Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 4 and 5: Introduction To Organic Chemistry and Alkanes/Alkenes
Chapter 4 and 5: Introduction To Organic Chemistry and Alkanes/Alkenes
Uploaded by
RXNOFCHM0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views1 pageThis document provides an overview of chapters 4 and 5 which cover introduction to organic chemistry, alkanes, and alkenes. Key topics discussed include definitions of organic chemistry, important hydrocarbon series, IUPAC nomenclature rules for naming organic compounds, types of isomerism, reaction mechanisms and classifications, properties of alkanes and alkenes, and common reactions like addition and substitution that alkenes undergo. Safety considerations for organic chemistry experiments are also briefly addressed.
Original Description:
Original Title
Chapter 4 and 5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of chapters 4 and 5 which cover introduction to organic chemistry, alkanes, and alkenes. Key topics discussed include definitions of organic chemistry, important hydrocarbon series, IUPAC nomenclature rules for naming organic compounds, types of isomerism, reaction mechanisms and classifications, properties of alkanes and alkenes, and common reactions like addition and substitution that alkenes undergo. Safety considerations for organic chemistry experiments are also briefly addressed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views1 pageChapter 4 and 5: Introduction To Organic Chemistry and Alkanes/Alkenes
Chapter 4 and 5: Introduction To Organic Chemistry and Alkanes/Alkenes
Uploaded by
RXNOFCHMThis document provides an overview of chapters 4 and 5 which cover introduction to organic chemistry, alkanes, and alkenes. Key topics discussed include definitions of organic chemistry, important hydrocarbon series, IUPAC nomenclature rules for naming organic compounds, types of isomerism, reaction mechanisms and classifications, properties of alkanes and alkenes, and common reactions like addition and substitution that alkenes undergo. Safety considerations for organic chemistry experiments are also briefly addressed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
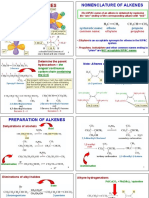
Chapter 4 and 5: Introduction to Organic
Chemistry and Alkanes/Alkenes
1.6. Introduction to Organic Fractional distillation from crude
Chemistry oil [a physical process]
Definitions Cracking [a chemical
Uses of different formula in process]
organic chemistry Catalytic reforming
Some of the important Combustion of alkane
homologous series of organic Problems with burning
compounds hydrocarbon fuel
Hydrocarbons Carbon di oxide
Systematic Nomenclature Carbon monoxide
IUPAC System for alkanes Nitrogen oxides
Naming alkenes Unburnt hydrocarbon
Naming Halogenoalkanes Catalytic converters
Naming alcohols Developing alternate fuels
Isomerism Carbon neutral
Structural isomerism Comparing fuels
Stereoisomerism Substitution reaction of alkanes
1 E-Z isomerism Chapter 4: Introduction toOrganic
Initiation
Chemistry and Alkanes
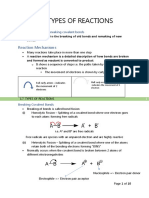
1.7. Types of Reaction Propagation
Reaction Mechanisms Termination
Breaking covalent bonds Further substitution of
Homolytic fission chloromethane
Heterolytic fission 1.9. Alkenes
Types of chemical species The nature of the C=C bond
Type of organic reactions in alkenes
Classifying reactions Addition reactions of alkenes
Addition Reaction with hydrogen
Substitution Reaction with halogen
Elimination Reaction with steam
Oxidation Reaction with Hydrogen
Reduction halides
Hydrolysis The mechanisms of addition
Polymerization reaction
Safety in organic chemistry – The test for a double bond (C=C)
hazard and risk Common additional polymers
Hazard warning symbols Polymerization reactions
1.8. Hydrocarbons Problems with polymers and
Alkanes from crude oil solutions
1|Page
You might also like
- A Level Organic Chemistry NotesDocument68 pagesA Level Organic Chemistry NotesTeejay Makazhu100% (13)
- Agilent Micro GC User InformationDocument160 pagesAgilent Micro GC User InformationRochim Bakti CahyonoNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry Important Topics For Exam 2023Document4 pages12th Chemistry Important Topics For Exam 2023jibranraja496No ratings yet
- OrganicChemistryFinalExamReview-Chad's PrepDocument27 pagesOrganicChemistryFinalExamReview-Chad's PrepAnna PriskaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2Document3 pagesOrganic Chemistry 266rdsmh2mwNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 AlkenesDocument10 pagesLesson 8 AlkenesSideka ResalsinghNo ratings yet
- Check List For Chemistry 2024Document3 pagesCheck List For Chemistry 2024hellobishnoi1744No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry EquilibriumDocument5 pagesChemistry: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Equilibriumandrilyazhini25No ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument81 pagesHydrocarbonmerlinNo ratings yet
- Chem Distributed SyllabusDocument1 pageChem Distributed SyllabusapocalypticNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ReactionsDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reactionsexvee.gNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sem 3 Check ListDocument4 pagesChemistry Sem 3 Check Listkai wenNo ratings yet
- NEET UG 2024 - Approved - Final - Removed - RemovedDocument3 pagesNEET UG 2024 - Approved - Final - Removed - Removedyadav2007princeNo ratings yet
- Chem FinalDocument3 pagesChem FinalohidinaNo ratings yet
- DAT Organic MasterContentDocument77 pagesDAT Organic MasterContentclaire LawNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro AlkanesDocument8 pages1 Intro Alkanesc21-0403-639No ratings yet
- Organic 2 PDFDocument864 pagesOrganic 2 PDFaisyahNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 CarboncompoundDocument76 pagesChapter2 CarboncompoundWENJINGNo ratings yet
- Name ReactionsDocument32 pagesName ReactionsM.NandabalanNo ratings yet
- Organic CompoundsDocument10 pagesOrganic Compoundsjorel marcoNo ratings yet
- CatalystDocument22 pagesCatalystAdan JavedNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For First Class 2013-2014 Msc. Ismail M.AliDocument26 pagesSyllabus For First Class 2013-2014 Msc. Ismail M.AliFilipe Gama FreireNo ratings yet
- UNIT - I - Chemical Process Technology: School of Bio and Chemical Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument78 pagesUNIT - I - Chemical Process Technology: School of Bio and Chemical Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringVineet klNo ratings yet
- Meerwein Ponndorf Verley - ReductionDocument6 pagesMeerwein Ponndorf Verley - ReductionAndey HemanthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document45 pagesChapter 5LOAN PHẠM THỊ PHƯƠNGNo ratings yet
- CH 2 10Document127 pagesCH 2 10active learning educationNo ratings yet
- Chem 217Document5 pagesChem 217Subhabrata MabhaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document11 pagesChapter 5Quỳnh Như PhạmNo ratings yet
- FHSC1124 Tutorial Ebook QDocument72 pagesFHSC1124 Tutorial Ebook QTeo CinnyNo ratings yet
- As Paper 2 2016Document343 pagesAs Paper 2 2016JuanaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6A, B & C Specification SheetDocument5 pagesTopic 6A, B & C Specification SheetNatalie RossetteNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - Introduction To Organic Chemistry Student VersionDocument35 pagesUnit 7 - Introduction To Organic Chemistry Student VersionKetia OssombaNo ratings yet
- Che 125: Chemical Reaction EngineeringDocument1 pageChe 125: Chemical Reaction EngineeringWendell Kim LlanetaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Index - Cr-1Document10 pagesCHEMISTRY Index - Cr-1Anand HNo ratings yet
- 5294 H+i Assignment No 2 M WaseemDocument6 pages5294 H+i Assignment No 2 M WaseemM WaseemNo ratings yet
- Znotes ChemDocument7 pagesZnotes ChemCaylinNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument25 pagesAldehydes and KetonesPatricia DinaNo ratings yet
- 70/70 Chemistry StrategyDocument15 pages70/70 Chemistry Strategybijondebbarma927No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes (Organic Chem)Document6 pagesChemistry Notes (Organic Chem)Teo Jia Ming NickolasNo ratings yet
- AS Chemistry Revision Checklist: Unit/Topic RED Amber Green 1 - Physical ChemistryDocument3 pagesAS Chemistry Revision Checklist: Unit/Topic RED Amber Green 1 - Physical ChemistryAtNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - Introduction To Organic Chemistry Student VersionDocument35 pagesUnit 7 - Introduction To Organic Chemistry Student VersionAmadu sallieuNo ratings yet
- Group Activity 1 (Ga1) General Inorganic Chemistry No. of Questions SubtopicsDocument2 pagesGroup Activity 1 (Ga1) General Inorganic Chemistry No. of Questions SubtopicsZyrah Marri CamerinoNo ratings yet
- White Minimalist Spending Tracker PlannerDocument1 pageWhite Minimalist Spending Tracker PlannerAtharva Pratap Singh 9ANo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Syllabus Updates For Neet (Ug) 2024Document3 pagesChemistry - Syllabus Updates For Neet (Ug) 2024Sarfraz KhanNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: Presenter: Shannon SmithDocument40 pagesHydrocarbons: Presenter: Shannon SmithShannon SmithNo ratings yet
- POINTER Mock Exam Grade 12 2019-2020Document3 pagesPOINTER Mock Exam Grade 12 2019-2020Alyamitha NadiyahNo ratings yet
- Ballini Eco Friendly Synthesis of Fine ChemicalsDocument312 pagesBallini Eco Friendly Synthesis of Fine ChemicalsenviconNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl ChemistryDocument53 pagesCarbonyl Chemistrysujithhr1233395No ratings yet
- BCHCT 131 Block-4eDocument100 pagesBCHCT 131 Block-4esarath chandranNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem II Lec 4Document46 pagesOrganic Chem II Lec 4Bình NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Physics Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesPhysics Organic Chemistrypmasingi.atworkNo ratings yet
- Palladium Reagents and Catalysts: New Perspectives for the 21st CenturyFrom EverandPalladium Reagents and Catalysts: New Perspectives for the 21st CenturyNo ratings yet
- JEE Chemistry StrategyDocument10 pagesJEE Chemistry Strategyarpitsharma2103No ratings yet
- Merged - Document (2 June)Document143 pagesMerged - Document (2 June)buntysharma8218No ratings yet
- Chemical Method of Wastes Disposal: By: Dr. Abdul GhaniDocument22 pagesChemical Method of Wastes Disposal: By: Dr. Abdul Ghanithe scholorsNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument6 pagesChemistryJmhonishkumarNo ratings yet
- Soil Chemistry KeywordsDocument8 pagesSoil Chemistry Keywordssobe64 sNo ratings yet
- 152 Sample-ChapterDocument5 pages152 Sample-ChapterUnnati SinariNo ratings yet
- Subject ChemDocument3 pagesSubject Chemvaishnavisoni32No ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2023-24Document3 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2023-24Rooh KSHIVNo ratings yet
- There Are 3 Main Types of Intermolecular ForcesDocument3 pagesThere Are 3 Main Types of Intermolecular ForcesRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- Speech About Jurassic Park FranchiseDocument2 pagesSpeech About Jurassic Park FranchiseRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- 1.8. HydrocarbonsDocument1 page1.8. HydrocarbonsRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- 1.7. Types of ReactionsDocument10 pages1.7. Types of ReactionsRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test 1: Date: 27/08/2020 Day: Thursday Topics/Chapters InvolvedDocument1 pageChemistry Test 1: Date: 27/08/2020 Day: Thursday Topics/Chapters InvolvedRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- 1.6. Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument16 pages1.6. Introduction To Organic ChemistryRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- Section A: MCQ (15 Marks) : Chapter 2 and 3 TestDocument15 pagesSection A: MCQ (15 Marks) : Chapter 2 and 3 TestRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test 2: Date: 24/09/2020 Day: Thursday Topics/Chapters InvolvedDocument2 pagesChemistry Test 2: Date: 24/09/2020 Day: Thursday Topics/Chapters InvolvedRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- PYQ On GravitationDocument10 pagesPYQ On GravitationRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocument1 pageChapter 2: Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- 8.6. Order of Filling OrbitalsDocument5 pages8.6. Order of Filling OrbitalsRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- Bring Notes To Show Me Next LessonDocument41 pagesBring Notes To Show Me Next LessonRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem - 1Document5 pagesOrganic Chem - 1RXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia BOARDS - (2018-19) CLASS: 10 Subject: ChemistryDocument7 pagesKuala Lumpur, Malaysia BOARDS - (2018-19) CLASS: 10 Subject: ChemistryRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- 10.SEC - Standards For The Connection of Small Scale Solar PV - v3 - Clean PDFDocument44 pages10.SEC - Standards For The Connection of Small Scale Solar PV - v3 - Clean PDFashrafNo ratings yet
- AFTERMATH Population Zero WorksheetDocument3 pagesAFTERMATH Population Zero WorksheetSergio PulidoNo ratings yet
- Hitachi Washing MachineDocument2 pagesHitachi Washing MachineAromaro AmarNo ratings yet
- The Quantum-Mechanical Model of The Atom: Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 1Document77 pagesThe Quantum-Mechanical Model of The Atom: Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 1ynottripNo ratings yet
- Daikin Room Air Conditioner ManualDocument30 pagesDaikin Room Air Conditioner ManualsmithworkNo ratings yet
- Shakir Hajj Services - VC0Document5 pagesShakir Hajj Services - VC0Ehsan Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Cavitation ErosionDocument7 pagesCavitation Erosion82ghost82No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 2 3Document178 pagesChapter 1 2 3sraves147100% (2)
- Nagapattinam - 611002.: E.G.S. Pillay Engineering CollegeDocument35 pagesNagapattinam - 611002.: E.G.S. Pillay Engineering CollegePrasath MurugesanNo ratings yet
- IIEE ANC RME Forum 2015Document231 pagesIIEE ANC RME Forum 2015Ray RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Electric Field and CapacitorsDocument17 pagesElectric Field and CapacitorsPraphul MalolNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: FORD Puma Common Rail System Functional PartsDocument18 pagesService Manual: FORD Puma Common Rail System Functional PartsbejoythomasNo ratings yet
- Form Qw-482 Suggested Format For Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS) (See QW-200.1, Section IX, ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code)Document2 pagesForm Qw-482 Suggested Format For Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS) (See QW-200.1, Section IX, ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code)mohammadNo ratings yet
- Polycab India Limited Test Report: Tested By: Yugdip Uttekar Approved By: Kajal SaluiDocument1 pagePolycab India Limited Test Report: Tested By: Yugdip Uttekar Approved By: Kajal SaluiAshwin SupeNo ratings yet
- D2002M WK T6Document4 pagesD2002M WK T6Charly Perez PlazaNo ratings yet
- ASTM 2017 - Annual HandbooksDocument7 pagesASTM 2017 - Annual HandbooksAkbar ShaikNo ratings yet
- Universal MotorDocument4 pagesUniversal MotorarunNo ratings yet
- Maperod C I Maperod GDocument4 pagesMaperod C I Maperod GdraganugNo ratings yet
- Madhu FinalDocument80 pagesMadhu FinalANU GRAPHICSNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Design Methods // John J. Mcketta JRDocument5 pagesHeat Transfer Design Methods // John J. Mcketta JRRizky Irfattah SNo ratings yet
- DPK SOS EN 6M21 0000 19 01 14 - 6M21G385 5 - StdRad - ScopeOfSupplyDocument3 pagesDPK SOS EN 6M21 0000 19 01 14 - 6M21G385 5 - StdRad - ScopeOfSupplyTau Omicron Sixty D90No ratings yet
- 9 Board C.QDocument40 pages9 Board C.QMohammad Anisuzzaman0% (1)
- Distance Relay Interview Questions With AnswersDocument3 pagesDistance Relay Interview Questions With Answersprabakaran79No ratings yet
- Life Cycle Assessment - Opportunities For Forest Products SectorDocument13 pagesLife Cycle Assessment - Opportunities For Forest Products SectorRAHUL SINGHNo ratings yet
- Azipod PresentationDocument18 pagesAzipod Presentationkhaihui100% (1)
- 1 143tecab5-Ie3Document1 page1 143tecab5-Ie3s bNo ratings yet
- Cause and Solutions For Low Generator Oil PressureDocument1 pageCause and Solutions For Low Generator Oil PressureMohamed Abd ElazizNo ratings yet
- Husqvarna K 760 Parts ListDocument61 pagesHusqvarna K 760 Parts Listszantho peter100% (2)