Professional Documents
Culture Documents
G DFE G DFE: Main Functions Good Sources
G DFE G DFE: Main Functions Good Sources
Uploaded by
mplennaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
G DFE G DFE: Main Functions Good Sources
G DFE G DFE: Main Functions Good Sources
Uploaded by
mplennaCopyright:
Available Formats
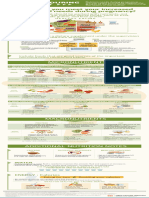
FOLATE (VITAMIN B9)
M AIN FUNC TIONS GOOD SOURCES
• Required for DNA synthesis Green Leafy Fortified Food &
Legumes Vegetables Supplements
beans ∙ peas ∙ lentils kale ∙ spinach
• Supports cell growth and repair • Lentils (cooked), • Spinach (cooked), • Sliced Bread
½ cup, 179 µg DFE ½ cup, 131 µg DFE (enriched),
1 slice, 84 µg DFE
• Helps prevent neural tube defects
DAILY RECOMMENDATION
µg = micrograms; DFE = Dietary Folate Equivalents
SPECIAL NOTES
400 600
µg DFE µg DFE • Folate is a general term that refers to both natural folates in food and folic acid, the
synthetic form used in supplements and fortified food.
• DFE = a unit of measure that accounts for differences in the absorption of naturally
occurring food folate and synthetic folic acid.
• To reduce the risk of neural tube defects, all women capable of becoming pregnant should
Adults Pregnant consume 400 µg folic acid/day in addition to the folate obtained from a varied diet.
Women
• Very high-dose folic acid supplementation (5,000 µg) can mask a vitamin B12 deficiency,
specifically signs of nerve damage.
© 2017 Linus Pauling Institute
You might also like
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument4 pagesVitamin and Mineral ChartGerarld Immanuel Kairupan100% (1)
- Typewriter Olivetti Linea98 SerManDocument66 pagesTypewriter Olivetti Linea98 SerManmplennaNo ratings yet
- Folate EngDocument5 pagesFolate Engrobysejoaca9No ratings yet
- Water Soluble VitaminsDocument36 pagesWater Soluble VitaminsMehak ElahiNo ratings yet
- Folic Acid Food Fact SheetDocument2 pagesFolic Acid Food Fact SheetKirubakaranNo ratings yet
- FN 2068Document2 pagesFN 2068Abbiola BreadyNo ratings yet
- GIS1012 Lifecycle Nutrition: Water Soluble Vitamin 3Document36 pagesGIS1012 Lifecycle Nutrition: Water Soluble Vitamin 3EdNo ratings yet
- Neufol (L Methylfolate)Document17 pagesNeufol (L Methylfolate)Asma SaleemNo ratings yet
- Folic Acid: Bda Food Fact SheetDocument2 pagesFolic Acid: Bda Food Fact SheetEshan Atharizz SetiawanNo ratings yet
- What To Know About Folic AcidDocument10 pagesWhat To Know About Folic AcidAnimal zoneNo ratings yet
- F2 CHP 3 Nutrition (Chinese)Document18 pagesF2 CHP 3 Nutrition (Chinese)ChuahSiewHoon100% (2)
- Attachment 4Document30 pagesAttachment 4Barak KilimoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition During1Document1 pageNutrition During1ranapress7No ratings yet
- Nutrients in Food - Micronutrients - E-ContentDocument23 pagesNutrients in Food - Micronutrients - E-ContentSAGAR SAWANTNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B Tetrahydrofolate Dihydrofolic Essential: Not Biologically ActiveDocument13 pagesVitamin B Tetrahydrofolate Dihydrofolic Essential: Not Biologically ActiveAbang ZakariaNo ratings yet
- F2 Chapter 3 NutritionDocument18 pagesF2 Chapter 3 NutritionJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- Ramos-Activity MineralsDocument7 pagesRamos-Activity MineralsChristian Vonne B. RamosNo ratings yet
- Folic AcidDocument2 pagesFolic AcidRoisinNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and MineralDocument41 pagesVitamin and MineralMADE ARY SARASMITANo ratings yet
- Diet and Neural Disease: Tujuan PembelajaranDocument21 pagesDiet and Neural Disease: Tujuan PembelajaranLia AgustinaNo ratings yet
- Increase Absorption:: Nutrient RDI Increase/decrease Absorption Sources Comments To Meet RDIDocument5 pagesIncrease Absorption:: Nutrient RDI Increase/decrease Absorption Sources Comments To Meet RDIStephanieNo ratings yet
- AntioxidantsDocument1 pageAntioxidantsRyhannahNo ratings yet
- Improving Bioavailability of Nutrients in Plant Fo PDFDocument10 pagesImproving Bioavailability of Nutrients in Plant Fo PDFTemesgen DeguNo ratings yet
- Human Development and Human BehaviorDocument11 pagesHuman Development and Human BehaviormirtchNo ratings yet
- Subeeka Akbar Advance NutritionDocument11 pagesSubeeka Akbar Advance NutritionSubeeka AkbarNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument42 pagesVitamins and MineralsCawen TaponNo ratings yet
- Nutri - RVWR - Water Soluble VitaminsDocument4 pagesNutri - RVWR - Water Soluble VitaminsDon Nikko Lemuel OctavianoNo ratings yet
- Human Nutrition Part 2Document30 pagesHuman Nutrition Part 2Sbahat FatimaNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Its Types With DetailDocument11 pagesVitamins and Its Types With DetailSummiyah ShahbazNo ratings yet
- Original 8Document1 pageOriginal 8api-119278633No ratings yet
- JG College of Nursing, AhmedabadDocument13 pagesJG College of Nursing, AhmedabadVinayak Srivastava100% (1)
- Herbal Hills: Wheat-O-PowerDocument47 pagesHerbal Hills: Wheat-O-PowerKamran AlamNo ratings yet
- Water Soluble VitaminsDocument20 pagesWater Soluble VitaminsFjane camotaNo ratings yet
- Vegan Vegetarian Dining Guide InfographicDocument2 pagesVegan Vegetarian Dining Guide Infographicapi-546555350No ratings yet
- Water Soluble Vitamins HandoutDocument5 pagesWater Soluble Vitamins HandoutMihaela NeacsuNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Minerals in Our Food PDFDocument5 pagesVitamins and Minerals in Our Food PDFRaman KatariaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - 2017 KalusuGalingan Quiz Show PDFDocument73 pagesReviewer - 2017 KalusuGalingan Quiz Show PDFFred Fernando100% (1)
- Bmjopen 2020 July 10 7 Inline Supplementary Material 1Document1 pageBmjopen 2020 July 10 7 Inline Supplementary Material 1Genix PharmaNo ratings yet
- AFOL PlusDocument18 pagesAFOL PlusFalcon ApolloNo ratings yet
- Modified Fibre Diet For The Prevention of Bowel Obstruction: My NutritionDocument5 pagesModified Fibre Diet For The Prevention of Bowel Obstruction: My NutritionDessa Danse OrientaleNo ratings yet
- Formarea Dintelui - Vitamine.4pptxDocument22 pagesFormarea Dintelui - Vitamine.4pptxRuxandra FitaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Notes Water Soluble VitaminsDocument14 pagesPresentation Notes Water Soluble VitaminsFriti FritiNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: IntroductionDocument16 pagesVitamins: IntroductionDarshan MishraNo ratings yet
- Water Soluble Vitamins 3211 BugwacandbrigoliDocument1 pageWater Soluble Vitamins 3211 BugwacandbrigoliBUGWAC MIRANEIL MAURINNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Gut HealthDocument2 pagesNutrition For Gut Healthapi-438302204No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyZIANAH JOY FAMYNo ratings yet
- Lec 5 Vitamins and HealthDocument14 pagesLec 5 Vitamins and HealthSherif AliNo ratings yet
- Angel Bds Water Soluble VitaminsDocument107 pagesAngel Bds Water Soluble Vitaminsseenuu53No ratings yet
- F2 Chapter 3 NutritionDocument17 pagesF2 Chapter 3 NutritionYAP SHAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Nutrient ChartDocument7 pagesNutrient ChartDanilo Clerigo Sr.No ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument26 pagesVitamins and MineralsAisha Doll100% (1)
- Vitamins & MineralsDocument8 pagesVitamins & Mineralswardahmohammad2022No ratings yet
- Power of SunflowerseedsDocument4 pagesPower of SunflowerseedspacifistlightNo ratings yet
- Calcium and Phosphate Balance With Kidney Disease Kidney Health Australia Fact SheetDocument4 pagesCalcium and Phosphate Balance With Kidney Disease Kidney Health Australia Fact SheetIender LegjonNo ratings yet
- Vitamin DDocument51 pagesVitamin DMeriam AntonyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 & 7Document21 pagesChapter 6 & 7Noor Asneeda Ishak (FBM)No ratings yet
- ch-7 Nutretion in DietDocument7 pagesch-7 Nutretion in Dietxhtk3em03zNo ratings yet
- Renal Vegetarian NutritionDocument2 pagesRenal Vegetarian NutritionSg Balaji100% (1)
- Folic Acid (Vitamin B9), A Simple Guide To The Vitamin, Functions And DeficiencyFrom EverandFolic Acid (Vitamin B9), A Simple Guide To The Vitamin, Functions And DeficiencyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Vitamin B3 Deficiency, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Its Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandVitamin B3 Deficiency, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Its Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 5.3W 2-Channel AF Power Amplifier: Package Dimensions FeaturesDocument12 pages5.3W 2-Channel AF Power Amplifier: Package Dimensions FeaturesmplennaNo ratings yet
- LongWave TransmitterDocument1 pageLongWave TransmittermplennaNo ratings yet
- PW 1979 02Document93 pagesPW 1979 02mplennaNo ratings yet
- Ampl 15 WDocument1 pageAmpl 15 WmplennaNo ratings yet
- Oscilador Baud Rate para 90HzDocument1 pageOscilador Baud Rate para 90HzmplennaNo ratings yet
- KA2297 DatasheetDocument6 pagesKA2297 DatasheetmplennaNo ratings yet
- Rider-Resonance and Alignment - John F. RiderDocument95 pagesRider-Resonance and Alignment - John F. RidermplennaNo ratings yet
- Babani 58 50 Circuits Using 7400 ICsDocument82 pagesBabani 58 50 Circuits Using 7400 ICsmplennaNo ratings yet
- Ha 11225Document6 pagesHa 11225mplennaNo ratings yet
- Radio Craft 33 Amplifier Builder's GuideDocument68 pagesRadio Craft 33 Amplifier Builder's GuidemplennaNo ratings yet
- Radio TV Experimenter 1965-02-03Document132 pagesRadio TV Experimenter 1965-02-03mplennaNo ratings yet
- Si861x/2x Data Sheet: Low-Power Single and Dual-Channel Digital IsolatorsDocument39 pagesSi861x/2x Data Sheet: Low-Power Single and Dual-Channel Digital IsolatorsmplennaNo ratings yet
- CD4020BC - CD4040BC - CD4060BC 14-Stage Ripple Carry Binary Counters - 12-Stage Ripple Carry Binary Counters - 14-Stage Ripple Carry Binary CountersDocument8 pagesCD4020BC - CD4040BC - CD4060BC 14-Stage Ripple Carry Binary Counters - 12-Stage Ripple Carry Binary Counters - 14-Stage Ripple Carry Binary CountersmplennaNo ratings yet
- YAESU FT 2000 Service ManualDocument206 pagesYAESU FT 2000 Service ManualmplennaNo ratings yet
- S I 4 8 2 2 / 2 6 / 2 7 / 4 0 / 4 4 A, S, L, D G: Ntenna Chematic Ayout AND Esign UidelinesDocument38 pagesS I 4 8 2 2 / 2 6 / 2 7 / 4 0 / 4 4 A, S, L, D G: Ntenna Chematic Ayout AND Esign UidelinesmplennaNo ratings yet
- Role of Vitamins D, E and C in Immunity and in AmmationDocument6 pagesRole of Vitamins D, E and C in Immunity and in AmmationmplennaNo ratings yet
- Typewriter-Facit 1832 1831 1830 1828Document69 pagesTypewriter-Facit 1832 1831 1830 1828mplennaNo ratings yet
- TS-120V Instruction ManualDocument27 pagesTS-120V Instruction ManualmplennaNo ratings yet
- FM/AM Tuner of Electronic Tuning Type: FunctionsDocument16 pagesFM/AM Tuner of Electronic Tuning Type: FunctionsmplennaNo ratings yet
- An 513Document11 pagesAn 513mplennaNo ratings yet
- TA2003Document7 pagesTA2003mplennaNo ratings yet
- Tea 5711Document28 pagesTea 5711mplennaNo ratings yet
- Tea 5551Document17 pagesTea 5551mplennaNo ratings yet
- Tea 5710Document19 pagesTea 5710mplennaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: TEA5591ADocument14 pagesData Sheet: TEA5591AmplennaNo ratings yet