials are required.
READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST
Write your Centre number, candidate number and name in the spaces at the top of the page.
Write in dark blue or black pen.
You may use a pencil for any diagrams or graphs.
Do not use staples, paper clips, highlighters, glue or correction fluid
DO NOT WRITE IN ANY BARCODES.
Answer all questions.
At the end of the examination, fasten all your work securely together.
‘The number of marks is given in brackets [ J at the end of each question or part question.
For Examiner's Use
1
2
Total
0c (cwisw) 501944
©UCLES 20:2
This document consists of 11 printed pages and 4 blank page.
UNIVERSITY o/ CAMBRIDGE
{p) International Examinations
[Turn over
1
2
The IGCSE class is investigating the stretching of a spring.
Fig. 1.1 shows the experimental set up.
clamp ———
Oy
Fig. 1.1
(a) On Fig. 1.1, measure the vertical distance d,, in mm, between the bottom of the spring
and the surface of the bench.
a
(b) The diagram is drawn 1/10" actual size. Calculate the actual distance Dy, in mm,
between the bottom of the spring and the surface of the bench.
mm (1)
ig mm [1]
(c) A student hangs a 1.0N load on the spring. He measures and records the distance D
between the bottom of the spring and the surface of the bench, and the value of the
load L.
He repeats the procedure using loads of 2.0N, 3.0N, 4.0N and 5.0N. The distance
readings are shown in Table 1.1
Calculate the extension e of the spring, for each set of readings, using the equation
e = (Dy — D), Record the values of Land e in Table 1.1.
Table 1.1
LIN Dimm e/mm
199
191
179
171
160
[2]
3
(d) Plot a graph of e/mm (y-axis) against L/N (x-axis).
[4]
(e) Determine the gradient G of the graph. Show clearly on the graph how you obtained the
necessary information.
G 2 ces]
(f) When making measurements, the student is careful to avoid a line-of-sight error.
‘Suggest one other precaution that the student should take when measuring the distance
D between the bottom of the spring and the surface of the bench.
[1]
(Total: 11]
2
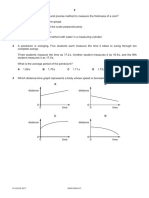
The IGCSE class is investigating the rate of cooling of water under different conditio
The apparatus is shown in Fig. 2.1.
thermometer
water —
Fig.2.1 Fig. 2.2
(a) Record the value of room temperature 4, shown on the thermometer in Fig. 2.2.
6,
(b) A student pours 150cm® of hot water into a beaker. She measures the tempera
the water at time t= 0 and records it in a table.
She starts a stopclock and records the temperature of the water at 30s intervals until
she has a total of six values up to time t= 150s. The readings are shown in Table 2.1
She repeats the procedure, using 250m? of hot water.
Table 2.1
volume of water
150m? 250m?
Y of or
0 84 85
30 79 79
60 74 75
90 | 70 72
120 68 70
150 66 68
() Complete the column headings in the table. 1)
(ii) State whether the rate of cooling is significantly faster, slower, or about the same
when using the larger volume of hot water. Justify your answer by reference to the
readings
statement cocoon
justification .
[2]
(c)_ If this experiment were to be repeated in order to check the results, it would be important
to control the conditions. Suggest two such conditions that should be controlled.
(2)
[Total: 6]
Page 2 Mark Scheme
Syllabus.
IGCSE - October/November 2012
0625
(a) do = 21 (mm)
(b) D, = 210 (mm) or 10 x candidate's (a)
(c) L values 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0
e values 1.0, 9.0, 21.0, 29.0, 40.0
(d) Graph:
Axes correctly labelled with quantity and unit and correct way around
Suitable scales
All plots correct to % small square
Good line judgement and a single, thin, continuous line
(e) Triangle method used and shown on the graph
Using at least half of ine
(f) Anyone from:
Always measure from same point on spring (top or bottom of ring)
Wait for spring/weight to stop bouncing
Use of horizontal aidiensure ruler is vertical
Bench surface not uniform
(a) = 240°C)
(b) (i) Table:
3, °C, °C
(il) About the same
Justified with reference to numbers in table
(6) Any two from:
Volumes of water
Room temperature/draughts
Same beaker
Initial water temperature
1]
[Total: 11]
(]
a
(1)
a
2
[Total: 6]
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5824)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Physics Ch2ForcesAndMotionp2p4p6worksheetwithanswersDocument14 pagesPhysics Ch2ForcesAndMotionp2p4p6worksheetwithanswerssupratik30No ratings yet
- Physics Ch2ForcesAndMotionp2p4p6worksheetwithanswersDocument14 pagesPhysics Ch2ForcesAndMotionp2p4p6worksheetwithanswerssupratik30No ratings yet
- International Olymic FOundation SAMPLE-CertificateDocument1 pageInternational Olymic FOundation SAMPLE-Certificatesupratik30No ratings yet
- Work, Power, & Efficiency Worksheet: Equations To Use: W F D P W/T For Ideal MachinesDocument1 pageWork, Power, & Efficiency Worksheet: Equations To Use: W F D P W/T For Ideal Machinessupratik30No ratings yet
- Ig1physics PDFDocument8 pagesIg1physics PDFsupratik30No ratings yet
- International Olympiad Foundation UserGuideDocument4 pagesInternational Olympiad Foundation UserGuidesupratik30No ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Revision Ch1 To 3Document16 pagesIGCSE Physics Revision Ch1 To 3supratik30No ratings yet
- 0625 - w15 - QP - 63with Ms PDFDocument9 pages0625 - w15 - QP - 63with Ms PDFsupratik30No ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency WorksheetDocument3 pagesEnergy Efficiency Worksheetsupratik30No ratings yet
- Genetically Modified Corn PDFDocument3 pagesGenetically Modified Corn PDFsupratik30No ratings yet
- Mixed Economy Advantages - : DisadvantagesDocument1 pageMixed Economy Advantages - : Disadvantagessupratik30No ratings yet
- Spanish Subject Pronouns PDFDocument2 pagesSpanish Subject Pronouns PDFsupratik30No ratings yet
- Guwahati University Application Form For Registration Certificate PDFDocument2 pagesGuwahati University Application Form For Registration Certificate PDFsupratik30No ratings yet