Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 viewsBreast Cellulitis
Breast Cellulitis
Uploaded by
vishwanathBreast cellulitis is a serious bacterial infection of the breast skin that is often caused by complications from breast surgery or cancer treatments. Symptoms include redness, swelling, tenderness, and pain of the breast. While most women recover from breast surgery without infection, about 1 in 20 develop breast cellulitis. If not treated promptly with antibiotics, breast cellulitis can lead to life-threatening complications such as blood infections or lymphedema.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Animal MagnetismDocument528 pagesAnimal MagnetismGrace Swan100% (1)
- La Mujer Del VendavalDocument44 pagesLa Mujer Del Vendavalkomaria88100% (1)
- Breast Cancer AssignmentDocument25 pagesBreast Cancer AssignmentTiger KneeNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis DefinitionDocument2 pagesCellulitis DefinitionBlossomNo ratings yet
- Treatment of CellulitisDocument2 pagesTreatment of CellulitistreatmentcellNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis Causes, Symptoms and Treatment at Safe Health Center in MT Pleasant, MIDocument13 pagesCellulitis Causes, Symptoms and Treatment at Safe Health Center in MT Pleasant, MINeeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Leg CellulitisDocument3 pagesLeg CellulitisJessica Pacris MaramagNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Andstreptococcus Are The Types of Bacteria That AreDocument28 pagesStaphylococcus Andstreptococcus Are The Types of Bacteria That AreMary Jhane VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis Causes, Symptoms, Treatment - When Should Someone Seek Medical Care For Cellulitis - EMedicineHealthDocument6 pagesCellulitis Causes, Symptoms, Treatment - When Should Someone Seek Medical Care For Cellulitis - EMedicineHealthginNo ratings yet
- FMS 1 - Week 7 Tutorial 1 LO PDFDocument17 pagesFMS 1 - Week 7 Tutorial 1 LO PDFAprillia AlmaasNo ratings yet
- CellulitisDocument11 pagesCellulitisJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument50 pagesBreast CancerZainab Idrees- F2FNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument6 pagesActivity IntoleranceRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument1 pageBreast CancerNeha MittalNo ratings yet
- Brest Cancer 1Document2 pagesBrest Cancer 1Anthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Brest Cancer 1Document2 pagesBrest Cancer 1Anthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Brest Cancer 1Document2 pagesBrest Cancer 1Anthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Inflamatory Brest CADocument9 pagesInflamatory Brest CAArri KurniawanNo ratings yet
- American Society (Pemeriksaan Penunjang)Document14 pagesAmerican Society (Pemeriksaan Penunjang)Envhy WinaNo ratings yet
- CellulitisDocument5 pagesCellulitisKrishna PendemNo ratings yet
- Living With Lymphoedema 2016 WebDocument40 pagesLiving With Lymphoedema 2016 Webremus_stoica23No ratings yet
- Presentation Medical TerminologyDocument26 pagesPresentation Medical TerminologySunaina BhartiNo ratings yet
- Types of Breast CancerDocument6 pagesTypes of Breast CancervivekNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Vaginal BleedingDocument4 pagesAbnormal Vaginal Bleedingmary ann tucaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Breast CancerDocument19 pagesStages of Breast CancerOktovianus PalulluNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis PathoDocument1 pageCellulitis Pathoanon_1303746470% (1)
- Cancer de MamaDocument3 pagesCancer de MamaJosena Dahana CupidonNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer PathophysiologyDocument17 pagesBreast Cancer PathophysiologySwit Tapican MaangNo ratings yet
- Monday PresentationsDocument20 pagesMonday PresentationsSunaina BhartiNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis ThesisDocument8 pagesCellulitis Thesisgbvjc1wy100% (2)
- Cellulite - FeedbackDocument4 pagesCellulite - FeedbackUnicorn SpiderNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer - DZMEDocument6 pagesBreast Cancer - DZMEMarife CompraNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectpreranaNo ratings yet
- Library-media-documents-Cellulitis and Erysipelas Jan 2012 - Lay Reviewed Jan 2012Document4 pagesLibrary-media-documents-Cellulitis and Erysipelas Jan 2012 - Lay Reviewed Jan 2012Syahbandrio WidyoNo ratings yet
- Nickson Jara: Breast MassDocument8 pagesNickson Jara: Breast Massbhez22100% (2)
- Breast Cancer: Presented By, Archana Devi M.SC Nuresing 1 Year Era College of Nursing LucknowDocument43 pagesBreast Cancer: Presented By, Archana Devi M.SC Nuresing 1 Year Era College of Nursing LucknowArchana VermaNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument7 pagesBreast CancerMary Jane TiangsonNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cysts Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & TreatmentDocument1 pageOvarian Cysts Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatmentian SalehNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Symptoms - Breast Cancer SignsDocument3 pagesBreast Cancer Symptoms - Breast Cancer SignsVenkatesh SubramanyaNo ratings yet
- Bening Breast DiseasesDocument41 pagesBening Breast DiseasesHillary RabinNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bhs InggrisDocument3 pagesTugas Bhs Inggrisnamira ramadhaniNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument11 pagesBreast CancerBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- Dian Pratiwi Abdullah K11115309: Created byDocument11 pagesDian Pratiwi Abdullah K11115309: Created bydian pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Benign Tumor Definition, Types, Causes & ManagementDocument12 pagesBenign Tumor Definition, Types, Causes & ManagementSa GhNo ratings yet
- CellulitisDocument3 pagesCellulitisFonjiakwe AmosNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer (Reaction Paper)Document2 pagesBreast Cancer (Reaction Paper)Maria Angela Del GallegoNo ratings yet
- Biology InvestigatoryDocument6 pagesBiology InvestigatoryAananthan Jayvardan100% (2)
- Cellulitis - Biology Science Fair Project IdeasDocument4 pagesCellulitis - Biology Science Fair Project IdeasEPFO AKURDINo ratings yet
- What Is Breast CancerDocument4 pagesWhat Is Breast CancerRj RiosNo ratings yet
- Bahaya Virus ChytomegalovirusDocument5 pagesBahaya Virus ChytomegalovirusJajang KusumaNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Symptoms, Types, Causes & TreatmentDocument1 pageBreast Cancer Symptoms, Types, Causes & Treatmentruth.abenaamoahNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts On Breast CancerDocument8 pagesFast Facts On Breast CancerTety KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument6 pagesBreast Cancerkohenoor1991No ratings yet
- MiscarriageDocument4 pagesMiscarriageJack BangcoyoNo ratings yet
- Cervicitis Symptoms, Treatment, Causes & TypesDocument1 pageCervicitis Symptoms, Treatment, Causes & Typesramit singlaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of BreastDocument23 pagesDiseases of BreastTalal AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Lymphedema Diet: A Beginner's Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Lymphedema Through Nutrition With Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanFrom EverandLymphedema Diet: A Beginner's Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Lymphedema Through Nutrition With Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Non-Cancerous Breast Conditions: Fibrocystic DiseaseDocument29 pagesNon-Cancerous Breast Conditions: Fibrocystic DiseaseAdinda RaNo ratings yet
- Album de InglesDocument8 pagesAlbum de Ingles夢於נмᷓNo ratings yet
- Breast MassesDocument10 pagesBreast MassesUdunk AdhinkNo ratings yet
- Jock Itch: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments - 1627880858481Document17 pagesJock Itch: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments - 1627880858481Aluko Damilare MosesNo ratings yet
- Exploratory Laparotomy Part 1Document3 pagesExploratory Laparotomy Part 1vishwanathNo ratings yet
- Colovesical Fistula Part 1Document2 pagesColovesical Fistula Part 1vishwanathNo ratings yet
- Expressive AphasiaDocument2 pagesExpressive AphasiavishwanathNo ratings yet
- Patent Foramen Ovale PFODocument3 pagesPatent Foramen Ovale PFOvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis ConditonDocument3 pagesCholelithiasis ConditonvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Achilles Tendon RuptureDocument3 pagesAchilles Tendon RupturevishwanathNo ratings yet
- Incentive Spirometry How To Use An Incentive SpirometerDocument2 pagesIncentive Spirometry How To Use An Incentive Spirometervishwanath100% (1)
- Chest PressureDocument9 pagesChest PressurevishwanathNo ratings yet
- DVT and TestsDocument4 pagesDVT and TestsvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis: Screening For Hepatitis CDocument2 pagesDiagnosis: Screening For Hepatitis CvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Causes: Hyperkalemia Can Happen If Your Kidneys Don't Work Properly andDocument3 pagesCauses: Hyperkalemia Can Happen If Your Kidneys Don't Work Properly andvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis OrenciaDocument8 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis OrenciavishwanathNo ratings yet
- Understanding Prostate CancerDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Prostate CancervishwanathNo ratings yet
- Cardiac EnzymesDocument3 pagesCardiac EnzymesvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Implantable Cardioverter DefibrillatorDocument5 pagesImplantable Cardioverter DefibrillatorvishwanathNo ratings yet
- What Is AnastomosisDocument11 pagesWhat Is AnastomosisvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Torsades de PointesDocument5 pagesTorsades de PointesvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Salter Harris FractureDocument10 pagesSalter Harris FracturevishwanathNo ratings yet
- Understanding DiaphoresisDocument7 pagesUnderstanding DiaphoresisvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Aaa Repair CardiologyDocument31 pagesAaa Repair CardiologyvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Achalasia What Is Achalasia?Document5 pagesAchalasia What Is Achalasia?vishwanathNo ratings yet
- Caring For Your Nephrostomy Tube: Kidney StonesDocument10 pagesCaring For Your Nephrostomy Tube: Kidney StonesvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker: ArrhythmiasDocument9 pagesPacemaker: ArrhythmiasvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Tap Presentation - Google SlidesDocument12 pagesTap Presentation - Google Slidesapi-208317298No ratings yet
- The Psychedelic SixtiesDocument13 pagesThe Psychedelic SixtiesD Hernandez100% (1)
- 9 Secrets of LongevityDocument18 pages9 Secrets of LongevityIanna J. L. PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Revision Oral Pathology: Dr. Nermine El BaheyDocument58 pagesRevision Oral Pathology: Dr. Nermine El BaheyEslam abokhalilNo ratings yet
- How To Fight FATFlammation! by Lori Schemek (An Excerpt)Document20 pagesHow To Fight FATFlammation! by Lori Schemek (An Excerpt)HarperOne (an imprint of HarperCollins)100% (1)
- Christ The King College College of Nursing and IHAP Calbayog CityDocument4 pagesChrist The King College College of Nursing and IHAP Calbayog CityMannuelle GacudNo ratings yet
- General Pathology Presentation (Cellulitis)Document17 pagesGeneral Pathology Presentation (Cellulitis)Lames Ali Sayed Ahmed AttiaNo ratings yet
- Unil EverDocument17 pagesUnil EverJovz BumohyaNo ratings yet
- LCC402 English For Oral ReportingDocument5 pagesLCC402 English For Oral Reportingm-5243143No ratings yet
- Behavioural Brain Research: ReviewDocument15 pagesBehavioural Brain Research: ReviewVazia Rahma HandikaNo ratings yet
- Algorithm in Hypertension-PduiDocument32 pagesAlgorithm in Hypertension-PduiMochamad BurhanudinNo ratings yet
- Methodical Manual For Independent Work of Students On 6 CourseDocument129 pagesMethodical Manual For Independent Work of Students On 6 CourseAzra AzmunaNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Ray AnnaDocument51 pagesChest X-Ray Annaapi-26159412100% (1)
- Mrsa 2Document17 pagesMrsa 2Henra HalimNo ratings yet
- Chronic Heart Failure (Gagal Jantung Kronik)Document15 pagesChronic Heart Failure (Gagal Jantung Kronik)Grup 9B Viscera tahun 2No ratings yet
- Vasculitesdiagdiferencial 20220511173912Document7 pagesVasculitesdiagdiferencial 20220511173912Isabelle JácomeNo ratings yet
- Soap 1Document7 pagesSoap 1api-248360288No ratings yet
- Drug Study 1Document5 pagesDrug Study 1Alen Alano100% (1)
- Sources of Different Vitamins and Diseases Caused by Their DeficiencyDocument2 pagesSources of Different Vitamins and Diseases Caused by Their DeficiencyPrashant SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Diabetes and PEMF TherapyDocument4 pagesDiabetes and PEMF Therapyklatifdg100% (1)
- Dec Vaspen NewsletterDocument7 pagesDec Vaspen Newsletterapi-287472804No ratings yet
- Bryonia Alba - Homoeopathic Materia Medica - by William BoerickeDocument3 pagesBryonia Alba - Homoeopathic Materia Medica - by William BoerickeAnand GuptaNo ratings yet
- To Decrease Temperature by Means Through Evaporation and ConductionDocument11 pagesTo Decrease Temperature by Means Through Evaporation and Conductioniaekawa100% (6)
- By Dr. Nouran Abou Khedr: Xeroderma PigmentosumDocument6 pagesBy Dr. Nouran Abou Khedr: Xeroderma PigmentosumBahaa ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Fe Del Mundo NCP 2Document7 pagesFe Del Mundo NCP 2Jenness VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 2006 Vol.33 Issues 4 Late Preterm Pregnancy and The NewbornDocument212 pages2006 Vol.33 Issues 4 Late Preterm Pregnancy and The Newbornviean25No ratings yet
- Indications and Contraindications of Laparoscopy1Document18 pagesIndications and Contraindications of Laparoscopy1drhiwaomer100% (2)
- Nutrition ManualDocument48 pagesNutrition ManualIrina Pirlog RusanovschiNo ratings yet
Breast Cellulitis
Breast Cellulitis
Uploaded by
vishwanath0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views5 pagesBreast cellulitis is a serious bacterial infection of the breast skin that is often caused by complications from breast surgery or cancer treatments. Symptoms include redness, swelling, tenderness, and pain of the breast. While most women recover from breast surgery without infection, about 1 in 20 develop breast cellulitis. If not treated promptly with antibiotics, breast cellulitis can lead to life-threatening complications such as blood infections or lymphedema.
Original Description:
Original Title
Breast cellulitis.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBreast cellulitis is a serious bacterial infection of the breast skin that is often caused by complications from breast surgery or cancer treatments. Symptoms include redness, swelling, tenderness, and pain of the breast. While most women recover from breast surgery without infection, about 1 in 20 develop breast cellulitis. If not treated promptly with antibiotics, breast cellulitis can lead to life-threatening complications such as blood infections or lymphedema.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views5 pagesBreast Cellulitis
Breast Cellulitis
Uploaded by
vishwanathBreast cellulitis is a serious bacterial infection of the breast skin that is often caused by complications from breast surgery or cancer treatments. Symptoms include redness, swelling, tenderness, and pain of the breast. While most women recover from breast surgery without infection, about 1 in 20 develop breast cellulitis. If not treated promptly with antibiotics, breast cellulitis can lead to life-threatening complications such as blood infections or lymphedema.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
Everything You Should Know About Breast
Cellulitis
Overview
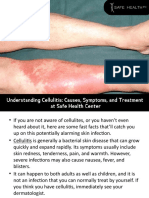
Breast cellulitis is a type of serious bacterial
infection that affects the skin of the breast.
This condition may occur from broken skin,
but it’s most often the result of complications
from surgery or cancer treatments. While
most women will go through breast surgery
without developing an infection, about 1 in 20
women are affected.
If not diagnosed and promptly treated, breast
cellulitis can lead to life-threatening
complications.
Symptoms
The symptoms of breast cellulitis tend to
occur shortly after the skin is broken in any
fashion. This includes breast cancer surgery
and other related incisions. If you have a
weakened immune system from cancer
treatments, then a simple cut can lead to
cellulitis.
Symptoms of breast cellulitis may include:
redness and swelling
tenderness
fever
chills
pain when touched
a wound that is oozing clear or yellow
fluids
rash
red streaks developing from the rash
See your doctor right away if you develop any
symptoms that may indicate breast cellulitis.
Read more: What is a breast infection? »
Causes
Cellulitis is a type of skin infection that can
occur anywhere in the body. It’s a bacterial
infection that affects skin tissues just
underneath the skin’s
surface. Staphylococcus
aureus and Streptococcus are the two most
common types of bacteria that cause cellulitis.
They can cause the infection by getting into
exposed cuts. A decreased immune system
can also increase your risk for cellulitis.
Breast cellulitis isn’t normally caused by
infected cuts like other forms of the infection.
Instead, this type of infection mostly manifests
itself from cancer treatments or surgeries.
Lymph node removal can weaken your
immune system and increase your risk for
cellulitis in the upper body. This includes your
breasts. This infection can also occur after
breast augmentation or reduction surgeries.
Breast cellulitis vs. inflammatory breast
cancer
Breast cellulitis can sometimes be caused
by inflammatory breast cancer. However,
these are two separate conditions. Cellulitis of
the breasts is sometimes mistaken for
inflammatory breast cancer, and vice versa.
Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare form of
breast cancer. Symptoms include:
redness
swelling
pain
Cellulitis can cause fever or chills, which
aren’t symptoms of inflammatory breast
cancer.
Any significant changes in your breasts
should be evaluated by a doctor as soon as
possible, however, so that they can determine
the cause.
Treatment
Breast cellulitis, as with other forms of
cellulitis, is treated with antibiotics. These are
typically taken for 7–10 days to make sure
that the infection doesn’t come back. Take the
entire prescription as directed. Your doctor will
likely want to see you after a couple of weeks
to make sure the infection has fully cleared
up.
Ask your doctor if you can take over-the-
counter (OTC) pain relievers, such as
acetaminophen (Tylenol), to help ease
discomfort while the antibiotics run their
course.
If you don’t respond to prescription antibiotics,
your doctor may recommend intravenous
antibiotics given at the hospital.
Complications
Left untreated, breast cellulitis can lead to
serious complications. A blood infection can
lead to poisoning (septicemia), which is
potentially fatal.
Breast cellulitis may also lead to lymphedema.
Lymphedema is a condition where your lymph
nodes are unable to properly drain. You may
especially be at risk if you’ve had one or more
lymph nodes removed.
You might also like
- Animal MagnetismDocument528 pagesAnimal MagnetismGrace Swan100% (1)
- La Mujer Del VendavalDocument44 pagesLa Mujer Del Vendavalkomaria88100% (1)
- Breast Cancer AssignmentDocument25 pagesBreast Cancer AssignmentTiger KneeNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis DefinitionDocument2 pagesCellulitis DefinitionBlossomNo ratings yet
- Treatment of CellulitisDocument2 pagesTreatment of CellulitistreatmentcellNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis Causes, Symptoms and Treatment at Safe Health Center in MT Pleasant, MIDocument13 pagesCellulitis Causes, Symptoms and Treatment at Safe Health Center in MT Pleasant, MINeeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Leg CellulitisDocument3 pagesLeg CellulitisJessica Pacris MaramagNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Andstreptococcus Are The Types of Bacteria That AreDocument28 pagesStaphylococcus Andstreptococcus Are The Types of Bacteria That AreMary Jhane VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis Causes, Symptoms, Treatment - When Should Someone Seek Medical Care For Cellulitis - EMedicineHealthDocument6 pagesCellulitis Causes, Symptoms, Treatment - When Should Someone Seek Medical Care For Cellulitis - EMedicineHealthginNo ratings yet
- FMS 1 - Week 7 Tutorial 1 LO PDFDocument17 pagesFMS 1 - Week 7 Tutorial 1 LO PDFAprillia AlmaasNo ratings yet
- CellulitisDocument11 pagesCellulitisJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument50 pagesBreast CancerZainab Idrees- F2FNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument6 pagesActivity IntoleranceRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument1 pageBreast CancerNeha MittalNo ratings yet
- Brest Cancer 1Document2 pagesBrest Cancer 1Anthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Brest Cancer 1Document2 pagesBrest Cancer 1Anthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Brest Cancer 1Document2 pagesBrest Cancer 1Anthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Inflamatory Brest CADocument9 pagesInflamatory Brest CAArri KurniawanNo ratings yet
- American Society (Pemeriksaan Penunjang)Document14 pagesAmerican Society (Pemeriksaan Penunjang)Envhy WinaNo ratings yet
- CellulitisDocument5 pagesCellulitisKrishna PendemNo ratings yet
- Living With Lymphoedema 2016 WebDocument40 pagesLiving With Lymphoedema 2016 Webremus_stoica23No ratings yet
- Presentation Medical TerminologyDocument26 pagesPresentation Medical TerminologySunaina BhartiNo ratings yet
- Types of Breast CancerDocument6 pagesTypes of Breast CancervivekNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Vaginal BleedingDocument4 pagesAbnormal Vaginal Bleedingmary ann tucaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Breast CancerDocument19 pagesStages of Breast CancerOktovianus PalulluNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis PathoDocument1 pageCellulitis Pathoanon_1303746470% (1)
- Cancer de MamaDocument3 pagesCancer de MamaJosena Dahana CupidonNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer PathophysiologyDocument17 pagesBreast Cancer PathophysiologySwit Tapican MaangNo ratings yet
- Monday PresentationsDocument20 pagesMonday PresentationsSunaina BhartiNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis ThesisDocument8 pagesCellulitis Thesisgbvjc1wy100% (2)
- Cellulite - FeedbackDocument4 pagesCellulite - FeedbackUnicorn SpiderNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer - DZMEDocument6 pagesBreast Cancer - DZMEMarife CompraNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectpreranaNo ratings yet
- Library-media-documents-Cellulitis and Erysipelas Jan 2012 - Lay Reviewed Jan 2012Document4 pagesLibrary-media-documents-Cellulitis and Erysipelas Jan 2012 - Lay Reviewed Jan 2012Syahbandrio WidyoNo ratings yet
- Nickson Jara: Breast MassDocument8 pagesNickson Jara: Breast Massbhez22100% (2)
- Breast Cancer: Presented By, Archana Devi M.SC Nuresing 1 Year Era College of Nursing LucknowDocument43 pagesBreast Cancer: Presented By, Archana Devi M.SC Nuresing 1 Year Era College of Nursing LucknowArchana VermaNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument7 pagesBreast CancerMary Jane TiangsonNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cysts Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & TreatmentDocument1 pageOvarian Cysts Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatmentian SalehNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Symptoms - Breast Cancer SignsDocument3 pagesBreast Cancer Symptoms - Breast Cancer SignsVenkatesh SubramanyaNo ratings yet
- Bening Breast DiseasesDocument41 pagesBening Breast DiseasesHillary RabinNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bhs InggrisDocument3 pagesTugas Bhs Inggrisnamira ramadhaniNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument11 pagesBreast CancerBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- Dian Pratiwi Abdullah K11115309: Created byDocument11 pagesDian Pratiwi Abdullah K11115309: Created bydian pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Benign Tumor Definition, Types, Causes & ManagementDocument12 pagesBenign Tumor Definition, Types, Causes & ManagementSa GhNo ratings yet
- CellulitisDocument3 pagesCellulitisFonjiakwe AmosNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer (Reaction Paper)Document2 pagesBreast Cancer (Reaction Paper)Maria Angela Del GallegoNo ratings yet
- Biology InvestigatoryDocument6 pagesBiology InvestigatoryAananthan Jayvardan100% (2)
- Cellulitis - Biology Science Fair Project IdeasDocument4 pagesCellulitis - Biology Science Fair Project IdeasEPFO AKURDINo ratings yet
- What Is Breast CancerDocument4 pagesWhat Is Breast CancerRj RiosNo ratings yet
- Bahaya Virus ChytomegalovirusDocument5 pagesBahaya Virus ChytomegalovirusJajang KusumaNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Symptoms, Types, Causes & TreatmentDocument1 pageBreast Cancer Symptoms, Types, Causes & Treatmentruth.abenaamoahNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts On Breast CancerDocument8 pagesFast Facts On Breast CancerTety KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument6 pagesBreast Cancerkohenoor1991No ratings yet
- MiscarriageDocument4 pagesMiscarriageJack BangcoyoNo ratings yet
- Cervicitis Symptoms, Treatment, Causes & TypesDocument1 pageCervicitis Symptoms, Treatment, Causes & Typesramit singlaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of BreastDocument23 pagesDiseases of BreastTalal AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Lymphedema Diet: A Beginner's Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Lymphedema Through Nutrition With Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanFrom EverandLymphedema Diet: A Beginner's Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Lymphedema Through Nutrition With Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Non-Cancerous Breast Conditions: Fibrocystic DiseaseDocument29 pagesNon-Cancerous Breast Conditions: Fibrocystic DiseaseAdinda RaNo ratings yet
- Album de InglesDocument8 pagesAlbum de Ingles夢於נмᷓNo ratings yet
- Breast MassesDocument10 pagesBreast MassesUdunk AdhinkNo ratings yet
- Jock Itch: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments - 1627880858481Document17 pagesJock Itch: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments - 1627880858481Aluko Damilare MosesNo ratings yet
- Exploratory Laparotomy Part 1Document3 pagesExploratory Laparotomy Part 1vishwanathNo ratings yet
- Colovesical Fistula Part 1Document2 pagesColovesical Fistula Part 1vishwanathNo ratings yet
- Expressive AphasiaDocument2 pagesExpressive AphasiavishwanathNo ratings yet
- Patent Foramen Ovale PFODocument3 pagesPatent Foramen Ovale PFOvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis ConditonDocument3 pagesCholelithiasis ConditonvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Achilles Tendon RuptureDocument3 pagesAchilles Tendon RupturevishwanathNo ratings yet
- Incentive Spirometry How To Use An Incentive SpirometerDocument2 pagesIncentive Spirometry How To Use An Incentive Spirometervishwanath100% (1)
- Chest PressureDocument9 pagesChest PressurevishwanathNo ratings yet
- DVT and TestsDocument4 pagesDVT and TestsvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis: Screening For Hepatitis CDocument2 pagesDiagnosis: Screening For Hepatitis CvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Causes: Hyperkalemia Can Happen If Your Kidneys Don't Work Properly andDocument3 pagesCauses: Hyperkalemia Can Happen If Your Kidneys Don't Work Properly andvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis OrenciaDocument8 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis OrenciavishwanathNo ratings yet
- Understanding Prostate CancerDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Prostate CancervishwanathNo ratings yet
- Cardiac EnzymesDocument3 pagesCardiac EnzymesvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Implantable Cardioverter DefibrillatorDocument5 pagesImplantable Cardioverter DefibrillatorvishwanathNo ratings yet
- What Is AnastomosisDocument11 pagesWhat Is AnastomosisvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Torsades de PointesDocument5 pagesTorsades de PointesvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Salter Harris FractureDocument10 pagesSalter Harris FracturevishwanathNo ratings yet
- Understanding DiaphoresisDocument7 pagesUnderstanding DiaphoresisvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Aaa Repair CardiologyDocument31 pagesAaa Repair CardiologyvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Achalasia What Is Achalasia?Document5 pagesAchalasia What Is Achalasia?vishwanathNo ratings yet
- Caring For Your Nephrostomy Tube: Kidney StonesDocument10 pagesCaring For Your Nephrostomy Tube: Kidney StonesvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker: ArrhythmiasDocument9 pagesPacemaker: ArrhythmiasvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Tap Presentation - Google SlidesDocument12 pagesTap Presentation - Google Slidesapi-208317298No ratings yet
- The Psychedelic SixtiesDocument13 pagesThe Psychedelic SixtiesD Hernandez100% (1)
- 9 Secrets of LongevityDocument18 pages9 Secrets of LongevityIanna J. L. PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Revision Oral Pathology: Dr. Nermine El BaheyDocument58 pagesRevision Oral Pathology: Dr. Nermine El BaheyEslam abokhalilNo ratings yet
- How To Fight FATFlammation! by Lori Schemek (An Excerpt)Document20 pagesHow To Fight FATFlammation! by Lori Schemek (An Excerpt)HarperOne (an imprint of HarperCollins)100% (1)
- Christ The King College College of Nursing and IHAP Calbayog CityDocument4 pagesChrist The King College College of Nursing and IHAP Calbayog CityMannuelle GacudNo ratings yet
- General Pathology Presentation (Cellulitis)Document17 pagesGeneral Pathology Presentation (Cellulitis)Lames Ali Sayed Ahmed AttiaNo ratings yet
- Unil EverDocument17 pagesUnil EverJovz BumohyaNo ratings yet
- LCC402 English For Oral ReportingDocument5 pagesLCC402 English For Oral Reportingm-5243143No ratings yet
- Behavioural Brain Research: ReviewDocument15 pagesBehavioural Brain Research: ReviewVazia Rahma HandikaNo ratings yet
- Algorithm in Hypertension-PduiDocument32 pagesAlgorithm in Hypertension-PduiMochamad BurhanudinNo ratings yet
- Methodical Manual For Independent Work of Students On 6 CourseDocument129 pagesMethodical Manual For Independent Work of Students On 6 CourseAzra AzmunaNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Ray AnnaDocument51 pagesChest X-Ray Annaapi-26159412100% (1)
- Mrsa 2Document17 pagesMrsa 2Henra HalimNo ratings yet
- Chronic Heart Failure (Gagal Jantung Kronik)Document15 pagesChronic Heart Failure (Gagal Jantung Kronik)Grup 9B Viscera tahun 2No ratings yet
- Vasculitesdiagdiferencial 20220511173912Document7 pagesVasculitesdiagdiferencial 20220511173912Isabelle JácomeNo ratings yet
- Soap 1Document7 pagesSoap 1api-248360288No ratings yet
- Drug Study 1Document5 pagesDrug Study 1Alen Alano100% (1)
- Sources of Different Vitamins and Diseases Caused by Their DeficiencyDocument2 pagesSources of Different Vitamins and Diseases Caused by Their DeficiencyPrashant SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Diabetes and PEMF TherapyDocument4 pagesDiabetes and PEMF Therapyklatifdg100% (1)
- Dec Vaspen NewsletterDocument7 pagesDec Vaspen Newsletterapi-287472804No ratings yet
- Bryonia Alba - Homoeopathic Materia Medica - by William BoerickeDocument3 pagesBryonia Alba - Homoeopathic Materia Medica - by William BoerickeAnand GuptaNo ratings yet
- To Decrease Temperature by Means Through Evaporation and ConductionDocument11 pagesTo Decrease Temperature by Means Through Evaporation and Conductioniaekawa100% (6)
- By Dr. Nouran Abou Khedr: Xeroderma PigmentosumDocument6 pagesBy Dr. Nouran Abou Khedr: Xeroderma PigmentosumBahaa ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Fe Del Mundo NCP 2Document7 pagesFe Del Mundo NCP 2Jenness VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 2006 Vol.33 Issues 4 Late Preterm Pregnancy and The NewbornDocument212 pages2006 Vol.33 Issues 4 Late Preterm Pregnancy and The Newbornviean25No ratings yet
- Indications and Contraindications of Laparoscopy1Document18 pagesIndications and Contraindications of Laparoscopy1drhiwaomer100% (2)
- Nutrition ManualDocument48 pagesNutrition ManualIrina Pirlog RusanovschiNo ratings yet